数据结构入门到入土——ArrayList与顺序表
目录
一,线性表
线性表 ( linear list ) 是 n 个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列...线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。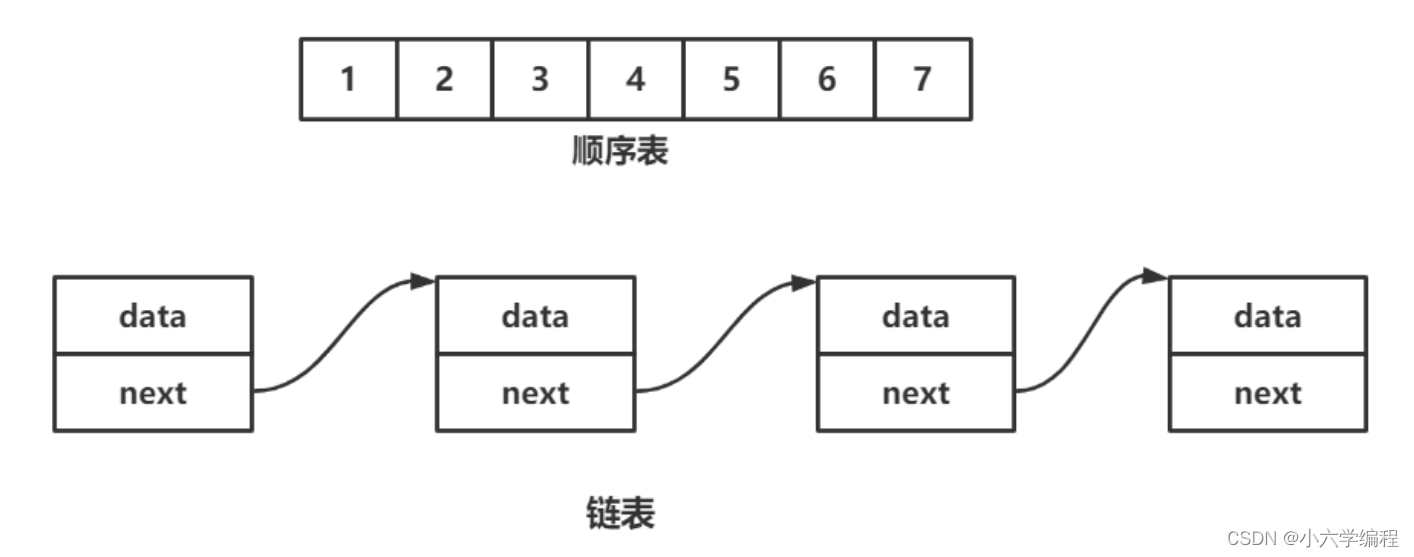
二,顺序表
1.接口实现
接口部分:
public interface IList {
// 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增
public void add(int data);
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data);
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind);
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int indexOf(int toFind);
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int get(int pos);
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
public void set(int pos, int value);
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove);
// 获取顺序表长度
public int size();
// 清空顺序表
public void clear();
// 打印顺序表,注意:该方法并不是顺序表中的方法,为了方便看测试结果给出的
public void display();
//判断顺序表是否已满
public boolean isFull();
//判断顺序表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty();
}
接口实现:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyArrayList implements IList{
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public static final int DEFINE_SIZE = 10;
public MyArrayList() {
this.elem = new int[DEFINE_SIZE];
}
public MyArrayList(int capacity) {
this.usedSize = capacity;
}
@Override
//新增元素,默认在数组最后新增
//1.检查数组是否已满
//2.满了扩容,未满新增
//usedSize++
public void add(int data) {
if (isFull()) {
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2 * elem.length);
}
this.elem[this.usedSize] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize ==elem.length;
}
@Override
//在 pos 位置新增元素
//1.检查数组是否已满
//2.满了扩容
//3.未满:在指定位置新增,原位置有元素就向后挪
//4.usedSize++
public void add(int pos, int data) {
if (isFull()) {
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2 * elem.length);
}
//新增
int i = this.usedSize;
while (i > pos) {
elem[i] = elem[i-1];
i--;
}
this.elem[pos] = data;
usedSize++;
}
@Override
// 判定是否包含某个元素
//1.顺序表是否为空
//2.查找元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
//查找元素
if (findVal(toFind) != 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int findVal(int val) {
for (int i = 0; i < elem.length; i++) {
if (elem[i] == val) {
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return usedSize == 0;
}
@Override
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
// 1.判断是否为空
// 2.为空抛空List异常
// 3.查找元素
// 4.获取下标
public int indexOf(int toFind) throws EmptyListException{
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyListException("空List异常");
}
//查找
if (findVal(toFind) == 0) {
//查询不到异常
throw new NotFindException("NotFindException");
}
return findVal(toFind);
}
@Override
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
// 1.判断是否为空
// 2.判断pos位置是否合法
// 3.获取
public int get(int pos) {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyListException("空List异常");
}
if (checkPos(pos)) {
//pos位置不合法
throw new PosException("pos位置不合法");
}
return this.elem[pos];
}
private boolean checkPos(int pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
// 1.判断是否为空
// 2.判断pos位置是否合法
// 3.设置
public void set(int pos, int value) {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyListException("空List异常");
}
if (checkPos(pos)) {
//pos位置不合法
throw new PosException("pos位置不合法");
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}
@Override
// 删除第一次出现的关键字key
// 是否为空?
// 查找关键字
public void remove(int toRemove) {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyListException("空List异常");
}
for (int i = indexOf(toRemove);i < this.usedSize - 1;i++) {
elem[i] = elem[i+1];
}
usedSize--;
}
@Override
// 获取顺序表长度
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}
@Override
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
this.usedSize = 0;
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.print("[");
if (this.usedSize == 0) {
System.out.println("]");
}
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if (i == this.usedSize - 1) {
System.out.println(this.elem[i] + "]");
} else {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] + ",");
}
}
}
}
三,ArrayList简介
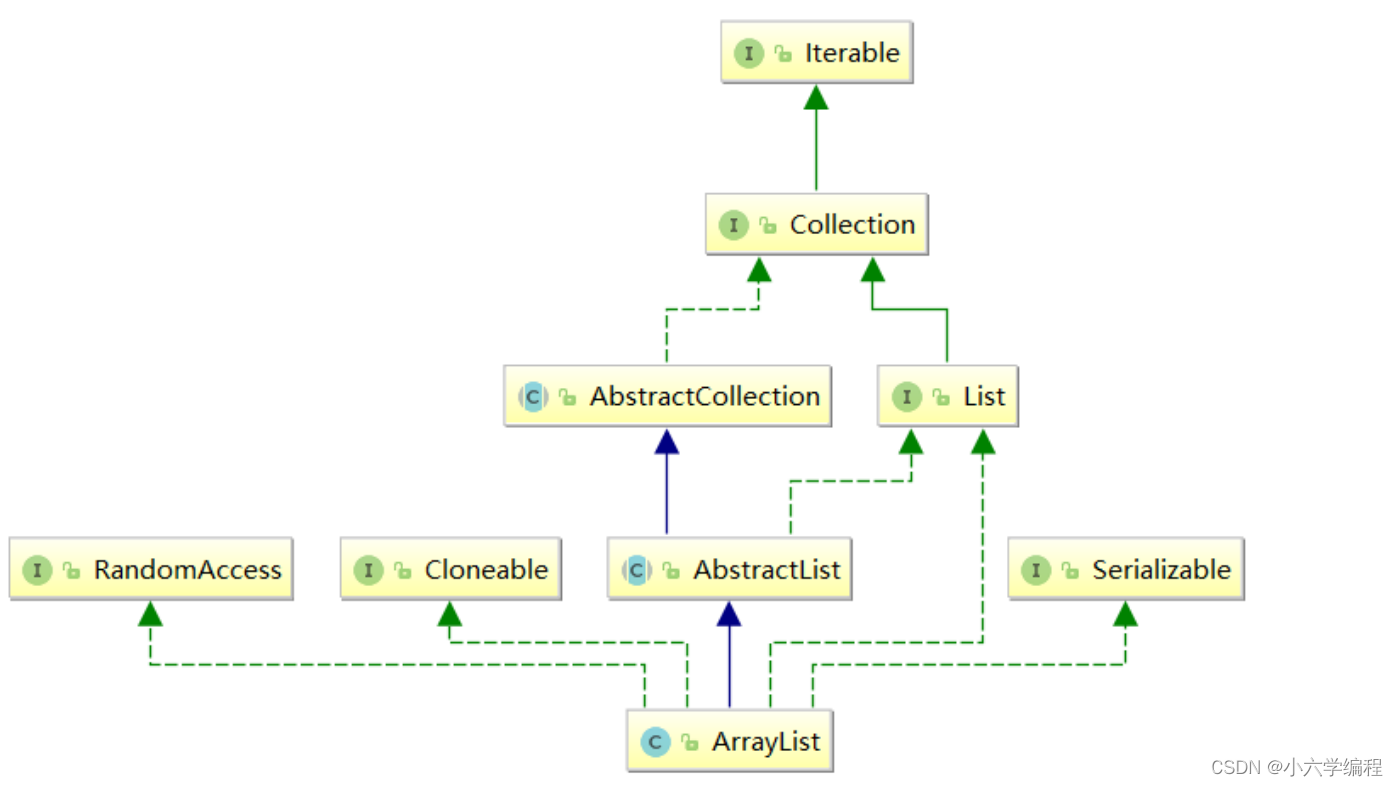
四,ArrayList使用
1.ArrayList的构造
| 方法 | 解释 |
|
ArrayList
()
| 无参构造 |
|
ArrayList
(Collection<? extends E> c)
| 利用其它Collection构造ArrayList |
|
ArrayList
(int initialCapacity)
| 指定顺序表初始容量 |
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ArrayList创建,推荐写法
// 构造一个空的列表
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
// 构造一个具有10个容量的列表
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(10);
list2.add(1);
list2.add(2);
list2.add(3);
// list2.add("hello"); // 编译失败,List<Integer>已经限定了,list2中只能存储整形元素
// list3构造好之后,与list中的元素一致
ArrayList<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>(list2);
// 避免省略类型,否则:任意类型的元素都可以存放,使用时将是一场灾难
List list4 = new ArrayList();
list4.add("111");
list4.add(100);
}
2.ArrayList常见操作
| 方法 | 解释 |
|
boolean
add
(E e)
| 尾插e |
|
void
add
(int index, E element)
| 将e插入到index位置 |
|
boolean
addAll
(Collection<? extends E> c)
| 尾插e中的元素 |
|
E
remove
(int index)
| 删除index位置元素 |
|
boolean
remove
(Object o)
| 删除遇到的第一个o |
|
E
get
(int index)
| 获取下标index位置元素 |
|
E
set
(int index, E element)
| 将下标index位置元素设置成element |
|
void
clear
()
| 清空 |
|
boolean
contains
(Object o)
| 判断o是否在线性表中 |
|
int
indexOf
(Object o)
| 返回第一个o所在下标 |
|
int
lastIndexOf
(Object o)
| 返回最后一个o的下标 |
|
List<E>
subList
(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
| 截取部分List |
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("JavaSE");
list.add("JavaWeb");
list.add("JavaEE");
list.add("JVM");
list.add("测试课程");
System.out.println(list);
// 获取list中有效元素个数
System.out.println(list.size());
// 获取和设置index位置上的元素,注意index必须介于[0, size)间
System.out.println(list.get(1));
list.set(1, "JavaWEB");
System.out.println(list.get(1));
// 在list的index位置插入指定元素,index及后续的元素统一往后搬移一个位置
list.add(1, "Java数据结构");
System.out.println(list);
// 删除指定元素,找到了就删除,该元素之后的元素统一往前搬移一个位置
list.remove("JVM");
System.out.println(list);
// 删除list中index位置上的元素,注意index不要超过list中有效元素个数,否则会抛出下标越界异常
list.remove(list.size()-1);
System.out.println(list);
// 检测list中是否包含指定元素,包含返回true,否则返回false
if(list.contains("测试课程")){
list.add("测试课程");
}
// 查找指定元素第一次出现的位置:indexOf从前往后找,lastIndexOf从后往前找
list.add("JavaSE");
System.out.println(list.indexOf("JavaSE"));
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("JavaSE"));
// 使用list中[0, 4)之间的元素构成一个新的SubList返回,但是和ArrayList共用一个elementData数组
List<String> ret = list.subList(0, 4);
System.out.println(ret);
list.clear();
System.out.println(list.size());
}
3.ArrayList的遍历
ArrayList的遍历有三种方式:for()+下标,for-each,使用迭代器
public static void main(String[] args) {
??? List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
??? list1.add(1);
??? list1.add(2);
??? list1.add(3);
??? list1.add(4);
??? list1.add(5);
??? //使用for()+下标遍历
??? for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) {
??????? System.out.print(list1.get(i) + " ");
??? }
??? System.out.println(" ");
??? //使用for-each遍历
??? for (Integer integer:list1) {
??????? System.out.print(integer + " ");
??? }
??? System.out.println(" ");
??? //使用迭代器遍历
??? Iterator<Integer> it = list1.iterator();
??? while (it.hasNext()) {
??????? System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
??? }
??? System.out.println(" ");
}
4.ArrayList的扩容机制
Object[] elementData; // 存放元素的空间
private static fifinal Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 默认空间
private static fifinal int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 默认容量大小
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private static fifinal int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// 获取旧空间大小
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 预计按照1.5倍方式扩容
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
// 如果用户需要扩容大小 超过 原空间1.5倍,按照用户所需大小扩容
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// 如果需要扩容大小超过MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,重新计算容量大小
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// 调用copyOf扩容
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 如果minCapacity小于0,抛出OutOfMemoryError异常
if (minCapacity < 0)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
【总结】
1. 检测是否真正需要扩容,如果是调用grow准备扩容
2. 预估需要库容的大小
????初步预估按照1.5倍大小扩容
????如果用户所需大小超过预估1.5倍大小,则按照用户所需大小扩容
????真正扩容之前检测是否能扩容成功,防止太大导致扩容失败
3. 使用copyOf进行扩容
五,ArrayLisit的具体使用
杨辉三角
class Solution {
//求杨辉三角方法
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();//二维数组
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
ret.add(list);
for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {
List<Integer> curRow = new ArrayList<>();//当前行
List<Integer> prevRow = ret.get(i-1);//上一行
curRow.add(1);//当前行首个元素为1
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
int val = prevRow.get(j-1) + prevRow.get(j);
curRow.add(val);
}
curRow.add(1);//当前行最后一个元素为1
ret.add(curRow);
}
return ret;
}
}
public class Test {
//方法使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
List<List<Integer>> mylist = new ArrayList<>();
mylist = solution.generate(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
List<Integer> arr = mylist.get(i);
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
}
完。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Android Studio读写低频RFID T5557卡源码
- nuxt3 路由相关
- 小红书开店要怎么运营?
- webgl排查问题小技巧之spector
- 【网络安全】一次SRC挖掘经历
- MySQL语句 | 在MySQL中解析JSON或将表中字段值合并为JSON
- 动手搓一个kubernetes管理平台(3)-后端框架
- vue打包后el-image图片不出来
- JavaScript 数学运算:解决精度丢失问题
- 一键在线获取APP公钥、包名、签名及备案信息方法介绍