Pytest自动化测试框架
1、pytest简介
pytest是Python的一种单元测试框架,与python自带的unittest测试框架类似,但是比unittest框架使用起来更简洁,效率更高。
- 执行测试过程中可以将某些测试跳过,或者对某些预期失败的case标记成失败
- 能够支持简单的单元测试和复杂的功能测试
- 支持重复执行失败的case
- 支持运行由nose, unittest编写的测试case
- 具有很多第三方插件,并且可以自定义扩展
- 方便的和持续集成工具集成
- 支持参数化
2、安装pytest
pip install pytest3、举例
(1)单测试case
执行测试的时候,我们只需要在测试文件test_sample所在的目录下,运行py.test即可。pytest会在当前目录及其子目录下寻找以test开头的py文件或者以test结尾的py文件(即测试文件),找到测试文件之后,进入到测试文件中寻找test_开头的测试函数并执行。
在当前目录下新建文件 test_champ.py
def func(x):
return x + 1
def test_answer():
assert func(3)==5在命令行输入py.test [-q],加上-q(quiet)输出结果会省去pytest版本信息,便可以看到执行的成功与失败的原因了
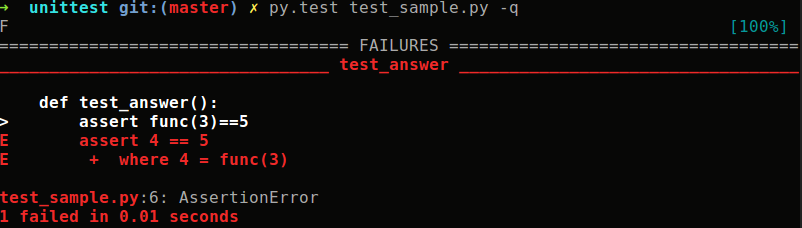
(2)多测试case
当需要编写多个测试样例的时候,我们可以将其放到一个测试类当中,如:
class TestClass:
def test_one(self):
assert "h" in "this"
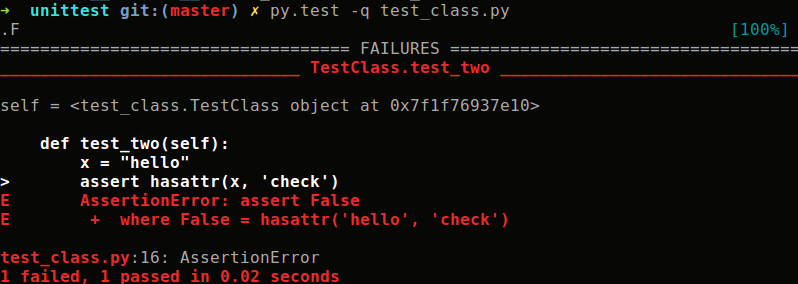
def test_two(self):
x = "hello"
assert hasattr(x,"check")我们可以通过执行测试文件的方法,执行上面的测试:py.test -q test_class.py
同时,在这我为大家准备了一份软件测试视频教程(含面试、接口、自动化、性能测试等),就在下方,需要的可以直接去观看,也可以直接【点击文末小卡片免费领取资料文档】
软件测试视频教程观看处:
【2024最新版】Python自动化测试15天从入门到精通,10个项目实战,允许白嫖。。。
4、pytest测试样例编写规则
通过上面2个实例,我们发现编写pytest测试样例非常简单,只需要按照下面的规则:
- 测试文件以test_开头(以_test结尾也可以)
- 测试类以Test开头,并且不能带有 __init__ 方法
- 测试函数以test_开头
- 断言使用基本的assert即可
5、如何执行pytest测试样例
执行测试样例的方法很多种,上面第一个实例是直接执行py.test,第二个实例是传递了测试文件给py.test。其实py.test有好多种方法执行测试:
py.test # run all tests below current dir
py.test test_mod.py # run tests in module
py.test somepath # run all tests below somepath
py.test -k stringexpr # only run tests with names that match the
# the "string expression", e.g. "MyClass and not method"
# will select TestMyClass.test_something
# but not TestMyClass.test_method_simple
py.test test_mod.py::test_func # only run tests that match the "node ID",
# e.g "test_mod.py::test_func" will select
# only test_func in test_mod.py6、测试报告
pytest可以方便的生成测试报告,即可以生成HTML的测试报告,也可以生成XML格式的测试报告用来与持续集成工具集成。
生成txt格式报告:
py.test --resultlog=path/log.txt?生成XML格式的报告:
py.test --junitxml=path/log.xml ?将测试报告发送到pastebin服务器,执行下面的命令会生成报告的网址
py.test test_report.py --pastebin=all?只发送失败的报告
py.test test_report.py --pastebin=failed 生成Html格式报告
这个需要安装pytest的第三方插件pytest-html:
pip install pytest-html
py.test test_report.py --html=path/log.html 7、如何获取帮助信息
py.test --version # shows where pytest was imported from
py.test --fixtures # show available builtin function arguments
py.test -h | --help # show help on command line and config file options 与Python自带的unitest测试框架中的setup、teardown类似,pytest提供了fixture函数用以在测试执行前和执行后进行必要的准备和清理工作。但是fixture函数对setup和teardown进行了很大的改进。
- fixture函数可以使用在测试函数中,测试类中,测试文件中以及整个测试工程中。
- fixture支持模块化,fixture可以相互嵌套
- fixture支持参数化
- fixture支持unittest类型的setup和teardown
setup完成测试前的初始化工作,teardown实现测试完成后的垃圾回首工作。如果测试的程序使用jdbc连接数据库,那么setUpBeforeClass()方法中就可以写上初始化数据库连接的一些代码,tearDownAfterClass()方法中就可以写上关闭数据库连接的一些代码。
8、最佳实践
其实对于测试而言,特别是在持续集成环境中,我们的所有测试最好是在虚拟环境中。这样不同的虚拟环境中的测试不会相互干扰的。
由于我们的实际工作中,在同一个Jekins中,运行了好多种不同项目册的测试,因此,各个测试项目运行在各自的虚拟环境中。
将pytest安装在虚拟环境中:
1、将当前目录创建为虚拟环境
virtualenv . # create a virtualenv directory in the current directory
source bin/activate # on unix 2、在虚拟环境中安装pytest:
pip install pytest ?9、断言的使用
①正常断言
# 子签名类,忽略中间打印的过程,直接表示出错的原因
# assert value == 0, "value was odd, should be even"
# 等于、不等、小于、大于
assert func(2)==3②异常断言
使用pytest.raise方法(需import pytest)
断言1除以0,将产生一个ZeroDivisionError类型的异常。
import pytest
def test_zero_division():
with pytest.raises(ZeroDivisionError):
1 / 0 有的时候,我们可能需要在测试中用到产生的异常中的某些信息,比如异常的类型type,异常的值value等等。下面我们修改下上面的测试
import pytest
def test_recursion_depth():
with pytest.raises(ZeroDivisionError) as excinfo:
1/0
assert excinfo.type == 'RuntimeError' 因为该测试断言产生的异常类型是RuntimeError,而实际上产生的异常类型是ZeroDivisionError,所以测试失败了。在测试结果中,可以看到assert子表达式excinfo.type的值。
最后感谢每一个认真阅读我文章的人,礼尚往来总是要有的,虽然不是什么很值钱的东西,如果你用得到的话可以直接拿走:
这些资料,对于做【软件测试】的朋友来说应该是最全面最完整的备战仓库,这个仓库也陪伴我走过了最艰难的路程,希望也能帮助到你!凡事要趁早,特别是技术行业,一定要提升技术功底。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- AIGC时代-GPT-4和DALL·E 3的结合
- 4S店汽车行业万能通用小程序源码系统:功能强大,集合汽车在线展示+在线预约+贷款计算器......附带完整的搭建教程
- Visual Studio使用Web Deploy发布.NET Web应用到指定服务器的IIS中
- 支Vue3的WebSocket插件并支持断线重连
- 如何使用 NFTScan NFT API 在 PlatON 网络上开发 Web3 应用
- Open CASCADE学习|创建拓朴
- 【动态规划】斐波那契数列模型
- 大一C语言文件相关知识
- 学习java第四天
- linux 系统下网卡phy读写程序