【c++】利用嵌套map创建多层树结构
通常树的深度都大于1,即树有多层,而树结构又可以用c++的map容器来实现,所以,本文给出了一种多层树结构的实现思路,同时也给出了相应的c++代码。
整体思路概述
? ? ? ? 首先定义一个节点类Node类,要包括children(用map容器实现),即用map结构来模拟子树,然后整棵树也用一个map结构来实现。因此,总体来说,就是用一个嵌套的map结构来实现多层树结构。以下给出每一步具体的描述 及相应的代码。
1、定义一个节点类Node类
????????定义树结构之前要先定义一个节点类Node类,要包括键、值、children等属性,并包括有参无参构造函数,此外,本文还实现了一个打印所有节点包括的键值对的函数(PrintTree函数)。
class Node {
public:
string key;
const char* value;
Node* left;
Node* right;
map<string, Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(const string& k) : key(k) {}
Node(const string& k, const char* v) :key(k), value(v) {}
void PrintTree(const Node& node, int level = 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < level; ++i) {
cout << " ";
}
cout << "- " << node.key << " " << node.value << endl;
for (const auto& pair : node.children) {
PrintTree(*pair.second, level + 1);
}
}
};2、(重难点)根据属性的键值对(存放在vector容器中)创建出对应的节点,存放到map容器中,并将其赋值给对应父节点的children属性
? ? ? ? 主要思路就是:将父节点的所有字节点全部放到一个map容器中,然后再把这个map容器赋值给父节点的children这个成员变量。
? ? ? ? 本文实现的数结构如下图所示,根节点是"DBUSER",然后有两个User实例,每个实例又包括Name、Password、Gender、Mobile和Email5个属性。
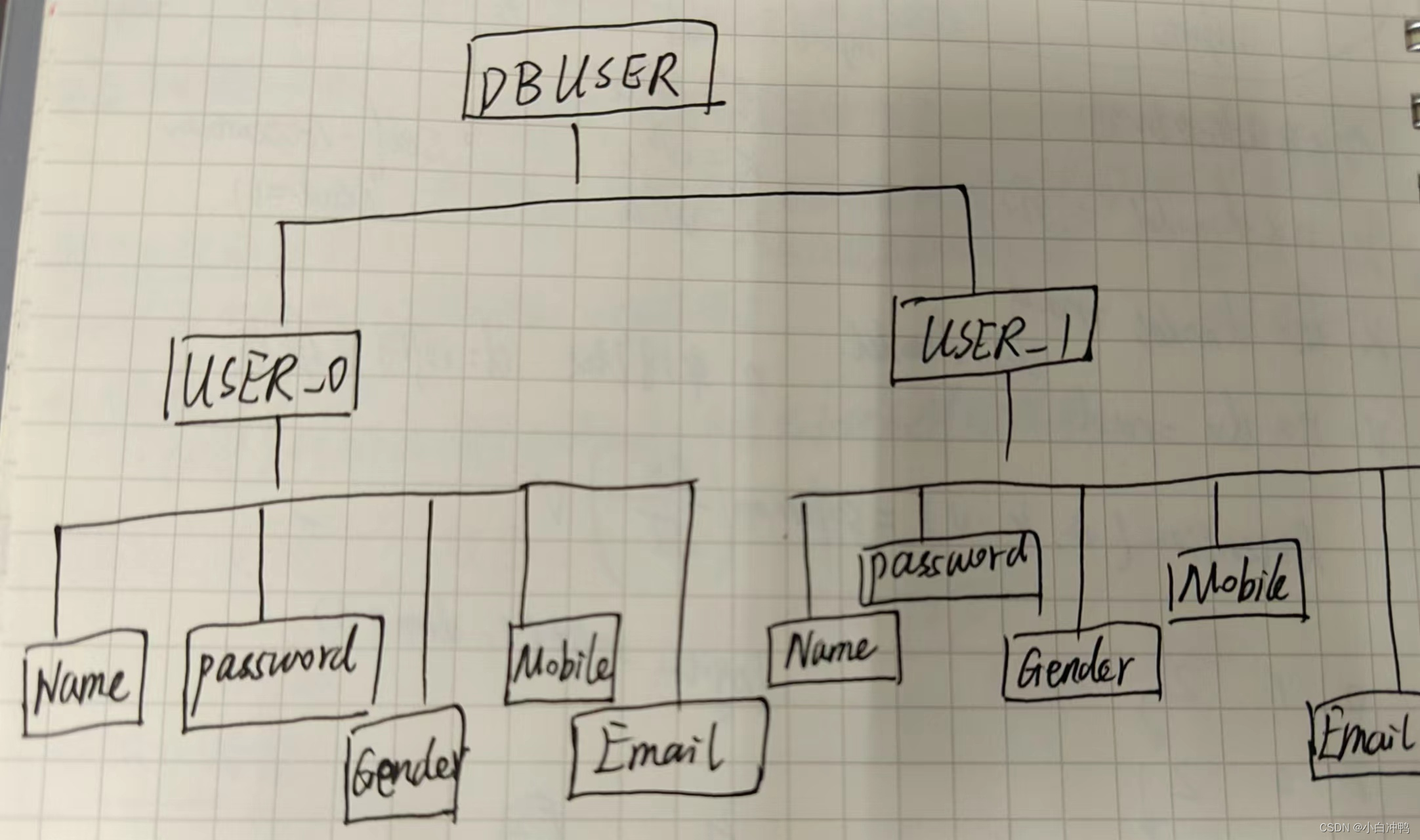
具体来说,实现过程如下:
? ? ? ? (1)首先创建两个User实例,并将其添加到new_users这个map容器中。(这就完成了以上树结构第一层的构建,之后直接将new_users赋值给根节点的children变量即可。这里根节点是第0层,所以这棵树一共有三层:0、1、2层。)
? ? ? ? (2)然后为每个User实例创建一个用于存放其所有子节点的map容器,即attribute。
? ? ? ? (3)然后根据vector容器infoVector中存放的键值对信息,通过Node类相应的有参构造函数,构造出相应的节点,将其加入到attribute中。
? ? ? ? 在这个过程中,考虑到每个User实例所包含的属性个数相同(都是5个,即以下代码中的end_index),而且是在User实例的循环中,所以采用这种方法来对infoVector中的所有键值对进行划分(每5个键值对为一组,进行构造节点、放入map容器等操作,这一点要理解清楚!!):固定end_index,每对5个键值对(即一组键值对)进行完操作之后,就将这5个键值对从infoVector中擦除,这样,对每个User实例的attribute,加入其中的都是infoVector的前5个键值对,这样就可以方便地用循环实现了。当然,擦除之后还要记得对infoVector进行一下判空操作,如果为空就说明所有的键值对信息已经处理完了,就要跳出循环,不要再进行操作了。
(可能说的还是有点不清楚【尴尬】【尴尬】hh,大家可以结合下面的代码看看,希望可以明白我的逻辑【抱拳】【抱拳】【抱拳】)
//构建新树
Node* newTreeRoot = nullptr; // 新树的根节点
insertNode(newTreeRoot,"DBUSER","");
map<string, Node*> new_users;
int end_index = (infoVector.size() / count);
for (int num = 0;num < count;num++) {
//创建User实例
string user_key = "User_" + to_string(num);
Node* user_node = new Node(user_key,"");
new_users.insert(make_pair(user_key,user_node));
//得到存储User实例的所有子节点的map
map<string, Node*> attribute;//创建用于存储User实例节点对应的属性键值对的map容器
int nnum = 0;
for (auto info = infoVector.begin();info != infoVector.end();++info) {
if (nnum < end_index) {
cout << info->first << ": " << info->second << endl;
Node* att = new Node(info->first, info->second);
attribute.insert(make_pair(info->first, att));
}
else {
break;
}
nnum++;
}
/*cout << "输出擦除前的infoVector:" << endl;
for (auto it = infoVector.begin();it != infoVector.end();++it) {
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;
}*/
//将infoVector中之前使用过的键值对擦除
infoVector.erase(infoVector.begin(), infoVector.begin() + end_index);
//判断当前的infoVector是否为空,若为空则跳出循环,否则继续
/*cout << "输出擦除后的infoVector:" << endl;
for (auto it = infoVector.begin();it != infoVector.end();++it) {
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;
}*/
//让User实例节点的children指针指向对应的map(即存放着该节点的所有子节点的map)
user_node->children = attribute;
if (infoVector.empty()) break;
}
//让根节点的children指针指向存放所有User实例节点的map
newTreeRoot->children = new_users;
cout << "输出多层树结构: " << endl;
newTreeRoot->PrintTree(*newTreeRoot);3、输出结果
运行以上代码,最后输出的树的结构如下:

以上就是全部内容了。
都看到这里了,希望大家能多多点赞 收藏 加关注,这对我很重要!!!希望大家能多多点赞 收藏 加关注,这对我很重要!!!希望大家能多多点赞 收藏 加关注,这对我很重要!!!(重要的事说三遍hh)【跪谢各位慷慨的大佬!!!】
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 支持二开可定制化的企业电子招标采购系统源码
- Graceful Response 构建 Spring Boot 下优雅的响应处理
- 解决:已经安装open3d,还是报错No module named ‘open3d‘的问题
- rog的笔记本,独显输出,混合输出,集显输出,自动调节,几种输出方式意味着什么,有什么区别
- CSS两种盒模型以及区别、CSS合并方法、CSS文件合并方法、label的作用是什么?如何美化CheckBox?
- MessageBox:拓宽业务边界,HubSpot与WhatsApp的完美融合
- AUTOSAR从入门到精通-存储配置(NvM)(七)
- 【GPU监控】Gpu-dcgm-exporter 监控
- 【洛谷篇】编程里你一定不知道的暗语,看看你知道几个?
- 中国大口径锻造圆钢市场销售渠道及未来投资走势预测报告2024-2030年