用一个简单的例子教你如何 自定义ASP.NET Core 中间件(一)
发布时间:2023年12月18日
提起中间件大家一定不陌生,我们也用过.NET core很多很好用的中间件,但是如何自己写一个中间件呢,可能大部分同学不清楚怎么写,我之前也不会,看了微软官方文档 【ASP.NET Core - 中间件】感觉讲的也不是很清楚,下面就用一个简单的例子告诉大家什么是中间件,怎么自定义一个中间件。
中间件是一种装配到应用管道以处理请求和响应的软件。 每个组件:
- 选择是否将请求传递到管道中的下一个组件。
- 可在管道中的下一个组件前后执行工作。
- 请求委托用于生成请求管道。 请求委托处理每个?
HTTP?请求。
一句话总结:中间件是比筛选器更底层,更上游的面向切面技术,其性能最高,可处理的应用范围远比过滤器广,如实现网关,URL?转发,限流等等。
ASP.NET Core 请求管道包含一系列请求委托,依次调用。 下图演示了这一概念。 沿黑色箭头执行。
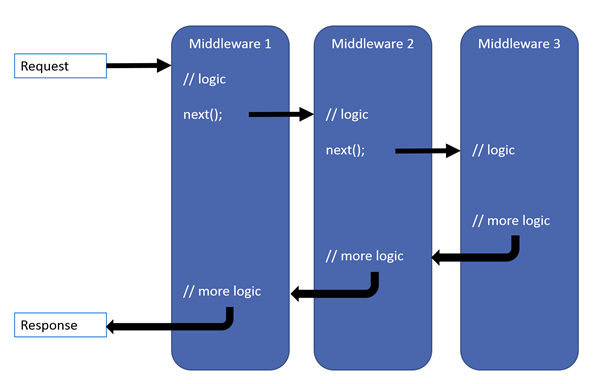
每个委托均可在下一个委托前后执行操作。 应尽早在管道中调用异常处理委托,这样它们就能捕获在管道的后期阶段发生的异常,也就是把app.UseExceptionHandler();异常处理代码放在最前面注入。
先来看一些常见的简单中间件
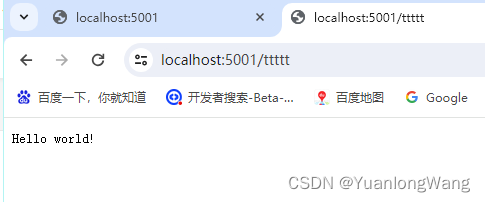
1、所有请求返回同一个结果
app.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello world!");
});?

2、拦截所有请求(可多个)
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
// 比如设置统一头
context.Response.Headers["test1"] = "111";
// 执行下一个中间件
await next.Invoke();
});
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
// 比如设置统一头
context.Response.Headers["test2"] = "222";
// 执行下一个中间件
await next.Invoke();
});
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
string headers = "";
foreach (var header in context.Response.Headers)
{
headers += header.Key + "=" + header.Value + "\n";
}
Console.WriteLine(headers);
// 执行下一个中间件
await next.Invoke();
});
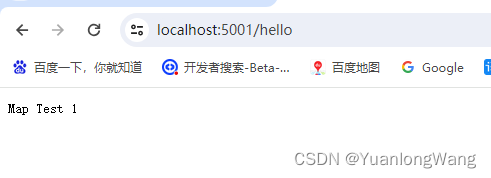
3、特定路由中间件(可多个)
app.Map("/hello", app => {
app.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Map Test 1");
});
});
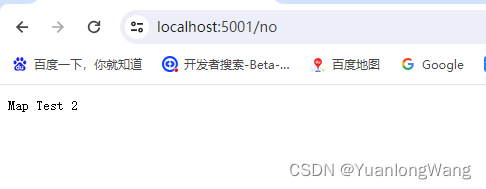
app.Map("/no", app => {
app.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Map Test 2");
});
}); ?
?
4、嵌套路由中间件(可多个)
app.Map("/level1", level1App => {
level1App.Map("/level2a", level2AApp => {
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
// 比如设置统一头
context.Response.Headers["test1"] = "111";
// 执行下一个中间件
await next.Invoke();
});
});
level1App.Map("/level2b", level2BApp => {
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
string headers = "";
foreach (var header in context.Response.Headers)
{
headers += header.Key + "=" + header.Value + "\n";
}
Console.WriteLine(headers);
// 执行下一个中间件
await next.Invoke();
});
});
});
下一章继续教大家如何自定义一个中间件:用一个简单的例子教你如何 自定义ASP.NET Core 中间件(二)-CSDN博客
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/lwpoor123/article/details/135062157
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!