南京大学-软件分析-课程05-数据流分析基础理论
1. 从另一个角度看迭代算法
用k个值来表示CFG中的k个节点,在每一轮迭代中更新对应的值。
迭代函数为
F
:
V
k
F:V^k
F:Vk—>
V
k
V^k
Vk
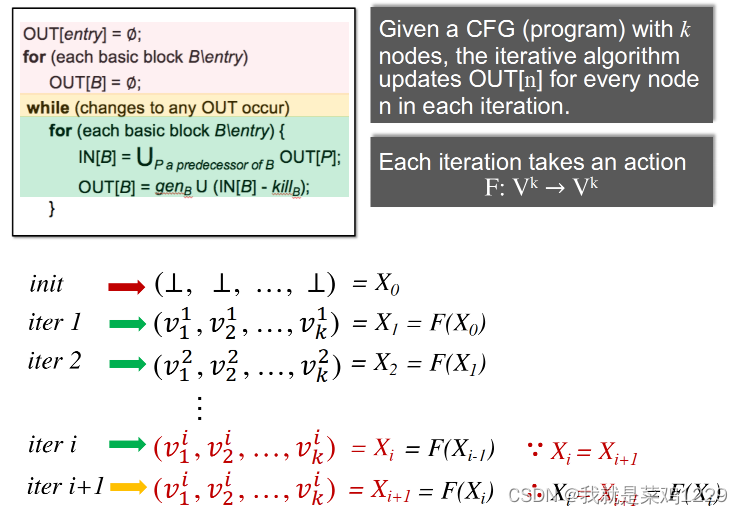
X is a fixed point of function F if X = F(X)
2. Partial Order(偏序)
当我们定义偏序集(partially ordered set,poset)时,我们将其表示为一个二元组 r (P, ?),其中 ?是一个二元运算符在P上定义偏序关系。有如下属性:
(1) ?x ∈ P, x ? x (Reflexivity)
(2) ?x, y ∈ P, x ? y ∧ y ? x ? x = y (Antisymmetry)
(3) ?x, y, z ∈ P, x ? y ∧ y ? z ? x ? z (Transitivity)
例子:
整数集上小于等于关系。
字符串的子串关系。
集合的子集关系。
3. Upper and Lower Bounds(上下界)
Given a poset (P, ?) and its subset S that S ? P, we say that
u ∈ P is an upper bound of S, if ?x ∈ S, x ? u. Similarly,
l ∈ P is an lower bound of S, if ?x ∈ S, l ? x.
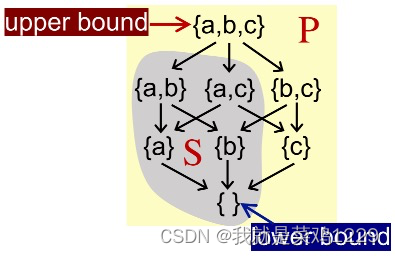
最小上界
我们定义S的最小上界least upper bound (lub or join), 记为 ?S,
对于S是每个上界u,有 ?S ? u.
最大下界
我们定义S的大下界greatest lower bound (glb, or meet), 记为 ?S,
对于S是每个下界l,有 l ? ?S.
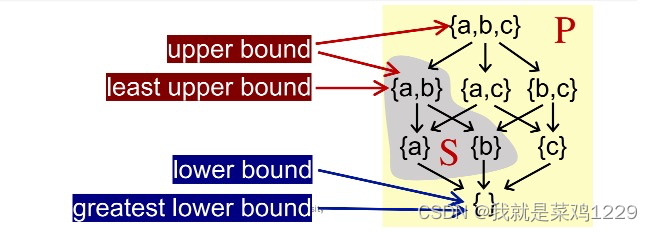
一般来说,如果S包含两个元素a和b。
?S can be written a ? b (the join of a and b),a和b的最小上界。
?S can be written a ? b (the meet of a and b),a和b的最大下界。
一些属性
- 不是每个偏序集都有最小上界(lub/join)和最大下界(glb/meet)。
- 如果有lub或glb,则一定唯一。
4. Lattice,Semilattice,Complete and Product Lattice(格、半格)
Lattice
Given a poset (P, ?), ?a, b ∈ P, if a ? b and a ? b exist, then (P, ?) is called a lattice
偏序集中任意两个元素都存在最大下界/最小上界。则这个偏序集可以被称为Lattice
Semilattice
对于最大下界/最小上界只存在一个的情况下,称之为半个,
Given a poset (P, ?), ?a, b ∈ P,
if only a ? b exists, then (P, ?) is called a join semilattice
if only a ? b exists, then (P, ?) is called a meet semilattice
Complete Lattice
Given a lattice (P, ?), for arbitrary subset S of P, if ?S and ?S exist, then (P, ?) is called a complete lattice
一个Lattice中的所有子集都有都有一个最小上界和一个最大下界。
Every complete lattice (P, ?) has
a greatest element T = ?P called top and
a least element ⊥ = ?P called bottom
每一个有限元素的lattice都是一个Complete Lattice
Product Lattice
Given lattices
L
1
L_1
L1? = (
P
1
P_1
P1?,
?
1
?_1
?1?),
L
2
L_2
L2? = (
P
2
P_2
P2?,
?
2
?_2
?2?), …,
L
n
L_n
Ln? = (
P
n
P_n
Pn?,
?
n
?_n
?n?), if for all i,(
P
i
P_i
Pi?,
?
i
?_i
?i?)has
?
i
?_i
?i? (least upper bound) and
?
i
?_i
?i? (greatest lower bound), then
we can have a product lattice
L
n
L_n
Ln? = (P, ?) that is defined by:
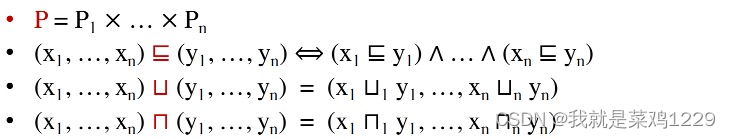
- product lattice 也是一个lattice
- 如果product lattice是一个complete的product,则这个product lattice也是complete的
5. 通过Lattice来进行数据流分析
一个数据流分析框架(D, L, F)包括:
D:数据流的方向,可以是前向(forwards)或后向(backwards)。
L:包括值域 V 和 meet ? 或 join ? 操作符的格(lattice)。
F:从 V 到 V 的转移函数(每个节点可能有自己的转移函数,也可能一样)。
回答以下问题
迭代算法(或称为IN/OUT方程系统)产生数据流分析的解决方案:
- 该算法是否保证终止或达到固定点,或者它总是有解吗?
- 如果是的话,解是否唯一,或者只有一个固定点?如果存在多个解,我们的解是否是最佳的(最精确的)?
- 该算法何时会达到固定点,或者我们何时可以得到解决方案?
6.单调性和不动点原理
单调性
A function f: L → L (L is a lattice) is monotonic if ?x, y ∈ L,x ? y ? f(x) ? f(y)
不动点原理
Given a complete lattice (L, ?), if
(1) f: L → L is monotonic and
(2) L is finite,
then
the least fixed point of f can be found by iteratingf(⊥), f(f(⊥)), …,
f
k
(
⊥
)
f^k(⊥)
fk(⊥) until a fixed point is reached
the greatest fixed point of f can be found by iteratingf(T), f(f(T)), …,
f
k
(
T
)
f^k(T)
fk(T) until a fixed point is reached
证明:
有限单调全格。
证明:能达到最大不动点
通过定义一个函数的最大下界⊥和转移函数f:L–>L,我们有⊥ ? f(⊥)。
由于单调,可以得出f(⊥) ? f(f(⊥)) =
f
2
f^2
f2(⊥)
重复f,得到⊥ ? f(⊥) ?
f
2
f^2
f2(⊥) ? … ?
f
i
f^i
fi(⊥)
因为L是有限的(假设高度为H),因此值在 ⊥、f(⊥)、
f
2
f^2
f2(⊥) 到
f
H
f^H
fH(⊥) 之间有界。
当 i > H 时,根据鸽笼原理,存在 k 和 j,使得
f
k
f^k
fk(⊥) =
f
j
f^j
fj(⊥)(假设 k < j ≤ H+1)。
进一步,由于
f
k
f^k
fk(⊥) ? … ?
f
j
f^j
fj(⊥)(f 的单调性),我们有
f
F
i
x
f^{Fix}
fFix =
f
k
f^k
fk(⊥) =
f
k
+
1
f^{k+1}
fk+1(⊥) = … =
f
j
f^{j}
fj(⊥)(反证法证明)。
鸽笼原理:鸽笼原理(Pigeonhole Principle)是一种基本的数学原理,它描述了分配物品到有限数量的容器时的一种必然性。简而言之,如果你要将 n 个物品放入不超过 m 个容器中,而 n 大于 m,那么至少有一个容器必然会包含两个或更多的物品。
由于L是有限元素,这里假设为H。如果在前H次没有到达不动点,则根据单调性此时 f H f^H fH应该为最大值,则下一次 f H + 1 f^{H+1} fH+1应该等于 f H f^H fH,否则将违背单调性。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!