模拟缓存穿透并提供解决方案
今天给大家模拟一下缓存穿透。
首先我们要清楚什么是缓存穿透,通俗一点对数据库中没有的数据进行操作。我们通常为了降低磁盘的io,往往会把热点数据或者是最近访问的数据添加进redis缓存,每次请求先访问redis缓存,如果没有数据再去查数据库,同时把数据库中的数据回写到redis缓存。缓存穿透就是对没有的数据进行操作,现在redis中进行查询(很显然是查询不到的),那么就会来查询数据库,如果是在高并发的环境下,会有很多次的请求直接打入数据库,数据库可能承受不住压力直接挂掉(这种场景一般是黑客发起了攻击导致的)。
先给大家模拟一下每次查询数据库的过程
我们选择1s执行1000条数据,并进行三次轮询。
我的表中仅仅有一条id为1的数据,我对这个数据进行查询
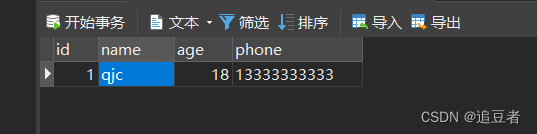
测试代码如下
?
package com.qjc.interview.Cache.penetration.controller;
import com.google.common.hash.BloomFilter;
import com.google.common.hash.Funnels;
import com.qjc.interview.Cache.penetration.pojo.User;
import com.qjc.interview.Cache.penetration.service.UserService;
import net.minidev.json.JSONValue;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Auther: QuJingChuan
* @Date: 2024/1/14 08:33
* @Description:
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class PenetrationController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String,String> redisTemplate;
@GetMapping("/queryById/{id}")
public User queryUserById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
//先从redis查询有无缓存对象
String userStr = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("缓存用户" + id);
if (userStr != null){
//redis缓存中有数据
System.out.println("从redis缓存中获取用户");
return JSONValue.parse(userStr,User.class);
}
User user = userService.SelectUserById(id);
System.out.println("从数据库中查询用户");
if (user ==null){
return null;
}
//回写进redis缓存
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("缓存用户"+id, JSONValue.toJSONString(user));
return user;
}
}我们进行对id为2的用户进行查询操作(id为2的用户并不存在) 采用jmeter做压测


结果如下
可以看到,查询id为2的数据并没有走缓存,而是一直对数据库进行请求,如果这里并发足够大,会把mysql进行击垮。
解决方案
1.当我们在操作一条不存在的数据的时候我们依然让它存入缓存,只不过结果为null
代码如下
package com.qjc.interview.Cache.penetration.controller;
import com.google.common.hash.BloomFilter;
import com.google.common.hash.Funnels;
import com.qjc.interview.Cache.penetration.pojo.User;
import com.qjc.interview.Cache.penetration.service.UserService;
import net.minidev.json.JSONValue;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Auther: QuJingChuan
* @Date: 2024/1/14 08:33
* @Description:
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class PenetrationController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String,String> redisTemplate;
@GetMapping("/queryById/{id}")
public User queryUserById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
//先从redis查询有无缓存对象
String userStr = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("缓存用户" + id);
if (userStr != null){
//redis缓存中有数据
System.out.println("从redis缓存中获取用户");
return JSONValue.parse(userStr,User.class);
}
User user = userService.SelectUserById(id);
System.out.println("从数据库中查询用户");
/* if (user ==null){
return null;
}*/
//回写进redis缓存
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("缓存用户"+id, JSONValue.toJSONString(user));
return user;
}
}可以看到在这里没有查询到对象仍然把它加入了缓存。
我们和刚才一样执行压力测试,结果如下。


由于这个代码不是线程安全的,所以在一开始的时候可能很多线程都像redis中回写了数据,不过还是可以看到,后面几乎全都是从redis缓存中去查数据,这样请求就几乎很少打入了数据库,解决了问题。
但是这样也有弊端,如果数据量大的话,占用了缓存太多的内存,可能会导致缓存中容量爆炸。
方法二?
使用布隆过滤器
那么首先什么是布隆过滤器呢?
布隆过滤器是一种空间效率高、适合大规模数据集的概率型数据结构,用于快速判断一个元素是否可能存在于一个集合中。它的主要应用场景是在大规模数据集合中进行快速的成员存在性判断,而不需要存储实际的元素。
布隆过滤器由一个位数组和多个哈希函数组成。当元素被加入布隆过滤器时,通过多个哈希函数将元素映射到位数组中的多个位置,将这些位置的值设为1。当需要判断一个元素是否存在于布隆过滤器中时,同样通过多个哈希函数计算出多个位置,如果所有位置的值都为1,则认为元素可能存在于布隆过滤器中,否则可以确定元素不存在。
布隆过滤器具有空间效率高、查询速度快的特点,但也存在一定的误判率。当判断元素可能存在时,可能会出现误判,即元素实际并不存在于布隆过滤器中,但布隆过滤器判断为存在。因此,在使用布隆过滤器时需要根据实际情况来设置位数组大小和哈希函数的个数,以及容忍的误判率,来平衡空间占用和误判率。
我这里采用的是谷歌的布隆过滤器,依赖如下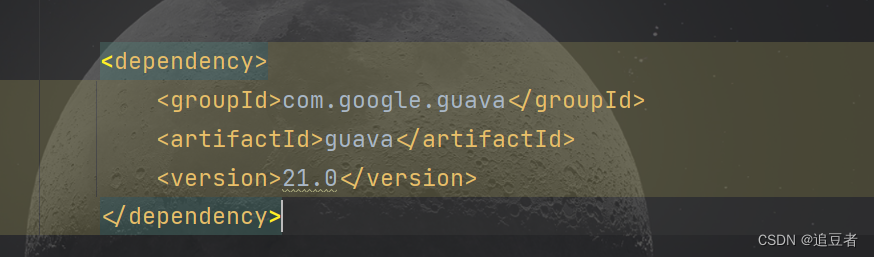
我们先进行一下小小的测试,看看它有什么用。
测试代码如下
?
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个布隆过滤器,设置预期插入元素的个数和期望的误判率
BloomFilter<Integer> bloomFilter = BloomFilter.create(Funnels.integerFunnel(),1000,0.05);
bloomFilter.put(1);
bloomFilter.put(2);
bloomFilter.put(3);
System.out.println("判断1元素是否在布隆过滤器内 " + bloomFilter.mightContain(1));
System.out.println("判断4元素是否在布隆过滤器内 " + bloomFilter.mightContain(4));
}测试结果如下
显然,布隆过滤器可以在很大概率上判断一个数是不是在bitmap中,那我们在业务中可以将数据的主键先进行初始化进入布隆过滤器,在查询时满足 以下顺序? 布隆过滤器 -> redis? ->数据库。
当布隆过滤器中没有数据时,很大概率这个数据在数据库中也不存在。(为什么说很大概率呢,因为布隆过滤器有一定的误判率,在开发过程中百分之5的误判率是在可以接受的范围内).
使用布隆过滤器的代码如下
package com.qjc.interview.Cache.penetration.controller;
import com.google.common.hash.BloomFilter;
import com.google.common.hash.Funnels;
import com.qjc.interview.Cache.penetration.pojo.User;
import com.qjc.interview.Cache.penetration.service.UserService;
import net.minidev.json.JSONValue;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Auther: QuJingChuan
* @Date: 2024/1/14 08:33
* @Description:
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class PenetrationController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String,String> redisTemplate;
@GetMapping("/queryById/{id}")
public User queryUserById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
//这个布隆过滤器用来存储integer类型的数据,初始化大小为1000.误判率在百分之5
BloomFilter<Integer> bloomFilter = BloomFilter.create(Funnels.integerFunnel(),1000,0.05);
//将表中的主键初始化进入布隆过滤器(因为我这里只有一条数据,我就直接加入进去了)
bloomFilter.put(1);
//判断布隆过滤器中是否有数据,没有直接返回.
if (!bloomFilter.mightContain(id)){
System.out.println("布隆过滤器中无数据,直接返回");
return null;
}
//先从redis查询有无缓存对象
String userStr = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("缓存用户" + id);
if (userStr != null){
//redis缓存中有数据
System.out.println("从redis缓存中获取用户");
return JSONValue.parse(userStr,User.class);
}
User user = userService.SelectUserById(id);
System.out.println("从数据库中获取用户");
if (user ==null){
return null;
}
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("缓存用户"+id, JSONValue.toJSONString(user));
return user;
}
}测试结果如下(查询id为2的数据)

这样就有效保护了数据库,布隆过滤器也是企业开发中和面试中经常问到的一个地方,希望大家喜欢我的博客。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- JavaScrip-初识JavaScript-知识点
- [AFCTF 2021]google authenticator
- 计算机网络 - 路由器查表过程模拟 C++(2024)
- winlogbeat收集Windows事件日志传给ELK
- 计算机网络之IP篇
- [go] 策略模式
- Vue中插槽的使用
- uniCloud 创建项目
- Java加密算法工具类(AES、DES、MD5、RSA)
- Shell命令与Linux操作系统:深入理解其原理和功能(2/2)