解决百度地图在模拟器上运行报 java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: No config chosen问题
解决百度地图在模拟器上运行报 java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: No config chosen 问题
1. 问题复现
在近期公司使用模拟器(网易MuMu)进行项目演示时,在进入存在百度地图(Android版本 7.4.2版本)之后,页面出现奔溃,后台日志为:
Back traces starts.
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: No config chosen
com.baidu.platform.comapi.map.h$a.chooseConfig(GLTextureView.java:655)
com.baidu.platform.comapi.map.h$e.a(GLTextureView.java:789)
com.baidu.platform.comapi.map.h$f.l(GLTextureView.java:1164)
com.baidu.platform.comapi.map.h$f.run(GLTextureView.java:1002)
2. 查找源码,定位问题
经过问题的复盘,找到了是位于源码位置报错的:
com.baidu.platform.comapi.map.h$a.chooseConfig(GLTextureView.java:655)
具体代码位置如下:
com.baidu.platform.comapi.map.h
类下面的一个抽象类 a ,实现了EGLConfigChooser 接口,在实现chooseConfig接口时报错:
private abstract class a implements EGLConfigChooser {
protected int[] a;
public a(int[] configSpec) {
this.a = this.a(configSpec);
}
public EGLConfig chooseConfig(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display) {
// 代码省略...
EGLConfig config = this.a(egl, display, configs);
if (config == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No config chosen");
} else {
return config;
}
}
abstract EGLConfig a(EGL10 var1, EGLDisplay var2, EGLConfig[] var3);
}
我们可以看到 EGLConfig这个类是由a方法返回的,我们可以看到,当config==null 时,会直接报出异常IllegalArgumentException,那么我们可以查看一下这个抽象类a是由谁来集成的?
通过搜索源码,它的继承方式是这样的:
package com.baidu.platform.comapi.map;
public class h extends TextureView {
private abstract class a implements EGLConfigChooser {
}
private class b extends com.baidu.platform.comapi.map.h.a {
private int[] j = new int[1];
protected int c;
protected int d;
protected int e;
protected int f;
protected int g;
protected int h;
public b(int redSize, int greenSize, int blueSize, int alphaSize, int depthSize, int stencilSize) {
super(new int[]{12324, redSize, 12323, greenSize, 12322, blueSize, 12321, alphaSize, 12325, depthSize, 12326, stencilSize, 12344});
this.c = redSize;
this.d = greenSize;
this.e = blueSize;
this.f = alphaSize;
this.g = depthSize;
this.h = stencilSize;
}
public EGLConfig a(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display, EGLConfig[] configs) {
EGLConfig[] var4 = configs;
int var5 = configs.length;
for(int var6 = 0; var6 < var5; ++var6) {
EGLConfig config = var4[var6];
int d = this.a(egl, display, config, 12325, 0);
int s = this.a(egl, display, config, 12326, 0);
if (d >= this.g && s >= this.h) {
int r = this.a(egl, display, config, 12324, 0);
int g = this.a(egl, display, config, 12323, 0);
int b = this.a(egl, display, config, 12322, 0);
int a = this.a(egl, display, config, 12321, 0);
if (r == this.c && g == this.d && b == this.e && a == this.f) {
return config;
}
}
}
return null;
}
private int a(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display, EGLConfig config, int attribute, int defaultValue) {
return egl.eglGetConfigAttrib(display, config, attribute, this.j) ? this.j[0] : defaultValue;
}
}
private class i extends com.baidu.platform.comapi.map.h.b {
public i(boolean withDepthBuffer) {
super(8, 8, 8, 0, withDepthBuffer ? 16 : 0, 0);
}
}
}
综上所属,h下面的a,b和i的关系为:

我们可以看到 h.c中其实没有a方法实现的,那么a方法的实现就是在h.b中了,我们可以来简单看一下h.b方法的实现:
public EGLConfig a(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display, EGLConfig[] configs) {
EGLConfig[] var4 = configs;
int var5 = configs.length;
for(int var6 = 0; var6 < var5; ++var6) {
EGLConfig config = var4[var6];
int d = this.a(egl, display, config, 12325, 0);
int s = this.a(egl, display, config, 12326, 0);
if (d >= this.g && s >= this.h) {
int r = this.a(egl, display, config, 12324, 0);
int g = this.a(egl, display, config, 12323, 0);
int b = this.a(egl, display, config, 12322, 0);
int a = this.a(egl, display, config, 12321, 0);
if (r == this.c && g == this.d && b == this.e && a == this.f) {
return config;
}
}
}
return null;
}
private int a(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display, EGLConfig config, int attribute, int defaultValue) {
return egl.eglGetConfigAttrib(display, config, attribute, this.j) ? this.j[0] : defaultValue;
}
这里我们可以看到,当执行r == this.c && g == this.d && b == this.e && a == this.f为真时,才能返回对应的config对象,如果都不匹配,那么将会导致返回null·,今儿导致程序奔溃。问题找到了,我们应该怎么去改它呢?
3. 通过源码去修复它
我也不拐弯抹角了,经过对源码的分析,列举一下自己对这个问题修复的看法。首先,我们知道了问题所在的地方,那么我们是否在方法类b中的a方法永远不返回null,那样就不会导致出现No config chosen异常,虽然这种方法会导致所选择的EGLConfig和所需要的config不匹配,导致页面存在拉伸或者压缩的问题,但是这相比于奔溃,应该会好很多。那么就按照这个说的干吧。
首先,要修改返回值,使用它原有的逻辑肯定是不行的,但是我们返现这个 h.a抽象类实现的是 EGLConfigChooser,它是来自android.opengl.GLSurfaceView下的一个接口,比较熟悉openGL的人应该比较熟悉它:
public interface EGLConfigChooser {
/**
* Choose a configuration from the list. Implementors typically
* implement this method by calling
* {@link EGL10#eglChooseConfig} and iterating through the results. Please consult the
* EGL specification available from The Khronos Group to learn how to call eglChooseConfig.
* @param egl the EGL10 for the current display.
* @param display the current display.
* @return the chosen configuration.
*/
EGLConfig chooseConfig(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display);
}
那我能不能自定义一下我们的h.a、h.b和h.i类呢,把源码拷一遍,然后把a方法返回值修改一下即可,好,那么说干就干:
h.a类如下:
public abstract class ParentEGLConfigChooser implements GLSurfaceView.EGLConfigChooser {
protected int[] a;
public ParentEGLConfigChooser(int[] configSpec) {
this.a = this.a(configSpec);
}
public EGLConfig chooseConfig(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display) {
int[] num_config = new int[1];
if (!egl.eglChooseConfig(display, this.a, (EGLConfig[])null, 0, num_config)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("eglChooseConfig failed");
} else {
int numConfigs = num_config[0];
if (numConfigs <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No configs match configSpec");
} else {
EGLConfig[] configs = new EGLConfig[numConfigs];
if (!egl.eglChooseConfig(display, this.a, configs, numConfigs, num_config)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("eglChooseConfig#2 failed");
} else {
EGLConfig config = this.a(egl, display, configs);
if (config == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No config chosen");
} else {
return config;
}
}
}
}
}
abstract EGLConfig a(EGL10 var1, EGLDisplay var2, EGLConfig[] var3);
private int[] a(int[] configSpec) {
int len = configSpec.length;
int[] newConfigSpec = new int[len + 2];
System.arraycopy(configSpec, 0, newConfigSpec, 0, len - 1);
newConfigSpec[len - 1] = 12352;
newConfigSpec[len] = 4;
newConfigSpec[len + 1] = 12344;
return newConfigSpec;
}
}
对于h.b类,我们可以实现如下:
public class SubEGLConfigChooser extends ParentEGLConfigChooser {
private final int[] j = new int[1];
protected int c;
protected int d;
protected int e;
protected int f;
protected int g;
protected int h;
public SubEGLConfigChooser(int redSize, int greenSize, int blueSize, int alphaSize, int depthSize, int stencilSize) {
super(new int[]{12324, redSize, 12323, greenSize, 12322, blueSize, 12321, alphaSize, 12325, depthSize, 12326, stencilSize, 12344});
this.c = redSize;
this.d = greenSize;
this.e = blueSize;
this.f = alphaSize;
this.g = depthSize;
this.h = stencilSize;
}
public EGLConfig a(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display, EGLConfig[] configs) {
BaseLog.i("----show the a------>>" + egl + "---->>" + display + "---->>" + Arrays.toString(configs));
for (EGLConfig config : configs) {
int d = this.a(egl, display, config, 12325);
int s = this.a(egl, display, config, 12326);
if (d >= this.g && s >= this.h) {
int r = this.a(egl, display, config, 12324);
int g = this.a(egl, display, config, 12323);
int b = this.a(egl, display, config, 12322);
int a = this.a(egl, display, config, 12321);
if (r == this.c && g == this.d && b == this.e && a == this.f) {
return config;
}
}
}
//TODO 直接修改这里,返回第一个 configs[0], 暂时还未发现任何异常
return configs[0];
}
private int a(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display, EGLConfig config, int attribute) {
return egl.eglGetConfigAttrib(display, config, attribute, this.j) ? this.j[0] : 0;
}
}
同样,对于h.i类,我们可以自定义类为:
public class TargetEGLConfigChooser extends SubEGLConfigChooser{
public TargetEGLConfigChooser() {
super(8, 8, 8, 0, 16 , 0);
}
}
这三个类我们已经写好了,那么如何将我们的TargetEGLConfigChooser 替换成目标h.i方法呢?这个可能要花一些时间,我们来大致了解一下 BaiduMap的基础架构,我们以 TextureMapView为例子:
TextureMapView是继承自ViewGroup, 它有一个私有属性值b,其类型为MapTextureView, 属性b在TextureMapView的初始化方法中被初始化:

在 MapTextureView中,首先它是继承自com.baidu.platform.comapi.map.h的:
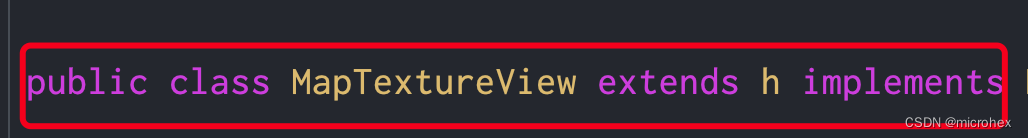
同时,我们在h类中找到了h,h是一个EGLConfigChooser类型的接口,
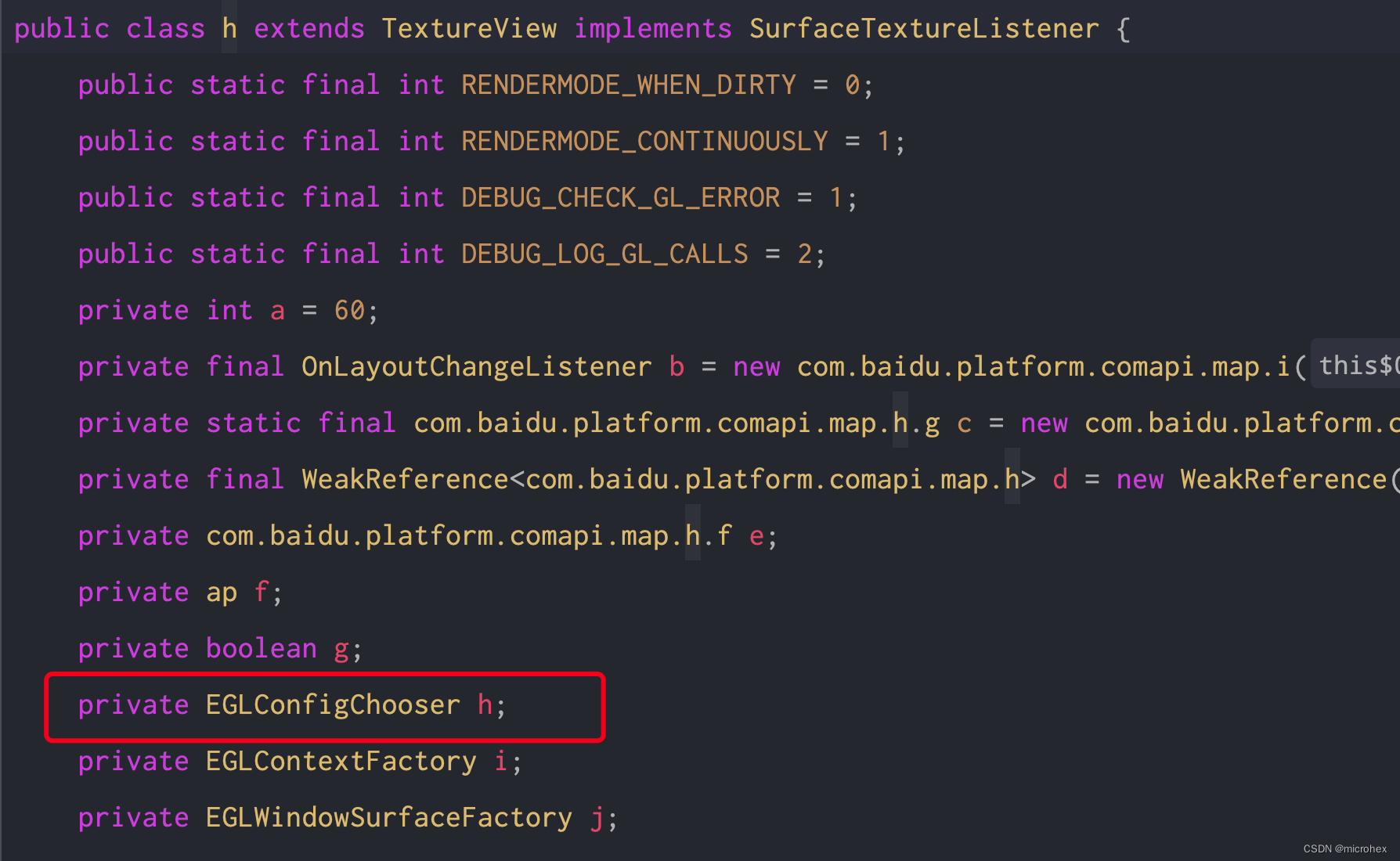
通过程序分析, 那么这个h的实现类就是咋们的h.i. 主要问题分析完成了,那么就好做了,直接使用反射,将我们的h的实现类直接由h.i替换成我们的 TargetEGLConfigChooser即可,代码很简单,就几行:
public class TextureMapViewFix {
public static void tryToFixException(TextureMapView mapView) {
try {
Field b = mapView.getClass().getDeclaredField("b"); // 找到b
b.setAccessible(true);
Object bObject = b.get(mapView);
BaseLog.i("bObject = " + bObject);
if (null == bObject) {
BaseLog.i("bObject is null and return");
return;
}
Field h = bObject.getClass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredField("h"); //找到其父类,然后查找子元素h
h.setAccessible(true);
Object aObject = h.get(bObject);
BaseLog.i("aObject = " + aObject);
h.set(bObject, new TargetEGLConfigChooser()); //替换成咋们自定义的目标类 TargetEGLConfigChooser
Object aObject1 = h.get(bObject);
BaseLog.i("aObject1 = " + aObject1); //检查是否更新成功
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4. 总结
可能baidu地图的源码是混淆的,所以啃起来不是特别的顺利,还是耐着性子看完了,问题其实并不复杂,弄清楚逻辑就比较简单了,可能就是java的反射需要点功底,其它的都好说。如果有任何问题,可以add v:javainstalling,备注:baidu.
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【绘图软件】自用安装教程
- EasyRecovery2024注册机包含激活码
- Mysql入门教程-存储过程
- Android读取assets文件下的JSON文件转String输出
- 快速排序总结
- 软件设计师6--流水线技术
- origin案例_绘制Spectrum,TRIR和曲线拟合
- 【代码随想录】刷题笔记Day43
- 2024北京港航疏浚技术装备展|第十二届北京国际智慧港航疏浚工程技术与装备展览会
- postgresql 查询字段 信息