Java学习(二十一)--JDBC/数据库连接池
为什么需要
?? ?传统JDBC数据库连接,使用DriverManager来获取;
- ?? ??? ?每次向数据库建立连接时都要将Connection加载到内存中,再验证IP地址、用户名和密码(0.05s~1s)时间。
- ?? ??? ?需要数据库连接时候,就向数据库要求一个,频繁地进行数据库连接将占用很多的系统资源,容易造成服务器崩溃
?? ?每次数据库连接,使用完后都得断开;若程序出现异常而未能关闭,将导致数据库内存泄露,最终将导致重启数据库;
?? ?传统获取连接的方式,不能控制创建的连接数量;若连接过多,也会导致内存泄露,MYSQL崩溃;
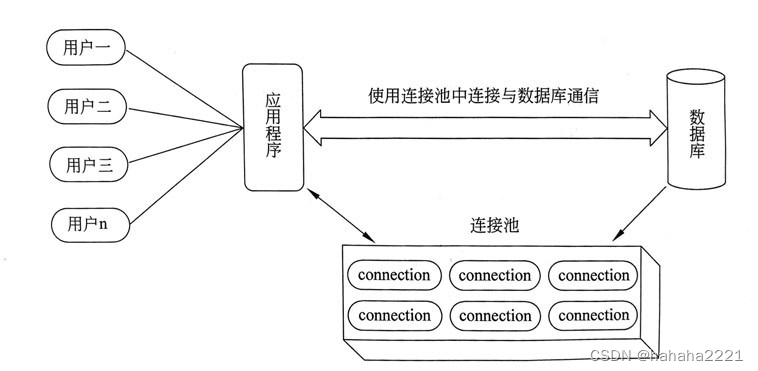
?? ?解决传统开发中的数据库连接问题,可采用数据库连接池技术(connection pool);
数据库连接池
基本介绍
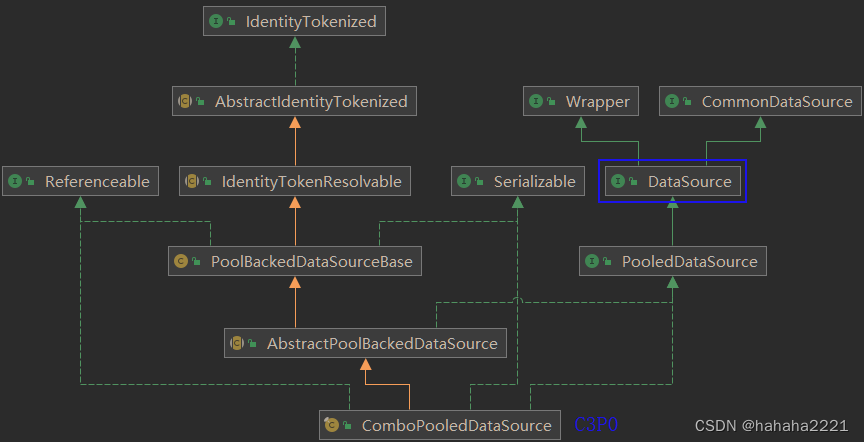
? ? JDBC的数据库连接池使用javax.sql.DataSource来表示,DataSource只是一个接口,该接口通常由第三方【服务器(Weblogic, WebSphere, Tomcat)】提供实现【提供.jar】。
?? ?通常被称为数据源,它包含连接池和连接池管理两个部分;
? ? DataSource用来取代DriverManager来获取Connection,获取速度快,同时可以大幅度提高数据库访问速度;
?
常用的数据库连接池
Apache Commons DBCP:
- Apache Commons DBCP(数据库连接池)是Apache软件基金会的一个项目,提供了一个稳定和可靠的连接池。
- 它是许多Java应用程序的首选选择。
- 速度相比C3P0较快,不稳定;
HikariCP:
- HikariCP是一个轻量级、高性能的数据库连接池,被广泛认为是目前性能最好的连接池之一。
- 它专注于快速的连接获取和释放,适用于高并发的应用程序。
- 在SpringBoot中默认集成,性能是诸多竞品中最好的;
C3P0:
- C3P0是一个开源的数据库连接池,具有许多配置选项,可用于调整连接池的行为。
- 它是一种稳定的连接池,被许多Java应用程序使用;
- c3p0历史悠久,代码及其复杂,不利于维护。并且存在deadlock的潜在风险。
Tomcat JDBC Pool:
- Tomcat JDBC Pool是Apache Tomcat项目的一部分,提供了一个性能良好的连接池。
- 它设计用于与Tomcat集成,但也可以作为独立的连接池使用。
H2 Database:
- H2 Database是一个嵌入式数据库,它包含了一个内置的连接池;
- 适用于小型应用程序和测试用例。
Druid(德鲁伊):
- Druid是一个开源的数据库连接池,具有监控和统计功能,可以帮助开发人员分析数据库连接的使用情况和性能。
- druid是?前企业应?中使?最 ?泛的之一;
- 阿里提供,集DBCP、C3P0、Proxool优点于一身
Bitronix Transaction Manager:
- Bitronix是一个支持分布式事务的连接池和事务管理器,适用于需要强大事务支持的应用程序;?
C3P0
连接步骤
 ?
?
连接方式一(不推荐)
读取相关的属性值和JDBC中的方式一样:使用properties配置文件。
@Test
public void testC3P0_01() throws Exception {
//1. 创建一个数据源对象
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
//2. 通过配置文件mysql.properties 获取相关连接的信息
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));
//读取相关的属性值
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
//给数据源 comboPooledDataSource 设置相关的参数
//注意:连接管理是由 comboPooledDataSource 来管理
comboPooledDataSource.setDriverClass(driver);
comboPooledDataSource.setJdbcUrl(url);
comboPooledDataSource.setUser(user);
comboPooledDataSource.setPassword(password);
//设置初始化连接数
comboPooledDataSource.setInitialPoolSize(10);
//最大连接数
comboPooledDataSource.setMaxPoolSize(50);
Connection connection = comboPooledDataSource.getConnection(); //这个方法就是从 DataSource 接口实现的
connection.close();
}
//配置文件mysql.properties
user=root
password=lhyroot123
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:13306/hsp_db02?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
连接方式二(推荐)
使用XML文件来配置相关信息
//1. 将c3p0 提供的 c3p0.config.xml 拷贝到 src目录下
//2. 该文件指定了连接数据库和连接池的相关参数
@Test
public void testC3P0_02() throws SQLException {
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource("jk");
Connection connection = comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();
connection.close();
}
c3p0-config.xml配置文件
<c3p0-config>
<!-- 数据源名称代表连接池 -->
<named-config name="jk">
<!-- 驱动类 -->
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<!-- url-->
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:13306/db_01</property>
<!-- 用户名 -->
<property name="user">root</property>
<!-- 密码 -->
<property name="password">root123</property>
<!-- 每次增长的连接数-->
<property name="acquireIncrement">5</property>
<!-- 初始的连接数 -->
<property name="initialPoolSize">10</property>
<!-- 最小连接数 -->
<property name="minPoolSize">5</property>
<!-- 最大连接数 -->
<property name="maxPoolSize">50</property>
<!-- 可连接的最多的命令对象数 -->
<property name="maxStatements">5</property>
<!-- 每个连接对象可连接的最多的命令对象数 -->
<property name="maxStatementsPerConnection">2</property>
</named-config>
</c3p0-config>
Druid(德鲁伊)
?连接步骤
 ?
?
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
// 工具类,完成 Druid的连接和关闭资源
public class JDBCDUtilsByDruid {
private static DataSource ds;
// 在static代码块去初始化
static {
try {
// 1.创建Properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 2.创建并加载流到Properties中
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\druid.properties"));
// 3.创建一个指定参数的数据库连接池, Druid 连接池
ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 在实际开发中,我们可以这样处理
// 1. 将编译异常转成 运行异常
// 2. 调用者,可以选择捕获该异常,也可以选择默认处理该异常,比较方便.
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 连接数据库, 返回Connection对象
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
return ds.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// 1. 将编译异常转成 运行异常
// 2. 调用者,可以选择捕获该异常,也可以选择默认处理该异常,比较方便.
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//关闭连接.
//注意:在数据库连接池技术中, close 不是真的断掉连接,而是把使用的 Connection 对象放回连接池
/*
1. ResultSet 结果集
2. Statement 或者 PreparedStatement
3. Connection
4. 如果需要关闭资源,就传入对象,否则传入 null
*/
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement) {
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet rs) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
close(connection, statement);
}
}
commons-dbutils(JDBC工具类库)
基本介绍
- ?? ?Apache组织提供的一个开源JDBC工具类库
- ?? ?对JDBC的封装,可极大简化jdbc编码的工作量? ?
- ? ? 下载地址:Apche_DbUtils下载地址
不足
- ?? ?SQL语句是固定的,不能通过参数传入,通用性不好,需进行改进,更方便执行
- ?? ?对于select操作,若有返回值,返回类型不能固定,需要适用泛型
- ?? ?若业务需求复杂,不能只靠一个java类完成
主要的类和接口
QueryRunner类
该类封装了SQL的执行,是线程安全的。可以实现增、删、改、查、批处理使用QueryRunner类实现查询。
//源码:
/**
* 分析 queryRunner.query方法:
* public <T> T query(Connection conn, String sql, ResultSetHandler<T> rsh, Object... params) throws SQLException {
* PreparedStatement stmt = null;//定义PreparedStatement
* ResultSet rs = null;//接收返回的 ResultSet
* Object result = null;//返回ArrayList
*
* try {
* stmt = this.prepareStatement(conn, sql);//创建PreparedStatement
* this.fillStatement(stmt, params);//对sql 进行 ? 赋值
* rs = this.wrap(stmt.executeQuery());//执行sql,返回resultset
* result = rsh.handle(rs);//返回的resultset --> arrayList[result] [使用到反射,对传入class对象处理]
* } catch (SQLException var33) {
* this.rethrow(var33, sql, params);
* } finally {
* try {
* this.close(rs);//关闭resultset
* } finally {
* this.close((Statement)stmt);//关闭preparedstatement对象
* }
* }
* return result;
* }
*/ResultSetHandler接口
该接口用于处理java.sql.ResultSet,将数据按要求转换为另一种形式。

应用案例
package com.lhy.jdbc;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.ScalarHandler;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.List;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class DBUtils_USE {
//使用apache-DBUtils 工具类 + druid 完成对表的crud操作
@Test
public void testQueryMany() throws SQLException { //返回结果是多行的情况
//1. 得到 连接 (druid)
Connection connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
//2. 使用 DBUtils 类和接口 , 先引入DBUtils 相关的jar , 加入到本Project
//3. 创建 QueryRunner
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
//4. 就可以执行相关的方法,返回ArrayList 结果集
//String sql = "select * from actor where id >= ?";
// 注意: sql 语句也可以查询部分列
String sql = "select id, name from actor where id >= ?";
// 解读
//(1) query 方法就是执行sql 语句,得到resultset ---封装到 --> ArrayList 集合中
//(2) 返回集合
//(3) connection: 连接
//(4) sql : 执行的sql语句
//(5) new BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class): 在将resultset -> Actor 对象 -> 封装到 ArrayList
// 底层使用反射机制 去获取Actor 类的属性,然后进行封装
//(6) 1 就是给 sql 语句中的? 赋值,可以有多个值,因为是可变参数Object... params
//(7) 底层得到的resultset ,会在query中关闭Resultset, 关闭PreparedStatment
List<Actor> list =
queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class), 1);
System.out.println("输出集合的信息");
for (Actor actor : list) {
System.out.print(actor);
}
//释放资源
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null,connection);
}
//演示 apache-dbutils + druid 完成 返回的结果是单行记录(单个对象)
@Test
public void testQuerySingle() throws SQLException {
//1. 得到 连接 (druid)
Connection connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
//2. 使用 DBUtils 类和接口 , 先引入DBUtils 相关的jar , 加入到本Project
//3. 创建 QueryRunner
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
//4. 就可以执行相关的方法,返回单个对象
String sql = "select * from actor where id = ?";
// 因为我们返回的单行记录<--->单个对象 , 使用的Hander 是 BeanHandler
Actor actor = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanHandler<>(Actor.class), 10);
System.out.println(actor);
// 释放资源
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null, connection);
}
//演示apache-dbutils + druid 完成查询结果是单行单列-返回的就是object
@Test
public void testScalar() throws SQLException {
//1. 得到 连接 (druid)
Connection connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
//2. 使用 DBUtils 类和接口 , 先引入DBUtils 相关的jar , 加入到本Project
//3. 创建 QueryRunner
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
//4. 就可以执行相关的方法,返回单行单列 , 返回的就是Object
String sql = "select name from actor where id = ?";
//老师解读: 因为返回的是一个对象, 使用的handler 就是 ScalarHandler
Object obj = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new ScalarHandler(), 4);
System.out.println(obj);
// 释放资源
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null, connection);
}
//演示apache-dbutils + druid 完成 dml (update, insert ,delete)
@Test
public void testDML() throws SQLException {
//1. 得到 连接 (druid)
Connection connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
//2. 使用 DBUtils 类和接口 , 先引入DBUtils 相关的jar , 加入到本Project
//3. 创建 QueryRunner
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
//4. 这里组织sql 完成 update, insert delete
//String sql = "update actor set name = ? where id = ?";
//String sql = "insert into actor values(null, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
String sql = "delete from actor where id = ?";
//老韩解读
//(1) 执行dml 操作是 queryRunner.update()
//(2) 返回的值是受影响的行数 (affected: 受影响)
//int affectedRow = queryRunner.update(connection, sql, "林青霞", "女", "1966-10-10", "116");
int affectedRow = queryRunner.update(connection, sql, 1000 );
System.out.println(affectedRow > 0 ? "执行成功" : "执行没有影响到表");
// 释放资源
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null, connection);
}
}工具类
Druid工具类
package com.lhy.jdbc;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
// 工具类,完成 Druid的连接和关闭资源
public class JDBCUtilsByDruid {
private static DataSource ds;
// 在static代码块去初始化
static {
try {
// 1.创建Properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 2.创建并加载流到Properties中
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\druid.properties"));
// 3.创建一个指定参数的数据库连接池, Druid 连接池
ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 在实际开发中,我们可以这样处理
// 1. 将编译异常转成 运行异常
// 2. 调用者,可以选择捕获该异常,也可以选择默认处理该异常,比较方便.
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 连接数据库, 返回Connection对象
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
return ds.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// 1. 将编译异常转成 运行异常
// 2. 调用者,可以选择捕获该异常,也可以选择默认处理该异常,比较方便.
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//关闭相关资源
/*
1. ResultSet 结果集
2. Statement 或者 PreparedStatement
3. Connection
4. 如果需要关闭资源,就传入对象,否则传入 null
*/
public static void close(Statement statement,Connection connection) {
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close( ResultSet rs, Statement statement,Connection connection) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
close(statement,connection);
}
}
其他
三层架构与面向结构编程
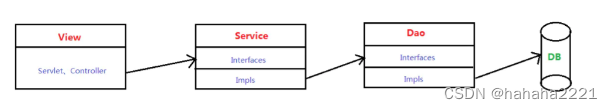
(1)三层架构
三层架构是指:视图层 View、服务层 Service,与持久层 Dao。它们分别完成不同的功能。
- View 层:用于接收用户提交请求。
- Service 层:用以实现系统的业务逻辑
- Dao 层:用以实现直接对数据库进行操作。
(2)面向接口 (抽象) 编程
面向接口编程:程序设计时,考虑易修改、易扩展,为Service层和DAO层设计接口,便于未来更换实现类;
在三层架构程序设计中,采用面向接口(抽象)编程。
实现方式
- 上层对下层的调用,是通过下层接口实现的
- 而下层对上层的真正服务提供者,是下层接口的实现类
特点:
- 服务标准(接口:规范相同)是相同的,服务提供者(实现类)可以更换。这就实现了层间解耦合与编程的灵活性
封装
(1)DAO封装 — (DAO Data Access Object 数据访问对象)
将对数据库中同?张数据表的JDBC操作?法封装到同?个Java类中,这个类就是访问此数据表的 数据访问对象
(2)DTO封装 — ( Data Transfer Object 数据传输对象(实体类))
在Java程序中创建?个属性与数据库表匹配的类,通过此类的对象封装查询到的数据,我们把?于传递JDBC增删查改操作的数据的对象称之为 数据传输对象
Service层的事务管理
(1)事务的概念
事务是指是程序中一系列严密的逻辑操作,而且所有操作必须全部成功完成,否则在每个操作中所作的所有更改都会被撤消。
(2)事务的四大特性
- 原子性(Atomicity):操作这些指令时,要么全部执行成功,要么全部不执行。只要其中一个指令执行失败,所有的指令都执行失败,数据进行回滚,回到执行指令前的数据状态。
- 一致性(Consistency): 事务的执行使数据从一个状态转换为另一个状态,但是对于整个数据的完整性保持稳定。
- 隔离性(Isolation): 隔离性是当多个用户并发访问数据库时,比如操作同一张表时,数据库为每一个用户开启的事务,不能被其他事务的操作所干扰,多个并发事务之间要相互隔离。
- 持久性(Durability): 当事务正确完成后,它对于数据的改变是永久性的。
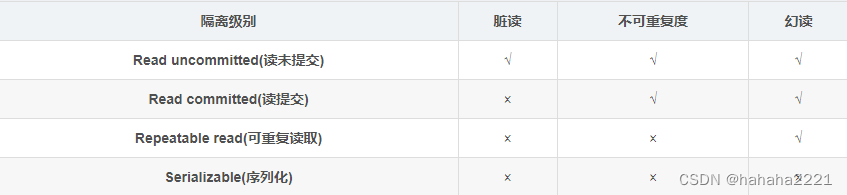
(3)事务的隔离级别
第一种隔离级别:Read uncommitted(读未提交)
- 如果一个事务已经开始写数据,则另外一个事务不允许同时进行写操作,但允许其他事务读此行数据,该隔离级别可以通过“排他写锁”,但是不排斥读线程实现。这样就避免了更新丢失,却可能出现脏读,也就是说事务B读取到了事务A未提交的数据
- 解决了更新丢失,但还是可能会出现脏读
第二种隔离级别:Read committed(读提交)
- 如果是一个读事务(线程),则允许其他事务读写,如果是写事务将会禁止其他事务访问该行数据,该隔离级别避免了脏读,但是可能出现不可重复读。事务A事先读取了数据,事务B紧接着更新了数据,并提交了事务,而事务A再次读取该数据时,数据已经发生了改变。
- 解决了更新丢失和脏读问题
第三种隔离级别:Repeatable read(可重复读取)
- 可重复读取是指在一个事务内,多次读同一个数据,在这个事务还没结束时,其他事务不能访问该数据(包括了读写),这样就可以在同一个事务内两次读到的数据是一样的,因此称为是可重复读隔离级别,读取数据的事务将会禁止写事务(但允许读事务),写事务则禁止任何其他事务(包括了读写),这样避免了不可重复读和脏读,但是有时可能会出现幻读。(读取数据的事务)可以通过“共享读镜”和“排他写锁”实现。
- 解决了更新丢失、脏读、不可重复读、但是还会出现幻读
第四种隔离级别:Serializable(序列化)
- 提供严格的事务隔离,它要求事务序列化执行,事务只能一个接着一个地执行,但不能并发执行,如果仅仅通过“行级锁”是无法实现序列化的,必须通过其他机制保证新插入的数据不会被执行查询操作的事务访问到。序列化是最高的事务隔离级别,同时代价也是最高的,性能很低,一般很少使用,在该级别下,事务顺序执行,不仅可以避免脏读、不可重复读,还避免了幻读
- 解决了更新丢失、脏读、不可重复读、幻读(虚读)
脏读
- 所谓脏读是指一个事务中访问到了另外一个事务未提交的数据
幻读
- 一个事务读取2次,得到的记录条数不一致
不可重复读
- 一个事务读取同一条记录2次,得到的结果不一致
MySQL事务管理:
- start transaction (开启事务)
- end transaction (结束事务)
- rollback (事务回滚)
- commit (提交事务)
(4)JDBC事务管理
- ?个事务中的多个DML操作需要基于同?个数据库连接
- 创建连接之后,设置事务?动提交(关闭?动提交connection.setAutoCommit(false);
- 当当前事务中的所有DML操作完成之后?动提交 connection.commit();
- 当事务中的任何?个步骤出现异常,在catch代码块中执?事务回滚
- connection.rollback();
(5)Service层简介
DAO负责特定的数据库操作,业务由service层进?管理
- 业务:指的是完成某一功能(软件提供的一个功能);例如:A给B转帐(其包含A账户减钱,B账户加钱),其整体为一个业务的操作
- Servcie进?业务处理,Service业务处理过程如果需要数据库操作,则调?DAO完成
- Service层的一个业务,可能需要调用一个或若干个DAO层对数据库进行处理
(6)Service层事务管理
事务管理要满?以下条件:
- 多个DML操作需使?同?个数据库连接
- 第?个DML操作之前设置事务?动提交
- 所有DML操作执?完成之后提交事务
- 出现异常则进?事务回滚
1.需要解决的问题
Servcie层事务可能涉及多个DAO层,其中多个数据库的DML操作是相互独?的,如何保证所有DML要么同时成功,要么同时失败呢?
解决办法:让Service事务中的多个DML使?同?个数据库连接
方式一:在Service获取连接对象,将连接对象传递到DAO中
分析: DAO类中的Connection对象需要通过Service传递给进来,这种对象传递本来也?可厚?,但是当我们通过?向接?开发时(?向接?,是为了能够灵活的定义实现类),容易造成接?的冗余(接?污染)
接口污染典型示例: 不同的数据库的数据库连接对象是不同的,MySQL的连接对象是Connection 但Oracle数据库则不是
方式二:使?ThreadLocal容器,实现多个DML操作使?相同的连接
不使用自定义List集合的原因:
存储Connection的容器可以使?List集合,使?List集合做容器,在多线程并发编程中会出现资源竞争问题,多个并发的线程使?的是同?个数据库连接对象(我们的要求是同?个事务中使?同?个连接,?并?多个线程共享同一个连接)
为了解决并发编程的连接对象共享问题,我们可以 使?ThreadLocal作为数据库连接对象的容器;
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!