软加密的设计和简单实现示例
发布时间:2024年01月04日
一、什么是软加密
软加密是指使用软件实现的加密算法和加密功能,而不是依赖硬件设备(如专用加密芯片)来执行加密操作。软加密通常通过软件库、算法和程序来实现数据的加密和解密,可以在通用计算设备上运行,如个人电脑、服务器和移动设备。
软加密的优点包括灵活性高、成本低、易于部署和维护。然而,由于软加密依赖于通用计算设备的处理能力,可能会受到性能和安全性方面的限制。相比之下,硬件加密通常能提供更高的性能和安全性,但成本较高且部署和维护相对复杂。
总的来说,软加密在许多情况下是一种有效的加密解决方案,特别是对于需要在通用计算设备上进行加密操作的场景。
二、软加密的实现
软加密主要有三种实现方式:
- 1、软件授权不与计算机硬件特征绑定。具体还分为两种:一是采用与一个软信息,如用户名等绑定的方式,一般用于个人用户授权;二是不绑定任何信息,只要序列号或授权文件验证通过,软件可以在任何机器上使用,通常用于大客户批量授权。授权的验证方式有直接比较、算法变换比较等方式。
- 2、软件授权与计算机硬件特征绑定。绑定的计算机硬件特征主要有CPU序列号、BIOS序列号、硬盘序列号、网卡MAC地址等。这种保护方式的许可证文件是在获得了计算机的硬件特征以后,由授权服务器将硬件特征与授权内容绑定后生成的。这种绑定计算机硬件的加密方式,如果使用类似网银数字证书的公私钥保护机制,是很难破解的。
- 3、软件授权与互联网上的授权服务器绑定。是云计算模式的授权方案,也称云授权。云授权的安全强度非常高,甚至比加密锁还要高。这是因为加密锁随软件卖出去后是无法跟踪和监测的,黑客可以花任意长的时间去破解它,而且一旦破解了可以大批量复制。而授权服务器有防火墙和完善的入侵检测技术,任何非法的访问和异常情况都可以监测得到,安全性要高的多。服务器授权也便于实现授权软件的跟踪管理、破解补救和升级更新。
三、软加密实现示例
本文以软加密实现的第二种方式为例,给大家展示一套简易的软加密系统实现方案:

效果展示如下:
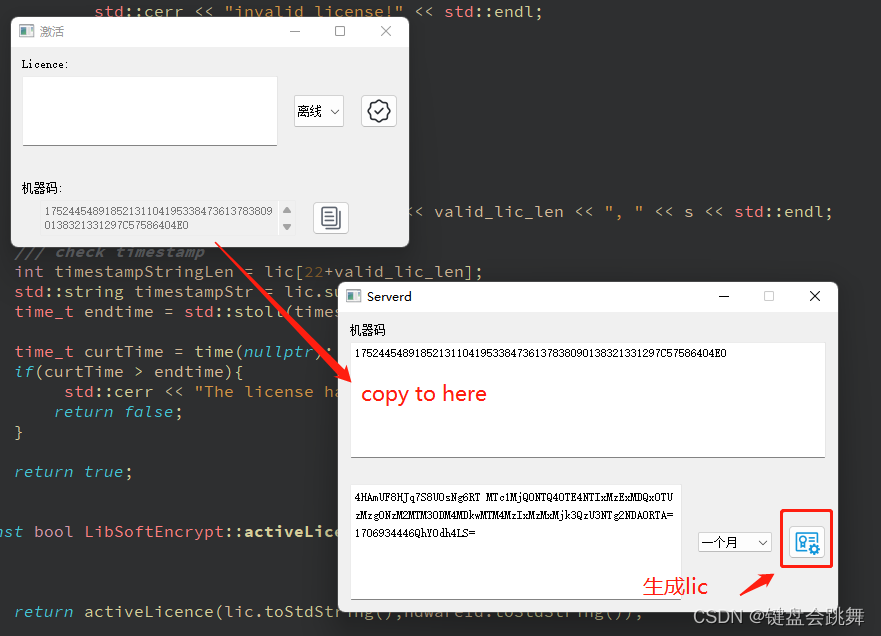
- 在客户端生成对应的机器码
- 将生成的机器码拷贝到服务端界面,选择lic的有效期限(自生成时间开始算起),生成
license。 - 将
license拷贝回客户端文本框,进行激活 - 激活成功,会在本地保存一个
license.lic的文件 - 下次登录客户端会先检查
license.lic文件,进行后台自动验证;不存在或者验证失败,则弹出激活界面
逻辑其实比较简单,这里只贴一贴软加密库部分的核心代码。
#ifndef LIBSOFTENCRYPT_H
#define LIBSOFTENCRYPT_H
#include "LibSoftEncrypt_global.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <functional>
class LIBSOFTENCRYPT_EXPORT LibSoftEncrypt
{
public:
LibSoftEncrypt();
typedef QString (*Custom_Encrypt_Func)(const QString&);
enum SoftEncryptType
{
CUSTOMER = 0x00001,
BASE64 = 0x0002,
RSA = 0x0003
};
const std::string GetHardwareID() const;
/**
* @brief generateLicense
* @param skey 机器码
* @param days 有效天数
* @param f 自定义加密函数
* @param type 加密类型,当自定义加密函数不为空时,type实际无效
* @return
*/
const QString generateLicense(const QString& skey,
time_t days,
Custom_Encrypt_Func f = nullptr,
SoftEncryptType type = BASE64) ;
/**
* @brief activeLicence
* @param lic 激活码
* @param hdwareId 硬件编码
* @return
*/
const bool activeLicence(const std::string &lic,const std::string& hdwareId ) const;
const bool activeLicence(const QString &lic,const QString& hdwareId ) const;
private:
Custom_Encrypt_Func m_f;
};
#endif // LIBSOFTENCRYPT_H
#include "libsoftencrypt.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <intrin.h> //__cpuid
#include <comdef.h>
#include <WbemIdl.h>
#include <QString>
#include <string>
#include "base64.h"
#include <random> // 随机字符
#include <iphlpapi.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "iphlpapi.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "wbemuuid.lib")
const std::string LibSoftEncrypt::GetHardwareID() const
{
std::string hardwareID;
// 获取CPU序列号
int cpuInfo[4] = { 0, 0, 0, 0 };
__cpuid(cpuInfo, 0x80000002);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
hardwareID += std::to_string(cpuInfo[i]);
}
// 获取硬盘序列号
DWORD volumeSerialNumber;
GetVolumeInformationA("C:\\", NULL, 0, &volumeSerialNumber, NULL, NULL, NULL, 0);
hardwareID += std::to_string(volumeSerialNumber);
// 获取网卡MAC地址
IP_ADAPTER_INFO AdapterInfo[16];
DWORD dwBufLen = sizeof(AdapterInfo);
DWORD dwStatus = GetAdaptersInfo(AdapterInfo, &dwBufLen);
if (dwStatus == ERROR_SUCCESS) {
for (int i = 0; i < AdapterInfo[0].AddressLength; ++i) {
char hex[3];
sprintf(hex, "%02X", AdapterInfo[0].Address[i]);
hardwareID += hex;
}
}
return hardwareID;
}
std::string GenerateLicense_base64(const std::string& machineCode)
{
std::string s = base64_encode(machineCode);
return s;
}
LibSoftEncrypt::LibSoftEncrypt()
{
}
const QString LibSoftEncrypt::generateLicense(const QString &skey, time_t days,
Custom_Encrypt_Func f,
SoftEncryptType type)
{
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* 0 ~ 19 20 1 21~ 21+len1 21+len1 +1 \
* ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ \
* 20个混淆字符 | 硬件编码字符长度 char | 加密方法 char | 硬件编码 | 时间戳长度 char | \
* ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*
* -----------------------------------------------------
* 21+len1 +1 + len2 | 21+len1 +1 + len2 +9 |
* -----------------------------------------------------
* 截止时间戳 | 9个随机混淆字符 | =
* -----------------------------------------------------
*
*/
std::string machineCode = skey.toStdString();
time_t startTime = time(nullptr);
time_t endTime = startTime + (days * 24 * 60 * 60);
std::string license;
if(nullptr == f){
switch (type) {
case BASE64:
license = GenerateLicense_base64(machineCode);
break;
default:
break;
}
}else{
m_f = f;
license = QString(m_f(skey)).toStdString();
}
/// 加入混淆字符
auto f_mixed = [](size_t n)->std::string{
std::string charset = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxy"\
"zABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789";
std::string result;
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution<> dis(0, charset.size() - 1);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
result += charset[dis(gen)];
}
return result;
};
std::cout << "Generated License: " << license << std::endl;
char clen_lic = license.length();
std::cout << "Generated License: " << license.length() << " ==> " << clen_lic << std::endl;
char clen_et = int(type);
license = f_mixed(20) + clen_lic + clen_et + license ;
license += std::to_string(endTime) + f_mixed(9) + "=" ;
std::cout << "Generated License: " << license << std::endl;
return QString::fromStdString(license);
}
const bool LibSoftEncrypt::activeLicence(const std::string &lic,
const std::string &hdwareId) const
{
int valid_lic_len = lic[20];
int lic_encrypt_type = lic[21];
std::string s = lic.substr(22,valid_lic_len);
/// lic is the same
switch (lic_encrypt_type) {
case BASE64:
if(s != GenerateLicense_base64(hdwareId)){
std::cerr << "invalid license!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
break;
case RAS:
break;
case CUSTOMER:
{
if(!m_f) {
return false;
}
if(QString::fromStdString(s) != m_f(QString::fromStdString(hdwareId)) ){
std::cerr << "invalid license!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
break;
}
default:
break;
}
std::cout << "activeLicence License: " << valid_lic_len << ", " << s << std::endl;
/// check timestamp
int timestampStringLen = lic[22+valid_lic_len];
std::string timestampStr = lic.substr(22+valid_lic_len,timestampStringLen);
time_t endtime = std::stoll(timestampStr);
time_t curtTime = time(nullptr);
if(curtTime > endtime){
std::cerr << "The license has expired!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
const bool LibSoftEncrypt::activeLicence(const QString &lic,
const QString& hdwareId) const
{
return activeLicence(lic.toStdString(),hdwareId.toStdString());
}
加密算法,这里简单采用base64,其他加密算法的实现,自行补充,不过后续博主也会逐渐完善的哈。
常见的加密算法普一下:
- RSA是一种非对称加密算法,它使用一对密钥(公钥和私钥)来加密和解密数据。公钥用于加密数据,私钥用于解密数据。RSA算法也可以用于数字签名和密钥交换。RSA算法的安全性基于大整数分解的困难性,即将一个大的合数分解为其质因数的难度。RSA算法的安全性取决于密钥的长度,通常使用较长的密钥长度以提供更高的安全性。RSA算法在许多领域得到了广泛应用,包括安全通信、数字签名、身份验证等
- AES(高级加密标准)是一种对称加密算法,被广泛应用于保护数据的安全性。它是一种块加密算法,能够以128位、192位或256位的密钥长度来加密数据块。AES算法使用相同的密钥来加密和解密数据,因此被称为对称加密算法。AES算法的安全性和性能都得到了广泛认可,它已成为许多安全通信协议和加密软件的首选算法。AES算法在许多领域得到了广泛应用,包括网络通信、数据库加密、文件加密等。
- …
三、小结
软加密除了一些加密算法库的使用之外,我们在生成lic证书的协议格式上同样可以做一些“手脚”,譬如字符混淆等等。聪明的你们肯定有更多的好方法和好主意,可以留言指导一二,不胜感激~
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39568531/article/details/135383470
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!