模型的 PSI(Population Stability Index)
发布时间:2024年01月22日
PSI(Population Stability Index)是一种用于评估两个数据集或时间点之间的分布变化的指标。它常用于监测模型在不同时间段或不同群体上的稳定性。PSI的计算基于两个分布的累积分布函数(CDF)之间的差异。
在模型监测和评估的背景下,通常将 PSI 用于检测模型在不同时间点或群体上的预测稳定性,尤其是在评估模型在生产环境中的性能变化时。
PSI的计算步骤如下:
- 分箱(Binning): 将数据按照预测概率或分数等进行分箱。分箱的目的是为了计算每个箱中的观测数和观测比例。
- 计算累积分布函数(CDF): 对于每个数据集或时间点,计算每个箱的累积分布函数,得到累积分布百分比。
- 计算PSI: 对于每个箱,计算两个时间点或群体之间的CDF差异,然后将这些差异进行累加,得到总的PSI。
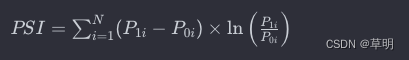
其中:
N是分箱的数量。P1i是时间点或群体1中第i个箱的累积分布比例。P0i是时间点或群体0中第i个箱的累积分布比例。
PSI的值越大,表示两个时间点或群体之间的分布变化越大,模型在不同时间点或群体上的预测稳定性越差。通常,PSI的阈值可以根据具体问题的要求和业务场景来确定。
在 scikit-learn 中,目前并没有专门用于计算 Population Stability Index (PSI) 的内置函数。计算 PSI 通常需要自定义代码,以下是一个简单的 Python 示例代码,用于计算两个分布之间的 PSI 值:
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import norm
def calculate_psi(expected, actual, bins=10):
# 分箱
expected_bins = np.histogram(expected, bins=bins)[0]
actual_bins = np.histogram(actual, bins=bins)[0]
# 计算累积分布函数(CDF)
expected_cdf = np.cumsum(expected_bins) / np.sum(expected_bins)
actual_cdf = np.cumsum(actual_bins) / np.sum(actual_bins)
# 计算 PSI
psi = np.sum((actual_cdf - expected_cdf) * np.log(actual_cdf / expected_cdf))
return psi
# 示例用法
expected_distribution = np.random.normal(0, 1, 1000)
actual_distribution = np.random.normal(0.2, 1.2, 1000)
psi_value = calculate_psi(expected_distribution, actual_distribution)
print("PSI:", psi_value)
上述代码中,calculate_psi 函数接受两个分布(expected 和 actual),并计算它们之间的 PSI 值。你可以根据实际情况调整分箱数量(bins 参数),以满足你的需求。
请注意,PSI 的计算方法可能因具体业务场景而异,上述示例代码仅提供了一种通用的计算方法。在实际应用中,你可能需要根据具体情况进行调整。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/galoiszhou/article/details/135619078
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- JanusGraph图数据库的应用以及知识图谱技术介绍
- 【OSG案例详细分析与讲解】之十二:【时间轴动画】
- Android开发中如何进行单元测试?
- np.concatenate函数
- 【低照度图像增强系列(2)】Retinex(SSR/MSR/MSRCR)算法详解与代码实现
- vue3 根据用户权限控制左侧菜单和路由拦截
- 基于探路者算法优化的Elman神经网络数据预测 - 附代码
- React Native性能优化指南
- 设计模式-状态模式
- 基于springboot在线学习平台源码和论文