SpringMVC系列之技术点定向爆破二
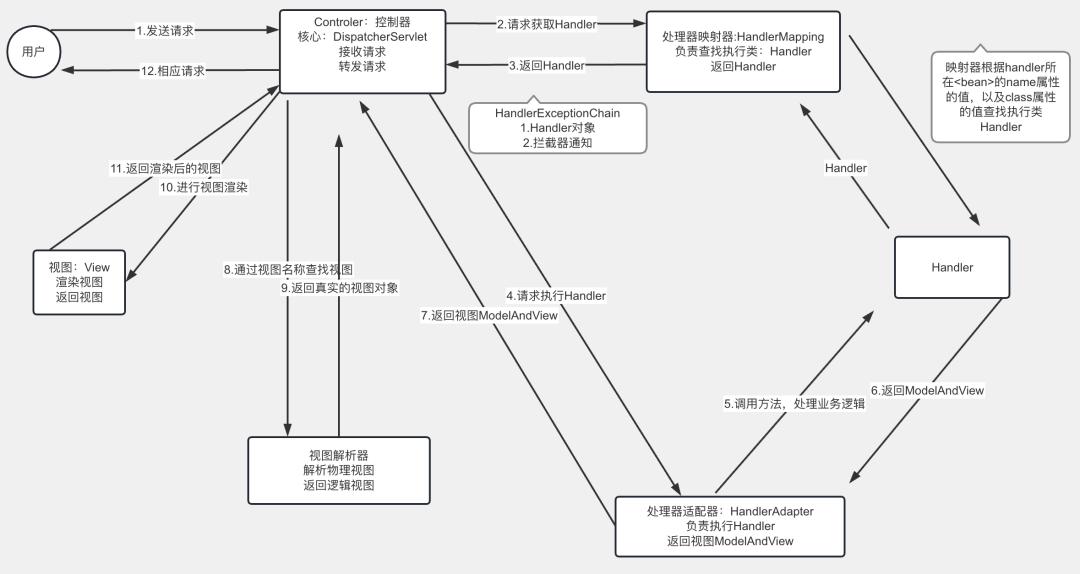
SpringMVC的运行流程
-
客户端发送请求
-
tomcat接收对应的请求
-
SpringMVC的核心调度器DispatcherServlet接收到所有请求
-
请求地址与@RequestMapping注解进行匹配,定位到具体的类和具体的处理方法(封装在Handler中)
-
核心调度器找到Handler后交给HandlerAdapter执行具体的Handler
-
执行后Controller将具体的执行结果(ModelAndView)返回给HandlerAdapter
-
核心调度器把ModelAndView交给视图解析器,视图解析器找到具体的jsp封装到View对象中
-
View视图把jsp转换成html内容再交给核心调度器
-
核心调度器把html内容返回给客户端。
RequestMapping注解
在Controller中通过RequestMapping注解来定义匹配请求的URL。
-
RequestMapping注解可以定义在类的上方,作为类的中多个方法的统一URL前缀。
-
RequestMapping注解定义在方法的上方,作为此次请求具体要执行的方法的限定。
/**
@Author: 索尔
*/
@Controller //声明这是一个控制器
@RequestMapping("/hello") //访问路径,等价于url-pattern
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/test1") //访问路径
public String hello1(){
System.out.println("hello world");//具体的业务逻辑
return "redirect:/index.jsp"; //跳转:/index.jsp
}
}RequestParam注解
RequestParam注解往往和RequestMapping注解配合使用,用来绑定请求参数和处理方法的参数。
我们来看下RequestParam注解的源码:
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestParam {
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
boolean required() default true;
String defaultValue() default "\n\t\t\n\t\t\n\ue000\ue001\ue002\n\t\t\t\t\n";
}-
@RequestParam(required = false/true,value = “参数名”,defaultValue = “”)?其中name和value等效这里用value,推荐使用value。 -
value:用于重命名参数,若使用了value,则前端请求时该参数必须与value相同
-
required:用来制定该参数是否必须传入
-
true:默认值,前端请求时默认必须传入
-
false:前端请求时可以不传,不传时后端收到的是null
-
-
defaultValue:如果设置了defaultValue,则required不会使用默认值true,而自动为false。当没有穿参数时,就使用默认值。
接收复杂类型的参数
-
设计User类,包含了多种复杂类型。
/**
@Author: 索尔
*/
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String[] hobbies;
private Address address;
private List<String> schools;
private List<User> family;
private Map<String,String> scores;
...
}-
设计Controller的处理方法,接收复杂类型的参数并打印
/**
* 接收复杂类型的参数
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/test3")
public String test3(User user){
System.out.println(user);
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}使用SpringMVC直接接收来自jsp发起的Get或着Post请求。
-
设计存放表单的jsp页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/demo/test3" method="post">
id:<input type="text" name="id"> <br/>
姓名:<input type="text" name="name"><br/>
爱好:<input type="checkbox" name="hobbies" value="阅读">阅读</input>
<input type="checkbox" name="hobbies" value="看片">看片</input>
<input type="checkbox" name="hobbies" value="音乐">音乐</input><br/>
所在城市:<input type="text" name="address.city">所在街道:<input type="text" name="address.street"><br/>
毕业院校:<input type="text" name="schools[0]"><input type="text" name="schools[1]"><br/>
家庭成员:
父亲:<input type="text" name="family[0].name">
母亲:<input type="text" name="family[1].name"><br/>
成绩:
计算机:<input type="text" name="scores['计算机']">
大学英语:<input type="text" name="scores['大学英语']"><br/>
<input type="submit" value="注册"/>
</form>
</body>
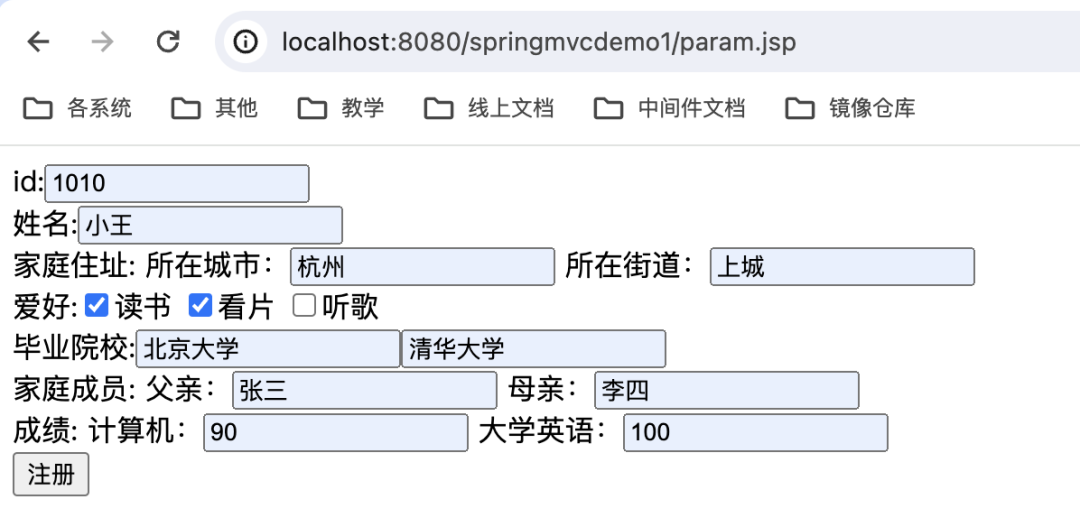
</html>注意List、Map、实体类中的实体类的参数命名方式。当填入表单数据后,程序可以收到指定类型的参数。
-
页面设定的参数内容:
-
后端接收到的结果:
User{id=1010, name='小王', address=Address{city='杭州', street='上城'}, hobbies=[读书, 看片], schools=[北京大学, 清华大学], family=[User{id=0, name='张三', address=null, hobbies=null, schools=null, family=null, scores=null}, User{id=0, name='李四', address=null, hobbies=null, schools=null, family=null, scores=null}], scores={大学英语=100, 计算机=90}}解决Post请求参数中文乱码问题
如果参数中包含中文,则会出现乱码问题。使用过滤器解决Post请求参数中文乱码问题。
在web.xml文件中配置过滤器:
<!--编码过滤器,解决乱码问题-->
<filter>
<filter-name>characterFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<!--设置编码格式为utf8-->
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--对request请求进行编码-->
<init-param>
<param-name>forceRequestEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--对response响应进行编码-->
<init-param>
<param-name>foreResponseEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<!--配置要过滤的servlet-->
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>characterFilter</filter-name>
<servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name>
</filter-mapping>获得请求头数据
在JavaWeb中,需要繁琐的操作才能获得请求头数据。SpringMVC提供了快速获得请求头数据的方法。
@RequestMapping("/getHeader")
public String getHeader(@RequestHeader("User-agent") String userAgent){
System.out.println(userAgent);
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}获取Cookie数据
同样的,JavaWeb获得Cookie的方式也非常繁琐。SpringMVC提供了@CookieValue来快速获得Cookie中的数据。
@RequestMapping("/getCookie")
public String getCookie(@CookieValue("JSESSIONID") String jsessionid){
System.out.println(jsessionid);
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}访问静态资源
在springmvc中,所有的请求都会被SpringMVC的核心处理器DispatcherServlet来处理,对于静态资源的请求也不例外。因此,需要告知SpringMVC,对于静态资源的请求不要去做处理,而是直接响应静态资源即可。通过springmvc的配置,完成静态资源的放行。
<!--配置访问静态资源-->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<!--将url中的路径映射到指定的资源文件夹-->
<mvc:resources mapping="/images/**" location="/images/" />另一种处理静态资源的方法:DispatcherServlet处理不了,则交给DefaultServlet处理。
<!--配置访问静态资源-->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<!--另一种处理静态资源的方法:DispatcherServlet处理不了,则交给DefaultServlet处理-->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler />配置视图解析器
为了返回指定的视图,需要告知视图解析器如何获取指定视图。
<!-- 视图解析器
作用:1.捕获后端控制器的返回值="index"
2.解析:在返回值的前后 拼接 ==> "/index.jsp"
-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<!-- 前缀 -->
<property name="prefix" value="/"></property>
<!-- 后缀 -->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>文件下载
文件上传和下载是处理复杂数据类型的另一种方式。首先我们来看下如何实现文件的下载。
文件下载的核心逻辑是通过封装响应消息,将下载内容发送给客户端。
@RequestMapping("/download")
public ResponseEntity<byte[]> download(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//设置下载文件信息
ServletContext context = request.getServletContext();
String realPath = context.getRealPath("/images/img.jpeg");
//创建输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(realPath);
byte[] bytes = new byte[fis.available()];
//读取文件内容,存入到字节数组中
fis.read(bytes);
fis.close();
//封装下载内容到响应消息中
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.set("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename=imp.jpeg");
return new ResponseEntity<byte[]>(bytes,headers, HttpStatus.OK);
}文件上传
文件上传的核心逻辑是读到客户端传递来的字节数据,再通过Java程序存入到指定位置。
文件上传需要引入第三方组件Commons-fileupload的支持。
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>-
编写上传界面
<body>
<form enctype="multipart/form-data" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/upload" method="post">
文件:<input type="file" name="uploadFile" />
<br/>
<input type="submit" value="上传">
</form>
</body>-
在spring中注册上传组件
<bean class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver" id="multipartResolver">
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"></property>
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="#{1024
*1024*
16}"></property>
</bean>-
编写后端上传接口
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String upload(MultipartFile uploadFile) throws IOException {
System.out.println(uploadFile.getOriginalFilename());
String path = "/Users/zeleishi/Documents/code/springmvc-demo1/out/upload/"+uploadFile.getOriginalFilename();
File file = new File(path);
uploadFile.transferTo(file);
return "success";
}总结
这一篇文章我们攻克了SpringMVC部分关键技术,建议小伙伴同时收藏SpringMVC系列三篇博文,攻克SpringMVC将变得轻而易举。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 力扣算法-Day16
- YOLOv5涨点改进:多层次特征融合(SDI),小目标涨点明显,| UNet v2,比UNet显存占用更少、参数更少
- 力扣刷题记录(18)LeetCode:474、518、377、322
- Web实战丨基于django+html+css+js的电子商务网站
- Mars3D与mars3d-cesium版本间兼容造成3dtiles和gltf数据处理相关记录
- maven项目可以运行但是打包后执行报错
- 服务器启动出现问题时,该如何处理?
- 竞赛保研 基于深度学习的人脸识别系统
- 【Vue计算属性详细介绍】
- 大数据之力:从数据湖到数据智能的升级之路