人工智能原理实验2(1)——八数码问题(BFS、DFS、UCS、IDS、A*算法)
发布时间:2024年01月21日
🧡🧡实验内容🧡🧡
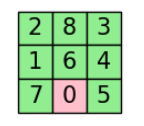
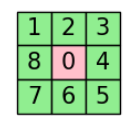
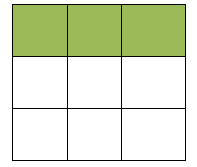
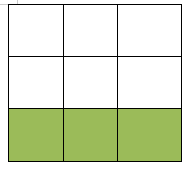
要求对空格执行空格左移、空格右移、空格上移和空格下移这四个操作使得棋盘从初始状态(左)到目标状态(右)
🧡🧡BFS、DFS实现🧡🧡
一些定义
表示数据结构:
open表的设计:
两者都是同一种open表数据结构(python 中的列表list),为实现不同的算法,在实现时只需要依据算法特点设定元素进出list的顺序即可
BFS:依据先进先出规则,新加入的状态节点放到list的末尾
DFS:依据先进后出规则,新加入的状态节点放入到list的首位
状态扩展规则表示:
八数码用一个3×3的矩阵来存储
通过交换空格(数字0)与其他数字的位置,实现状态扩展
考虑特殊边界情况:
- 当空格(数字0)在矩阵的最左一列时,不能向左移动
- 当空格(数字0)在矩阵的最右一列时,不能向右移动
- 当空格(数字0)在矩阵的最上一行时,不能向上移动
- 当空格(数字0)在矩阵的最下一行时,不能向下移动
👇代码逻辑👇
BFS代码
# BFS
import numpy as np
import copy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
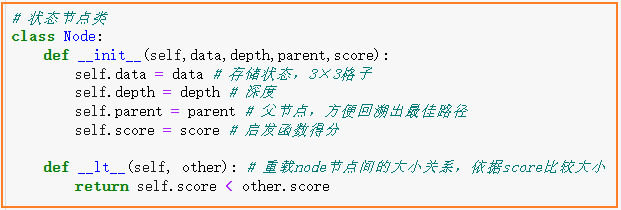
# 状态节点类
class Node:
def __init__(self,data,depth,parent):
self.data=data # 存储状态,3×3格子
self.depth=depth # 深度
self.parent = parent # 父节点,方便回溯出最佳路径
# BFS_solve
class BFS:
# 初始化
def __init__(self,initial,goals):
self.initial=Node(np.reshape(initial,(3,3)),0,"None") # 初始状态
self.goals=Node(np.reshape(goals,(3,3)),0,"None") # 目标状态
self.open_=[self.initial] # 将初始状态加入open表
self.close_=[] # close表
# 展示最终路径
def __show_path(self,node):
arr=node.data
# 创建颜色映射,0用红色表示,其他用绿色表示
colors = [['pink' if num == 0 else 'lightgreen' for num in row] for row in arr]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(1.2, 1.2))
ax.axis('off') # 隐藏坐标轴
# 创建表格对象
table = plt.table(cellText=arr,
cellColours=colors,
loc='center',
cellLoc='center')
table.set_fontsize(15) # 设置格子的字体大小
table.scale(1, 1) # 调整表格布局
# 设置单元格的宽度和高度
cell_width = 1.0 / 3.0
cell_height = 1.0 / 3.0
# 设置每个单元格的宽度和高度相等,使其为正方形
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
cell = table.get_celld()[(i, j)]
cell.set_width(cell_width)
cell.set_height(cell_height)
plt.show() # 显示图像
# 交换格子位置
def __move(self,n,postion,row,col):
if postion =="left":
n[row,col] , n[row,col-1] = n[row,col-1], n[row,col]
elif postion == "right":
n[row,col] , n[row,col+1] = n[row,col+1], n[row,col]
elif postion == "up":
n[row,col] , n[row-1,col] = n[row-1,col], n[row,col]
elif postion == "down":
n[row,col] , n[row+1,col] = n[row+1,col], n[row,col]
return n
# 判断新状态和close表和open表是否重复状态
def __is_exist(self,three_result,close_,open_):
for i in range(len(close_)):
if (three_result == close_[i].data).all():
return True
for i in range(len(open_)):
if (three_result == open_[i].data).all():
return True
return False
def solve(self):
cnt = 0 # 遍历节点次数
depth=1 # 深度
while self.open_:
# 打印open和close表,观察它们的变化
# print(f"====👇👇👇遍历第{cnt}个节点时: open表👇👇👇====")
# for state in self.open_:
# print(state.data)
# print(f"====👇👇👇遍历第{cnt}个节点时: close表👇👇👇====")
# for state in self.close_:
# print(state.data)
cnt = cnt+1
# 初始化算子
direction=['up', 'down', 'right', 'left']
# 从open表中删除第一个状态并放入close表中
n = self.open_.pop(0)
self.close_.append(n)
# 打印过程
# print(f"==== 层数:{n.depth} ====")
# print(f"访问第{cnt}个节点:\n{n.data}")
# ==================结束条件==================
if (n.data == self.goals.data).all():
resultAll=[]
resultAll.append(n)
while n.parent!="None": # 回溯路径
resultAll.append(n.parent)
n = n.parent
resultAll_len=len(resultAll)
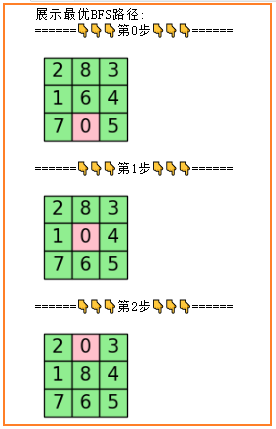
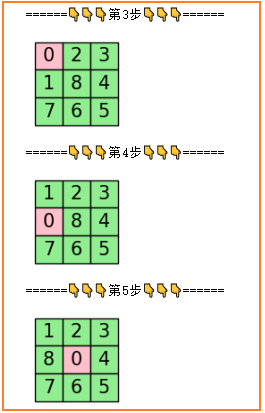
print("展示最优BFS路径: ")
for j in range(resultAll_len):
print(f"======👇👇👇第{j}步👇👇👇======")
result = resultAll.pop(-1) # 弹出
self.__show_path(result)
print("==================BFS结束搜索==================")
print(f"总共遍历的节点数目:{cnt}")
print(f"找到的可行路径的节点数目:{resultAll_len}")
break
# ==================生成n的所有子状态,并加入到open表后方================
# 找出空格位置
postion = np.where(n.data == 0)
i = postion[0]
j = postion[1]
length_down=n.data.shape[0]
length_right=n.data.shape[1]
# 避免误操作
if i==0: # 清除上操作:在第一行,不能向上移动
direction.remove("up")
if j==0: # 清除左操作:在第一列,不能向左移动
direction.remove("left")
if i == length_down-1: # 清除下操作:在末行,不能向下移动
direction.remove("down")
if j == length_right-1: # 清除右操作:在末列,不能向右移动
direction.remove("right")
# 遍历所有可能子状态
for p in range(len(direction)):
copy_n = copy.deepcopy(n)
three_result = self.__move(copy_n.data,direction[p],i,j)
# 判断是否存在于close表
if (self.__is_exist(three_result,self.close_,self.open_)):
continue
self.open_.append(Node(three_result,n.depth+1,n)) # 插入到open尾部,先进先出
# 初始化状态
initial_state=[2,8,3,1,6,4,7,0,5]
goal_state=[1,2,3,8,0,4,7,6,5]
start_time = time.time() # 记录程序开始时间
bfs = BFS(initial_state,goal_state)
bfs.solve()
end_time = time.time() # 记录程序结束时间
print(f"程序的运行时间为:{(end_time-start_time)*1000} ms")
DFS代码
# DFS
import numpy as np
import copy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
# 状态节点类
class Node:
def __init__(self,data,depth,parent):
self.data=data # 存储状态,3×3格子
self.depth=depth # 深度
self.parent = parent # 父节点,方便回溯出最佳路径
# BFS_solve
class DFS:
# 初始化
def __init__(self,initial,goals):
self.initial=Node(np.reshape(initial,(3,3)),0,"None") # 初始状态
self.goals=Node(np.reshape(goals,(3,3)),0,"None") # 目标状态
self.open_=[self.initial] # 将初始状态加入open表
self.close_=[] # close表
self.max_depth=10 # 最大搜索深度
# 展示最终路径
def __show_path(self,node):
arr=node.data
# 创建颜色映射,0用红色表示,其他用绿色表示
colors = [['pink' if num == 0 else 'lightgreen' for num in row] for row in arr]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(1.2, 1.2))
ax.axis('off') # 隐藏坐标轴
# 创建表格对象
table = plt.table(cellText=arr,
cellColours=colors,
loc='center',
cellLoc='center')
table.set_fontsize(15) # 设置格子的字体大小
table.scale(1, 1) # 调整表格布局
# 设置单元格的宽度和高度
cell_width = 1.0 / 3.0
cell_height = 1.0 / 3.0
# 设置每个单元格的宽度和高度相等,使其为正方形
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
cell = table.get_celld()[(i, j)]
cell.set_width(cell_width)
cell.set_height(cell_height)
plt.show() # 显示图像
# 交换格子位置
def __move(self,n,postion,row,col):
if postion =="left":
n[row,col] , n[row,col-1] = n[row,col-1], n[row,col]
elif postion == "right":
n[row,col] , n[row,col+1] = n[row,col+1], n[row,col]
elif postion == "up":
n[row,col] , n[row-1,col] = n[row-1,col], n[row,col]
elif postion == "down":
n[row,col] , n[row+1,col] = n[row+1,col], n[row,col]
return n
# 判断新状态和close表和open表是否重复状态
def __is_exist(self,three_result,close_,open_):
for i in range(len(close_)):
if (three_result == close_[i].data).all():
return True
for i in range(len(open_)):
if (three_result == open_[i].data).all():
return True
return False
def solve(self):
#遍历个数
cnt = 0
depth=1
while self.open_:
# 打印open和close表,观察它们的变化
# print(f"====👇👇👇遍历第{cnt}个节点时: open表👇👇👇====")
# for state in self.open_:
# print(state.data)
# print(f"====👇👇👇遍历第{cnt}个节点时: close表👇👇👇====")
# for state in self.close_:
# print(state.data)
cnt = cnt+1
# 初始化算子
direction=['up', 'down', 'right', 'left']
# 从open表中删除第一个状态并放入close表中
n = self.open_.pop(0)
self.close_.append(n)
# 打印过程
# print(f"==== 层数:{n.depth} ====")
# print(f"访问第{cnt}个节点:\n{n.data}")
# ==================结束条件==================
if (n.data == self.goals.data).all():
resultAll=[]
resultAll.append(n)
while n.parent!="None": # 回溯路径
resultAll.append(n.parent)
n = n.parent
resultAll_len=len(resultAll)
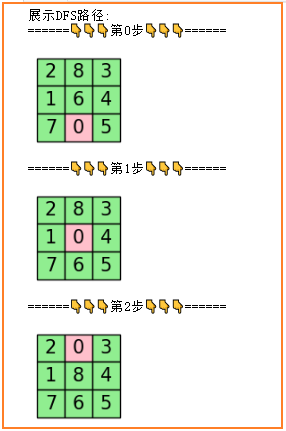
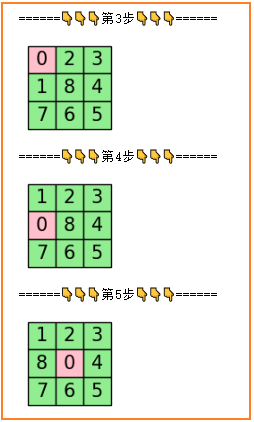
print("展示DFS路径: ")
for j in range(resultAll_len):
print(f"======👇👇👇第{j}步👇👇👇======")
result = resultAll.pop(-1) # 弹出
self.__show_path(result)
print("==================DFS结束搜索==================")
print(f"总共遍历的节点数目:{cnt}")
print(f"找到的可行路径的节点数目:{resultAll_len}")
break
# ==================生成n的所有子状态,并加入到open表================
# 找出空格位置
postion = np.where(n.data == 0)
i = postion[0]
j = postion[1]
length_down=n.data.shape[0]
length_right=n.data.shape[1]
# 避免误操作
if i==0: # 清除上操作:在第一行,不能向上移动
direction.remove("up")
if j==0: # 清除左操作:在第一列,不能向左移动
direction.remove("left")
if i == length_down-1: # 清除下操作:在末行,不能向下移动
direction.remove("down")
if j == length_right-1: # 清除右操作:在末列,不能向右移动
direction.remove("right")
# 设定搜索的最大深度,不然会一直递归下去
if n.depth>=self.max_depth:
continue
# 遍历所有可能子状态
for p in range(len(direction)):
copy_n = copy.deepcopy(n)
three_result = self.__move(copy_n.data,direction[p],i,j)
# 判断是否存在于close表
if (self.__is_exist(three_result,self.close_,self.open_)):
continue
self.open_.insert(0,Node(three_result,n.depth+1,n)) # 新状态插入到open表最前面,确保往下深度搜索
# 初始化状态
initial_state=[2,8,3,1,6,4,7,0,5]
goal_state=[1,2,3,8,0,4,7,6,5]
start_time = time.time() # 记录程序开始时间
dfs = DFS(initial_state,goal_state)
dfs.solve()
end_time = time.time() # 记录程序结束时间
print(f"程序的运行时间为:{(end_time-start_time)*1000} ms")
运行结果(最优路径展示)
BFS
DFS(设置最高深度为10时的结果)
🧡🧡UCS、IDS🧡🧡
BFS、DFS的拔高算法
UCS代码实现
# UCS
import numpy as np
import heapq
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
# 状态节点类
class Node:
def __init__(self, data, cost, parent):
self.data = data # 存储状态,3×3格子
self.cost = cost # 代价
self.parent = parent # 父节点,方便回溯出最佳路径
# UCS_solve
class UCS:
# 初始化
def __init__(self, initial, goals):
self.initial = Node(np.reshape(initial, (3, 3)), 0, "None") # 初始状态
self.goals = Node(np.reshape(goals, (3, 3)), 0, "None") # 目标状态
self.open_ = [] # open表使用优先队列
self.close_ = [] # close表
# 展示最终路径
def __show_path(self, node):
arr = node.data
# 创建颜色映射,0用红色表示,其他用绿色表示
colors = [['pink' if num == 0 else 'lightgreen' for num in row] for row in arr]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(1.2, 1.2))
ax.axis('off') # 隐藏坐标轴
# 创建表格对象
table = plt.table(cellText=arr,
cellColours=colors,
loc='center',
cellLoc='center')
table.set_fontsize(15) # 设置格子的字体大小
table.scale(1, 1) # 调整表格布局
# 设置单元格的宽度和高度
cell_width = 1.0 / 3.0
cell_height = 1.0 / 3.0
# 设置每个单元格的宽度和高度相等,使其为正方形
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
cell = table.get_celld()[(i, j)]
cell.set_width(cell_width)
cell.set_height(cell_height)
plt.show() # 显示图像
# 交换格子位置
def __move(self, n, postion, row, col):
if postion == "left":
n[row, col], n[row, col - 1] = n[row, col - 1], n[row, col]
elif postion == "right":
n[row, col], n[row, col + 1] = n[row, col + 1], n[row, col]
elif postion == "up":
n[row, col], n[row - 1, col] = n[row - 1, col], n[row, col]
elif postion == "down":
n[row, col], n[row + 1, col] = n[row + 1, col], n[row, col]
return n
# 判断新状态和close表和open表是否重复状态
def __is_exist(self, three_result, close_, open_):
for i in range(len(close_)):
if (three_result == close_[i].data).all():
return True
for i in range(len(open_)):
if (three_result == open_[i][2].data).all():
return True
return False
def solve(self):
# 添加初始状态到open表,优先队列加入三元组(cost,id,Node)
heapq.heappush(self.open_, (0, id(self.initial), self.initial))
cnt=0
while self.open_:
# 取出代价最小的节点
cost, _, node = heapq.heappop(self.open_)
self.close_.append(node)
cnt+=1
if (node.data == self.goals.data).all():
resultAll = []
resultAll.append(node)
while node.parent != "None": # 回溯路径
resultAll.append(node.parent)
node = node.parent
resultAll_len = len(resultAll)
print("展示UCS路径: ")
for j in range(resultAll_len):
print(f"======👇👇👇第{j}步👇👇👇======")
result = resultAll.pop(-1) # 弹出
self.__show_path(result)
print("==================UCS结束搜索==================")
print(f"总共遍历的节点数目:{cnt}")
print(f"找到的可行路径的节点数目:{resultAll_len}")
break
# ======================生成n的所有子状态,并加入到open表====================
postion = np.where(node.data == 0)
i = postion[0][0]
j = postion[1][0]
direction = ['up', 'down', 'right', 'left']
length_down = node.data.shape[0]
length_right = node.data.shape[1]
# 避免误操作
if i==0: # 清除上操作:在第一行,不能向上移动
direction.remove("up")
if j==0: # 清除左操作:在第一列,不能向左移动
direction.remove("left")
if i == length_down-1: # 清除下操作:在末行,不能向下移动
direction.remove("down")
if j == length_right-1: # 清除右操作:在末列,不能向右移动
direction.remove("right")
# 遍历所有可能子状态
for p in range(len(direction)):
copy_n = np.copy(node.data)
new_data = self.__move(copy_n, direction[p], i, j)
if self.__is_exist(new_data, self.close_, self.open_):
continue
new_node = Node(new_data, node.cost + 1, node)
heapq.heappush(self.open_, (new_node.cost, id(new_node), new_node))
# 初始化状态
initial_state = [2, 8, 3, 1, 6, 4, 7, 0, 5]
goal_state = [1, 2, 3, 8, 0, 4, 7, 6, 5]
start_time = time.time() # 记录程序开始时间
ucs = UCS(initial_state, goal_state)
ucs.solve()
end_time = time.time() # 记录程序结束时间
print(f"程序的运行时间为:{(end_time-start_time)*1000} ms")
IDS代码实现
# IDS
# 状态节点类
import copy
class Node:
def __init__(self,data,depth,parent):
self.data=data # 存储状态,3×3格子
self.depth=depth # 深度
self.parent = parent # 父节点,方便回溯出最佳路径
class IDS:
# 初始化
def __init__(self,initial,goals):
self.initial=Node(np.reshape(initial,(3,3)),0,"None") # 初始状态
self.goals=Node(np.reshape(goals,(3,3)),0,"None") # 目标状态
self.max_depth=10 # 最大搜索深度
# 展示最终路径
def __show_path(self,node):
arr=node.data
# 创建颜色映射,0用红色表示,其他用绿色表示
colors = [['pink' if num == 0 else 'lightgreen' for num in row] for row in arr]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(1.2, 1.2))
ax.axis('off') # 隐藏坐标轴
# 创建表格对象
table = plt.table(cellText=arr,
cellColours=colors,
loc='center',
cellLoc='center')
table.set_fontsize(15) # 设置格子的字体大小
table.scale(1, 1) # 调整表格布局
# 设置单元格的宽度和高度
cell_width = 1.0 / 3.0
cell_height = 1.0 / 3.0
# 设置每个单元格的宽度和高度相等,使其为正方形
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
cell = table.get_celld()[(i, j)]
cell.set_width(cell_width)
cell.set_height(cell_height)
plt.show() # 显示图像
# 交换格子位置
def __move(self,n,postion,row,col):
if postion =="left":
n[row,col] , n[row,col-1] = n[row,col-1], n[row,col]
elif postion == "right":
n[row,col] , n[row,col+1] = n[row,col+1], n[row,col]
elif postion == "up":
n[row,col] , n[row-1,col] = n[row-1,col], n[row,col]
elif postion == "down":
n[row,col] , n[row+1,col] = n[row+1,col], n[row,col]
return n
def __depth_limited_DFS(self, node, depth_limit):
if (node.data == self.goals.data).all():
return [node]
if depth_limit <= 0:
return []
if node.depth >= depth_limit:
return []
direction=['up', 'down', 'right', 'left']
# ======================生成n的所有子状态====================
postion = np.where(node.data == 0)
i = postion[0]
j = postion[1]
length_down=node.data.shape[0]
length_right=node.data.shape[1]
result = []
# 避免误操作
if i==0: # 清除上操作:在第一行,不能向上移动
direction.remove("up")
if j==0: # 清除左操作:在第一列,不能向左移动
direction.remove("left")
if i == length_down-1: # 清除下操作:在末行,不能向下移动
direction.remove("down")
if j == length_right-1: # 清除右操作:在末列,不能向右移动
direction.remove("right")
for p in range(len(direction)):
copy_n = copy.deepcopy(node)
three_result = self.__move(copy_n.data,direction[p], i, j)
child_node = Node(three_result, node.depth + 1, node)
result.append(child_node)
res = self.__depth_limited_DFS(child_node, depth_limit - 1)
if res:
return [child_node] + res
return []
def solve(self):
for depth_limit in range(self.max_depth + 1):
result = self.__depth_limited_DFS(self.initial, depth_limit)
if result:
print("展示IDS路径: ")
for node in result:
self.__show_path(node)
print("==================IDS结束搜索==================")
print(f"找到的可行路径的节点数目:{len(result)}")
return
print("未找到可行路径")
# 初始化状态
initial_state=[2,8,3,1,6,4,7,0,5]
goal_state=[1,2,3,8,0,4,7,6,5]
start_time = time.time() # 记录程序开始时间
ids = IDS(initial_state,goal_state)
ids.solve()
end_time = time.time() # 记录程序结束时间
print(f"程序的运行时间为:{(end_time-start_time)*1000} ms")
🧡🧡A*实现🧡🧡
表示数据结构
相比之前BFS多加了启发函数得分,以及重载了open表对于各个状态节点的排序规则,让启发函数得分小的排在open表前面
open表的设计
依据启发函数得分的原则,每次取出启发函数得分score最小的状态节点
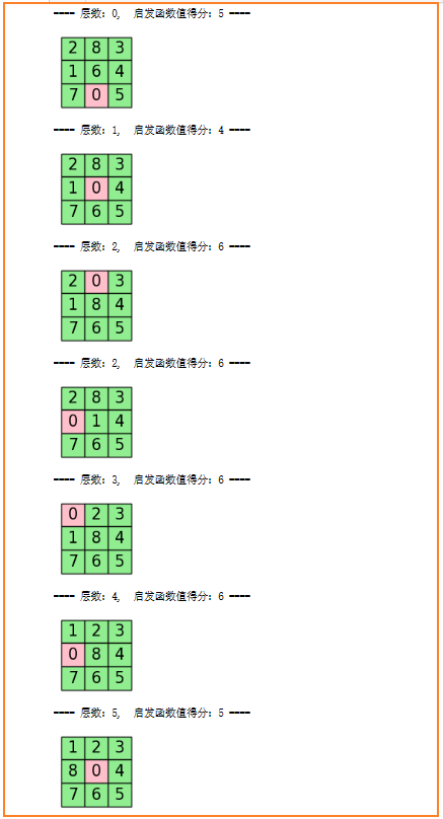
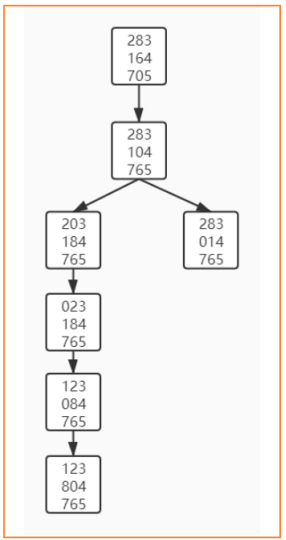
搜索空间展示
左图为代码结果,右图为左图形象化的空间图(手画)
A*代码
# A*
import numpy as np
import copy
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
# 状态节点类
class Node:
def __init__(self,data,depth,parent,score):
self.data = data # 存储状态,3×3格子
self.depth = depth # 深度
self.parent = parent # 父节点,方便回溯出最佳路径
self.score = score # 启发函数得分
def __lt__(self, other): # 重载node节点间的大小关系,依据score比较大小
return self.score < other.score
class A:
def __init__(self,initial,goals):
self.initial=Node(np.reshape(initial,(3,3)),0,"None",0) # 初始状态
self.goals=Node(np.reshape(goals,(3,3)),0,"None",0) # 目标状态
self.open_=[self.initial] # 将初始状态加入open表
self.close_=[]
self.__cal_score(self.initial,self.goals) # 初始节点启发函数得分
# 估价函数——错位数
def __cal_score(self,node,goals):
gn = node.depth # g(n):当前状态的深度
hn = np.count_nonzero(node.data-goals.data) # h(n):当前状态与目标状态的不同位置个数
node.score = gn+hn
# node.score = gn
node.score = hn
return node
# 估价函数——曼哈顿距离
def __cal_score_manhattan(self,node,goals):
distance=0
arr=node.data
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
if arr[i][j]!=0:
x,y=divmod(arr[i][j]-1,3)
distance+=abs(x-i)+abs(y-j)
node.score=distance
return node
# 估价函数——欧式距离
def __cal_score_euclidean(self,node,goals):
distance=0
arr=node.data
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
if arr[i][j]!=0:
x, y = divmod(arr[i][j] - 1, 3)
distance += ((x - i) ** 2 + (y - j) ** 2) ** 0.5
node.score=distance
return node
# 展示最终路径
def __show_path(self,node):
arr=node.data
# 创建颜色映射,0用红色表示,其他用绿色表示
colors = [['pink' if num == 0 else 'lightgreen' for num in row] for row in arr]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(1.2, 1.2))
ax.axis('off') # 隐藏坐标轴
# 创建表格对象
table = plt.table(cellText=arr,
cellColours=colors,
loc='center',
cellLoc='center')
table.set_fontsize(15) # 设置格子的字体大小
table.scale(1, 1) # 调整表格布局
# 设置单元格的宽度和高度
cell_width = 1.0 / 3.0
cell_height = 1.0 / 3.0
# 设置每个单元格的宽度和高度相等,使其为正方形
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
cell = table.get_celld()[(i, j)]
cell.set_width(cell_width)
cell.set_height(cell_height)
plt.show() # 显示图像
# 交换格子位置
def __move(self,n,postion,row,col):
if postion =="left":
n[row,col] , n[row,col-1] = n[row,col-1], n[row,col]
elif postion == "right":
n[row,col] , n[row,col+1] = n[row,col+1], n[row,col]
elif postion == "up":
n[row,col] , n[row-1,col] = n[row-1,col], n[row,col]
elif postion == "down":
n[row,col] , n[row+1,col] = n[row+1,col], n[row,col]
return n
# 判断新状态和close表和open表是否重复状态
def __is_exist(self,three_result,close_,open_):
for i in range(len(close_)):
if (three_result == close_[i].data).all():
return True
for i in range(len(open_)):
if (three_result == open_[i].data).all():
return True
return False
def solve(self):
cnt = 0 # 遍历节点次数
depth =1
while self.open_:
# 打印open和close表,观察它们的变化
# print(f"====👇👇👇遍历第{cnt}个节点时: open表👇👇👇====")
# for state in self.open_:
# print(state.data)
# print(f"====👇👇👇遍历第{cnt}个节点时: close表👇👇👇====")
# for state in self.close_:
# print(state.data)
cnt = cnt+1
#初始化算子
direction=['up', 'down', 'right', 'left']
#从open表中删除第一个状态并放入close表中
n = self.open_.pop(0)
self.close_.append(n)
# 打印过程
# print(f"==== 层数:{n.depth}, 启发函数值得分:{n.score} ====")
# print(f"访问第{cnt}个节点:\n{n.data}")
# self.__show_path(n)
# ==================结束条件==================
if (n.data == self.goals.data).all():
resultAll=[]
resultAll.append(n)
while n.parent!="None": # 回溯路径
resultAll.append(n.parent)
n = n.parent
resultAll_len=len(resultAll)
print("展示最优A*路径: ")
for j in range(resultAll_len):
print(f"======👇👇👇第{j}步👇👇👇======")
result = resultAll.pop(-1) # 弹出
self.__show_path(result)
print("==================A*结束搜索==================")
print(f"总共遍历的节点数目:{cnt}")
print(f"找到的可行路径的节点数目:{resultAll_len}")
break
# ==================生成n的所有子状态,并加入到open表后方================
# 找出空格位置
postion = np.where(n.data == 0)
i = postion[0]
j = postion[1]
length_down=n.data.shape[0]
length_right=n.data.shape[1]
# 避免误操作
if i==0: # 清除上操作:在第一行,不能向上移动
direction.remove("up")
if j==0: # 清除左操作:在第一列,不能向左移动
direction.remove("left")
if i == length_down-1: # 清除下操作:在末行,不能向下移动
direction.remove("down")
if j == length_right-1: # 清除右操作:在末列,不能向右移动
direction.remove("right")
# 遍历所有可能子状态
for p in range(len(direction)):
copy_n = copy.deepcopy(n)
three_result = self.__move(copy_n.data,direction[p],i,j)
# 判断是否存在于close表
if (self.__is_exist(three_result,self.close_,self.open_)):
continue
# 评估当前节点的启发函数得分score
score_t = self.__cal_score(Node(three_result,n.depth+1,n,0),self.goals) # 错位数
# score_t = self.__cal_score_manhattan(Node(three_result,n.depth+1,n,0),self.goals) # 曼哈顿距离
# score_t = self.__cal_score_euclidean(Node(three_result,n.depth+1,n,0),self.goals) # 欧式距离
self.open_.append(score_t)
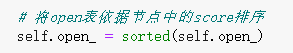
# 将open表依据节点中的score排序
self.open_ = sorted(self.open_)
# 初始化状态
initial_state=[2,8,3,1,6,4,7,0,5]
goal_state=[1,2,3,8,0,4,7,6,5]
#初始化类
start_time = time.time() # 记录程序开始时间
a = A(initial_state,goal_state)
a.solve()
end_time = time.time() # 记录程序结束时间
print(f"程序的运行时间为:{(end_time-start_time)*1000} ms")
open表和close表的变化
内容过多,就不一一列举了,详情去代码运行输出吧
(省略余下)…
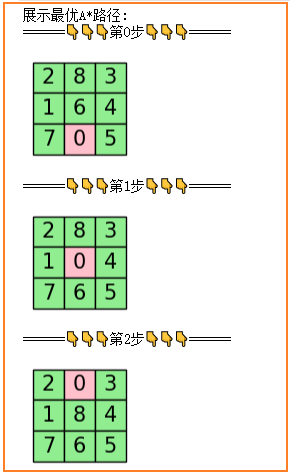
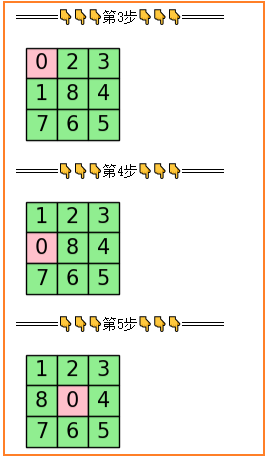
最优路径展示
🧡🧡总结🧡🧡
从以上结果可以看出:
- DFS无限往下递归,直到找到目标节点才结束(作为无信息搜索,每一次扩展都像在“碰运气”,>如果不设置搜索的最大深度,搜索次数几乎可以接近无限),因此找到的不一定是最短的路线。
- BFS每一次扩展的点,都是距离出发点最近、步骤最少的。如此这样递推,当扩展到目标点的时候,也是距离出发点最近的。这样的路径自然形成了最短的路线。
- A*算法在盲目搜索的基础上,会对节点的open表进行一个排序,使用估价函数去计算启发函数得分score,这样目标明确,能够迅速找出一个尽可能最优的局部最优解。
- 可以看到A算法效率远远高于DFS算法和BFS算法(遍历节点数少,运行时间短),但是A算法也有缺点,不能搜索到所有解,当需要搜索所有能到达终点的路径时,往往要使用DFS才能实现。
👇时间复杂度、空间复杂度对比👇
深度优先搜索DFS:
- 时间复杂度:在一般情况下为 O(b^m),其中 b 是分支因子,m 是搜索树最大深度。在最坏情况下,可能需要搜索整个状态空间,因此时间复杂度较高。
- 空间复杂度:取决于搜索树的深度,为 O(bm),其中 b 是分支因子,m 是搜索树最大深度。
一致代价搜索UCS:
- 时间复杂度: O(b^( C/ε)),其中 b 是分支因子,C 是最低成本解的代价,每一步代价至少为ε。
- 空间复杂度:和时间复杂度相似
迭代加深的深度优先搜索算法 IDS:
- 时间复杂度: O(b^d),其中 b 是分支因子,d 是最浅的解的深度。迭代加深的主要特点是在每次搜索中限制深度,
- 空间复杂度: O(bd),其中 b 是分支因子,d 是最浅的解的深度,取决于搜索树的深度,与深度优先搜索相似。
- IDS综合了BFS和DFS的优点:时间复杂度只比BFS稍差一点,而空间复杂度与深搜相同,比广搜小很多
A*搜索算法:
- 时间复杂度:取决于启发式函数的质量。在最坏情况下,时间复杂度为指数级的 O(b^d),其中 b 是分支因子,d 是最浅的解的深度。但是在实际应用中,由于启发式函数的使用,A*搜索通常能够在较短的时间内找到最优解。
- 空间复杂度:取决于许多因素,包括搜索树的宽度、深度和启发式函数的质量。在最坏情况下,空间复杂度为 O(b^d),但通常情况下能够比较好地控制空间占用。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/luohaojia123/article/details/135694772
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 解密Python高级特性:深度探讨装饰器与上下文管理器的魔法
- 解决curl请求报错-bash: -F:未找到命令
- HarmonyOS应用开发者高级认证
- 写代码的调试工具和断点调试debugger
- 在Multisim中定位555芯片的方法及操作步骤解析
- Python学习之路-注释
- BurpSuite Pro 2023.12.1.2下载与破解-最新版BurpSuite Pro
- 【C语言题解】【洛谷P1980 计数问题】
- 【AI视野·今日Sound 声学论文速览 第四十五期】Wed, 10 Jan 2024
- 数据结构-数据结构导论