关于lora的理解
非常推荐看参考中的文章,对lora的原理和代码,包括细节都讲得很清楚!
?参考:【OpenLLM 007】大模型炼丹术之小参数撬动大模型-万字长文全面解读PEFT参数高效微调技术 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)图解大模型微调系列之:大模型低秩适配器LoRA(原理篇) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
一、为什么选lora
目前主流的微调方法:全参数微调、Adapter Tuning、Prefix Tuning和LoRA。
全参数微调太贵,没钱玩不起。Adapter Tuning是往大模型中额外的模块,会导致训练和推理的延迟。Prefix Tuning是在输入添加前缀,导致减少有效数据长度。
二、lora的原理

对比可以看出,lora把全参数微调的用矩阵A和B代替了。
lora的公式如下:
r:秩,r越大代表当前的A和B矩阵参数越多,也就越接近全参数微调,但是带来的噪声也就越多。
A:shape为[r, d],用高斯初始化。
B:shape为[d, r],初始化为0。
/r:缩放比例,lora的作者发现数据在经过B但是还没有经过激活层时的数值的波动幅度与r有相关性,所以需要除以r来消除。
可以解释为大模型对新知识的侧重,越大就越重视。两个结合在一起就是
/r。
对A和B初始化是为了在训练刚开始不给模型带来额外的噪声(就是数据经过AB值为0)。参考文章的作者去问了lora的作者得到答复如下:

r的取值:lora作者通过实验得到r的取值设为4,8的效果跟64差不多,甚至要好一点

三、peft的lora代码
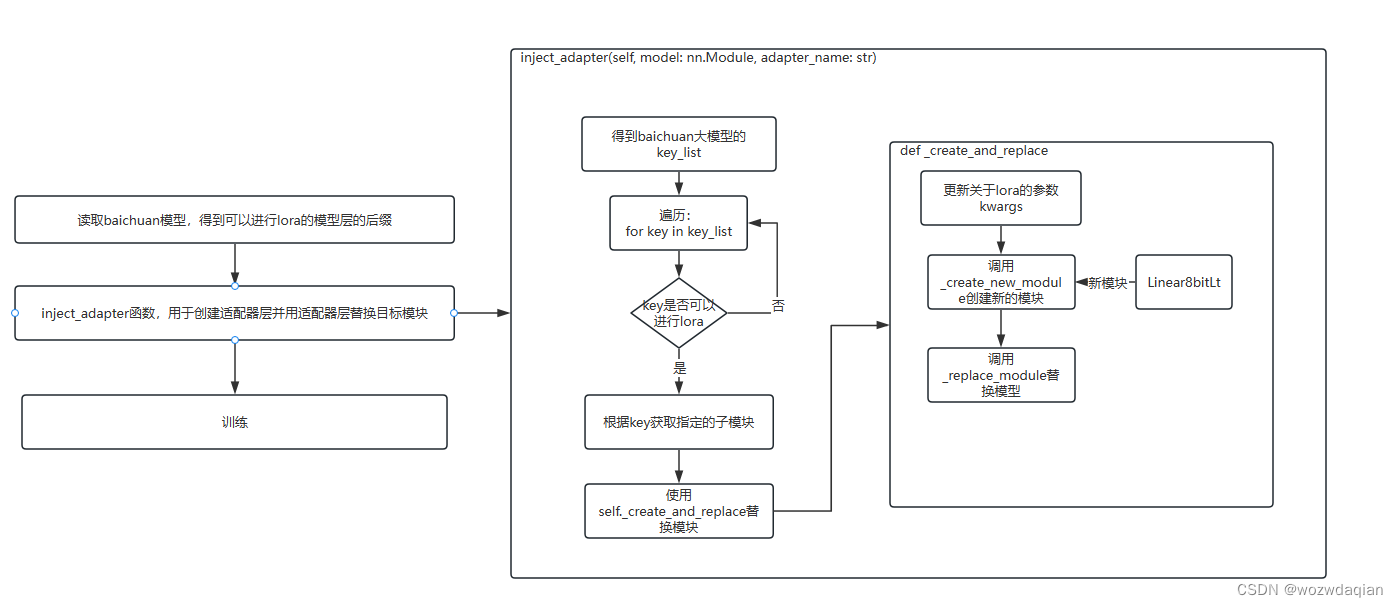
这是我根据自己理解画的图,可能不大详细,有什么问题欢迎提出来。
下面是与lora有关的函数的添加注释版本,源代码太长了,我把一些代码用pass代替:
inject_adapter函数,调用函数创建和替换lora模块,冻结参数
def inject_adapter(self, model: nn.Module, adapter_name: str):
r"""
创建适配器层并用适配器层替换目标模块。
This method is called under the hood by `peft.mapping.get_peft_model` if a non-prompt tuning adapter class is passed.
The corresponding PEFT config is directly retrieved from the `peft_config` attribute of the BaseTuner class.
Args:
model (`nn.Module`):
The model to be tuned.
adapter_name (`str`):
The adapter name.
"""
# 得到lora参数
peft_config = self.peft_config[adapter_name]
self._check_new_adapter_config(peft_config)
is_target_modules_in_base_model = False
# 得到baichuan大模型的key
key_list = [key for key, _ in model.named_modules()]
model_config = getattr(model, "config", {"model_type": "custom"})
if hasattr(model_config, "to_dict"):
model_config = model_config.to_dict()
peft_config = self._prepare_adapter_config(peft_config, model_config)
for key in key_list:
# 只有后缀是down_proj,up_proj,W_pack,gate_proj,o_proj才进行替换
if not self._check_target_module_exists(peft_config, key):
continue
is_target_modules_in_base_model = True
# 从模型中获取指定的子模块,返回子模块的父模块,子模块,子模块名
parent, target, target_name = _get_submodules(model, key)
optionnal_kwargs = {
"loaded_in_8bit": getattr(model, "is_loaded_in_8bit", False),
"loaded_in_4bit": getattr(model, "is_loaded_in_4bit", False),
"current_key": key,
}
# 替换
self._create_and_replace(peft_config, adapter_name, target, target_name, parent, **optionnal_kwargs)
self._mark_only_adapters_as_trainable()
if self.peft_config[adapter_name].inference_mode:
for n, p in self.model.named_parameters():
if adapter_name in n:
p.requires_grad = False_create_and_replace函数:创建和替换lora模块
def _create_and_replace(
self,
lora_config,
adapter_name,
target,
target_name,
parent,
**optionnal_kwargs,
):
bias = hasattr(target, "bias") and target.bias is not None
kwargs = {
# lora的秩,矩阵A和矩阵B相连接的宽度,r<<d
"r": lora_config.r,
# 归一化超参数,减少改变r rr时需要重新训练的计算量
"lora_alpha": lora_config.lora_alpha,
# lora层的dropout比率
"lora_dropout": lora_config.lora_dropout,
# 只有应用在Conv1D层时置为True,其他情况False
"fan_in_fan_out": lora_config.fan_in_fan_out,
# 布尔值,是否初始化权重
"init_lora_weights": lora_config.init_lora_weights,
}
kwargs["loaded_in_8bit"] = optionnal_kwargs.pop("loaded_in_8bit", False)
kwargs["loaded_in_4bit"] = optionnal_kwargs.pop("loaded_in_4bit", False)
kwargs["bias"] = bias
quantization_config = get_quantization_config(self.model, method="gptq")
if quantization_config is not None:
kwargs["gptq_quantization_config"] = quantization_config
if isinstance(target, LoraLayer) and isinstance(target, torch.nn.Conv2d):
pass
elif isinstance(target, LoraLayer) and isinstance(target, torch.nn.Embedding):
pass
elif isinstance(target, LoraLayer):
pass
else:
# 创建新的module
new_module = self._create_new_module(lora_config, adapter_name, target, **kwargs)
# 替换
self._replace_module(parent, target_name, new_module, target)_create_new_module:创建新模块,如果是8bit训练新模块为Linear8bitLt,4bit训练新模块为Linear4bitLt,否则为Linear。
def _create_new_module(lora_config, adapter_name, target, **kwargs):
# 值为None
gptq_quantization_config = kwargs.get("gptq_quantization_config", None)
# 根据量化配置文件获取正确的 AutoGPTQQuantLinear 类,因为配置文件是None,所以AutoGPTQQuantLinear也是None
AutoGPTQQuantLinear = get_auto_gptq_quant_linear(gptq_quantization_config)
loaded_in_8bit = kwargs.pop("loaded_in_8bit", False)
loaded_in_4bit = kwargs.pop("loaded_in_4bit", False)
bias = kwargs.pop("bias", False)
if loaded_in_8bit and isinstance(target, bnb.nn.Linear8bitLt):
eightbit_kwargs = kwargs.copy()
eightbit_kwargs.update(
{
"has_fp16_weights": target.state.has_fp16_weights,
"memory_efficient_backward": target.state.memory_efficient_backward,
"threshold": target.state.threshold,
"index": target.index,
}
)
new_module = Linear8bitLt(
adapter_name, target.in_features, target.out_features, bias=bias, **eightbit_kwargs
)
elif loaded_in_4bit and is_bnb_4bit_available() and isinstance(target, bnb.nn.Linear4bit):
pass
elif AutoGPTQQuantLinear is not None and isinstance(target, AutoGPTQQuantLinear):
pass
elif isinstance(target, torch.nn.Embedding):
pass
elif isinstance(target, torch.nn.Conv2d):
pass
else:
pass
return new_module替换模块
def _replace_module(parent, child_name, new_module, child):
"""
将父模块中的子模块替换为新模块,同时设置新模块的属性与子模块相同。
参数:
parent:父模块
child_name:子模块名称
new_module:新模块
child:子模块
"""
# 设置新模块为父模块的子模块
setattr(parent, child_name, new_module)
# 设置新模块的权重属性与子模块相同
new_module.weight = child.weight
# 如果子模块存在偏差属性,且偏差不为空,则设置新模块的偏差属性与子模块相同
if hasattr(child, "bias"):
if child.bias is not None:
new_module.bias = child.bias
# 如果子模块存在状态属性,设置新模块的状态属性与子模块相同,并将新模块移动到与子模块权重属性相同的设备上
if getattr(child, "state", None) is not None:
new_module.state = child.state
new_module.to(child.weight.device)
# 将新模块中的特定模块移动到与子模块权重属性相同的设备上
for name, module in new_module.named_modules():
if "lora_" in name:
module.to(child.weight.device)
if "ranknum" in name:
module.to(child.weight.device)Linea8bits class
class Linear8bitLt(bnb.nn.Linear8bitLt, LoraLayer):
# Linear8bitLt类继承自bnb.nn.Linear8bitLt类和LoraLayer类
def __init__(
self,
adapter_name, # 适配器名称
in_features, # 输入特征数量
out_features, # 输出特征数量
r: int = 0, # r值(Lora的参数)
lora_alpha: int = 1, # Lora的alpha值
lora_dropout: float = 0.0, # Lora的dropout值
**kwargs, # 其他关键字参数
):
bnb.nn.Linear8bitLt.__init__(
self,
in_features,
out_features,
bias=kwargs.get("bias", True),
has_fp16_weights=kwargs.get("has_fp16_weights", True),
memory_efficient_backward=kwargs.get("memory_efficient_backward", False),
threshold=kwargs.get("threshold", 0.0),
index=kwargs.get("index", None),
)
LoraLayer.__init__(self, in_features=in_features, out_features=out_features)
# 将权重参数设置为不可训练
self.weight.requires_grad = False
# 是否初始化Lora权重,默认为True
init_lora_weights = kwargs.pop("init_lora_weights", True)
# 创建Lora层
self.update_layer(adapter_name, r, lora_alpha, lora_dropout, init_lora_weights)
# 当前激活的适配器名称,默认为adapter_name
self.active_adapter = adapter_name
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):
# 调用父类的前向传播方法,得到输出结果
result = super().forward(x)
# 根据条件判断是否启用Lora
if self.disable_adapters or self.active_adapter not in self.lora_A.keys():
return result
elif self.r[self.active_adapter] > 0:
# 检查是否启用了自动混合精度
if not torch.is_autocast_enabled():
expected_dtype = result.dtype
if x.dtype != torch.float32:
x = x.float()
# Lora计算过程:先输入A模型,再输入B模型,最后乘以self.scaling
output = (
self.lora_B[self.active_adapter](
self.lora_A[self.active_adapter](self.lora_dropout[self.active_adapter](x))
).to(expected_dtype)
* self.scaling[self.active_adapter]
)
else:
output = (
self.lora_B[self.active_adapter](
self.lora_A[self.active_adapter](self.lora_dropout[self.active_adapter](x))
)
* self.scaling[self.active_adapter]
)
# 将Lora计算结果加到原有结果中
result += output
return result本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 算法基础之数字三角形
- 职称为什么要提前报名??? ??
- 16bit半精度浮点加乘法(用于结果验证)-图形测试小程序(python)
- simulink代码生成(十)——eQEP模块
- Golang 搭建 WebSocket 应用(八) - 完整代码
- 如何信任机器学习模型的预测结果?
- 在接口实现类中,加不加@Override的区别
- 宝塔+Let‘s Encrypt给网站安装免费SSL证书
- 计算机创新协会冬令营——暴力枚举题目06
- zabbix