HW03 -实物图像识别-改进:图像增强、网络架构,K折交叉验证
发布时间:2023年12月21日
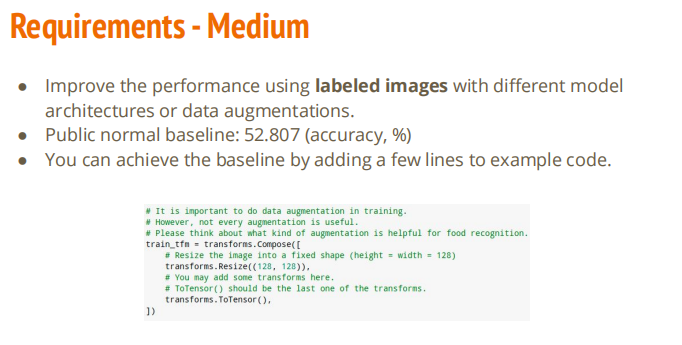
修改模型架构或者进行图像增强
# Normally, We don't need augmentations in testing and validation.
# All we need here is to resize the PIL image and transform it into Tensor.
test_tfm = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((128, 128)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
#transforms.Normalize((0.485, 0.456, 0.406), (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)),
])
# However, it is also possible to use augmentation in the testing phase.
# You may use train_tfm to produce a variety of images and then test using ensemble methods
train_tfm = transforms.Compose([
# Resize the image into a fixed shape (height = width = 128)
#transforms.CenterCrop()
transforms.RandomResizedCrop((128, 128), scale=(0.7, 1.0)),
#transforms.AutoAugment(transforms.AutoAugmentPolicy.IMAGENET),
#transforms.Normalize((0.485, 0.456, 0.406), (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(0.5),
transforms.RandomVerticalFlip(0.5),
transforms.RandomRotation(180),
transforms.RandomAffine(30),
#transforms.RandomInvert(p=0.2),
#transforms.RandomPosterize(bits=2),
#transforms.RandomSolarize(threshold=192.0, p=0.2),
#transforms.RandomEqualize(p=0.2),
transforms.RandomGrayscale(p=0.2),
transforms.ToTensor(),
#transforms.RandomApply(torch.nn.ModuleList([]))
# You may add some transforms here.
# ToTensor() should be the last one of the transforms.
])
修改模型架构, 建立 resudial
class Residual_Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ic, oc, stride=1):
# torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding)
# torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size, stride, padding)
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(ic, oc, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oc),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(oc, oc, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oc),
)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = None
if stride != 1 or (ic != oc):
self.downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(ic, oc, kernel_size=1, stride=stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(oc),
)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.conv2(out)
if self.downsample:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
return self.relu(out)
class Classifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, num_layers, num_classes=11):
super().__init__()
self.preconv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.layer0 = self.make_residual(block, 32, 64, num_layers[0], stride=2)
self.layer1 = self.make_residual(block, 64, 128, num_layers[1], stride=2)
self.layer2 = self.make_residual(block, 128, 256, num_layers[2], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self.make_residual(block, 256, 512, num_layers[3], stride=2)
#self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(2)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(0.4),
nn.Linear(512*4*4, 512),
nn.BatchNorm1d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(0.2),
nn.Linear(512, 11),
)
def make_residual(self, block, ic, oc, num_layer, stride=1):
layers = []
layers.append(block(ic, oc, stride))
for i in range(1, num_layer):
layers.append(block(oc, oc))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
# [3, 128, 128]
out = self.preconv(x) # [32, 64, 64]
out = self.layer0(out) # [64, 32, 32]
out = self.layer1(out) # [128, 16, 16]
out = self.layer2(out) # [256, 8, 8]
out = self.layer3(out) # [512, 4, 4]
#out = self.avgpool(out) # [512, 2, 2]
out = self.fc(out.view(out.size(0), -1))
return out
修改损失函数,使用Focalloss
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, class_num, alpha=None, gamma=2, size_average=True):
super().__init__()
if alpha is None:
self.alpha = Variable(torch.ones(class_num, 1))
else:
if isinstance(alpha, Variable):
self.alpha = alpha
else:
self.alpha = Variable(alpha)
self.gamma = gamma
self.class_num = class_num
self.size_average = size_average
def forward(self, inputs, targets):
N = inputs.size(0)
C = inputs.size(1)
P = F.softmax(inputs, dim=1)
class_mask = inputs.data.new(N, C).fill_(0)
class_mask = Variable(class_mask)
ids = targets.view(-1, 1)
class_mask.scatter_(1, ids.data, 1.)
if inputs.is_cuda and not self.alpha.is_cuda:
self.alpha = self.alpha.cuda()
alpha = self.alpha[ids.data.view(-1)]
probs = (P*class_mask).sum(1).view(-1, 1)
log_p = probs.log()
batch_loss = -alpha*(torch.pow((1-probs), self.gamma))*log_p
if self.size_average:
loss = batch_loss.mean()
else:
loss = batch_loss.sum()
return loss
class MyCrossEntropy(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, class_num):
pass
K 折交叉验证
k_fold = 4
num = len(total_files) // k_fold
# "cuda" only when GPUs are available.
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print(device)
# The number of training epochs and patience.
# Initialize a model, and put it on the device specified.
#from torchsummary import summary
#summary(model, (3, 128, 128))
# For the classification task, we use cross-entropy as the measurement of performance.
#criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Initialize optimizer, you may fine-tune some hyperparameters such as learning rate on your own.
# Initialize trackers, these are not parameters and should not be changed
test_fold = k_fold
for i in range(test_fold):
fold = i+1
print(f'\n\nStarting Fold: {fold} ********************************************')
model = Classifier(Residual_Block, num_layers).to(device)
criterion = FocalLoss(11, alpha=alpha)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0004, weight_decay=2e-5)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingWarmRestarts(optimizer, T_0=16, T_mult=1)
stale = 0
best_acc = 0
val_data = total_files[i*num: (i+1)*num]
train_data = total_files[:i*num] + total_files[(i+1)*num:]
train_set = FoodDataset(tfm=train_tfm, files=train_data)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, pin_memory=True)
valid_set = FoodDataset(tfm=test_tfm, files=val_data)
valid_loader = DataLoader(valid_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, pin_memory=True)
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
# ---------- Training ----------
# Make sure the model is in train mode before training.
model.train()
# These are used to record information in training.
train_loss = []
train_accs = []
lr = optimizer.param_groups[0]["lr"]
pbar = tqdm(train_loader)
pbar.set_description(f'T: {epoch+1:03d}/{n_epochs:03d}')
for batch in pbar:
# A batch consists of image data and corresponding labels.
imgs, labels = batch
#imgs = imgs.half()
#print(imgs.shape,labels.shape)
# Forward the data. (Make sure data and model are on the same device.)
logits = model(imgs.to(device))
# Calculate the cross-entropy loss.
# We don't need to apply softmax before computing cross-entropy as it is done automatically.
loss = criterion(logits, labels.to(device))
# Gradients stored in the parameters in the previous step should be cleared out first.
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Compute the gradients for parameters.
loss.backward()
# Clip the gradient norms for stable training.
grad_norm = nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=10)
# Update the parameters with computed gradients.
optimizer.step()
# Compute the accuracy for current batch.
acc = (logits.argmax(dim=-1) == labels.to(device)).float().mean()
# Record the loss and accuracy.
train_loss.append(loss.item())
train_accs.append(acc)
pbar.set_postfix({'lr':lr, 'b_loss':loss.item(), 'b_acc':acc.item(),
'loss':sum(train_loss)/len(train_loss), 'acc': sum(train_accs).item()/len(train_accs)})
scheduler.step()
# Make sure the model is in eval mode so that some modules like dropout are disabled and work normally.
model.eval()
# These are used to record information in validation.
valid_loss = []
valid_accs = []
# Iterate the validation set by batches.
pbar = tqdm(valid_loader)
pbar.set_description(f'V: {epoch+1:03d}/{n_epochs:03d}')
for batch in pbar:
# A batch consists of image data and corresponding labels.
imgs, labels = batch
#imgs = imgs.half()
# We don't need gradient in validation.
# Using torch.no_grad() accelerates the forward process.
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(imgs.to(device))
# We can still compute the loss (but not the gradient).
loss = criterion(logits, labels.to(device))
# Compute the accuracy for current batch.
acc = (logits.argmax(dim=-1) == labels.to(device)).float().mean()
# Record the loss and accuracy.
valid_loss.append(loss.item())
valid_accs.append(acc)
pbar.set_postfix({'v_loss':sum(valid_loss)/len(valid_loss),
'v_acc': sum(valid_accs).item()/len(valid_accs)})
#break
# The average loss and accuracy for entire validation set is the average of the recorded values.
valid_loss = sum(valid_loss) / len(valid_loss)
valid_acc = sum(valid_accs) / len(valid_accs)
if valid_acc > best_acc:
print(f"Best model found at fold {fold} epoch {epoch+1}, acc={valid_acc:.5f}, saving model")
torch.save(model.state_dict(), f"Fold_{fold}_best.ckpt")
# only save best to prevent output memory exceed error
best_acc = valid_acc
stale = 0
else:
stale += 1
if stale > patience:
print(f"No improvment {patience} consecutive epochs, early stopping")
break
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39107270/article/details/135137587
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Dinky创建Flink实例报错
- Flowable中6种部署方式
- helm---自动化一键部署
- 手机流量卡信号弱强好坏是哪些因素来决定的呢?
- Bind for 0.0.0.0:2379 failed: port is already allocated
- 交换机03_基本配置
- 【LeetCode:228. 汇总区间 | 枚举 + 哈希表】
- Spark的内核调度
- 面试 Java 基础八股文五问五答第五期
- react-native生命周期函数