Java 并发编程初探 synchronized、volatile、wait、notify
一、新启线程的方式
类Thread
接口Runnable
这两种是在Thread类中官方提到的方法
a.join join()方法是让a线程先执行,执行完后继续执行主线程
二、线程中断
private static class UseThread extends Thread{
public UseThread(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(!isInterrupted()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+" in InterruptedException interrupt flag is "
+isInterrupted());
//资源释放
interrupt();
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " I am extends Thread.");
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+" interrupt flag is "+isInterrupted());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread endThread = new UseThread("HasInterrputEx");
endThread.start();
Thread.sleep(500);
endThread.interrupt();
}
interrupt是发送一个中断请求,并不是立马中断,甚至线程可以不理会中断请求
需要注意,阻塞方法中抛出InterruptedException异常后,如果需要继续中断,需要手动再中断一次
不建议去使用stop、suspend,因为带有很大的强制性,容易引发死锁。
三、线程优先级
通过指定优先级可以指定线程执行的优先级的高低
可以通过Thread.setPriority(int )方法设置优先级,范围1-10 默认5。这个优先级不一定能生效,要看具体的环境,有可能环境最高的优先级是5
四、守护线程
守护线程(Daemon Thread)是一种在后台提供服务的线程,他的存在不会阻止程序的终止。当所有的非守护线程结束时,守护线程会自动被终止。通常守护线程用于执行一些后台任务,比如垃圾回收等。
UseThread thread=new UseThread();
thread.setDaemon(true);
通过setDaemon方法将线程设置为守护线程
注:守护线程中finally代码块不一定生效
结束线程时,普通线程先结束,守护线程再结束。
五、synchronized
注意锁对象要用不会变化的对象就行
六、volatile 最轻量的同步机制
volatile可以保证可见性
public class MyClass {
private static boolean ready=false;
private static int num=1;
private static class PrintThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("PrintThread is Running");
while(!ready);
System.out.println("number="+num);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new PrintThread().start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
num=100;
ready=true;
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("main dead");
}
}
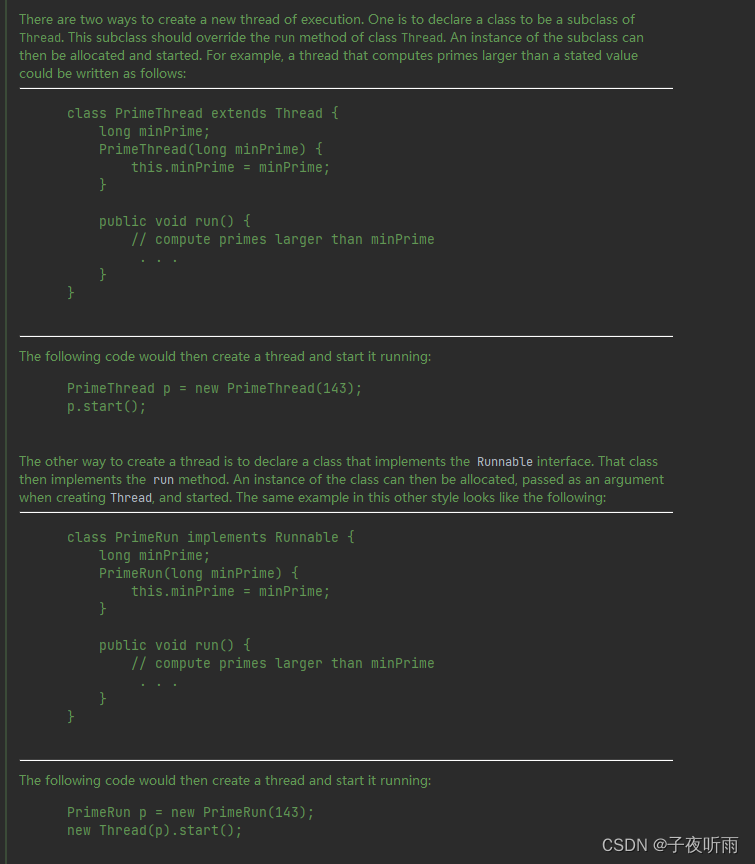
上面的demo中,通过在主线程设置read为true来让打印线程打印num,但是read的修改对于子线程来说是不可见的,所以不会执行num的打印。 之前做过通过一个变量值来控制线程的结束,就要注意给这个变量值加上volatile关键字来保证可见性。
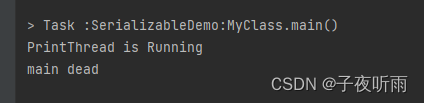
给ready加上volatile关键字:
private static volatile boolean ready=false;
之后运行
但是volatile无法保证操作的原子性
所以volatile适合于一写多读的场景(一个线程写,多个线程读)
七、线程间协作
等待-通知
wait() 等待 是Object的方法 调用wait时会释放持有的锁 唤醒后会重新竞争锁
notify() notifyAll() 通知
notifyAll会使原来在该对象上等待被唤醒的所有线程全部退出等待状态,会去重新竞争锁
notify会选择一个等待状态的线程进行通知,并使它获得该对象上的锁,不会惊动其他同样在等待状态的线程
需注意:3个方法都需要在同步代码块中使用(synchronized)
wait notify实现的消费者 生产者
/**
*类说明:快递实体类
*/
public class Express {
public final static String CITY = "ShangHai";
private int km;/*快递运输里程数*/
private String site;/*快递到达地点*/
public Express() {
}
public Express(int km, String site) {
this.km = km;
this.site = site;
}
/* 变化公里数,然后通知处于wait状态并需要处理公里数的线程进行业务处理*/
public synchronized void changeKm(){
this.km = 101;
notifyAll();
}
/* 变化地点,然后通知处于wait状态并需要处理地点的线程进行业务处理*/
public synchronized void changeSite(){
this.site = "BeiJing";
notifyAll();
}
/*线程等待公里的变化*/
public synchronized void waitKm(){
while(this.km<100){
try {
wait();
System.out.println("Check KM thread["
+Thread.currentThread().getId()
+"] is be notified");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("the Km is "+this.km+",I will change db");
}
/*线程等待目的地的变化*/
public synchronized void waitSite(){
while(this.site.equals(CITY)){//快递到达目的地
try {
wait();
System.out.println("Check Site thread["+Thread.currentThread().getId()
+"] is be notified");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("the site is "+this.site+",I will call user");
}
}
public class MyClass {
private static Express express=new Express(0,Express.CITY);
private static class checkKm extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
express.waitKm();
}
}
private static class checkSite extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
express.waitSite();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
new checkSite().start();
}
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
new checkKm().start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
express.changeSite();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
各创建三个线程用来处理公里数变化和目的地变化,线程刚启动时,由于不满足条件,线程会进入等待状态。当调用改变公里数或者改变目的地的方法时,会唤醒线程。线程会去判断公里数是否大于100或者目的地是否为北京,如果是会跳出while循环,线程任务结束(3个线程都会结束任务)。
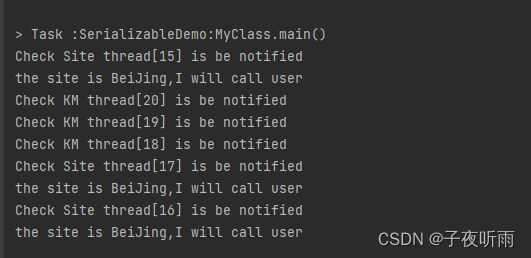
wait notify实战案例
不知道对不对,欢迎指正
采用多线程技术,例如wait/notify,设计实现一个符合生产者和消费者问题的程序,对某一个对象(枪膛)进行操作,其最大容量是20颗子弹,生产者线程是一个压入线程,它不断向枪膛中压入子弹,消费者线程是一个射出线程,它不断从枪膛中射出子弹。请实现上面的程序。
public class Gun {
public volatile int bullet=0;
public void load(){
while(bullet<=20){
synchronized (this){
try {
if(bullet<20){
bullet++;
System.out.println("Load Thread "+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" load a bullet,the total of bullet is :"+bullet);
}
Thread.sleep(500);
if(bullet==20) wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
public void shoot(){
synchronized (this){
bullet--;
System.out.println("Shoot Thread "+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" Shoot,bullets left :"+bullet);
if(bullet<10)
notifyAll();
}
}
}
public class MyClass {
private static Gun gun=new Gun();
private static class load extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
gun.load();
}
}
private static class shoot extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
if(gun.bullet>0)
gun.shoot();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i=0;i<3;i++){
new load().start();
}
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
new shoot().start();
}
}
}
运行结果:
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!