人工智能原理实验1(1)——猴子摘香蕉问题
🧡🧡实验内容🧡🧡
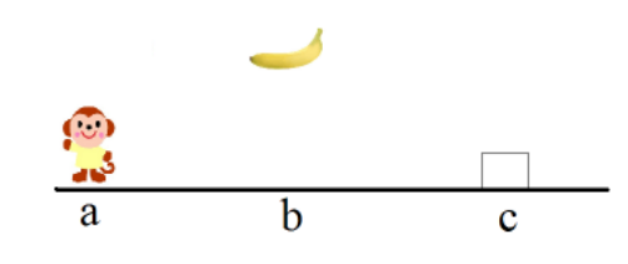
求解猴子摘香蕉问题:房内有一个猴子,一个箱子,天花板上挂了一串香蕉,其位置如图1所示,猴子为了拿到香蕉,它必须把箱子搬到香蕉下面,然后再爬到箱子上。请定义必要的谓词,列出问题的初始化状态(即下图所示状态),目标状态(猴子拿到了香蕉,站在箱子上,箱子位于位置b)。
🧡🧡代码实现🧡🧡
#include <stdio.h>
struct State
{
int monkey; /*-1:Monkey at A; 0: Monkey at B;1: Monkey at C;*/
int box; /*-1:box at A; 0:box at B;1: box at C;*/
int banana; /* 0:Banana at B */
int monbox; /*-1: monkey not on the box; 1: monkey on the box;*/
};
struct State States [150]; // 每一步状态 (monkey,box,banana,monbox)
char* routesave[150]; // 输出路径
bool isEnd; // 递归到最深处结果就退出,不再输出冗余中间过程
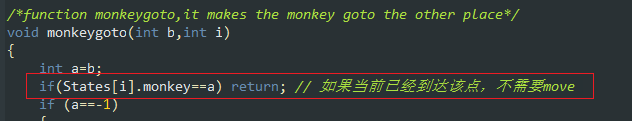
/*function monkeygoto,it makes the monkey goto the other place*/
void monkeygoto(int b,int i)
{
int a=b;
if(States[i].monkey==a) return; // 如果当前已经到达该点,不需要move
if (a==-1)
{
routesave[i] = "Monkey go to A";
States[i+1]=States[i];
States[i+1].monkey=-1;
}
else if(a==0)
{
routesave[i] = "Monkey go to B";
States[i+1]=States[i];
States[i+1].monkey=0;
}
else if(a==1)
{
routesave[i] = "Monkey go to C";
States[i+1]=States[i];
States[i+1].monkey=1;
}
else
{
printf("parameter is wrong");
}
}
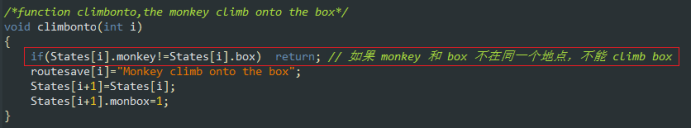
/*function climbonto,the monkey climb onto the box*/
void climbonto(int i)
{
if(States[i].monkey!=States[i].box) return; // 如果 monkey 和 box 不在同一个地点,不能 climb box
routesave[i]="Monkey climb onto the box";
States[i+1]=States[i];
States[i+1].monbox=1;
}
/*function climbdown,monkey climb down from the box*/
void climbdown(int i)
{
routesave[i]="Monkey climb down from the box";
States[i+1]=States[i];
States[i+1].monbox=-1;
}
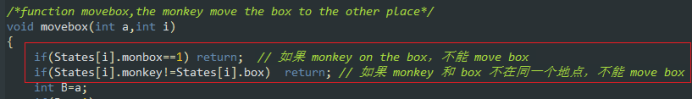
/*function movebox,the monkey move the box to the other place*/
void movebox(int a,int i)
{
if(States[i].monbox==1) return; // 如果 monkey on the box,不能 move box
if(States[i].monkey!=States[i].box) return; // 如果 monkey 和 box 不在同一个地点,不能 move box
int B=a;
if(B==-1)
{
routesave[i] = "monkey move box to A";
States[i+1]=States[i];
States[i+1].monkey=-1;
States[i+1].box=-1;
}
else if(B==0)
{
routesave[i] = "monkey move box to B";
States[i+1]=States[i];
States[i+1].monkey=0;
States[i+1].box=0;
}
else if(B==1)
{
routesave[i] = "monkey move box to C";
States[i+1]=States[i];
States[i+1].monkey=1;
States[i+1].box=1;
}
else
{
printf("parameter is wrong");
}
}
/*function reach,if the monkey,box,and banana are at the same place,the monkey reach banana*/
void reach(int i)
{
routesave[i]="Monkey reach the banana";
}
/*output the solution to the problem*/
void showSolution(int i)
{
int c;
printf ("%s \n", "Result to problem:");
for(c=0; c<i+1; c++)
{
printf ("Step %d : %s \n",c+1,routesave[c]);
}
printf("\n");
}
/*perform next step*/
void nextStep(int i)
{
int c;
int j;
// 终止条件
if(i>=150)
{
printf("%s \n", "steplength reached 150,have problem ");
return;
}
for (c=0; c<i; c++) /*if the current state is same to previous,retrospect 是否跟之前的状态重复*/
{
if(States[c].monkey==States[i].monkey&&States[c].box==States[i].box&&States[c].banana==States[i].banana&&States[c].monbox==States[i].monbox)
{
return;
}
}
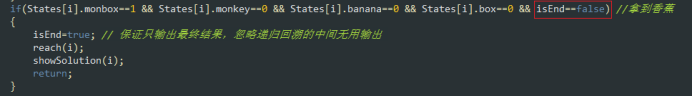
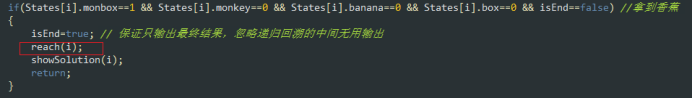
if(States[i].monbox==1 && States[i].monkey==0 && States[i].banana==0 && States[i].box==0 && isEnd==false) //拿到香蕉
{
isEnd=true; // 保证只输出最终结果,忽略递归回溯的中间无用输出
reach(i);
showSolution(i);
return;
}
// 递归
j=i+1;
if(States[i].monkey==0) // 猴子在b
{
if(States[i].box==0) // 箱子在b
{
if(States[i].monbox==-1) // 猴子不在箱子上
{
climbonto(i);
nextStep(j);
}
else // 猴子在箱子上
{
nextStep(j);
}
}
else if(States[i].box==1) // 箱子在c
{
monkeygoto(1,i);
nextStep(j);
movebox(0,i);
nextStep(j);
climbonto(i);
nextStep(j);
}
else /*box==-1*/ // 箱子在a
{
monkeygoto(-1,i);
nextStep(j);
movebox(0,i);
nextStep(j);
climbonto(i);
nextStep(j);
}
}
/*end if*/
if(States[i].monkey==-1) // 猴子在a
{
if(States[i].box==-1)
{
if(States[i].monbox==-1)
{
movebox(0,i);
nextStep(j);
climbonto(i);
nextStep(j);
}
else
{
climbdown(i);
nextStep(j);
movebox(0,i);
nextStep(j);
climbonto(i);
nextStep(j);
}
}
else if(States[i].box==0)
{
monkeygoto(0,i);
nextStep(j);
climbonto(i);
nextStep(j);
}
else
{
monkeygoto(1,i);
nextStep(j);
movebox(0,i);
nextStep(j);
climbonto(i);
nextStep(j);
}
}
/*end if*/
if(States[i].monkey==1) // 猴子在c
{
if (States[i].box==1)
{
if(States[i].monbox==-1)
{
movebox(0,i);
nextStep(j);
climbonto(i);
nextStep(j);
}
else
{
climbdown(i);
nextStep(j);
movebox(0,i);
nextStep(j);
climbonto(i);
nextStep(j);
}
}
else if(States[i].box==-1)
{
monkeygoto(-1,i);
nextStep(j);
movebox(0,i);
nextStep(j);
movebox(0,i);
nextStep(j);
climbonto(i);
nextStep(j);
}
else
{
monkeygoto(0,i);
nextStep(j);
movebox(0,i);
nextStep(j);
climbonto(i);
reach(i+1);
nextStep(j);
}
}
/*end if*/
}
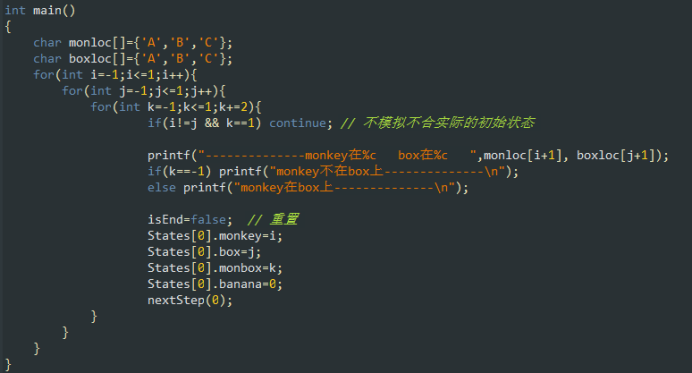
int main()
{
char monloc[]={'A','B','C'};
char boxloc[]={'A','B','C'};
for(int i=-1;i<=1;i++){
for(int j=-1;j<=1;j++){
for(int k=-1;k<=1;k+=2){
if(i!=j && k==1) continue; // 不模拟不合实际的初始状态
printf("--------------monkey在%c box在%c ",monloc[i+1], boxloc[j+1]);
if(k==-1) printf("monkey不在box上--------------\n");
else printf("monkey在box上--------------\n");
isEnd=false; // 重置
States[0].monkey=i;
States[0].box=j;
States[0].monbox=k;
States[0].banana=0;
nextStep(0);
}
}
}
}
🧡🧡实验结果解释🧡🧡
目标状态:monkey拿到了banana,站在box上,且均位于B处。
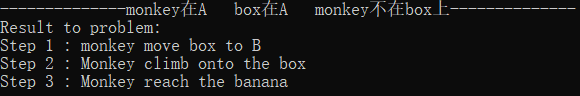
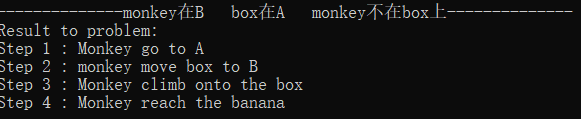
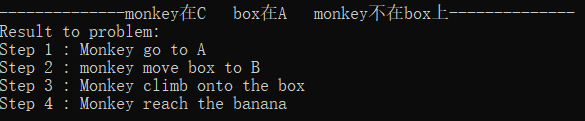
初始状态1:monkey在A box在A monkey不在box上
解释:Monkey先移动box到B处,再爬上box,即可reach banana
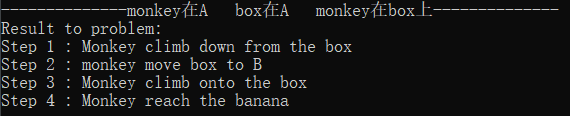
初始状态2:monkey在A box在A monkey在box上
解释:Monkey先从box爬下,然后移动box到B处,再爬上box,即可reach banana
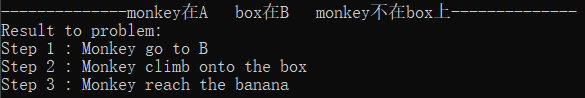
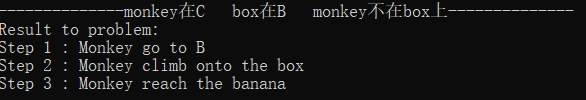
初始状态3:monkey在A box在B monkey不在box上
解释:Monkey移动到B处,再爬上box,即可reach banana
初始状态4:monkey在A box在C monkey不在box上
解释:Monkey先移动到C处,然后移动box到B处,再爬上box,即可reach banana
初始状态5:monkey在B box在A monkey不在box上
解释:Monkey先移动到A处,然后移动box到B处,再爬上box,即可reach banana
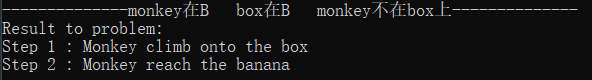
初始状态6:monkey在B box在B monkey不在box上
解释:Mokey爬上box,即可reach banana
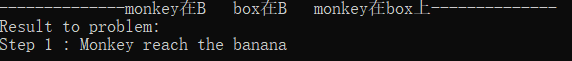
初始状态7:monkey在B box在B monkey在box上
解释:符合目标状态,直接reach banana
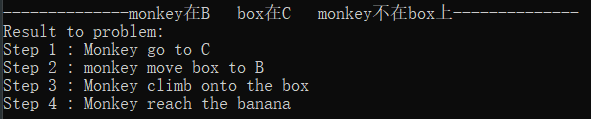
初始状态8:monkey在B box在C monkey不在box上
解释:Monkey先移动到C处,然后将box移动到B处,再爬上box,即可reach banana
初始状态9:monkey在C box在A monkey不在box上
解释:Monkey先移动到A处,然后将box移动到B处,再爬上box,即可reach banana
初始状态10:monkey在C box在B monkey不在box上
解释:Monkey先移动到B处,再爬上box,即可reach banana
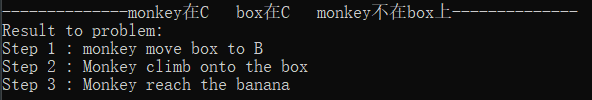
初始状态11:monkey在C box在C monkey不在box上
解释:Monkey先移动box到B处,再爬上box,即可reach banana
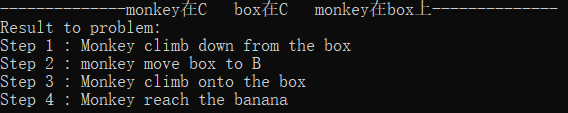
初始状态12:monkey在C box在C monkey在box上
解释:Monkey先从box爬下,然后移动box到B处,再爬上box,即可reach banana
🧡总结🧡
完善猴子摘香蕉问题参考代码,代码中有什么问题?应该如何修改会更好。
- 代码中nextStep函数为递归函数,因此在遍历到最终结果后,再回溯时会输出多余无用的中间结果。
解决:设置一个变量isEnd,值为true表示已经递归到最深处,此后不再输出;值为false表示还维递归到最深处。将该变量加入到递归终止条件判断中即可
- 输出中会出现不合实际的动作,可以在相应的动作函数中增加动作执行的先决条件:
movebox:猴子和箱子必须在同一地点才能移动箱子,在箱子上面则不能移动箱子
climbonto:,猴子和箱子必须在同一地点才能爬上箱子
movegoto:,已经达到目的地点,则不需要继续移动
- 若初始状态就已经达到了目标状态(上述初始状态7),这时判断终止条件时会直接执行
因此直接跳出程序,无输出。
解决:将reach()动作函数放在终止条件内,更为合理,同时删除递归程序段中的reach(i+1)
- 调试初始状态比较麻烦
解决:添加for循环(monkey的位置、box的位置、monkey是否在box上),遍历输出所有初始状态,另外要注意不能模拟不合实际的初始状态(例如monkey和box不在同一位置,但是monkey在box上,明显不合实际,不模拟)
- 整个程序核心思想是固定banana的位置(只在B处),再通过判断monkey和box的相对于banana的位置来采取进一步动作,那么其实可以通过改变banana的位置,使程序更加一般化。
暂时想不到好的解决方案。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- STM32 Hal库FreeRtos查看所有任务的内存栈信息使用情况剩余空间 仅需一个函数搞定 超简单
- C++——多态
- 职场增值,从中国人民大学与加拿大女王大学金融硕士项目开始
- Oracle-游标
- 一分钟带你了解支持向量机(SVM)
- 求100之内的素数。
- RDMA原理浅析
- Docker容器中配置和启用Java Flight Recorder(JFR)
- 一月 Intel、NVIDIA 轮放大招,AMD 彻底绷不住了
- c++学习笔记-STL案例-机房预约系统2-创建身份类