Java语法---使用sort进行排序
发布时间:2023年12月23日
目录
一、升序
升序排序就是按照从小到大排序。(注意,想进行排序的话,基本数据类型要换成包装类,就像int型要写成Integer)
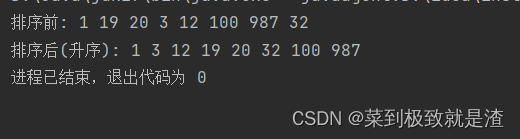
public static void main(String[] args) { Integer[] a={1,19,20,3,12,100,987,32}; System.out.print("排序前: "); for(int i:a){ System.out.print(i+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.print("排序后(升序): "); //开始使用sort进行升序排序 Arrays.sort(a); for(int i:a){ System.out.print(i+" "); } }
二、降序
想要使用sort进行降序排序,我们需要使用Comparator接口,这里有两种方式可以实现,一种是类实现接口,一种是匿名内部类,我们都讲一下。
(1)类实现接口
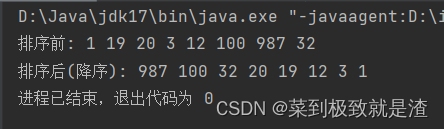
//程序入口 public class main1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer[] a={1,19,20,3,12,100,987,32}; System.out.print("排序前: "); for(int i:a){ System.out.print(i+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.print("排序后(降序): "); Arrays.sort(a,new myCom()); for(int i:a){ System.out.print(i+" "); } } } //排序类 class myCom implements Comparator<Integer>{ @Override public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) { return o2-o1; } }
(2)匿名内部类
public static void main(String[] args) { Integer[] a={1,19,20,3,12,100,987,32}; System.out.print("排序前: "); for(int i:a){ System.out.print(i+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.print("排序后(降序): "); Arrays.sort(a, new Comparator<Integer>() { @Override public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) { return o2-o1; } }); for(int i:a){ System.out.print(i+" "); } }
?
三、自定义排序规则
?这里我们自定义一个学生类,有name属性和age属性,我们按照年龄从大到小排序,如果年龄相等,就按照名字降序。
?
public static void main(String[] args) { student[] students=new student[5]; //这里创建对象数组的时候,还要new一下,别忘了!这个很容易忽略,当然,你也可以声明数组的时候就初始化数据 students[0]=new student(); students[0].setAge(10); students[0].setName("bac"); students[1]=new student(); students[1].setAge(10); students[1].setName("cac"); students[2]=new student(); students[2].setAge(10); students[2].setName("aac"); students[3]=new student(); students[3].setAge(18); students[3].setName("op"); students[4]=new student(); students[4].setAge(8); students[4].setName("lisi"); System.out.println(students[0]); System.out.print("排序之前"); for(int i=0;i<students.length;i++){ System.out.println(students[i].getName()+" "+students[i].getAge()); } Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator<student>() { @Override public int compare(student o1, student o2) { if(o1.getAge()==o2.getAge()){ return o2.getName().compareTo(o1.getName()); } return o2.getAge()-o1.getAge(); } }); System.out.println(); for(int i=0;i<students.length;i++){ System.out.println(students[i].getName()+" "+students[i].getAge()); } }
四、集合中的sort排序
前面介绍的sort是数组的排序,集合中其实也一样,只不过Arrays.sort换成了Collections.sort
(1)升序
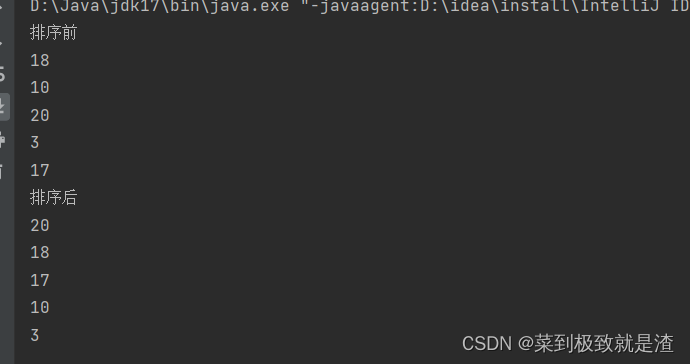
public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> integerList=new ArrayList<>(); integerList.add(18); integerList.add(10); integerList.add(20); integerList.add(3); integerList.add(17); System.out.println("排序前"); for(Integer i:integerList){ System.out.println(i); } System.out.println("排序后"); //进行升序排序 Collections.sort(integerList); for(Integer i:integerList){ System.out.println(i); } }
(2)降序
与上面一样有两种方式实现,匿名内部类和类的实现接口,这里我就只写了匿名内部类的方法,另外一种可以看上面的数组排序。
public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> integerList=new ArrayList<>(); integerList.add(18); integerList.add(10); integerList.add(20); integerList.add(3); integerList.add(17); System.out.println("排序前"); for(Integer i:integerList){ System.out.println(i); } System.out.println("排序后"); Collections.sort(integerList, new Comparator<Integer>() { @Override public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) { return o2-o1; } }); for(Integer i:integerList){ System.out.println(i); } }
(3)自定义排序?
还是和上面的需求一样,年龄从小到大排序,年龄一样按照名字大的在前面
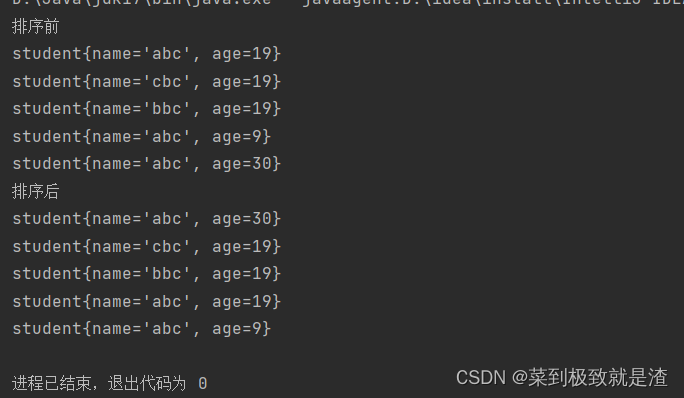
public static void main(String[] args) { List<student> students=new ArrayList<>(); students.add(new student("abc",19)); students.add(new student("cbc",19)); students.add(new student("bbc",19)); students.add(new student("abc",9)); students.add(new student("abc",30)); System.out.println("排序前"); for(student i:students){ System.out.println(i); } System.out.println("排序后"); //进行自定义排序 Collections.sort(students, new Comparator<student>() { @Override public int compare(student o1, student o2) { if(o1.getAge()==o2.getAge()){ return o2.getName().compareTo(o1.getName()); } return o2.getAge()-o1.getAge(); } }); for(student i:students){ System.out.println(i); } }?
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/gaoqiandr/article/details/135175326
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 分割、合并、转换、重组:强大的自部署 PDF 处理工具 | 开源日报 No.143
- YoloV5改进策略:BAM瓶颈注意力模块|BAM详解以及代码注释|CBAM姊妹篇|有效涨点
- Halcon计算共生矩阵并导出其灰度值特征cooc_feature_image
- 代码随想录算法训练营第四十五天|70. 爬楼梯 (进阶)、322. 零钱兑换 、279.完全平方数
- 三、MySQL---练习(单表查询)
- 很实用的ChatGPT网站——httpchat-zh.com
- MySQL面试题 | 10.精选MySQL面试题
- PPT怎么做成二维码?扫二维码就能获得文档
- pycharm debug显示的变量过多
- 武汉灰京文化:技术先锋辐射游戏行业,带来全新体验乐趣无穷!