【Java 中锁的种类】
发布时间:2023年12月28日
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、公平锁和非公平锁
遵守先来后到的是公平锁,不遵守的是非公平锁
- synchronized 是非公平锁
- ReentrantLock 默认是非公平锁,可通过传入参数来变成公平锁。
// 默认的无参构造方法是非公平锁的
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
/**
* fair == true,是公平锁
* fair == false,是非公平锁
*/
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
优缺点
- 公平锁能够保证任务的有序进行,所有的线程都能得到资源,不会饿死在队列中。缺点是吞吐量会下降很多,队列里面除了第一个线程,其他的线程都会阻塞,cpu唤醒阻塞线程的开销会很大。
- 非公平锁可以减少CPU唤醒线程的开销,整体的吞吐量比公平锁高,CPU也不必取唤醒所有线程,会减少唤起线程的数量。缺点是可能导致队列中间的线程一直获取不到锁或者长时间获取不到锁,导致饥饿现象。
二、可重入锁(递归锁)
指的是同一线程外层函数获得锁之后﹐内层递归函数仍然能获取该锁的代码,在同一个线程在外层方法获取锁的时候,在进入内层方法会自动获取锁,也就是说线程可以进入任何一个它已经拥有的锁所同步着的代码块
synchronized 和 ReentrantLock 都是可重入锁
代码示例
class Phone implements Runnable{
// 证明 synchronized 是可重入锁
/**
* 两个 synchronized 能够嵌套式使用
*
*
*/
public synchronized void sendMessage() {
// 调用该方法第一次加锁
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\tsendMessage");
// 第二次加锁,使用 sendMessage 的锁,即共用同一把锁
sendEmail();
}
public synchronized void sendEmail() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\tsendEmail");
}
// 证明 ReentrantLock
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
get();
}
public void get() {
// ReentrantLock 需要手动加锁解锁
// 但是要一一配对,只要配对,多少都可以
// 如果这里 lock 两次,unlock 一次就会导致线程一直阻塞等待解锁
lock.lock();
// lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\tget");
// 方法内部再次加锁
set();
} finally {
// 不配对,会一直死锁
lock.unlock();
// lock.unlock();
}
}
public void set() {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\tset");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone phone = new Phone();
new Thread(() -> {
phone.sendMessage();
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
phone.sendEmail();
}, "t2").start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("#######################");
System.out.println();
new Thread(phone, "t3").start();
new Thread(phone, "t4").start();
}
}
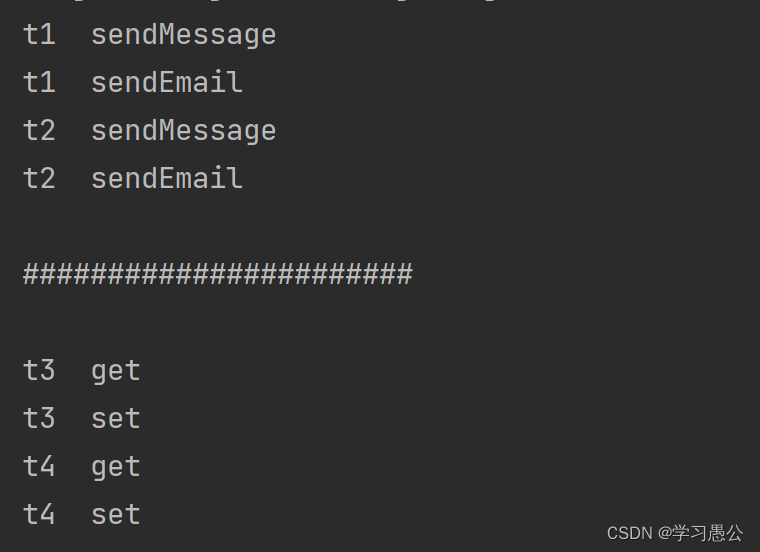
输出结果
嵌套调用成功,输出的顺序和我们预想的相同。
synchronized 加锁和释放锁的原理
monitorenter 和 monitorexit 指令,monitor计数器
monitorenter指令:
- monitor计数器为0,意味着目前还没有被获得,那这个线程就会执行一次 monitorenter 指令立刻获得这把锁,然后把锁计数器+1,一旦+1,别的线程再想获取,就需要等待。
- 如果这个monitor已经拿到了这个锁的所有权,又重入了这把锁,那锁计数器就会累加,变成2,并且随着重入的次数,会一直累加,但是累加的仅仅是锁计数器,不会再执行一次 monitorenter 指令。(即重复加锁,monitorenter 指令只执行一次,锁计数器不断累加)
- 这把锁已经被别的线程获取了,等待锁释放。
monitorexit指令:将锁计数器减1,每执行一次 monitorexit 命令锁计数器就减1(这一点与 monitorenter 不同),当锁计数器为0,释放锁。
三、自旋锁
是指尝试获取锁的线程不会立即阻塞,而是采用循环的方式去尝试获取锁,这样的好处是减少线程上下文切换的消耗,缺点是循环会消耗CPU
synchronized 和 ReentrantLock 都是自旋锁,他们都会根据使用场景自动调整自旋时间。
代码示例
class SpinLockDemo {
// 原子引用线程
AtomicReference<Thread> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();
public void myLock() {
// 此时 atomicReference 内的线程为 null
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\tcome in");
// CAS 自旋
// 将 thread 内的线程赋给 atomicReference,一直自旋直到成功
while (!atomicReference.compareAndSet(null, thread)) {
}
}
public void myUnLock() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
// 解锁
atomicReference.compareAndSet(thread, null);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\tcome out");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpinLockDemo spinLockDemo = new SpinLockDemo();
new Thread(() -> {
spinLockDemo.myLock();
// 暂停一会线程,模拟一直占用,不能释放锁
try {
System.out.println("阻塞中......");
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
spinLockDemo.myUnLock();
}, "AA").start();
}
}
输出结果

四、独占锁(写锁)/共享锁(读锁)/互斥锁
独占锁:指该锁一次只能被一个线程所持有。对 ReentrantLock 和 Synchronized 而言都是独占锁
共享锁:指该锁可被多个线程所持有
ReentrantReadWriteLock
- 对 ReentrantReadWriteLock 其读锁是共亨锁,其写锁是独占锁。读写锁分离既保证了数据的一致性,又保证了高并发性
- 读锁的共享锁可保证并发读是非常高效的,读写,写读,写写的过程是互斥的(互斥锁)。
- 写操作是独占的,原子的,不许分割。
代码示例
class MyCache {// 资源类(缓存操作,需要较高地并发操作)
private volatile Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// 这个锁不足以满足,多个线程的同时读写
// private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 读写锁分离
// private ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();// XXXXXXXXX
/**
* 写操作,不可共享
* @param key
* @param val
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public void put(String key, Object val) throws InterruptedException {
try {
// 拿到 writeLock,加锁
// readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();// XXXXXXXXX
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t正在写入:" + key);
Thread.sleep(300);
map.put(key, val);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t写入完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 解锁
// readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();// XXXXXXXXX
}
}
/**
* 读操作,可以共享
* @param key
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public void get(String key) throws InterruptedException {
try {
// 拿到 readLock 加锁
// readWriteLock.readLock().lock();// XXXXXXXXX
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t正在读取");
Thread.sleep(300);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t读取完成:" + map.get(key));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 解锁
// readWriteLock.readLock().unlock();// XXXXXXXXX
}
}
}
public class ZZZZZZZZZZ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyCache myCache = new MyCache();
// 写
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
final int tmpInt = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
myCache.put(tmpInt + "", tmpInt + "");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
// 读
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
final int tmpInt = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
myCache.get(tmpInt + "");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
输出结果(加锁前)
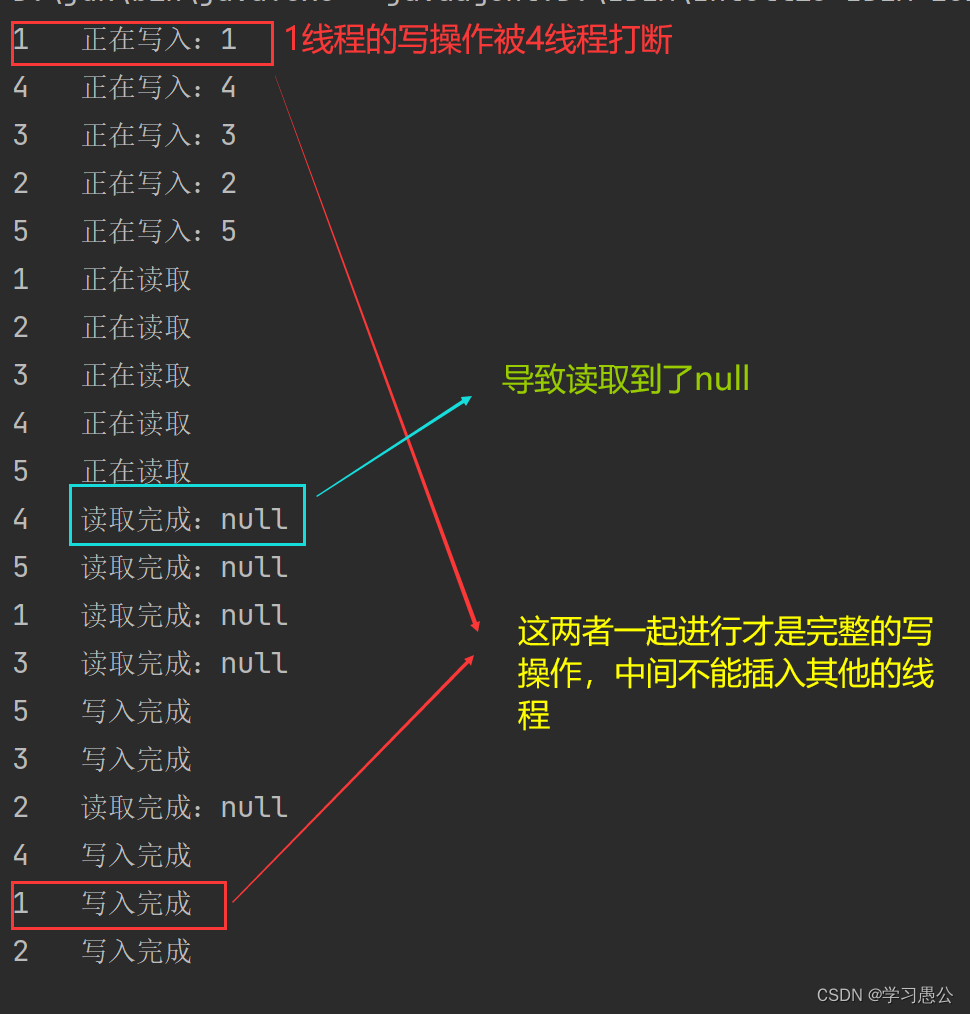
输出结果(加锁后)
将代码注释有XXXXXXXXX的代码解开,就是加锁后版本

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_69269392/article/details/135255730
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 如何使用 YOLOv8 做对象检测
- python 飞书 机器人
- 通过myBatis将sql语句返回的值自动包装成一个java对象(3)
- SVR, adaboost, MLP, GBDT, XGBOOST, LIGHTGBM以及随机森林模型参数优化+模型训练+shap解释
- 2023年度佳作:AIGC、AGI、GhatGPT 与人工智能大模型的创新与前景展望
- 【NetApp数据恢复】NetApp存储中Oracle数据库数据恢复案例
- DML语言(重点)———delete
- 算法与数据结构--最小生成树算法
- Linux网络基础
- JavaScript使用教程(三):对象