day17【LeetCode力扣】24.两两交换链表中的节点
发布时间:2024年01月14日
day17【LeetCode力扣】24.两两交换链表中的节点
1.题目描述
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
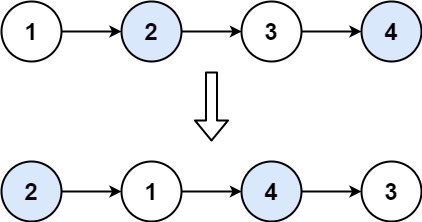
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1]
输出:[1]
2.题解
简单的模拟反转链表,建议新建一个虚拟头结点,这样方便进行各种操作。
【双指针】
c++
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummyhead=new ListNode(0);
dummyhead->next=head;
ListNode* cur=dummyhead;
while(cur->next!=nullptr&&cur->next->next!=nullptr){
ListNode* temp=cur->next;
ListNode* temp1=cur->next->next->next;
cur->next=cur->next->next;
cur->next->next=temp;
cur->next->next->next=temp1;
cur=cur->next->next;
}
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy_head=ListNode(next=head)
cur=dummy_head
while cur.next and cur.next.next:
temp=cur.next
temp1=cur.next.next.next
cur.next=cur.next.next
cur.next.next=temp
cur.next.next.next=temp1
cur=cur.next.next
return dummy_head.next
【递归】
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
pre=head
cur=head.next
temp=head.next.next
cur.next=pre
pre.next=self.swapPairs(temp)
return cur
建议大家在做题的时候,或者说在学习的时候,结合着画图一起来学,这样子算法实现就不会那么抽象了,图和代码相结合,理解起来会容易很多~~
<u>如果觉得作者写的不错,求给博主一个大大的点赞支持一下,你们的支持是我更新的最大动力!</u>
? 如果觉得作者写的不错,求给博主一个大大的点赞支持一下,你们的支持是我更新的最大动力!
? 如果觉得作者写的不错,求给博主一个大大的点赞支持一下,你们的支持是我更新的最大动力!
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/canGfly/article/details/135508872
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- top命令详解
- 246.【2023年华为OD机试真题(C卷)】分月饼(动态规划-Java&Python&C++&JS实现)
- 深入理解计算机系统(1):开始
- Linux Mint 21.3 代号为“Virginia”开启下载
- SSM农产品朔源管理系统----计算机毕业设计
- Go语言中的秘密武器:魔力般的Map数据结构解密
- 基于ssm的图书馆书库管理系统+vue论文
- 计算机组成原理 存储器概述,主存系统模型和RAM和ROM
- 执行方法 将图片转base64
- git-crypt实现数据加密(macOS版)