第8章-第4节-Java中字节流的缓冲流
发布时间:2024年01月13日
1、缓冲流:属于高级IO流,并不能直接读写数据,需要依赖于基础流。缓冲流的目的是为了提高文件的读写效率?那么是如何提高文件的读写效率的呢?
在内存中设置一个缓冲区,缓冲区的默认大小是8192字节(8K),从文件中读取的内容,先存储到缓冲区,当缓冲区内容填充满了之后,才会将缓冲区的内容通过输出流写出到文件,这样,就减少了文件之间的传输次数,从而提高了文件的读写效率
2、缓冲字节输入流/缓冲字节输出流(读入与写出)
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) | 创建字节缓冲输出流对象 |
| BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) | 创建字节缓冲输入流对象 |
1)、案例:
// 创建一个字节缓冲输入流
BufferedInputStream bis =
new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("day16_io\\01.jpg"));
// 创建一个字节缓冲输出流
BufferedOutputStream bos =
new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day16_io\\02.jpg"));
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 2. 具体的读写操作
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len = bis.read(bs);
while(len != -1){
bos.write(bs, 0, len);
len = bis.read(bs);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
// 3. 关闭资源
bis.close();
bos.close();?2)、练习复制视频文件
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
/**
* 缓冲流
*/
try {
bis =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D://hecheng.mp4"));
bos =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D://"+ UUID.randomUUID()+".mp4"));
//1. 记录起始时间点
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
byte [] nums = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len = bis.read(nums)) != -1){
bos.write(nums,0,len);
}
//2. 记录终点毫秒数
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("复制成功!时间长:"+(end-start));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (bis != null) {
bis.close();
}
if (bos != null) {
bos.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}3、字节流总结:
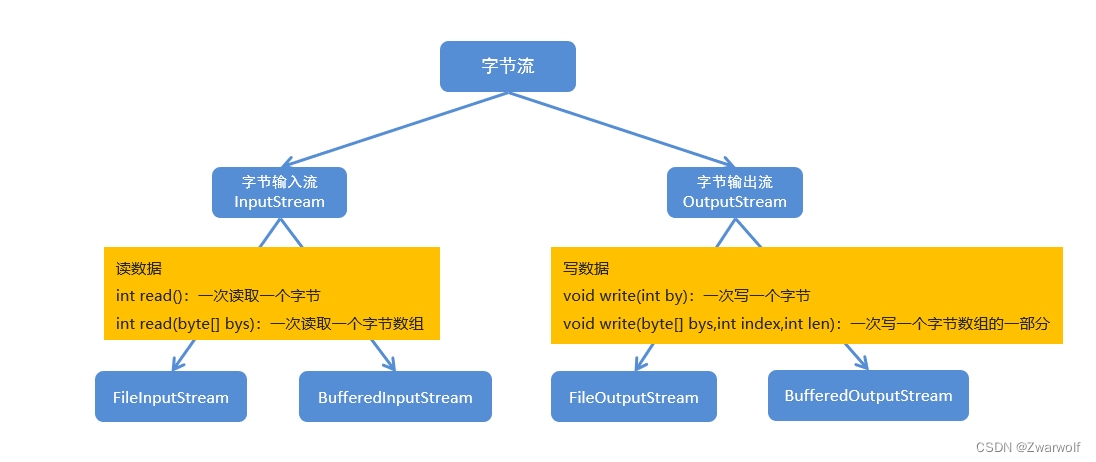 ?
?
?关于字节缓冲流,还可以看看我这篇博客:Java下字节缓冲流的读入和写出
本电子书目录:?《Java基础的重点知识点全集》
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/jnbbwyth/article/details/135568721
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章