03--数据库连接池
1、数据库连接池
1.1 JDBC数据库连接池的必要性
在使用开发基于数据库的web程序时,传统的模式基本是按以下步骤:
- 在主程序(如servlet、beans)中建立数据库连接
- 进行sql操作
- 断开数据库连接
这种模式开发,存在的问题:
- 普通的JDBC数据库连接使用 DriverManager 来获取,每次向数据库建立连接的时候都要将 Connection 加载到内存中,再验证用户名和密码(得花费0.05s~1s的时间)。需要数据库连接的时候,就向数据库要求一个,执行完成后再断开连接。这样的方式将会消耗大量的资源和时间。数据库的连接资源并没有得到很好的重复利用。若同时有几百人甚至几千人在线,频繁的进行数据库连接操作将占用很多的系统资源,严重的甚至会造成服务器的崩溃。
- 对于每一次数据库连接,使用完后都得断开。否则,如果程序出现异常而未能关闭,将会导致数据库系统中的内存泄漏,最终将导致重启数据库。(回忆:何为Java的内存泄漏?)
- 这种开发不能控制被创建的连接对象数,系统资源会被毫无顾及的分配出去,如连接过多,也可能导致内存泄漏,服务器崩溃。
1.2 数据库连接池技术
为解决传统开发中的数据库连接问题,可以采用数据库连接池技术。
数据库连接池的基本思想:就是为数据库连接建立一个“缓冲池”。预先在缓冲池中放入一定数量的连接,当需要建立数据库连接时,只需从“缓冲池”中取出一个,使用完毕之后再放回去。
数据库连接池负责分配、管理和释放数据库连接,它允许应用程序重复使用一个现有的数据库连接,而不是重新建立一个。
数据库连接池在初始化时将创建一定数量的数据库连接放到连接池中,这些数据库连接的数量是由最小数据库连接数来设定的。无论这些数据库连接是否被使用,连接池都将一直保证至少拥有这么多的连接数量。连接池的最大数据库连接数量限定了这个连接池能占有的最大连接数,当应用程序向连接池请求的连接数超过最大连接数量时,这些请求将被加入到等待队列中。
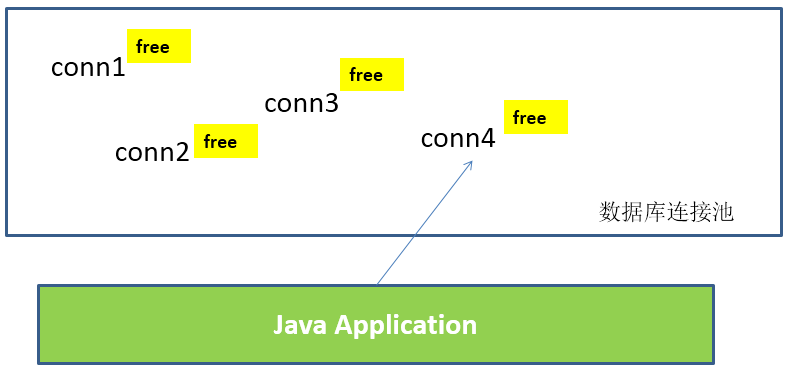
工作原理:

数据库连接池技术的优点
1. 资源重用
由于数据库连接得以重用,避免了频繁创建,释放连接引起的大量性能开销。在减少系统消耗的基础上,另一方面也增加了系统运行环境的平稳性。
2. 更快的系统反应速度
数据库连接池在初始化过程中,往往已经创建了若干数据库连接置于连接池中备用。此时连接的初始化工作均已完成。对于业务请求处理而言,直接利用现有可用连接,避免了数据库连接初始化和释放过程的时间开销,从而减少了系统的响应时间
3. 新的资源分配手段
对于多应用共享同一数据库的系统而言,可在应用层通过数据库连接池的配置,实现某一应用最大可用数据库连接数的限制,避免某一应用独占所有的数据库资源
4. 统一的连接管理,避免数据库连接泄漏
在较为完善的数据库连接池实现中,可根据预先的占用超时设定,强制回收被占用连接,从而避免了常规数据库连接操作中可能出现的资源泄露
1.3 多种开源的数据库连接池
JDBC 的数据库连接池使用 javax.sql.DataSource 来表示,DataSource 只是一个接口,该接口通常由服务器(Weblogic, WebSphere, Tomcat)提供实现,也有一些开源组织提供实现:
- DBCP 是Apache提供的数据库连接池。tomcat 服务器自带dbcp数据库连接池。速度相对c3p0较快,但因自身存在BUG,Hibernate3已不再提供支持。
- C3P0 是一个开源组织提供的一个数据库连接池,速度相对较慢,稳定性还可以。hibernate官方推荐使用
- Proxool 是sourceforge下的一个开源项目数据库连接池,有监控连接池状态的功能,稳定性较c3p0差一点
- BoneCP 是一个开源组织提供的数据库连接池,速度快
- Druid 是阿里提供的数据库连接池,据说是集DBCP 、C3P0 、Proxool 优点于一身的数据库连接池,但是速度不确定是否有BoneCP快
DataSource 通常被称为数据源,它包含连接池和连接池管理两个部分,习惯上也经常把 DataSource 称为连接池
DataSource用来取代DriverManager来获取Connection,获取速度快,同时可以大幅度提高数据库访问速度。
特别注意:
- 数据源和数据库连接不同,数据源无需创建多个,它是产生数据库连接的工厂,因此整个应用只需要一个数据源即可。
- 当数据库访问结束后,程序还是像以前一样关闭数据库连接:conn.close(); 但conn.close()并没有关闭数据库的物理连接,它仅仅把数据库连接释放,归还给了数据库连接池。
1.3.1 C3P0数据库连接池
获取连接方式一
// 方式一:
@Test
public void Test01() throws Exception {
// 获取C3P0数据库连接池
ComboPooledDataSource cpds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
cpds.setDriverClass("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
cpds.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yunhe");
cpds.setUser("root");
cpds.setPassword("123456");
//通过设置相关的参数,对数据库连接池进行管理:
//设置初始时数据库连接池中的连接数
cpds.setInitialPoolSize(10);
Connection conn = cpds.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn);
//销毁c3p0数据库连接池,一般不使用
// DataSources.destroy(cpds);
}获取连接方式二
package com.suyv.c3p0;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* @Author: 憨憨浩浩
* @CreateTime: 2024-01-11 11:30
* @Description: 测试c3p0的连接
*/
public class C3P0Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
// 获取C3P0数据库连接池
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn);
}
}其中,src下的配置文件为:【c3p0-config.xml】
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<c3p0-config>
<named-config name="helloc3p0">
<!-- 获取连接的4个基本信息 -->
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test</property>
<property name="user">root</property>
<property name="password">123456</property>
<!-- 涉及到数据库连接池的管理的相关属性的设置 -->
<!-- 若数据库中连接数不足时, 一次向数据库服务器申请多少个连接 -->
<property name="acquireIncrement">5</property>
<!-- 初始化数据库连接池时连接的数量 -->
<property name="initialPoolSize">5</property>
<!-- 数据库连接池中的最小的数据库连接数 -->
<property name="minPoolSize">5</property>
<!-- 数据库连接池中的最大的数据库连接数 -->
<property name="maxPoolSize">10</property>
<!-- C3P0 数据库连接池可以维护的 Statement 的个数 -->
<property name="maxStatements">20</property>
<!-- 每个连接同时可以使用的 Statement 对象的个数 -->
<property name="maxStatementsPerConnection">5</property>
</named-config>
</c3p0-config>1.3.2 DBCP数据库连接池
DBCP 是 Apache 软件基金组织下的开源连接池实现,该连接池依赖该组织下的另一个开源系统:Common-pool。如需使用该连接池实现,应在系统中增加如下两个 jar 文件:
- Commons-dbcp.jar:连接池的实现
- Commons-pool.jar:连接池实现的依赖库
Tomcat 的连接池正是采用该连接池来实现的。该数据库连接池既可以与应用服务器整合使用,也可由应用程序独立使用。
数据源和数据库连接不同,数据源无需创建多个,它是产生数据库连接的工厂,因此整个应用只需要一个数据源即可。
当数据库访问结束后,程序还是像以前一样关闭数据库连接:conn.close(); 但上面的代码并没有关闭数据库的物理连接,它仅仅把数据库连接释放,归还给了数据库连接池。
获取连接方式一:
package com.suyv.dbcp;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* @Author: 憨憨浩浩
* @CreateTime: 2024-01-11 14:07
* @Description: 测试DBCP的连接
*/
public class DBCPDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yunhe");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("123456");
dataSource.setInitialSize(10);
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn);
}
}获取连接方式二:
package com.suyv.dbcp;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @Author: 憨憨浩浩
* @CreateTime: 2024-01-11 14:07
* @Description: 测试DBCP的连接
*/
public class DBCPDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(DBCPDemo02.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dbcp.properties"));
DataSource dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn);
}
}其中,src下的配置文件为:【dbcp.properties】
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yunhe
username=root
password=123456
initialSize=103.3.3 Druid(德鲁伊)数据库连接池
Druid是阿里巴巴开源平台上一个数据库连接池实现,它结合了C3P0、DBCP、Proxool等DB池的优点,同时加入了日志监控,可以很好的监控DB池连接和SQL的执行情况,可以说是针对监控而生的DB连接池,可以说是目前最好的连接池之一。
package com.suyv.druid;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @Author: 憨憨浩浩
* @CreateTime: 2024-01-11 12:15
* @Description: 测试Druid的连接
*/
public class DruidDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(DruidDemo01.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties"));
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn);
}
}其中,src下的配置文件为:【druid.properties】
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yunhe
username=root
password=123456
initialSize=10
maxActive=20
maxWait=1000
filters=wall2、Apache-DBUtils实现CRUD操作
2.1 Apache-DBUtils简介
commons-dbutils 是 Apache 组织提供的一个开源 JDBC工具类库,它是对JDBC的简单封装,学习成本极低,并且使用dbutils能极大简化jdbc编码的工作量,同时也不会影响程序的性能。
API介绍:
- org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner
- org.apache.commons.dbutils.ResultSetHandler
- 工具类:org.apache.commons.dbutils.DbUtils
API包说明:
2.2 主要API的使用
2.2.1 DbUtils
DbUtils :提供如关闭连接、装载JDBC驱动程序等常规工作的工具类,里面的所有方法都是静态的。主要方法如下:
- public static void close(…) throws java.sql.SQLException: DbUtils类提供了三个重载的关闭方法。这些方法检查所提供的参数是不是NULL,如果不是的话,它们就关闭Connection、Statement和ResultSet。
- public static void closeQuietly(…): 这一类方法不仅能在Connection、Statement和ResultSet为NULL情况下避免关闭,还能隐藏一些在程序中抛出的SQLEeception。
- public static void commitAndClose(Connection conn)throws SQLException: 用来提交连接的事务,然后关闭连接
- public static void commitAndCloseQuietly(Connection conn): 用来提交连接,然后关闭连接,并且在关闭连接时不抛出SQL异常。
- public static void rollback(Connection conn)throws SQLException:允许conn为null,因为方法内部做了判断
- public static void rollbackAndClose(Connection conn)throws SQLException
- rollbackAndCloseQuietly(Connection)
- public static boolean loadDriver(java.lang.String driverClassName):这一方装载并注册JDBC驱动程序,如果成功就返回true。使用该方法,你不需要捕捉这个异常ClassNotFoundException。
2.2.2 QueryRunner类
该类简单化了SQL查询,它与ResultSetHandler组合在一起使用可以完成大部分的数据库操作,能够大大减少编码量。
QueryRunner类提供了两个构造器:
- 默认的构造器
- 需要一个 javax.sql.DataSource 来作参数的构造器
QueryRunner类的主要方法:
更新
- public int update(Connection conn, String sql, Object... params) throws SQLException:用来执行一个更新(插入、更新或删除)操作。
插入
- public ?T insert(Connection conn,String sql,ResultSetHandler rsh, Object... params) throws SQLException:只支持INSERT语句,其中 rsh - The handler used to create the result object from the ResultSet of auto-generated keys. ?返回值: An object generated by the handler.即自动生成的键值
批处理
- public int[] batch(Connection conn,String sql,Object[][] params)throws SQLException: INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE语句
- public ?T insertBatch(Connection conn,String sql,ResultSetHandler rsh,Object[][] params)throws SQLException:只支持INSERT语句
查询
- public Object query(Connection conn, String sql, ResultSetHandler rsh,Object... params) throws SQLException:执行一个查询操作,在这个查询中,对象数组中的每个元素值被用来作为查询语句的置换参数。该方法会自行处理 PreparedStatement 和 ResultSet 的创建和关闭。
测试
// 测试添加
@Test
public void testInsert() throws Exception {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "insert into customers(name,email,birth)values(?,?,?)";
int count = runner.update(conn, sql, "何成飞", "he@qq.com", "1992-09-08");
System.out.println("添加了" + count + "条记录");
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}// 测试删除
@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception {
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "delete from customers where id < ?";
int count = runner.update(conn, sql,3);
System.out.println("删除了" + count + "条记录");
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}2.2.3 ResultSetHandler接口及实现类
该接口用于处理 java.sql.ResultSet,将数据按要求转换为另一种形式。
ResultSetHandler 接口提供了一个单独的方法:Object handle (java.sql.ResultSet .rs)。
接口的主要实现类:
- ArrayHandler:把结果集中的第一行数据转成对象数组。
- ArrayListHandler:把结果集中的每一行数据都转成一个数组,再存放到List中。
- BeanHandler:将结果集中的第一行数据封装到一个对应的JavaBean实例中。
- BeanListHandler:将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个对应的JavaBean实例中,存放到List里。
- ColumnListHandler:将结果集中某一列的数据存放到List中。
- KeyedHandler(name):将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个Map里,再把这些map再存到一个map里,其key为指定的key。
- MapHandler:将结果集中的第一行数据封装到一个Map里,key是列名,value就是对应的值。
- MapListHandler:将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个Map里,然后再存放到List
- ScalarHandler:查询单个值对象
测试
/*
* 测试查询:查询一条记录
*
* 使用ResultSetHandler的实现类:BeanHandler
*/
@Test
public void testQueryInstance() throws Exception{
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?";
//
BeanHandler<Customer> handler = new BeanHandler<>(Customer.class);
Customer customer = runner.query(conn, sql, handler, 23);
System.out.println(customer);
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}/*
* 测试查询:查询多条记录构成的集合
*
* 使用ResultSetHandler的实现类:BeanListHandler
*/
@Test
public void testQueryList() throws Exception{
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id < ?";
//
BeanListHandler<Customer> handler = new BeanListHandler<>(Customer.class);
List<Customer> list = runner.query(conn, sql, handler, 23);
list.forEach(System.out::println);
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}/*
* 自定义ResultSetHandler的实现类
*/
@Test
public void testQueryInstance1() throws Exception{
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth from customers where id = ?";
ResultSetHandler<Customer> handler = new ResultSetHandler<Customer>() {
@Override
public Customer handle(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
System.out.println("handle");
// return new Customer(1,"Tom","tom@126.com",new Date(123323432L));
if(rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String email = rs.getString("email");
Date birth = rs.getDate("birth");
return new Customer(id, name, email, birth);
}
return null;
}
};
Customer customer = runner.query(conn, sql, handler, 23);
System.out.println(customer);
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}/*
* 如何查询类似于最大的,最小的,平均的,总和,个数相关的数据,
* 使用ScalarHandler
*
*/
@Test
public void testQueryValue() throws Exception{
QueryRunner runner = new QueryRunner();
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection3();
//测试一:
// String sql = "select count(*) from customers where id < ?";
// ScalarHandler handler = new ScalarHandler();
// long count = (long) runner.query(conn, sql, handler, 20);
// System.out.println(count);
//测试二:
String sql = "select max(birth) from customers";
ScalarHandler handler = new ScalarHandler();
Date birth = (Date) runner.query(conn, sql, handler);
System.out.println(birth);
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, null);
}本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!