Vue中的组件
在应用程序的开发中,组件是不可缺少的。在Vue的使用中,同样也会用到组件。
1、组件的名字唯一;
2、组件以Html形式书写;
3、组件可以复用;
4、组件可以嵌套;
5、组件可以相互调用;
6、组件分为可视化组件和非可视化组件。
一般情况下,组件写在一个单独的文件中,在使用的时候按需引入和使用。
一、组件的定义和使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Vue组件的定义与使用</title>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="demo1" style="background-color: aquamarine;">
<p>这是demo1组件</p>
<my-html1></my-html1>
<my-html2></my-html2>
<my-html3></my-html3>
<my-html5></my-html5>
</div>
<div id="demo2" style="background-color: darksalmon;">
<p>这是demo2组件</p>
<my-html1></my-html1>
<my-html2></my-html2>
<my-html4></my-html4>
<my-html6></my-html6>
</div>
<template id="component5">
<div>
<p>组件5</p>
</div>
</template>
<script type="text/x-template" id="component6">
<div>
<p>{{ mytitle }}</p>
</div>
</script>
<script>
var mycompponet5={
template:"#component5"
}
//创建组件模板对象
const mytemplate=Vue.extend ({
template:`
<div>
<p>标签组件1</p>
</div>
`
});
//注册全局组件
Vue.component('my-html1',mytemplate);
Vue.component('my-html5',mycompponet5);
Vue.component('my-html6',{
template:'#component6',
data(){
{ return {mytitle:"组件6"} }
}
});
//注册组件的另外方式是直接写内容
Vue.component('my-html2',{
data(){ return {count:1} },
template:`<button v-on:click="count++">按钮组件2,点击数:{{count}}</button>`
});
const myhtml3={
data(){ return { count:0} },
template:`<button v-on:click="count++">按钮组件3,点击数:{{count}}</button>`
}
//创建vue对象
const vueApp1=new Vue({
el:'#demo1',
components:{
'my-html3':myhtml3
}
});
const vueApp2=new Vue({
el:'#demo2',
components:{
'my-html4':{
data(){ return { count:0} },
template:`<button v-on:click="count++">按钮组件4,点击数:{{count}}</button>`
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html> 显示结果:
从上面的代码中可以看出,vue的组件有多种写法,可以根据个人喜好选择。
二、组件的嵌套
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Vue组件的嵌套</title>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="demo" style="background-color: aquamarine;">
<my-html1></my-html1>
<my-html2></my-html2>
</div>
<script>
//创建组件模板对象
const AloneTemplate={
template:`
<div>
<p>独立的组件1</p>
</div>
`
};
Vue.component('my-html1',{
data(){ return {count:1} },
template:`<div><button>按钮组件</button><childcomponet></childcomponet></div>`,
components:{
'childcomponet':AloneTemplate
}
});
Vue.component('my-html2',{
data(){ return {count:1} },
template:`<div><button>按钮组件</button><childcomponet></childcomponet></div>`,
components:{
'childcomponet':{
template:`
<div>
<p>独立的组件2{{count}}</p>
</div>
`
}
}
});
//创建vue对象
const vueApp1=new Vue({
el:'#demo'
});
</script>
</body>
</html>上面是组件嵌套的两种写法。
三、组件的传值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Vue的通信</title>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="demo" style="background-color: aquamarine;">
<html-a v-bind:incomepara1="worker" v-bind:incomepara2="program"></html-a>
</div>
<script>
const AloneTemplate={
data(){ return { name:'人员列表' } },
template:`
<div>
<p>{{name}}</p>
<p>人员1:{{ incomepara1.name +"--"+incomepara1.age}}</p>
<p>人员2:{{incomepara2.name}}--{{incomepara2.age}}</p>
</div>
`,
props:['incomepara1','incomepara2']
};
const vueApp=new Vue({
el:'#demo',
data:{
worker:{ name:"json",age:37 },
program:{ name:"sdf",age:31 }
},
components:{'html-a':AloneTemplate}
});
</script>
</body>
</html> props是一个数组,它起到桥梁的作用,可以传递多个参数,具体的参数可以是数组、变量名,也可是对象,传递对象就可以传递丰富的参数值。
props可以理解为代理,对于组件而言,通过v-bind让props的参数指向父项的具体参数,对于组件内部就可以直接使用了。
v-bind的绑定时括号里面可以是运算表达式。
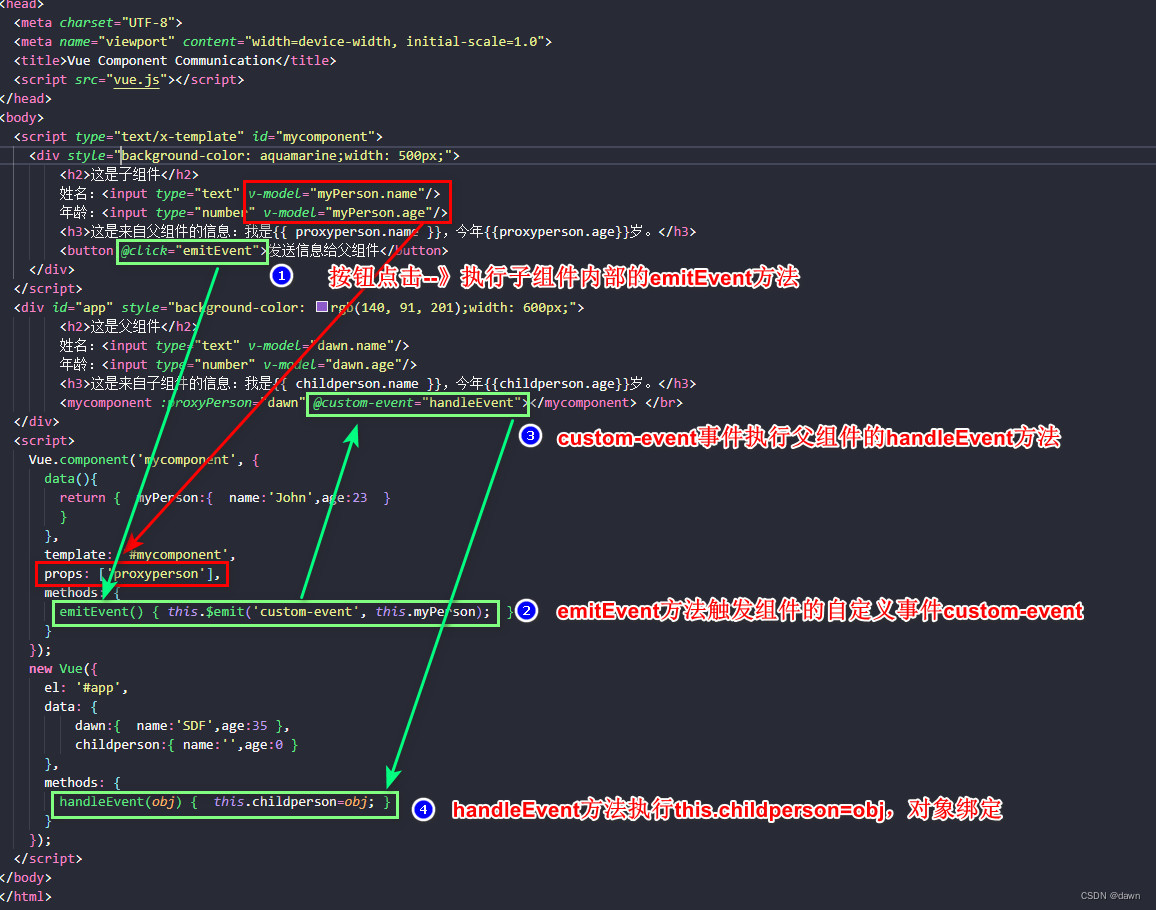
下面是一个子组件与父组件相互通信的例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Vue Component Communication</title>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/x-template" id="mycomponent">
<div style="background-color: aquamarine;width: 500px;">
<h2>这是子组件</h2>
姓名:<input type="text" v-model="myPerson.name"/>
年龄:<input type="number" v-model="myPerson.age"/>
<h3>这是来自父组件的信息:我是{{ proxyperson.name }},今年{{proxyperson.age}}岁。</h3>
<button @click="emitEvent">发送信息给父组件</button>
</div>
</script>
<div id="app" style="background-color: rgb(140, 91, 201);width: 600px;">
<h2>这是父组件</h2>
姓名:<input type="text" v-model="dawn.name"/>
年龄:<input type="number" v-model="dawn.age"/>
<h3>这是来自子组件的信息:我是{{ childperson.name }},今年{{childperson.age}}岁。</h3>
<mycomponent :proxyPerson="dawn" @custom-event="handleEvent"></mycomponent> </br>
</div>
<script>
Vue.component('mycomponent', {
data(){
return { myPerson:{ name:'John',age:23 }
}
},
template: '#mycomponent',
props: ['proxyperson'],
methods: {
emitEvent() { this.$emit('custom-event', this.myPerson); }
}
});
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
dawn:{ name:'SDF',age:35 },
childperson:{ name:'',age:0 }
},
methods: {
handleEvent(obj) { this.childperson=obj; }
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>显示结果:

父组件中的信息变化与子组件中的信息同步,这是因为prop起到了绑定对象的作用,子组件中的信息变化在点击按钮【发送信息给父组件】后因为对象绑定了,在自定义的事件custom-event中调用了父组件的方法handleEvent(obj),所以也是实时变化同步。
2023年一月份的时候学习vue,写了三篇文章,分别是:
1、Vue组件化编程的基础知识要点
2、Vue组件化编程的组件通信
3、三种简洁易行的方法解决基于Vue.js的组件通信
一年过去了,我都快忘记了,以前是断断续续地学,并没有做个项目,看来学习需要实时跟进并且要加以适当的练习。
编程就是这样,学会容易,上手也很快,但是不做项目加以巩固,等于没有学!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【转】git如何使用.gitignore文件设置忽略文件规则
- 网络安全运营关键绩效指标
- QMainWindow_菜单栏和工具栏创建
- jmeter性能测试
- linux 压力测试 AB ApacheBench
- NPOI 导出Excel
- 使用Python库pyqt5制作TXT阅读器-------UI设计
- 聊聊Git中的引用
- 前端--基础 常用标签 - ( 内部链接,空链接,下载链接,网页元素连接)
- PyTorch深度学习实战(29)——神经风格迁移