谭浩强【C语言程序设计】第五章习题详解
发布时间:2024年01月19日

目录
2.请补充例5.7程序,分别统计当“fabs(t)>=1e-6”和“fabs(t)>=1e-8”时执行循环体的次数。
4.输入一行字符,分别统计出其中英文字母、空格、数字和其他字符的个数。
5. 求Sn=a+aa+aaa+ ... +aa...(n个a)a之值,其中a是一个数字,n表示a的位数,n由键盘输入。例如:2+22+222+2222+22222 (此时n=5)
8. 输出所有的“水仙花数”,所谓“水仙花数”是指一个 3 位数,其各位数字立方和等于该数本身。例如,153是水仙花数,因为153=13+53+33。
10. 有一个分数序列2/1, 3/2, 5/3, 8/5, 13/8, 21/13, ...求出这个数列的前20项之和。
11.一个球从100m高度自由落下,每次落地后反弹回原高度的一半,再落下,再反弹。求它在第10次落地时共经过多少米,第10次反弹多高。
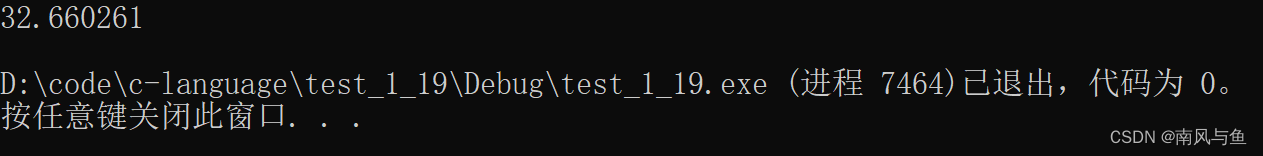
13. 用迭代法求 x=根号下a。求平方根的迭代公式为x(n+1)= 1/2(x的n次方 + a/x的n次方)要求前后两次求出的x的差的绝对值小于 10??。
14. 用牛顿迭代法求下面方程在 1.5 附近的根:2x3-4x2+3x-6=0
15. 用二分法求下面方程在(-10,10)的根:2x3-4x2+3x-6=0
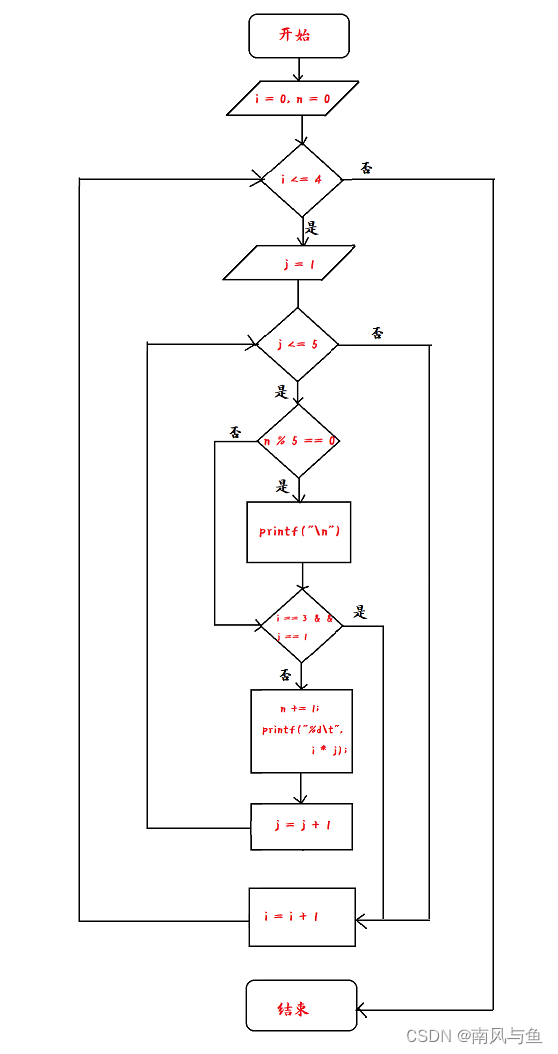
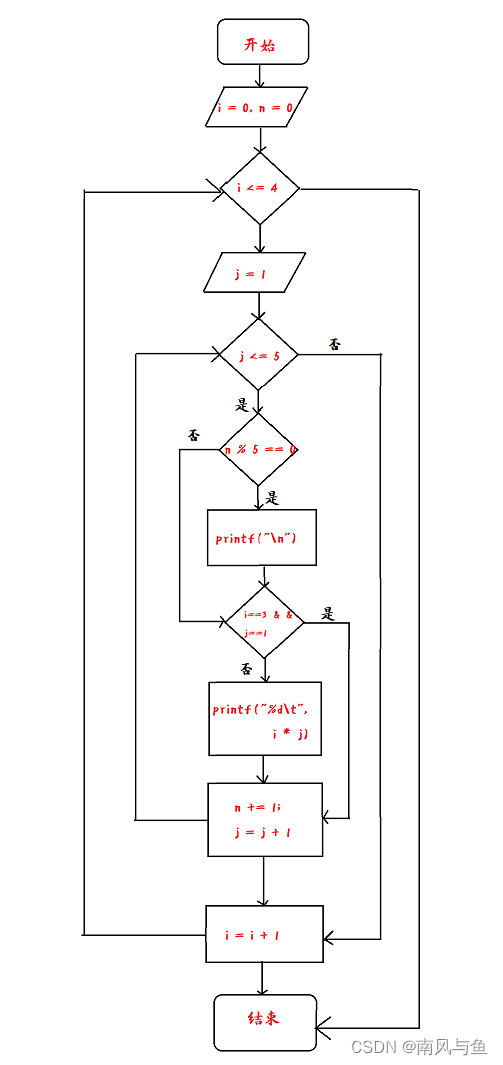
1.请画出例5.6 中给出的 3个程序段的流程图。
🌴流程图1:
🌴 流程图2:
🌴 流程图3:
2.请补充例5.7程序,分别统计当“fabs(t)>=1e-6”和“fabs(t)>=1e-8”时执行循环体的次数。
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int main() { int sign = 1; double pi = 0.0, n = 1.0, term = 1.0; int count = 0; while (fabs(term) >= 1e-8) { count++; pi = pi + term; n = n + 2; sign = -sign; term = sign / n; } pi = pi * 4; printf("pi=%10.8f\n", pi); printf("count = %d\n", count); return 0; }
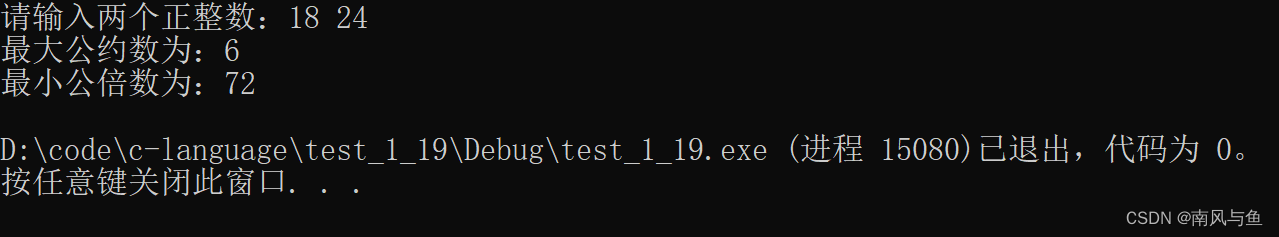
3.输入两个正整数m 和n,求其最大公约数和最小公倍数。
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int m, n; printf("请输入两个正整数:"); scanf("%d%d", &m, &n); //选取较大值,保存在n当中 if (n < m) { int tmp = n; n = m; m = tmp; } //为最小公倍数保存两者的乘积,因为在 //辗转相除法的时候,m,n当中的值会变化 int total = m * n; //最大公约数 int r = -1;//r代表余数 while (m != 0) { r = n % m; //为下一次计算做准备、 n = m; m = r; } //最大公约数经上面计算,已经保存在n当中了 printf("最大公约数为:%d\n", n); printf("最小公倍数为:%d\n", total / n); return 0; }
4.输入一行字符,分别统计出其中英文字母、空格、数字和其他字符的个数。
#include <stdio.h> int main() { //英文字符 int eng_char = 0; //空格 int space_char = 0; //数字字符 int digit_char = 0; //其他字符 int other_char = 0; char c; while ((c = getchar()) != '\n') { if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z' || c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') { eng_char++; } else if (c == ' ') { space_char++; } else if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') { digit_char++; } else { other_char++; } } printf("英文字符:%d,空格字符:%d, 数字字符:%d, 其它字符:%d", eng_char, space_char, digit_char, other_char); return 0; }
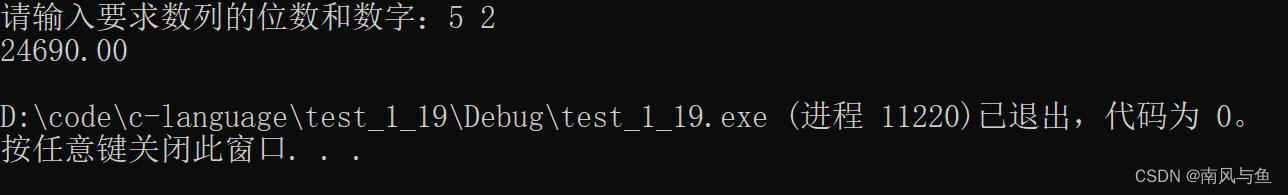
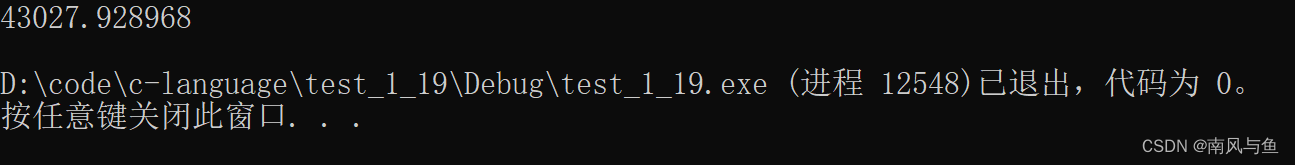
5. 求Sn=a+aa+aaa+ ... +aa...(n个a)a之值,其中a是一个数字,n表示a的位数,n由键盘输入。例如:
2+22+222+2222+22222 (此时n=5)
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int main() { int n = 0; double a, signle_num = 0.0, total_sum = 0.0; printf("请输入要求数列的位数和数字:"); scanf("%d %lf", &n, &a); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { signle_num += a * pow(10, i); total_sum += signle_num; } printf("%.2lf\n", total_sum); return 0; }
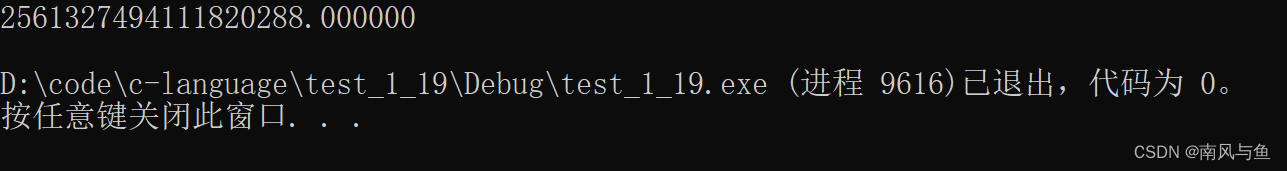
6.求(即求?1!+2!+3!+4!+…+20!)。
#include <stdio.h> int main() { double total_sum = 0.0; for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) { double single_num = 1.0; for (int j = i; j > 0; j--) { single_num *= j; } total_sum += single_num; } printf("%lf\n", total_sum); return 0; }
7.求。
第一个式子指:求1~100的和,1+2+3+...+100,求和之后,和为整数。
第二个式子指:求1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2 +...+ 50^2,求和之后,和为整数。
第三个式子指:求1/1 + 1/2 + 1/3 +...+ 1/10,求和结果为浮点数。
#include <stdio.h> int main() { double total_sum = 0.0, sum1 = 0.0, sum2 = 0.0, sum3 = 0.0; //1~100 for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { //1+2+3+...+100 sum1 += 1; //1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2 +...+ 50^2 if (i <= 50) { sum2 += i * i; } //1/1 + 1/2 + 1/3 +...+ 1/10 if (i <= 10) { sum3 += 1.0 / i; } } total_sum = sum1 + sum2 + sum3; printf("%lf\n", total_sum); return 0; }
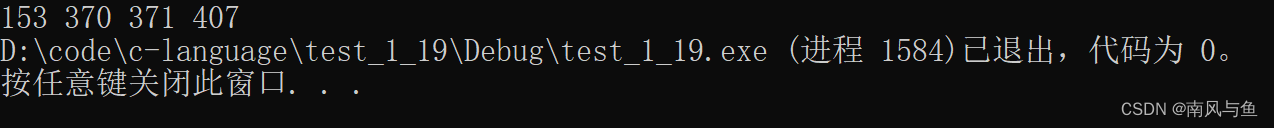
8. 输出所有的“水仙花数”,所谓“水仙花数”是指一个 3 位数,其各位数字立方和等于该数本身。例如,153是水仙花数,因为153=13+53+33。
#include <stdio.h> int main() { //a表示百位,b表示十位,c表示个位 int a, b, c; //获取100~999 for (int i = 100; i <= 999; i++) { //获取三位数当中的每一位 a = i / 100; b = (i / 10) % 10; c = i % 10; if (a * a * a + b * b * b + c * c * c == i) { printf("%d ", i); } } return 0; }
9.一个数如果恰好等于它的因子之和,这个数就称为“完数”。例如,6的因子为1,2,3,而6=1+2+3,因此6是“完数”。编程序找出 1000之内的所有完数,并按下面格式输出其因子:
6 its factors are 1,2,3
#include <stdio.h> int main() { for (int data = 2; data <= 1000; data++) { int factor_sum = 0; for (int factor = 1; factor <= data / 2; factor++) { if (data % factor == 0) { factor_sum += factor; } } //判断是否为完数 if (factor_sum == data) { printf("%d its factors are ", data); for (int factor = 1; factor <= data / 2; factor++) { if (data % factor == 0) { printf("%d, ", factor); } } printf("\n"); } } return 0; }
10. 有一个分数序列
2/1, 3/2, 5/3, 8/5, 13/8, 21/13, ...
求出这个数列的前20项之和。
#include <stdio.h> int main() { //a: 分子 //b: 分母 double a = 2.0, b = 1.0, total_sum = 0.0; for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) { //1.将分式的结果累加到total_sum当中 total_sum += a / b; //2.求下一个分式的值 double tmp = a; a = a + b; b = tmp; } printf("%lf\n", total_sum); return 0; }
11.一个球从100m高度自由落下,每次落地后反弹回原高度的一半,再落下,再反弹。求它在第10次落地时共经过多少米,第10次反弹多高。
#include <stdio.h> int main() { //定义小球经过的米数 double total_sum = 0.0; //定义高度 double total_m = 100.0; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { //下落+回弹 total_sum += total_m; total_m /= 2; total_sum += total_m; } //第10次回弹的距离从总距离当中除掉 total_sum -= total_m; printf("小球经过%lf米,第10次反弹%lf米\n", total_sum, total_m); return 0; }
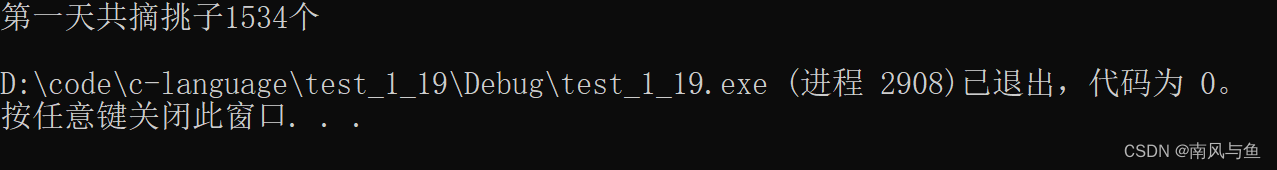
12. 猴子吃桃问题。猴子第1天摘下若干个桃子,当即吃了一半,还不过瘾,又多吃了一个。第2天早上又将剩下的桃子吃掉一半,又多吃了一个。以后每天早上都吃了前一天剩下的一半零一个。到第10天早上想再吃时,就只剩一个桃子了。求第1天共摘多少个桃子。
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int day = 9; int cur_day_count = 1; int prev_day_count; while (day > 0) { prev_day_count = (cur_day_count + 1) * 2; cur_day_count = prev_day_count; day--; } printf("第一天共摘挑子%d个\n", prev_day_count); return 0; }
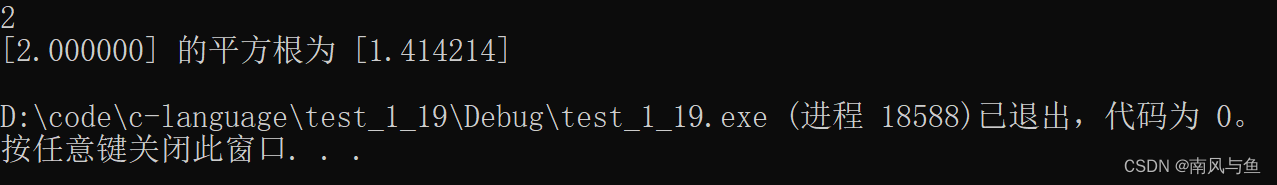
13. 用迭代法求 x=根号下a。求平方根的迭代公式为
x(n+1)= 1/2(x的n次方 + a/x的n次方)
要求前后两次求出的x的差的绝对值小于 10??。
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int main() { float a, x0, x1; scanf("%f", &a); //计算x0和x1的值 x0 = a / 2; x1 = (x0 + a / x0) / 2; //判断是否小于10^-5 while (fabs(x0 - x1) >= 1e-5) { //更新x0和x1的值 x0 = x1; x1 = (x0 + a / x0) / 2; } printf("[%f] 的平方根为 [%f]\n", a, x1); return 0; }
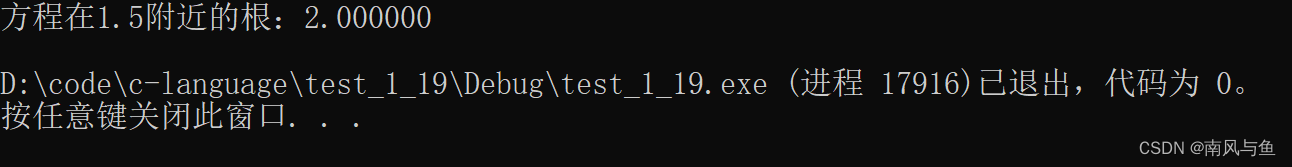
14. 用牛顿迭代法求下面方程在 1.5 附近的根:
2x3-4x2+3x-6=0
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int main() { //x0 ---> xn //x1 ---> xn+1 //f ---> f(xn) //f1 ---> f`(xn) double x0, x1, f, f1; x1 = 1.5; do { x0 = x1; f = ((2 * x0 - 4) * x0 + 3) * x0 - 6; f1 = (6 * x0 - 8) * x0 + 3; x1 = x0 - f / f1; } while (fabs(x1 - x0) >= 1e-5); printf("方程在1.5附近的根:%lf\n", x1); return 0; }
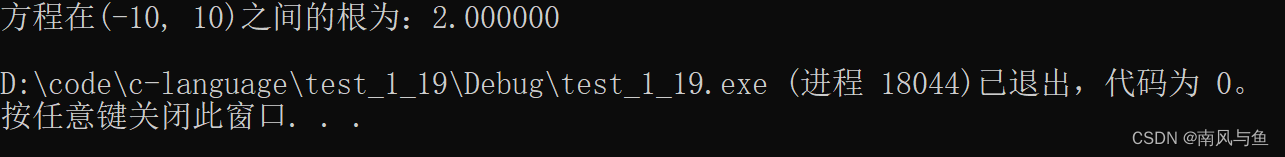
15. 用二分法求下面方程在(-10,10)的根:
2x3-4x2+3x-6=0
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int main() { double left = -10, right = 10, mid; double tmp = 10; while (fabs(tmp) > 1e-5) { mid = (left + right) / 2; tmp = ((2 * mid - 4) * mid + 3) * mid - 6; if (tmp > 0) { right = mid; } else if (tmp < 0) { left = mid; } } printf("方程在(-10, 10)之间的根为:%lf\n", mid); return 0; }
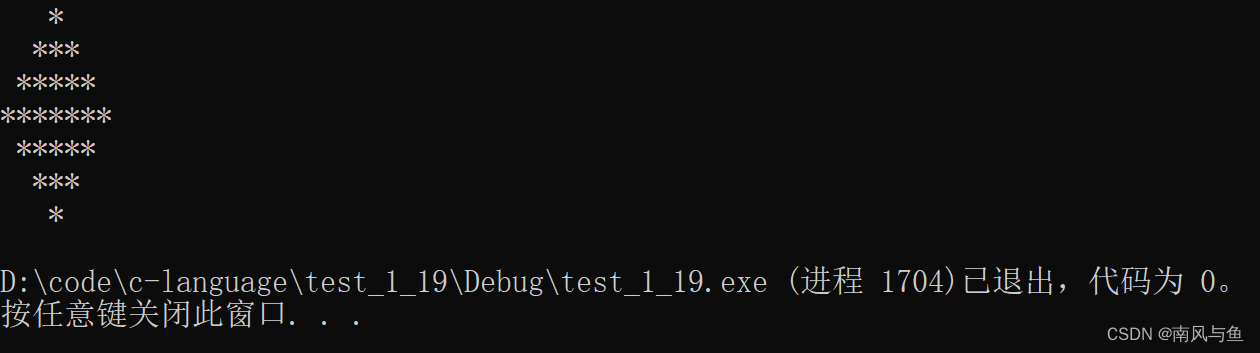
16.输出7行的菱形:
#include <stdio.h> int main() { //打印上半部分 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { //打印空格 for (int j = 3 - i; j > 0; j--) { printf(" "); } //打印* for (int j = 2 * i + 1; j > 0; j--) { printf("*"); } printf("\n"); } //打印下半部分 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { //打印空格 for (int j = i + 1; j > 0; j--) { printf(" "); } //打印* for (int j = 7 - 2 * (i + 1); j > 0; j--) { printf("*"); } printf("\n"); } return 0; }
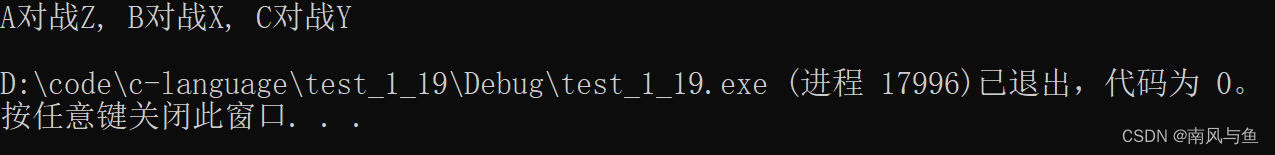
17.两个乒乓球队进行比赛,各出3 人。甲队为 A,B,C3 人,乙队为 X,Y,Z3人。已抽签决定比赛名单。有人向队员打听比赛的名单,A 说他不和X 比,C说他不和X,Z 比,请编程序找出 3对赛手的名单。
?
#include <stdio.h> int main() { //1.列举A的所有对战对象 for (int A = 'X'; A <= 'Z'; A++) { //2.列举B的所有对战对象 for (int B = 'X'; B <= 'Z'; B++) { //3.列举C的所有对战对象 for (int C = 'X'; C <= 'Z'; C++) { if (A != 'X' && C != 'X' && C != 'Z' && A != B && A != C && B != C) { printf("A对战%c, B对战%c, C对战%c\n", A, B, C); } } } } return 0; }
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_65931202/article/details/135661345
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【Docker】部署mysql 和 tomcat
- Ubuntu 常用命令之 less 命令用法介绍
- 卖流量卡这么赚钱么,为什么网上都是在推广流量卡的!
- 说说Vue生命周期的理解?在created和mounted这两个生命周期中请求数据有什么区别
- 智能充电桩嵌入式控制系统设计方案
- RT-Smart elf 动态加载技术 : elf 加载原理与流程
- Could not find annotations-4.9.0.jar 异常
- Python 面向对象之封装和装饰器property
- 小程序面试题 | 15.精选小程序面试题
- C++ | 六、栈 Stack、队列 Queue