c++:类和对象(1),封装
发布时间:2024年01月23日
C++面向对象的三大特性:封装、继承、多态。
封装
封装的意义一:
- 将属性和行为作为一个整体,表现生活中的事物
- 将属性和行为加以权限控制
类中的属性和行为,我们统一称为成员
属性也叫: 成员属性 成员变量
行为也叫: 成员函数 成员方法
格式:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class 类名
{
//访问权限
public:
//属性
//行为
};例子:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const double pai = 3.14;
//设计一个圆类,求圆的周长
//圆求周长的公式:2*Π*半径
//class代表要设计一个类,类后面紧跟着的就是类名称
class Circle
{
//访问权限
//公共权限
public:
//属性
//半径
int m_r;
//行为
//获取圆的周长
double zhouchang()
{
return 2 * pai * m_r;
}
};
int main()
{
//通过圆类 创建具体的(对象)
//实例化 (通过一个类 创建一个对象的过程)
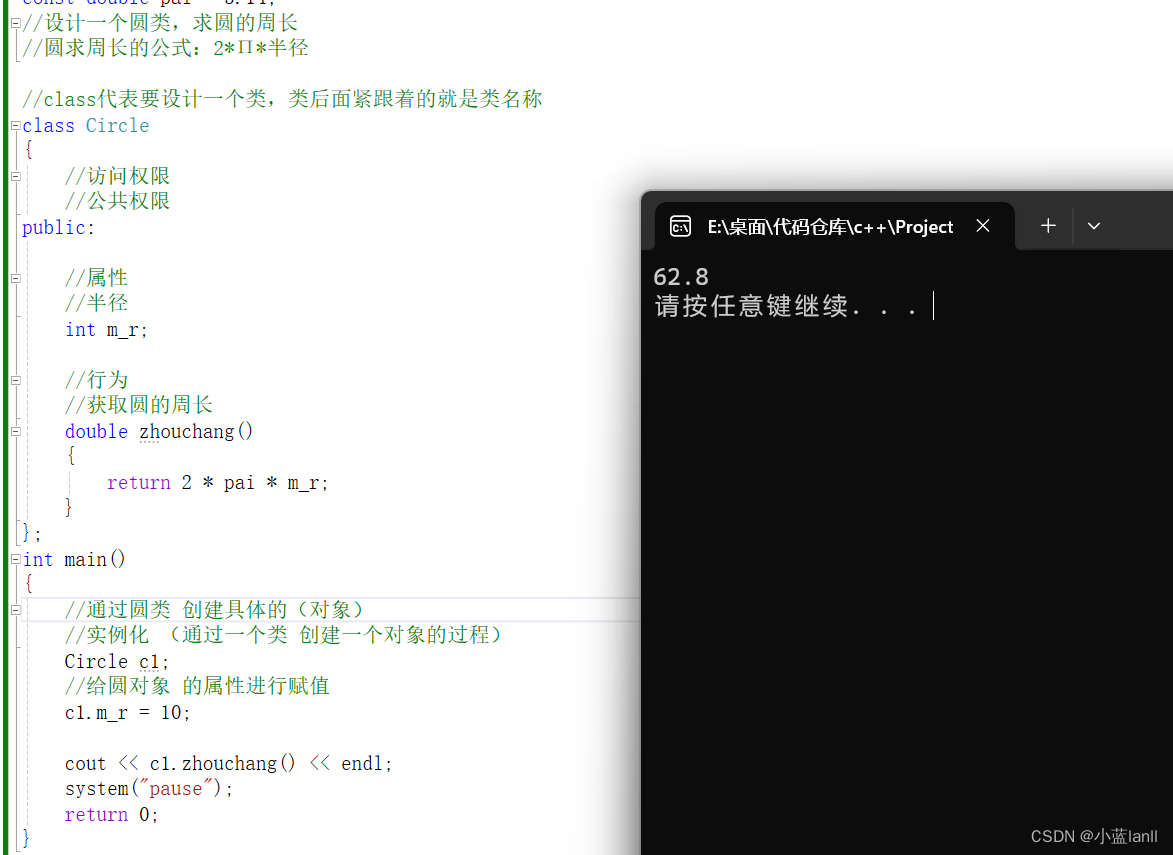
Circle c1;
//给圆对象 的属性进行赋值
c1.m_r = 10;
cout << c1.zhouchang() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
封装的意义二:
类在设计时,可以把属性和行为放在不同的权限下,加以控制
访问权限有三种:
- public? ? ? ? ? ?公共权限(成员 在类内可以访问,类外可以访问)
- protected? ? ?保护权限(成员 在类内可以访问,类外不可以访问)子类可以访问父类
- private? ? ? ? ? 私有权限(成员 在类内可以访问,类外不可以访问)子类不能访问父类? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ??
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? (后续更新子类和父类)
例子?
?类内可以访问示例:
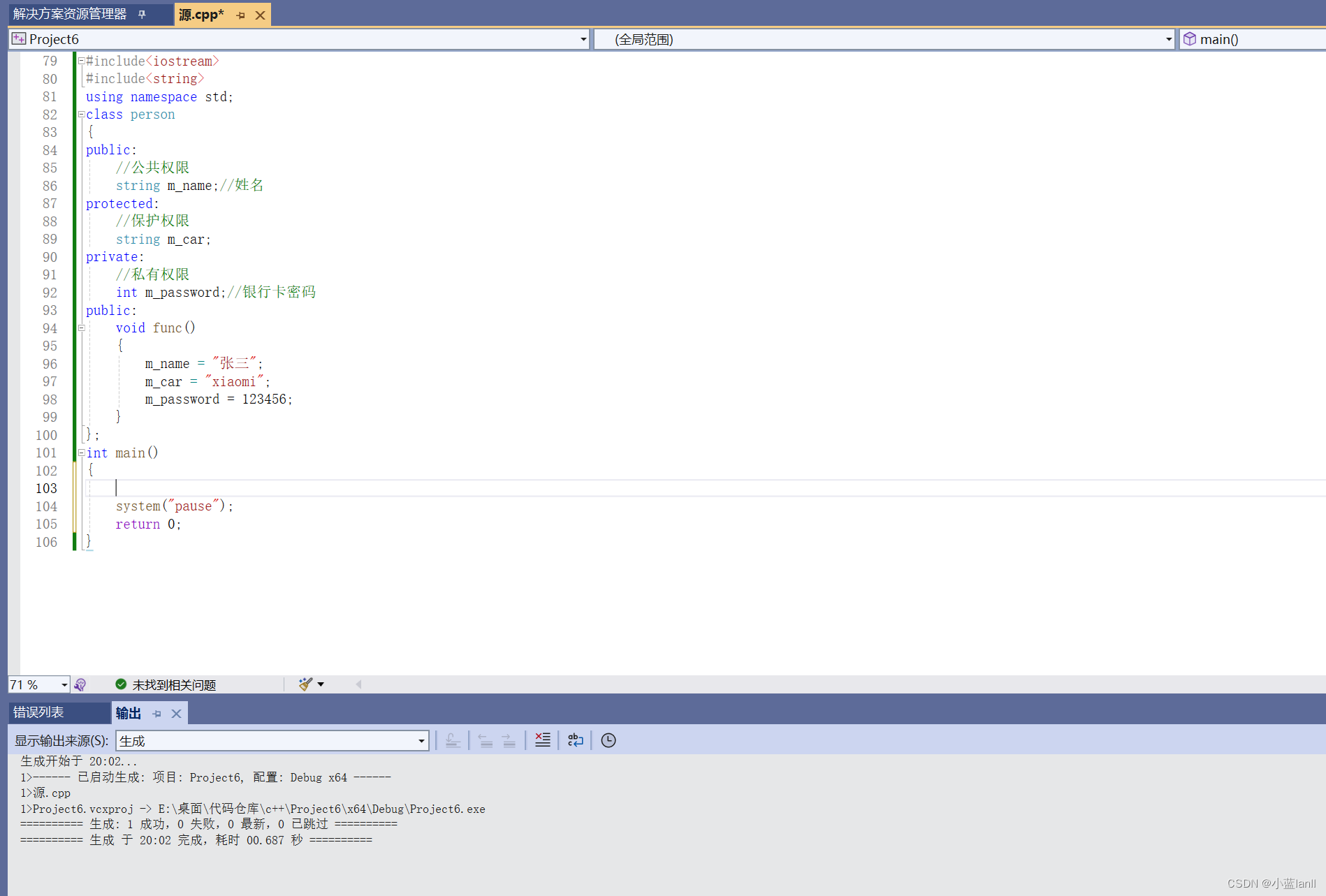
这个段代码可以正常运行,说明三者都可以在类内正常访问。
类外访问示例:
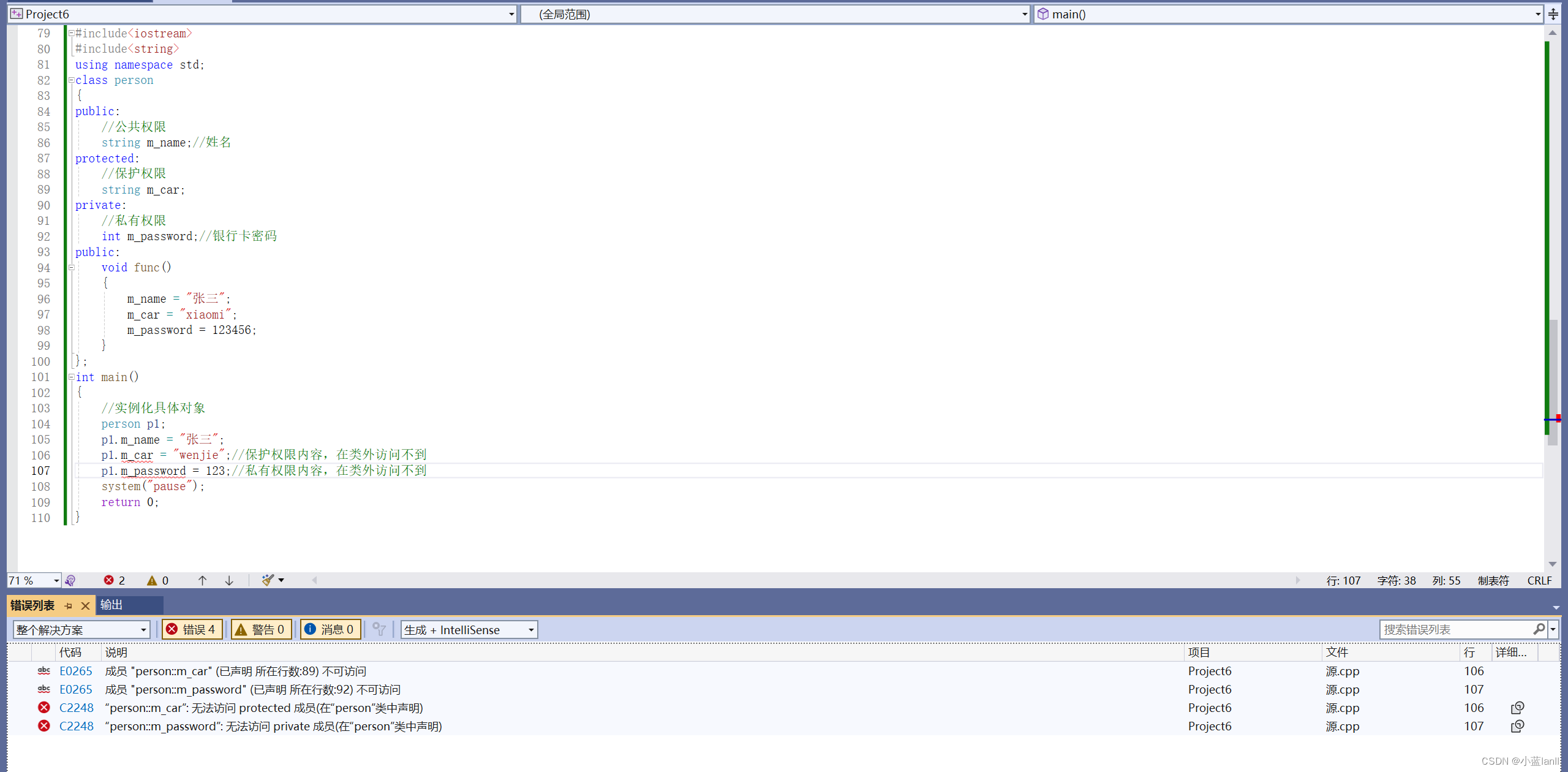 ?这段代码中,在类外访问公共权限的姓名是正常的,在类外访问保护权限和私有权限的汽车和银行卡密码发生报错,解释了访问权限的作用。
?这段代码中,在类外访问公共权限的姓名是正常的,在类外访问保护权限和私有权限的汽车和银行卡密码发生报错,解释了访问权限的作用。
struct和class的区别
在c++中,struct和class唯一的区别就在于默认的访问权限不同。
区别:
- struct默认权限为公共
- class默认权限为私有
?示例:
下面代码中,我创建了class和struct两端变量。
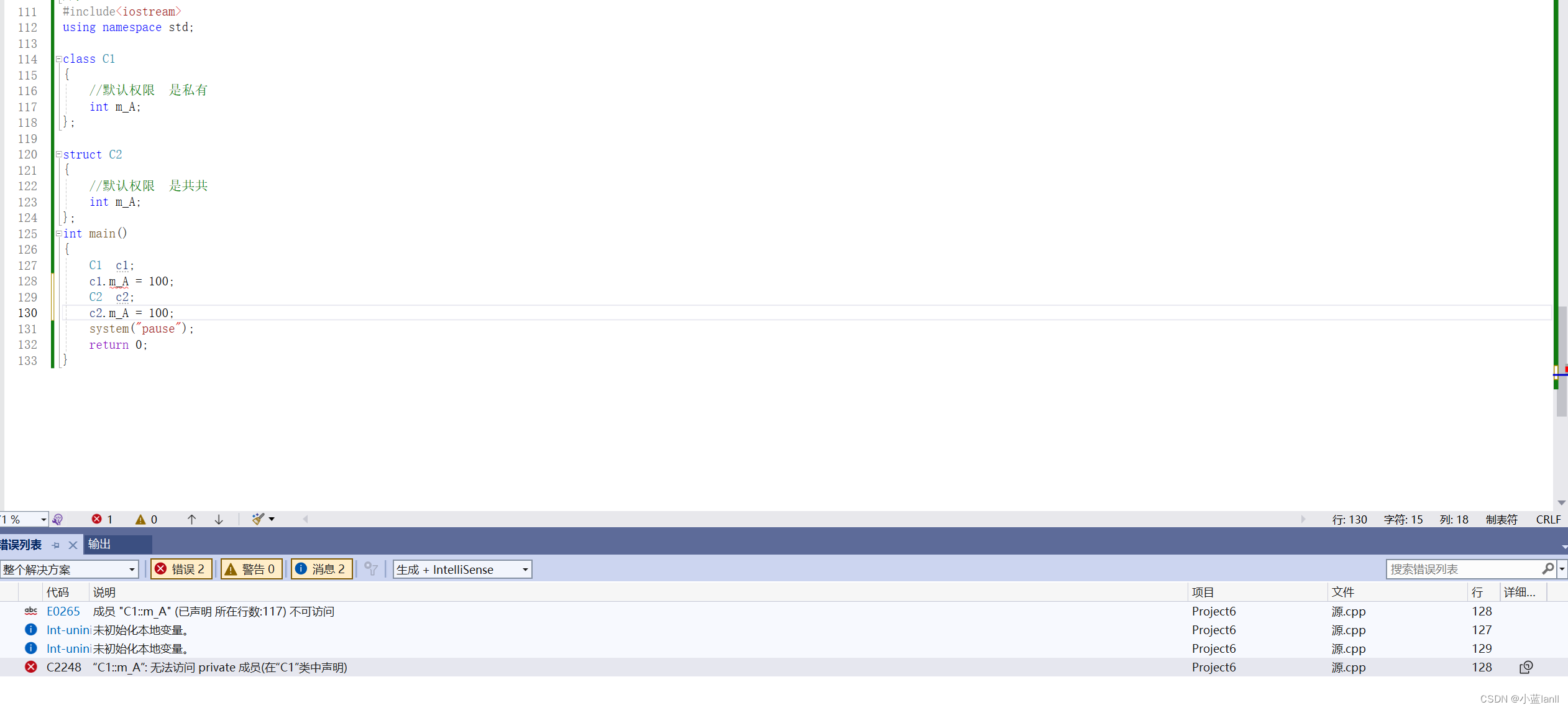
此时,我们可以看到struct可以正常的进行访问,class报错提示是private成员,不能进行正常访问。?
成员属性设置为私有
- 优点1:将所有成员属性设置为私有,可以自己控制读写权限
- 优点2:对于写权限,我们可以检测数据的有效性
?示例:
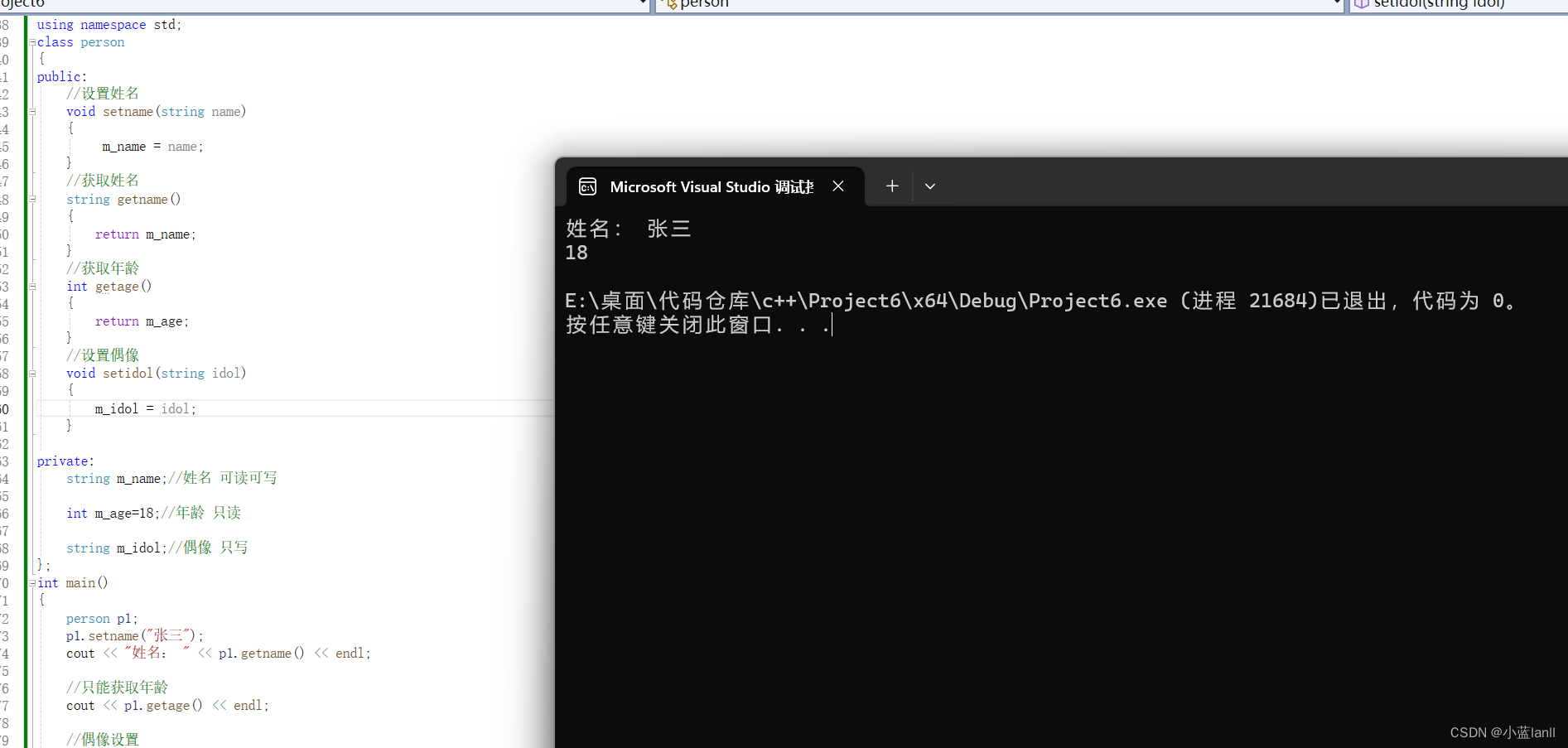
通过上面这段代码,我们可以通过选择设置或者不设置对应功能的函数,达到可读可写,只可读,只可写这三种效果。?
练习:设计立方体类
- 设计立方体类
- 求出立方体的面积和体积
- 分别用全局函数和成员函数判断两个立方体是否相等
1.设计立方体类,2.求出立方体的面积和体积
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//创建立方体的类
class Cube
{
public:
//长
void steL(int l)
{
m_L = l;
}
int steL()
{
return m_L;
}
//宽
void steW(int w)
{
m_W = w;
}
int steW()
{
return m_W;
}
//高
void steH(int h)
{
m_H = h;
}
int steH()
{
return m_H;
}
//获取立方体面积
int calculateS()
{
return 2*(m_H * m_L + m_H * m_W + m_L * m_W);
}
//获取立方体体积
int calculateV()
{
return m_H * m_L * m_W;
}
private:
int m_L;//长
int m_W;//宽
int m_H;//高
};
int main()
{
//创建一个立方体的对象
Cube c1;
c1.steH(10);
c1.steL(10);
c1.steW(10);
cout << c1.calculateS() << endl << c1.calculateV() << endl;
//第二个立方体
Cube c2;
c2.steH(10);
c2.steL(10);
c2.steW(10);
}运行结果:
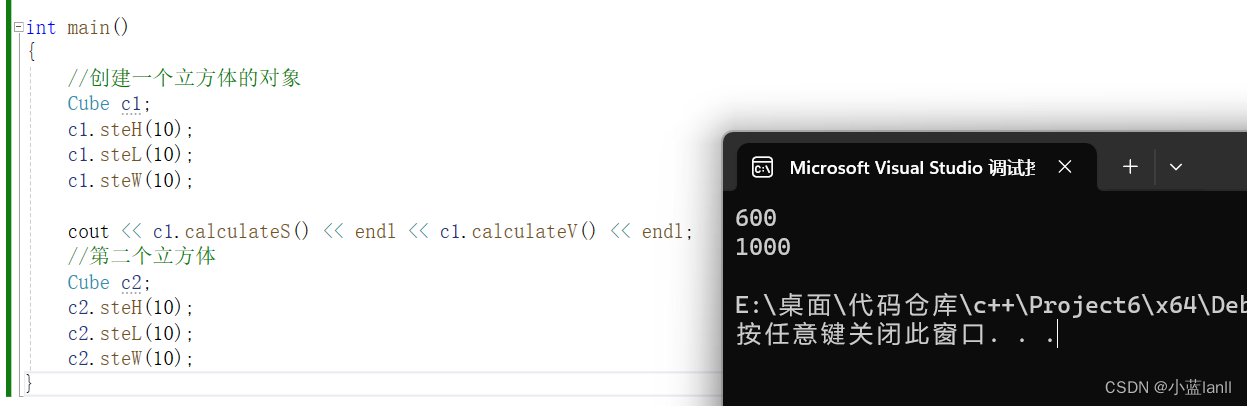 ?
?
3.分别用全局函数和成员函数判断两个立方体是否相等
全局函数
//利用全局函数做判断 两个立方体是否相等
//位置:全局
bool isSame(Cube &c1, Cube &c2)
{
//面积和体积同时相等,说明是同一个立方体,长宽高的数值可以互相调换
if ((c1.calculateS() == c2.calculateS()) && (c1.calculateV() == c1.calculateV()))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}bool ret=isSame(c1, c2);
if (ret)
{
cout << "c1和c2是相等的" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "c1和c2是不相等的" << endl;
}成员函数
bool isSameByClass(Cube&c)
{
if ((calculateS() == c.calculateS()) && (calculateV() == c.calculateV()))//类内可以访问私有成员
{
return true;
}
return false;
}完整代码:?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//创建立方体的类
class Cube
{
public:
//长
void steL(int l)
{
m_L = l;
}
int steL()
{
return m_L;
}
//宽
void steW(int w)
{
m_W = w;
}
int steW()
{
return m_W;
}
//高
void steH(int h)
{
m_H = h;
}
int steH()
{
return m_H;
}
//获取立方体面积
int calculateS()
{
return 2*(m_H * m_L + m_H * m_W + m_L * m_W);
}
//获取立方体体积
int calculateV()
{
return m_H * m_L * m_W;
}
//利用成员函数判断两个立方体是否相等
bool isSameByClass(Cube&c)
{
if ((calculateS() == c.calculateS()) && (calculateV() == c.calculateV()))//类内可以访问私有成员
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
private:
int m_L;//长
int m_W;//宽
int m_H;//高
};
//利用全局函数做判断 两个立方体是否相等
bool isSame(Cube &c1, Cube &c2)
{
if ((c1.calculateS() == c2.calculateS()) && (c1.calculateV() == c1.calculateV()))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
//创建一个立方体的对象
Cube c1;
c1.steH(10);
c1.steL(10);
c1.steW(10);
cout << c1.calculateS() << endl << c1.calculateV() << endl;
//第二个立方体
Cube c2;
c2.steH(10);
c2.steL(10);
c2.steW(10);
// bool ret=isSame(c1, c2);
//if (ret)
//{
// cout << "c1和c2是相等的" << endl;
//}
//else
//{
// cout << "c1和c2是不相等的" << endl;
//}
bool ret = c1.isSameByClass(c2);
if (ret)
{
cout << "c1和c2是相等的" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "c1和c2是不相等的" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2303_80025768/article/details/135755581
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章