从零学Java 集合概述
发布时间:2024年01月10日
Java 集合概述
1 什么是集合?
概念:对象的容器,定义了对多个对象进行操作的常用方法;可实现数组的功能。
和数组区别:
- 数组长度固定,集合长度不固定。
- 数组可以存储基本类型和引用类型,集合只能存储引用类型。
2 Collection体系集合
Collection体系结构的根接口,代表一组对象,称为“集合”。
- List接口的特点:有序有下标、元素可重复
- Set接口的特点:无序无下标、元素不能重复
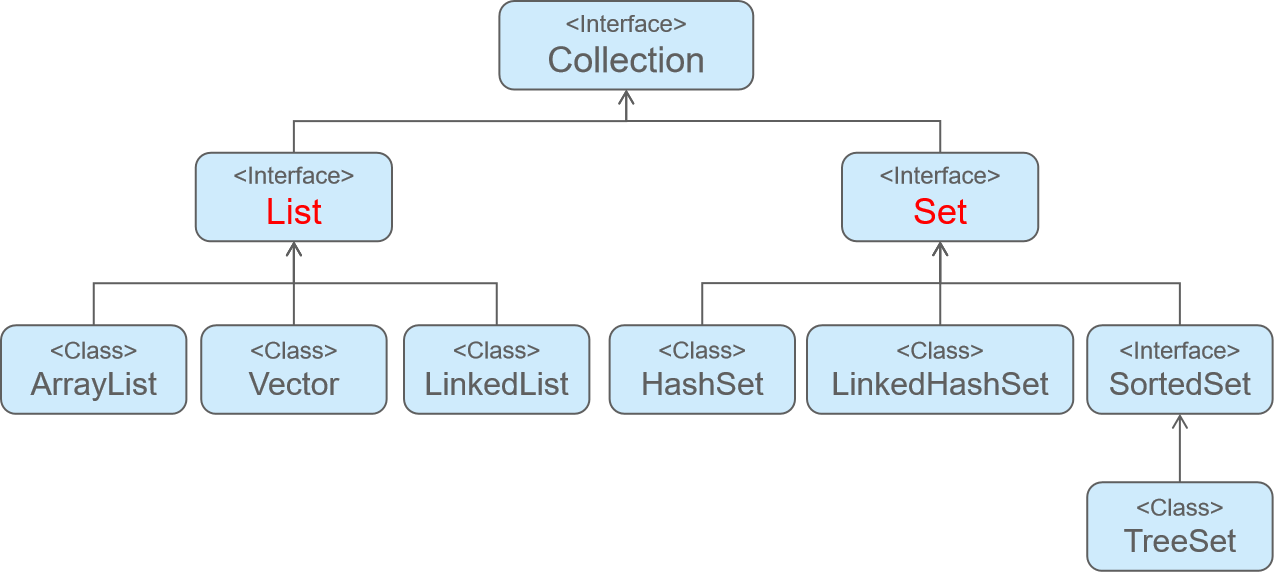
2.1 Collection父接口
特点:代表一组任意类型的对象。
2.1.1 常用方法
eg:
/**
* @author 胡昊龙
* @version 1.0
* @description: TODO
* @date 2024/1/10 11:09
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Collection接口的使用
//创建集合
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
Collection collection1 = new ArrayList();
//1 添加单个元素
collection.add("北京");
collection.add("上海");
collection.add("杭州");
collection.add("哈尔滨");
collection.add("北京");
collection1.add("廊坊");
collection1.add("保定");
collection1.add("保定");
//1.1 添加整个集合
collection.addAll(collection1);
System.out.println("元素个数: "+collection1.size());
System.out.println("打印: "+collection1);
System.out.println("元素个数: "+collection.size());
System.out.println("打印: "+collection);
//2 删除
//2.1 删除一个元素
collection.remove("北京");
System.out.println("删除以后: "+collection);
//2.2 清空
collection1.clear();
System.out.println("清空: "+collection1);
//3 遍历
//3.1 增强for
System.out.println("增强for-----------");
for (Object o : collection) {
System.out.println(o);
}
//3.2 迭代器:集合中专门用来遍历集合的
System.out.println("迭代器------------");
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
//3.2.1 it.hasNext(); 判断是否还有元素
//3.2.2 it.next(); 获取下一个元素
while (it.hasNext()){
Object next = it.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
//3.2.3 it.remove(); 删除元素
//4 判断
//4.1 判断元素是否存在
System.out.println(collection.contains("哈尔滨"));
//4.2 判断集合是否为空
System.out.println(collection1.isEmpty());
}
}
2.1.2 Iterator 接口
Iterator:迭代器用来遍历集合的统一接口。
- hasNext();判断是否还有元素
- next();获取元素
- remove();删除元素。
//3.2 迭代器:集合中专门用来遍历集合的
System.out.println("迭代器------------");
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
//3.2.1 it.hasNext(); 判断是否还有元素
//3.2.2 it.next(); 获取下一个元素
while (it.hasNext()){
Object next = it.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
//3.2.3 it.remove(); 删除当前元素
//it.remove();
注意:
- 不能执行多次next()。
- 在使用迭代器过程中,不能使用集合的删除方法,只能使用迭代器的删除方法,
否则出现并发修改异常(ConcurrentModificationException)
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_50858647/article/details/135511095
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【正点原子STM32】STM32基础知识(F1F4F7H7 STM32系统框架、寻址范围、存储器映射的存储器功能划分、寄存器映射)
- CUDA+Anaconda+Pytorch环境安装
- Android 10.0 SystemUI禁用长按recent键的分屏功能
- pyhackrf2 修改bw问题
- 在机械硬盘和固态硬盘上分别打一个压缩包,时间相差几倍
- 记一个常用的时间、日期 格式化方法
- 开年安全锦囊|保护现代Web应用程序的 7 大关键举措
- 人工智能岗位可以考什么证书?考试难不难?
- 基于WEB职业培训管理系统
- 如何在线生成App:将网页封装成APP