数据安全之散列函数(五)- MD5 JDK 源码解析
上一篇文章 数据安全之散列函数(四)- MD5 算法原理详解 中我们讲了 MD5 的原理,现在我们来看看 JDK 中的源码是如何实现的。
首先来看 JDK 中的 MD5 怎么使用的。
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
byte[] toChapter1 = "hello".getBytes();
byte[] toChapter2 = " ".getBytes();
byte[] toChapter3 = "world".getBytes();
md.update(toChapter1);
md.update(toChapter2);
md.update(toChapter3);
byte[] toChapter1Digest = md.digest();
OpenJDK 中 MD5 的实现类是 sun.security.provider.MD5 ,父类构造函数第一个参数 algorithm 代表算法名称,第二个参数 digestLength 代表摘要的长度(算法结果的长度),第三个参数代表每次处理的块大小,这里的单位都是 byte,就是我们前面所说的结果是 128-bit,每次处理的块大小是 512-bit。
// Standard constructor, creates a new MD5 instance.
public MD5() {
super("MD5", 16, 64); // DigestBase(String algorithm, int digestLength, int blockSize)
state = new int[4];
implReset();
}
implReset() 方法,state[4] 就对应的
(
H
1
,
H
2
,
H
3
,
H
4
)
(H1,H2,H3,H4)
(H1,H2,H3,H4),初始值分别
h
1
=
0
x
67452301
,
h
2
=
0
x
e
f
c
d
a
b
89
,
h
3
=
0
x
98
b
a
d
c
f
e
,
h
4
=
0
x
10325476
h1 = 0x67452301, h2 = 0xefcdab89, h3 = 0x98badcfe, h4 = 0x10325476
h1=0x67452301,h2=0xefcdab89,h3=0x98badcfe,h4=0x10325476 4个16进制常量,每处理完一个 512-bit 的分块,state[4] 值就会更新,作为下一个分块的初始值(如图 1 所示)。
/**
* Reset the state of this object.
*/
void implReset() {
// Load magic initialization constants.
state[0] = 0x67452301;
state[1] = 0xefcdab89;
state[2] = 0x98badcfe;
state[3] = 0x10325476;
}
再看 update() ,MD5 对象中维护着一个缓存 buffer 用于存放不满 512-bit 待处理数据,缓存大小是构造函数中传入的 blockSize 决定的即 512-bit。然后将状态设置为处理中(IN_PROGRESS)。
buffer = new byte[blockSize];
/**
* Updates the digest using the specified array of bytes.
*
* @param input the array of bytes.
*/
public void update(byte[] input) {
engineUpdate(input, 0, input.length);
state = IN_PROGRESS;
}
真正的 update() 操作是交给 engineUpdate() 方法完成的。update()可以被多次调用,满 512-bit 才会被处理,如果不满则会被存放在 buffer 中等待下次处理。MD5 engineUpdate() 处理示意图:
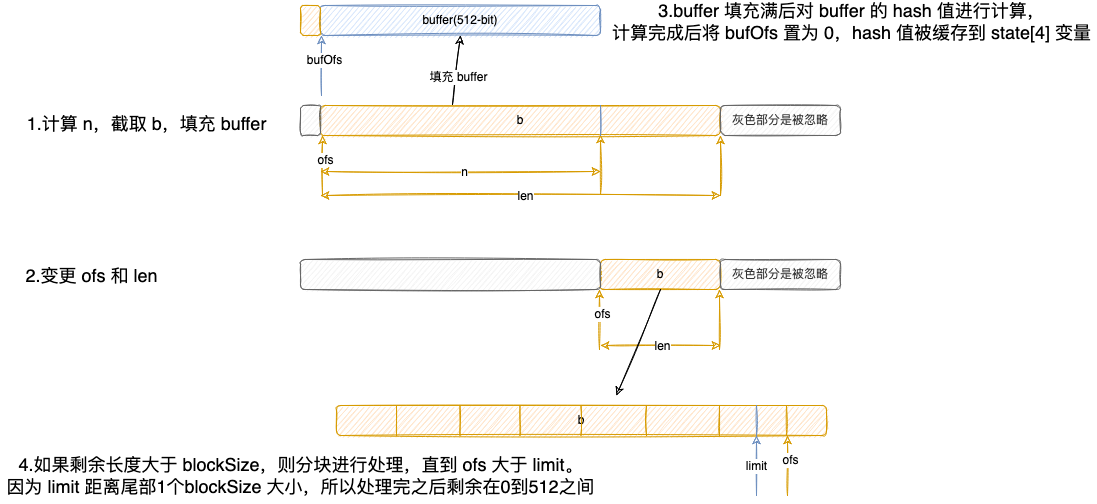
图 4
// array update. See JCA doc.
protected final void engineUpdate(byte[] b, int ofs, int len) {
if (len == 0) {
return;
}
if ((ofs < 0) || (len < 0) || (ofs > b.length - len)) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
// 以上都是数据校验
if (bytesProcessed < 0) { // todo 什么情况下 byteProcessed 会小于 0
engineReset(); // 状态重置,将 buffer 重置为 (byte)Ox0000
}
bytesProcessed += len;
// if buffer is not empty, we need to fill it before proceeding
// 如果 buffer 不为空,将 b 放入 buffer, 如果 b 大于 buffer 剩余的长度,则进行截取
if (bufOfs != 0) {
// 1.计算 n,截取 b,填充 buffer
int n = Math.min(len, blockSize - bufOfs); // 原文长度和剩余 buffer 长度选择小的
System.arraycopy(b, ofs, buffer, bufOfs, n); // 截取原文使之可以完全放入剩余的 buffer
// 2.变更 ofs 和 len
bufOfs += n; // buffer 的 offset + n
ofs += n; // 原文的 offset + n
len -= n; // 原文的 length -n
// 3.buffer 填充满后对 buffer 的 hash 值进行计算,计算完成后将 bufOfs 置为 0,hash 值被缓存到 state[4] 变量
if (bufOfs >= blockSize) { // 如果 buffer 满了就进行一次计算
// compress completed block now
implCompress(buffer, 0); // 计算 hash 值,并进行缓存
bufOfs = 0; // 处理完成后将 buffer 置空
}
}
// compress complete blocks
// 4.如果剩余长度大于 blockSize,则分块进行处理,直到 ofs 大于 limit。因为 limit 距离尾部1个blockSize 大小,所以处理完之后剩余在0到512之间
if (len >= blockSize) {
int limit = ofs + len;
ofs = implCompressMultiBlock(b, ofs, limit - blockSize);
len = limit - ofs;
}
// copy remainder to buffer
if (len > 0) { // 如果剩余长度小于处理块的长度,且大于 0 则放入 buffer,等待下次处理
System.arraycopy(b, ofs, buffer, 0, len);
bufOfs = len;
}
}
update()中关键算法就是implCompress(buffer, 0)计算 hash。如下代码,首先将 512-bit 的大块分为 16 个 32-bit 的小块,
void implCompress0(byte[] buf, int ofs) {
int a = state[0];
int b = state[1];
int c = state[2];
int d = state[3];
// 将 512-bit 的块,分成 16 个 32-bit 的小块,如上图2
int x0 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs);
int x1 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 4);
int x2 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 8);
int x3 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 12);
int x4 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 16);
int x5 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 20);
int x6 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 24);
int x7 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 28);
int x8 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 32);
int x9 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 36);
int x10 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 40);
int x11 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 44);
int x12 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 48);
int x13 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 52);
int x14 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 56);
int x15 = (int) LE.INT_ARRAY.get(buf, ofs + 60);
// 进行四轮处理 MD5 计算步骤
/* Round 1 */
a = FF ( a, b, c, d, x0, S11, 0xd76aa478); /* 1 */
d = FF ( d, a, b, c, x1, S12, 0xe8c7b756); /* 2 */
c = FF ( c, d, a, b, x2, S13, 0x242070db); /* 3 */
b = FF ( b, c, d, a, x3, S14, 0xc1bdceee); /* 4 */
a = FF ( a, b, c, d, x4, S11, 0xf57c0faf); /* 5 */
d = FF ( d, a, b, c, x5, S12, 0x4787c62a); /* 6 */
c = FF ( c, d, a, b, x6, S13, 0xa8304613); /* 7 */
b = FF ( b, c, d, a, x7, S14, 0xfd469501); /* 8 */
a = FF ( a, b, c, d, x8, S11, 0x698098d8); /* 9 */
d = FF ( d, a, b, c, x9, S12, 0x8b44f7af); /* 10 */
c = FF ( c, d, a, b, x10, S13, 0xffff5bb1); /* 11 */
b = FF ( b, c, d, a, x11, S14, 0x895cd7be); /* 12 */
a = FF ( a, b, c, d, x12, S11, 0x6b901122); /* 13 */
d = FF ( d, a, b, c, x13, S12, 0xfd987193); /* 14 */
c = FF ( c, d, a, b, x14, S13, 0xa679438e); /* 15 */
b = FF ( b, c, d, a, x15, S14, 0x49b40821); /* 16 */
/* Round 2 */
a = GG ( a, b, c, d, x1, S21, 0xf61e2562); /* 17 */
d = GG ( d, a, b, c, x6, S22, 0xc040b340); /* 18 */
c = GG ( c, d, a, b, x11, S23, 0x265e5a51); /* 19 */
b = GG ( b, c, d, a, x0, S24, 0xe9b6c7aa); /* 20 */
a = GG ( a, b, c, d, x5, S21, 0xd62f105d); /* 21 */
d = GG ( d, a, b, c, x10, S22, 0x2441453); /* 22 */
c = GG ( c, d, a, b, x15, S23, 0xd8a1e681); /* 23 */
b = GG ( b, c, d, a, x4, S24, 0xe7d3fbc8); /* 24 */
a = GG ( a, b, c, d, x9, S21, 0x21e1cde6); /* 25 */
d = GG ( d, a, b, c, x14, S22, 0xc33707d6); /* 26 */
c = GG ( c, d, a, b, x3, S23, 0xf4d50d87); /* 27 */
b = GG ( b, c, d, a, x8, S24, 0x455a14ed); /* 28 */
a = GG ( a, b, c, d, x13, S21, 0xa9e3e905); /* 29 */
d = GG ( d, a, b, c, x2, S22, 0xfcefa3f8); /* 30 */
c = GG ( c, d, a, b, x7, S23, 0x676f02d9); /* 31 */
b = GG ( b, c, d, a, x12, S24, 0x8d2a4c8a); /* 32 */
/* Round 3 */
a = HH ( a, b, c, d, x5, S31, 0xfffa3942); /* 33 */
d = HH ( d, a, b, c, x8, S32, 0x8771f681); /* 34 */
c = HH ( c, d, a, b, x11, S33, 0x6d9d6122); /* 35 */
b = HH ( b, c, d, a, x14, S34, 0xfde5380c); /* 36 */
a = HH ( a, b, c, d, x1, S31, 0xa4beea44); /* 37 */
d = HH ( d, a, b, c, x4, S32, 0x4bdecfa9); /* 38 */
c = HH ( c, d, a, b, x7, S33, 0xf6bb4b60); /* 39 */
b = HH ( b, c, d, a, x10, S34, 0xbebfbc70); /* 40 */
a = HH ( a, b, c, d, x13, S31, 0x289b7ec6); /* 41 */
d = HH ( d, a, b, c, x0, S32, 0xeaa127fa); /* 42 */
c = HH ( c, d, a, b, x3, S33, 0xd4ef3085); /* 43 */
b = HH ( b, c, d, a, x6, S34, 0x4881d05); /* 44 */
a = HH ( a, b, c, d, x9, S31, 0xd9d4d039); /* 45 */
d = HH ( d, a, b, c, x12, S32, 0xe6db99e5); /* 46 */
c = HH ( c, d, a, b, x15, S33, 0x1fa27cf8); /* 47 */
b = HH ( b, c, d, a, x2, S34, 0xc4ac5665); /* 48 */
/* Round 4 */
a = II ( a, b, c, d, x0, S41, 0xf4292244); /* 49 */
d = II ( d, a, b, c, x7, S42, 0x432aff97); /* 50 */
c = II ( c, d, a, b, x14, S43, 0xab9423a7); /* 51 */
b = II ( b, c, d, a, x5, S44, 0xfc93a039); /* 52 */
a = II ( a, b, c, d, x12, S41, 0x655b59c3); /* 53 */
d = II ( d, a, b, c, x3, S42, 0x8f0ccc92); /* 54 */
c = II ( c, d, a, b, x10, S43, 0xffeff47d); /* 55 */
b = II ( b, c, d, a, x1, S44, 0x85845dd1); /* 56 */
a = II ( a, b, c, d, x8, S41, 0x6fa87e4f); /* 57 */
d = II ( d, a, b, c, x15, S42, 0xfe2ce6e0); /* 58 */
c = II ( c, d, a, b, x6, S43, 0xa3014314); /* 59 */
b = II ( b, c, d, a, x13, S44, 0x4e0811a1); /* 60 */
a = II ( a, b, c, d, x4, S41, 0xf7537e82); /* 61 */
d = II ( d, a, b, c, x11, S42, 0xbd3af235); /* 62 */
c = II ( c, d, a, b, x2, S43, 0x2ad7d2bb); /* 63 */
b = II ( b, c, d, a, x9, S44, 0xeb86d391); /* 64 */
state[0] += a;
state[1] += b;
state[2] += c;
state[3] += d;
}
再来看 a = FF ( a, b, c, d, x0, S11, 0xd76aa478) 方法的具体实现。文档中的实现方式是
t
←
(
A
+
F
(
B
,
C
,
D
)
+
X
[
z
[
j
]
]
+
y
[
j
]
)
,
(
A
,
B
,
C
,
D
)
←
(
D
,
(
B
+
t
?
s
[
j
]
)
,
B
,
C
)
t \leftarrow (A + F(B,C,D) + X[z[j]] + y[j]),(A,B,C,D) \leftarrow(D,(B + t \hookleftarrow s[j]), B , C)
t←(A+F(B,C,D)+X[z[j]]+y[j]),(A,B,C,D)←(D,(B+t?s[j]),B,C),再来看代码实现:
private static int FF(int a, int b, int c, int d, int x, int s, int ac) {
a += ((b & c) | ((~b) & d)) + x + ac; // 上面算法第一部分
return ((a << s) | (a >>> (32 - s))) + b; // 上面算法第二部分
}
(b & c) | ((~b) & d)实现算法
f
(
u
,
v
,
w
)
f(u, v, w)
f(u,v,w)。
x
x
x 对应的
X
[
z
[
j
]
]
X[z[j]]
X[z[j]],ac 就是
y
[
j
]
y[j]
y[j],s 就是
s
[
j
]
s[j]
s[j]。所以这段代码就是实现上面这个算法。
((a << s) | (a >>> (32 - s)))代码是对循环左移的实现。
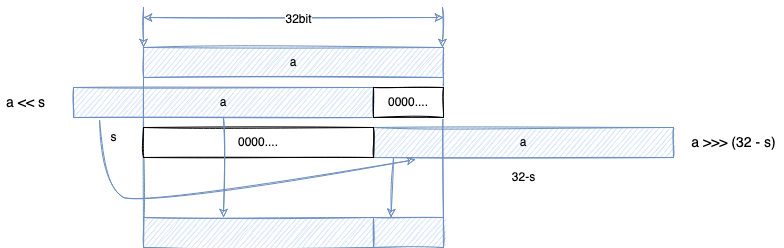
图 5
然后来看 FF 的参参数 a = FF ( a, b, c, d, x0, S11, 0xd76aa478) ,
x
0
x_0
x0? 这个 0 取值就是
z
z
z 常量,S11 就是
s
s
s 常量。而
0
x
d
76
a
a
478
0xd76aa478
0xd76aa478 就是
a
b
s
(
s
i
n
(
j
+
1
)
)
,
j
=
0
abs(sin(j + 1)),j = 0
abs(sin(j+1)),j=0 的前32个bit位,大家可以使用下面代码计算下。
public void testSinh() throws Exception {
for (int j = 0; j <= 63; j++) {
double d = Math.abs(Math.sin(j + 1));
System.out.println(binary2Hex(decimal2Binary(d)));
}
}
// 将二进制字符串转化为 16 进制
public static String binary2Hex(String s) {
int len = s.length();
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i += 4) {
char s1 = hexStr.charAt(Integer.valueOf(s.substring(i, i + 4), 2));
result.append(s1);
}
return result.toString();
}
public static String decimal2Binary(double value) throws Exception {
assert value <= 1; // sin(x) 在 0-1 之间,所以只计算小数部分。
double r = value;
// 将小数部分前 32 位转化为二进制
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int count = 32; // 限制小数部分位数最多为32位
double num = 0;
while (count > 0) {
count--;
num = r * 2;
if (num >= 1) {
stringBuilder.append(1);
r = num - 1;
} else {
stringBuilder.append(0);
r = num;
}
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
最后调用 md.digest() 方法结束,该方法对 buffer 内的数据进行填充,最后一次计算 MD5 值然后返回。
void implDigest(byte[] out, int ofs) {
long bitsProcessed = bytesProcessed << 3; // 左移3位等于*8,将byte长度转换为bit长度
// 计算预处理中 r 的值
int index = (int)bytesProcessed & 0x3f;
int padLen = (index < 56) ? (56 - index) : (120 - index); //处理填充 56*8=448,120*8=960=448+512
engineUpdate(padding, 0, padLen);
i2bLittle4((int)bitsProcessed, buffer, 56); // 将明文长度的低位放在 byte bu数组56、57、58、59位
i2bLittle4((int)(bitsProcessed >>> 32), buffer, 60); // 将明文长度的高位位放在 60、61、62、63
implCompress(buffer, 0);
i2bLittle(state, 0, out, ofs, 16);
}
void implDigest(byte[] out, int ofs) {
long bitsProcessed = bytesProcessed << 3;
int index = (int)bytesProcessed & 0x3f;
int padLen = (index < 56) ? (56 - index) : (120 - index);
engineUpdate(padding, 0, padLen);
i2bBig4((int)(bitsProcessed >>> 32), buffer, 56);
i2bBig4((int)bitsProcessed, buffer, 60);
implCompress(buffer, 0);
i2bBig(state, 0, out, ofs, 20);
}
系列文章:
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!