MySQL 高级(进阶) SQL 语句
目录
一、实验环境准备
#创建两个数据表,为实验提供环境:
use kgc; #选择数据库,有则直接使用 无则按照以下步骤自建即可。
表一:
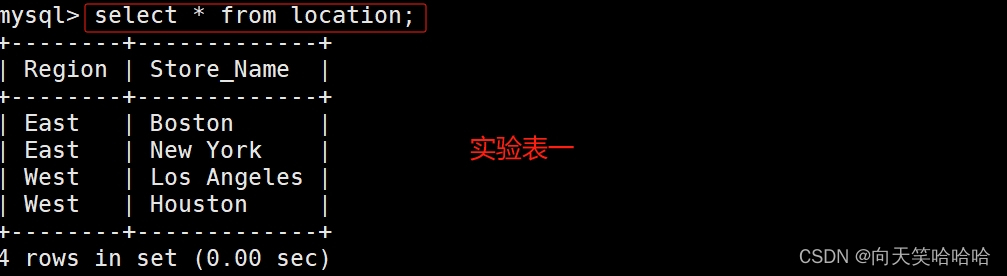
create table location (Region char(20),Store_Name char(20));
insert into location values('East','Boston');
insert into location values('East','New York');
insert into location values('West','Los Angeles');
insert into location values('West','Houston');
location 表格
+----------+--------------+
| Region | Store_Name |
|----------+--------------|
| East | Boston |
| East | New York |
| West | Los Angeles |
| West | Houston |
+----------+--------------+
表二:
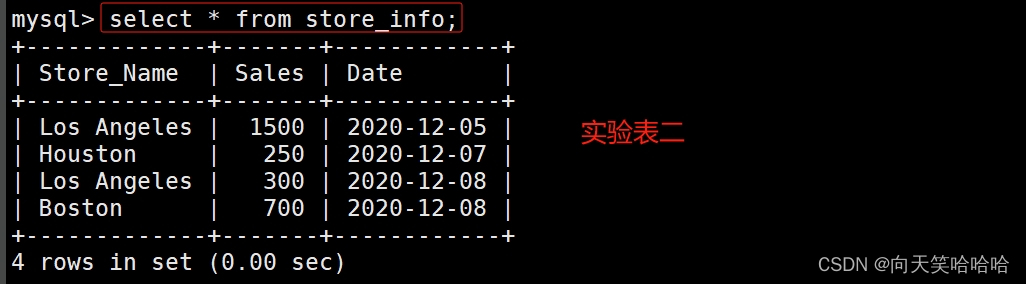
create table store_info (Store_Name char(20),Sales int(10),Date char(10));
insert into store_info values('Los Angeles','1500','2020-12-05');
insert into store_info values('Houston','250','2020-12-07');
insert into store_info values('Los Angeles','300','2020-12-08');
insert into store_info values('Boston','700','2020-12-08');
Store_Info 表格
+--------------+---------+------------+
| Store_Name | Sales | Date |
|--------------+---------+------------|
| Los Angeles | 1500 | 2020-12-05 |
| Houston | 250 | 2020-12-07 |
| Los Angeles | 300 | 2020-12-08 |
| Boston | 700 | 2020-12-08 |
+--------------+---------+------------+
二、MySQL高阶查询
1、语句与命令
1、---- select ----显示表格中一个或数个字段的所有数据记录
语法:select "字段" from "表名";
select Store_Name from Store_Info;
2、---- distinct ----不显示重复的数据记录
语法:select distinct "字段" from "表名";
select distinct store_name from store_info;
3、---- where ----有条件查询
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "条件";
select store_name from store_info where sales > 1000;
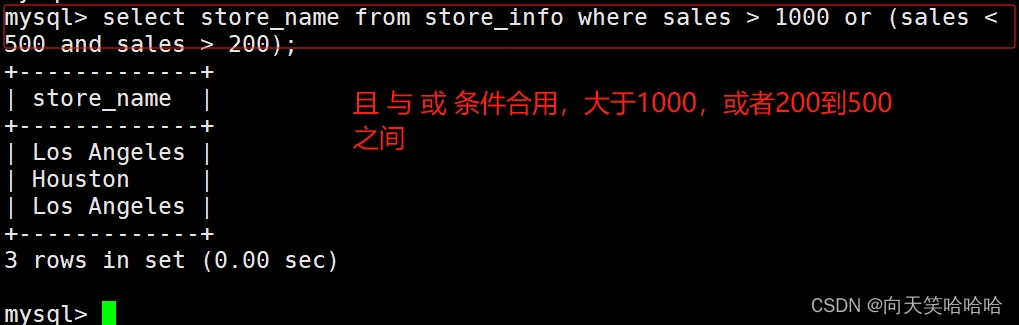
4、---- and or ----且 或
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "条件1" {[and|or] "条件2"}+ ;
select store_name from store_info where sales > 1000 or (sales < 500 and sales > 200);
5、---- in ----显示已知的值的数据记录
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "字段" in ('值1', '值2', ...);
select * from store_info where store_name in ('los angeles','houstton');
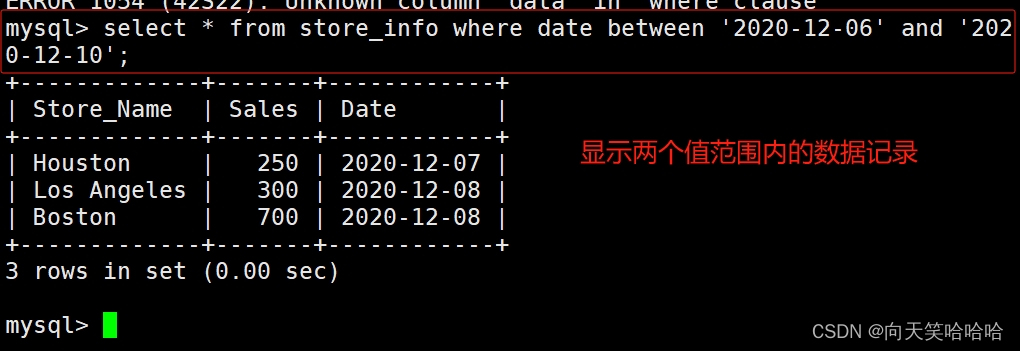
6、---- between ----显示两个值范围内的数据记录
语法:select "字段"from "表名" where "字段" between '值1' and '值2';
select * from store_info where date between '2020-12-06' and '20200-12-10';
7、---- 通配符 ----通常通配符都是跟 like 一起使用的
% :百分号表示零个、一个或多个字符
_ :下划线表示单个字符
1)'A_Z':所有以 'A' 起头,另一个任何值的字符,且以 'Z' 为结尾的字符串。例如,'ABZ' 和 'A2Z' 都符合这一个模式,而 'AKKZ' 并不符合 (因为在 A 和 Z 之间有两个字符,而不是一个字符)。
2)'ABC%': 所有以 'ABC' 起头的字符串。例如,'ABCD' 和 'ABCABC' 都符合这个模式。
3)'%XYZ': 所有以 'XYZ' 结尾的字符串。例如,'WXYZ' 和 'ZZXYZ' 都符合这个模式。
4)'%AN%': 所有含有 'AN'这个模式的字符串。例如,'LOS ANGELES' 和 'SAN FRANCISCO' 都符合这个模式。
5)'_AN%':所有第二个字母为 'A' 和第三个字母为 'N' 的字符串。例如,'SAN FRANCISCO' 符合这个模式,而 'LOS ANGELES' 则不符合这个模式。
例:---- like ----匹配一个模式来找出我们要的数据记录
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "字段" like {模式};
select * from store_info where store_name like '%os%';
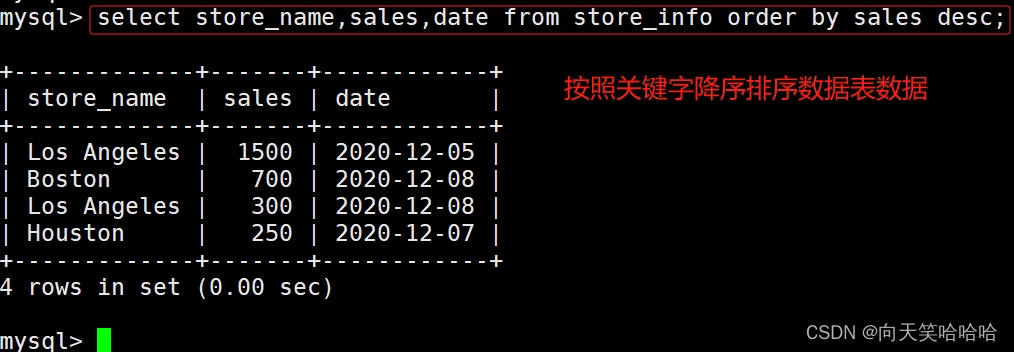
8、---- order by ----按关键字排序
语法:select "字段" from "表名" [where "条件"] order by "字段" [asc, desc];
#asc 是按照升序进行排序的,是默认的排序方式。
#desc 是按降序方式进行排序。
select store_name,sales,date from store_info order by sales desc;2、实验实操
1、---- select ----显示表格中一个或数个字段的所有数据记录
语法:select "字段" from "表名";
select Store_Name from Store_Info;
2、---- distinct ----不显示重复的数据记录
语法:select distinct "字段" from "表名";
select distinct store_name from store_info;
3、---- where ----有条件查询
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "条件";
select store_name from store_info where sales > 1000;
4、---- and or ----且 或
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "条件1" {[and|or] "条件2"}+ ;
select store_name from store_info where sales > 1000 or (sales < 500 and sales > 200);
5、---- in ----显示已知的值的数据记录
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "字段" in ('值1', '值2', ...);
select * from store_info where store_name in ('los angeles','houstton');
6、---- between ----显示两个值范围内的数据记录
语法:select "字段"from "表名" where "字段" between '值1' and '值2';
select * from store_info where date between '2020-12-06' and '20200-12-10';
7、---- 通配符 ----通常通配符都是跟 like 一起使用的
% :百分号表示零个、一个或多个字符
_ :下划线表示单个字符1)'A_Z':所有以 'A' 起头,另一个任何值的字符,且以 'Z' 为结尾的字符串。例如,'ABZ' 和 'A2Z' 都符合这一个模式,而 'AKKZ' 并不符合 (因为在 A 和 Z 之间有两个字符,而不是一个字符)。
2)'ABC%': 所有以 'ABC' 起头的字符串。例如,'ABCD' 和 'ABCABC' 都符合这个模式。
3)'%XYZ': 所有以 'XYZ' 结尾的字符串。例如,'WXYZ' 和 'ZZXYZ' 都符合这个模式。
4)'%AN%': 所有含有 'AN'这个模式的字符串。例如,'LOS ANGELES' 和 'SAN FRANCISCO' 都符合这个模式。
5)'_AN%':所有第二个字母为 'A' 和第三个字母为 'N' 的字符串。例如,'SAN FRANCISCO' 符合这个模式,而 'LOS ANGELES' 则不符合这个模式。
例:---- like ----匹配一个模式来找出我们要的数据记录
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "字段" like {模式};
select * from store_info where store_name like '%os%';
8、---- order by ----按关键字排序
语法:select "字段" from "表名" [where "条件"] order by "字段" [asc, desc];
#asc 是按照升序进行排序的,是默认的排序方式。
#desc 是按降序方式进行排序。
select store_name,sales,date from store_info order by sales desc;
三、MySQL函数
1、语句与命令
#数学函数:
abs(x) 返回 x 的绝对值
rand() 返回 0 到 1 的随机数
mod(x,y) 返回 x 除以 y 以后的余数
power(x,y) 返回 x 的 y 次方
round(x) 返回离 x 最近的整数
round(x,y) 保留 x 的 y 位小数四舍五入后的值
sqrt(x) 返回 x 的平方根
truncate(x,y) 返回数字 x 截断为 y 位小数的值
ceil(x) 返回大于或等于 x 的最小整数
floor(x) 返回小于或等于 x 的最大整数
greatest(x1,x2...) 返回集合中最大的值,也可以返回多个字段的最大的值
least(x1,x2...) 返回集合中最小的值,也可以返回多个字段的最小的值
函数输出值的效果展示:
select abs(-1), rand(), mod(5,3), power(2,3), round(1.89);
select round(1.8937,3), truncate(1.235,2), ceil(5.2), floor(2.1), least(1.89,3,6.1,2.1);
#聚合函数:
avg() 返回指定列的平均值
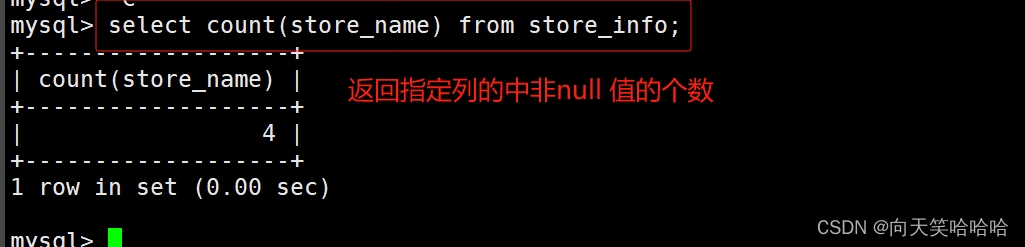
count() 返回指定列中非 NULL 值的个数
max() 返回指定列的最大值
min() 返回指定列的最小值
sum(x) 返回指定列的所有值之和
聚合函数运用:
select avg(sales) from store_info;
#返回指定列的平均值
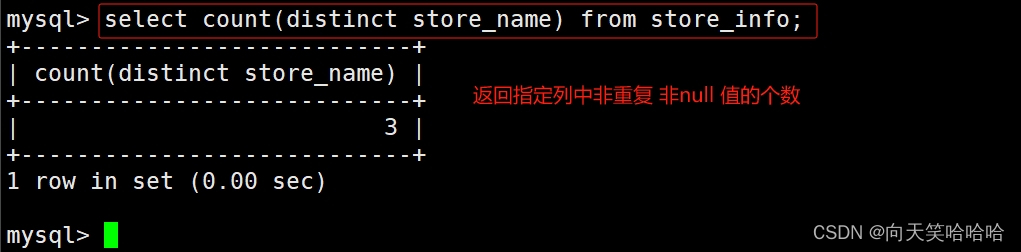
select count(store_name) from store_info;
#返回指定列中非NULL 值的个数
select count(distinct store_name) from store_info;
#返回指定列中非重复,非NULL 值的个数
select max(sales) from store_info;
#返回指定列的最大值
select min(sales) from store_info;
#返回指定列的最小值
select sum(sales) from store_info;
#返回指定列的所有值之和
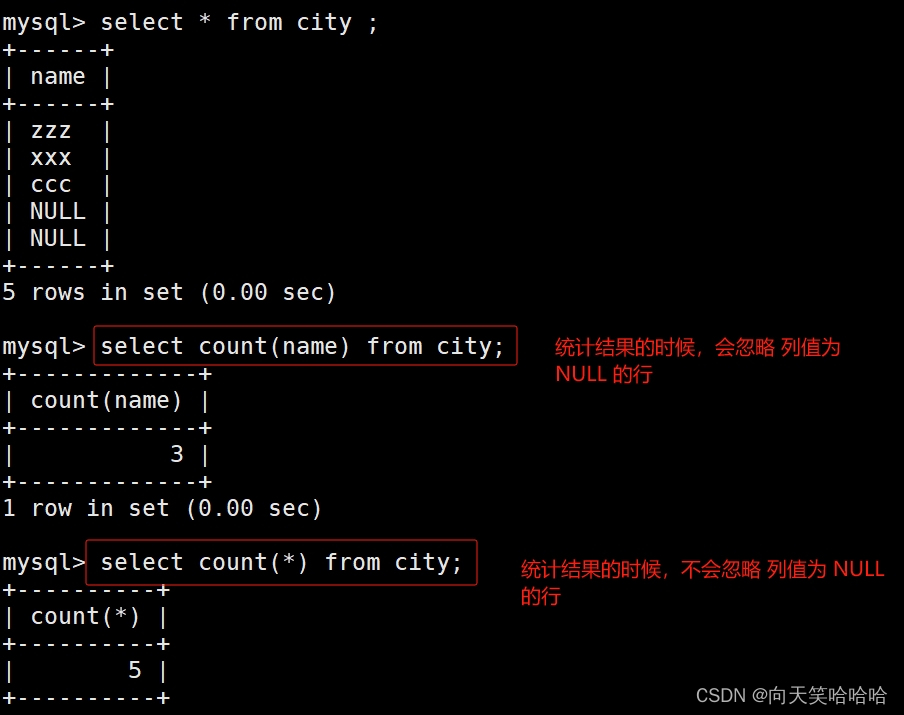
City 表格
+----------+
| name |
| -------- |
| beijing |
| nanjing |
| shanghai |
| <null> |
| <null> |
+----------+
select count(name) from city;
select count(*) from city;
#count(列名) 只包括列名那一列的行数,在统计结果的时候,会忽略列值为 NULL 的行
#count(*) 包括了所有的列的行数,在统计结果的时候,不会忽略列值为 NULL 的行
#字符串函数:
concat(x,y) 将提供的参数 x 和 y 拼接成一个字符串
substr(x,y) 获取从字符串x中的第y个位置开始的字符串,跟substring()函数作用相同
substr(x,y,z) 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始长度为 z 的字符串
trim() 返回去除指定格式的值
length(x) 返回字符串 x 的长度
replace(x,y,z) 将字符串 z 替代字符串 x 中的字符串 y
upper(x) 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成大写字母
lower(x) 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成小写字母
left(x,y) 返回字符串 x 的前 y 个字符
right(x,y) 返回字符串 x 的后 y 个字符
repeat(x,y) 将字符串 x 重复 y 次
space(x) 返回 x 个空格
strcmp(x,y) 比较 x 和 y,返回的值可以为-1,0,1
reverse(x) 将字符串 x 反转
select concat(region,store_name) from location where store_name = 'boston';
#将参数 region 和 store_name 拼接成一个字符串
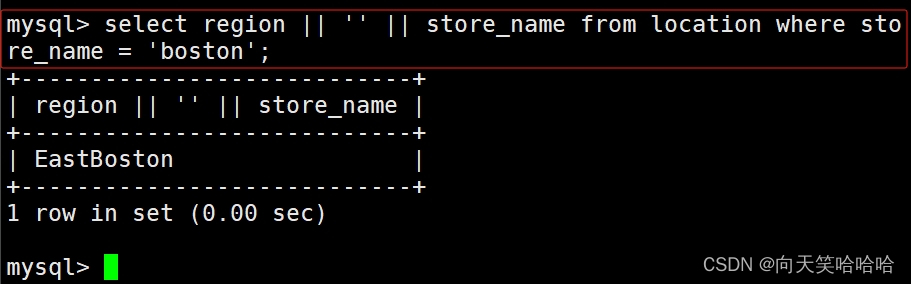
select region || '' || store_name from location where store_name = 'boston';
#如sql_mode开启了PIPES_AS_CONCAT,"||"视为字符串的连接操作符而非或运算符,和字符串的拼接函数Concat相类似,这和Oracle数据库使用方法一样的
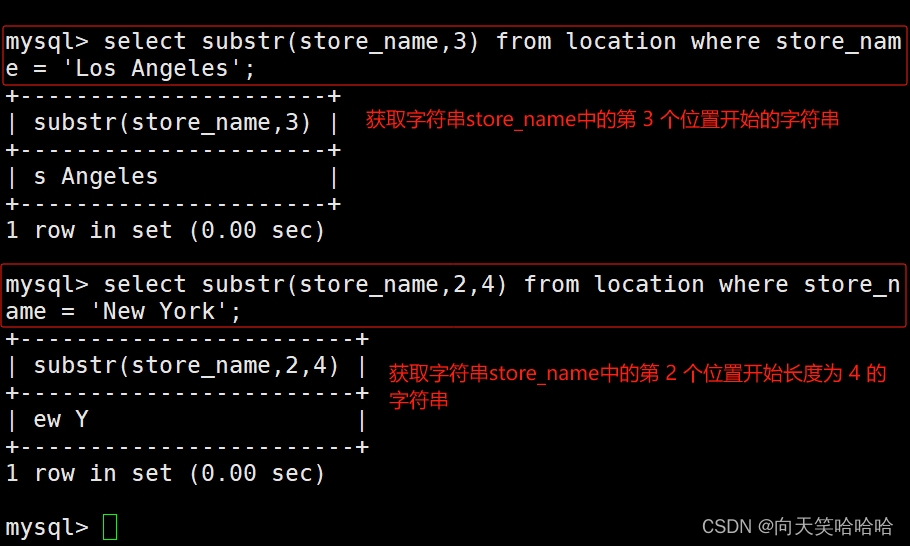
select substr(store_name,3) from location where store_name = 'Los Angeles';
#获取字符串store_name中的第 3 个位置开始的字符串
select substr(store_name,2,4) from location where store_name ame = 'New York';
#获取字符串store_name中的第 2 个位置开始长度为 4 的字符串
select trim ([ [位置] [要移除的字符串] from ] 字符串);
#[位置]:的值可以为 leading (起头), tralling (结尾), both (起头及结尾)。
#[要移除的字符串]:从字串的起头、结尾,或起头及结尾移除的字符串。缺省时为空格。
select trim(leading 'ne' from 'new york');
#去除 new york 字符串中的开头 ne 字符
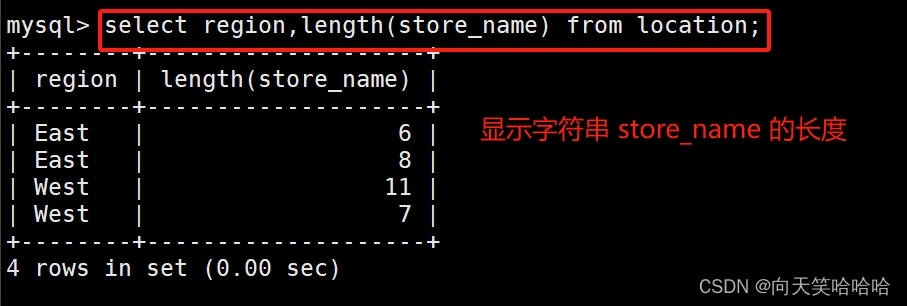
select region,length(store_name) from location;
#显示字符串 store_name 的长度
select replace(region,'ast','astern')from location;
#将字符串 region 替代字符串 'ast' 中的字符串'astern'2、实验操作
#数学函数:
abs(x)?? ??? ??? ??? ?返回 x 的绝对值
rand()?? ??? ??? ??? ?返回 0 到 1 的随机数
mod(x,y)?? ??? ??? ?返回 x 除以 y 以后的余数
power(x,y)?? ??? ??? ?返回 x 的 y 次方
round(x)?? ??? ??? ?返回离 x 最近的整数
round(x,y)?? ??? ??? ?保留 x 的 y 位小数四舍五入后的值
sqrt(x)?? ??? ??? ??? ?返回 x 的平方根
truncate(x,y)?? ??? ?返回数字 x 截断为 y 位小数的值
ceil(x)?? ??? ??? ??? ?返回大于或等于 x 的最小整数
floor(x)?? ??? ??? ?返回小于或等于 x 的最大整数
greatest(x1,x2...)?? ?返回集合中最大的值,也可以返回多个字段的最大的值
least(x1,x2...)?? ??? ?返回集合中最小的值,也可以返回多个字段的最小的值函数输出值的效果展示:
select abs(-1), rand(), mod(5,3), power(2,3), round(1.89);
select round(1.8937,3), truncate(1.235,2), ceil(5.2), floor(2.1), least(1.89,3,6.1,2.1);
?#聚合函数:
avg()?? ??? ??? ??? ?返回指定列的平均值
count()?? ??? ??? ??? ?返回指定列中非 NULL 值的个数
max()?? ??? ??? ??? ?返回指定列的最大值
min()?? ??? ??? ??? ?返回指定列的最小值
sum(x)?? ??? ??? ??? ?返回指定列的所有值之和聚合函数运用:
select avg(sales) from store_info;
#返回指定列的平均值
select count(store_name) from store_info;
#返回指定列中非NULL 值的个数
select count(distinct store_name) from store_info;
#返回指定列中非重复,非NULL 值的个数
select max(sales) from store_info;
#返回指定列的最大值
select min(sales) from store_info;
#返回指定列的最小值
select sum(sales) from store_info;
#返回指定列的所有值之和
City 表格?
+----------+| name ? ? |
| -------- |
| beijing ?|
| nanjing ?|
| shanghai |
| <null> ? |
| <null> ? |+----------+
select count(name) from city;
select count(*) from city;
#count(列名) 只包括列名那一列的行数,在统计结果的时候,会忽略列值为 NULL 的行
#count(*) 包括了所有的列的行数,在统计结果的时候,不会忽略列值为 NULL 的行
#字符串函数:
concat(x,y)?? ??? ?将提供的参数 x 和 y 拼接成一个字符串
substr(x,y)?? ??? ?获取从字符串x中的第y个位置开始的字符串,跟substring()函数作用相同
substr(x,y,z)?? ?获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始长度为 z 的字符串
trim()?? ??? ??? ?返回去除指定格式的值
length(x)?? ??? ?返回字符串 x 的长度
replace(x,y,z)?? ?将字符串 z 替代字符串 x 中的字符串 y
upper(x)?? ??? ?将字符串 x 的所有字母变成大写字母
lower(x)?? ??? ?将字符串 x 的所有字母变成小写字母
left(x,y)?? ??? ?返回字符串 x 的前 y 个字符
right(x,y)?? ??? ?返回字符串 x 的后 y 个字符
repeat(x,y)?? ??? ?将字符串 x 重复 y 次
space(x)?? ??? ?返回 x 个空格
strcmp(x,y)?? ??? ?比较 x 和 y,返回的值可以为-1,0,1
reverse(x)?? ??? ?将字符串 x 反转select concat(region,store_name) from location where store_name = 'boston';
#将参数 region 和 store_name 拼接成一个字符串
select region || '' || store_name from location where store_name = 'boston';
#如sql_mode开启了PIPES_AS_CONCAT,"||"视为字符串的连接操作符而非或运算符,和字符串的拼接函数Concat相类似,这和Oracle数据库使用方法一样的
select substr(store_name,3) from location where store_name = 'Los Angeles';
#获取字符串store_name中的第 3 个位置开始的字符串select substr(store_name,2,4) from location where store_name ame = 'New York';
#获取字符串store_name中的第 2 个位置开始长度为 4 的字符串
select trim ([ [位置] [要移除的字符串] from ] 字符串);
#[位置]:的值可以为 leading (起头), tralling (结尾), both (起头及结尾)。?
#[要移除的字符串]:从字串的起头、结尾,或起头及结尾移除的字符串。缺省时为空格。
select trim(leading 'ne' from 'new york');
#去除 new york 字符串中的开头 ne 字符
select region,length(store_name) from location;
#显示字符串 store_name 的长度
select replace(region,'ast','astern')from location;
#将字符串 region 替代字符串 'ast' 中的字符串'astern'
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 第二节 K8S 的架构
- MySQL存储过程和触发器
- pulsar原来是这样操作topic的
- linux 如何生成rsa,Linux 生成rsa 格式不对
- 嵌入式学习 Day4
- EBU7140 Security and Authentication(一)常见加密算法
- 如何修复卡在恢复模式的Android 手机并恢复丢失的数据
- 共探开源AI基础设施,九州未来受邀出席第十七届中国大数据技术大会
- 数字 IC 笔试易混淆整理
- 用git bash调用md5sum进行批量MD5计算