深入理解stressapptest
文章目录
??团队博客: 汽车电子社区
一、概述
??stressapptest是一款免费的开源软件,支持用于测试Linux系统的稳定性和可靠性。它可以利用多个CPU/Core,甚至可以访问主内存的所有部分来测试系统的稳定性,以此推断系统是否存在内存泄漏或其他性能方面的问题。
??stressapptest的主要目标是发现难以重现的系统稳定性问题和其他体现在Java虚拟机、KVM Hypervisor和Hadoop集群等普通用例中的Linux系统中的性能问题。它还包括多个测试模式和选项以支持不同测试场景,比如随机测试、循环测试、全内存测试、持续测试等。
二、安装
2.1、源码编译安装
// 1.下载源码
git clone https://github.com/stressapptest/stressapptest.git
cd stressapptest
./configure
make
sudo make install
2.2、命令行安装
??Ubuntu下执行如下命令进行安装:
sudo apt-get install stressapptest
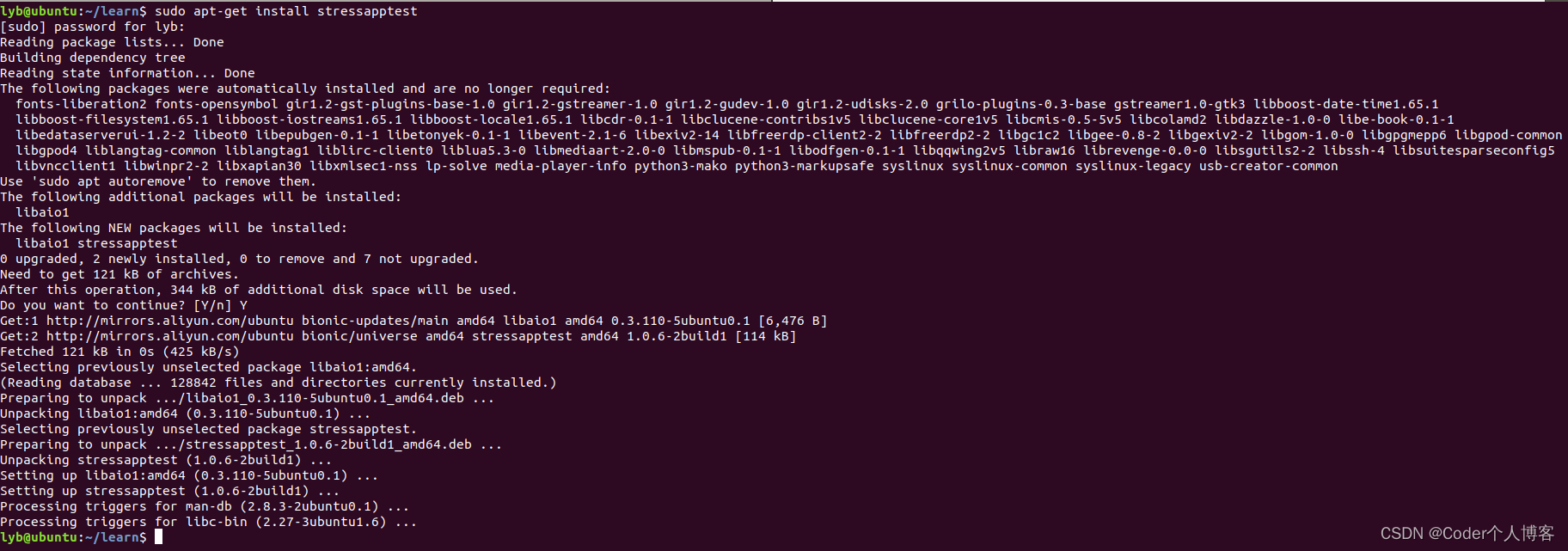
2.3、安装确认
??执行如下命令来确认stressapptest 是否安装成功:
stressapptest -h
lyb@ubuntu:~/learn$ stressapptest -h
Stats: SAT revision 1.0.6_autoconf, 64 bit binary
Log: buildd @ lgw01-amd64-022 on Thu Apr 5 10:28:35 UTC 2018 from open source release
Usage: ./sat(32|64) [options]
-M mbytes megabytes of ram to test
-H mbytes minimum megabytes of hugepages to require
-s seconds number of seconds to run
-m threads number of memory copy threads to run
-i threads number of memory invert threads to run
-C threads number of memory CPU stress threads to run
--findfiles find locations to do disk IO automatically
-d device add a direct write disk thread with block device (or file) 'device'
-f filename add a disk thread with tempfile 'filename'
-l logfile log output to file 'logfile'
--max_errors n exit early after finding 'n' errors
-v level verbosity (0-20), default is 8
-W Use more CPU-stressful memory copy
-A run in degraded mode on incompatible systems
-p pagesize size in bytes of memory chunks
--filesize size size of disk IO tempfiles
-n ipaddr add a network thread connecting to system at 'ipaddr'
--listen run a thread to listen for and respond to network threads.
--no_errors run without checking for ECC or other errors
--force_errors inject false errors to test error handling
--force_errors_like_crazy inject a lot of false errors to test error handling
-F don't result check each transaction
--stop_on_errors Stop after finding the first error.
--read-block-size size of block for reading (-d)
--write-block-size size of block for writing (-d). If not defined, the size of block for writing will be defined as the size of block for reading
--segment-size size of segments to split disk into (-d)
--cache-size size of disk cache (-d)
--blocks-per-segment number of blocks to read/write per segment per iteration (-d)
--read-threshold maximum time (in us) a block read should take (-d)
--write-threshold maximum time (in us) a block write should take (-d)
--random-threads number of random threads for each disk write thread (-d)
--destructive write/wipe disk partition (-d)
--monitor_mode only do ECC error polling, no stress load.
--cc_test do the cache coherency testing
--cc_inc_count number of times to increment the cacheline's member
--cc_line_count number of cache line sized datastructures to allocate for the cache coherency threads to operate
--paddr_base allocate memory starting from this address
--pause_delay delay (in seconds) between power spikes
--pause_duration duration (in seconds) of each pause
--local_numa choose memory regions associated with each CPU to be tested by that CPU
--remote_numa choose memory regions not associated with each CPU to be tested by that CPU
--interleave_size bytes size in bytes of each channel's data as interleaved between memory channels
--channel_width bits width in bits of each memory channel
--memory_channel u1,u2 defines a comma-separated list of names
for dram packages in a memory channel.
Use multiple times to define multiple channels.
lyb@ubuntu:~/learn$
三、重要参数详解
3.1、查询支持的参数
??执行如下命令来确认stressapptest支持的参数:
stressapptest -h
lyb@ubuntu:~/learn$ stressapptest -h
Stats: SAT revision 1.0.6_autoconf, 64 bit binary
Log: buildd @ lgw01-amd64-022 on Thu Apr 5 10:28:35 UTC 2018 from open source release
Usage: ./sat(32|64) [options]
-M mbytes megabytes of ram to test
-H mbytes minimum megabytes of hugepages to require
-s seconds number of seconds to run
-m threads number of memory copy threads to run
-i threads number of memory invert threads to run
-C threads number of memory CPU stress threads to run
--findfiles find locations to do disk IO automatically
-d device add a direct write disk thread with block device (or file) 'device'
-f filename add a disk thread with tempfile 'filename'
-l logfile log output to file 'logfile'
--max_errors n exit early after finding 'n' errors
-v level verbosity (0-20), default is 8
-W Use more CPU-stressful memory copy
-A run in degraded mode on incompatible systems
-p pagesize size in bytes of memory chunks
--filesize size size of disk IO tempfiles
-n ipaddr add a network thread connecting to system at 'ipaddr'
--listen run a thread to listen for and respond to network threads.
--no_errors run without checking for ECC or other errors
--force_errors inject false errors to test error handling
--force_errors_like_crazy inject a lot of false errors to test error handling
-F don't result check each transaction
--stop_on_errors Stop after finding the first error.
--read-block-size size of block for reading (-d)
--write-block-size size of block for writing (-d). If not defined, the size of block for writing will be defined as the size of block for reading
--segment-size size of segments to split disk into (-d)
--cache-size size of disk cache (-d)
--blocks-per-segment number of blocks to read/write per segment per iteration (-d)
--read-threshold maximum time (in us) a block read should take (-d)
--write-threshold maximum time (in us) a block write should take (-d)
--random-threads number of random threads for each disk write thread (-d)
--destructive write/wipe disk partition (-d)
--monitor_mode only do ECC error polling, no stress load.
--cc_test do the cache coherency testing
--cc_inc_count number of times to increment the cacheline's member
--cc_line_count number of cache line sized datastructures to allocate for the cache coherency threads to operate
--paddr_base allocate memory starting from this address
--pause_delay delay (in seconds) between power spikes
--pause_duration duration (in seconds) of each pause
--local_numa choose memory regions associated with each CPU to be tested by that CPU
--remote_numa choose memory regions not associated with each CPU to be tested by that CPU
--interleave_size bytes size in bytes of each channel's data as interleaved between memory channels
--channel_width bits width in bits of each memory channel
--memory_channel u1,u2 defines a comma-separated list of names
for dram packages in a memory channel.
Use multiple times to define multiple channels.
lyb@ubuntu:~/learn$
3.2、参数说明
??选项说明:
????-s或–timeout: 指定测试运行的总时间,以秒为单位。默认值为0(无限制)。
????-M或–vm-bytes: 指定应用程序所需的内存量,以字节、千字节、兆字节或吉字节为单位。例如,“-M 2048m”表示分配2GB的内存。默认值为0(自动计算)。
????-m或–vm-pattern: 指定要使用的内存模式,如线性、随机、步进等。默认值为“linear”(线性)。
????-c或–cpu-cores: 指定要使用的CPU核心数。例如,“-c 4”将在四个核心上运行测试。默认值为0(使用所有可用核心)。
????–affinity: 将应用程序绑定到指定的CPU核心上,以避免跨核心调度带来的额外开销。例如,“–affinity 0,2,4”将绑定应用程序到第1、3和5个CPU核心上。
????–matrix: 启用矩阵测试模式,该模式可以对整个系统进行更全面的测试,并且需要更长时间才能完成。
????–quiet: 禁止输出详细信息和统计数据,只显示结果摘要信息。
????–log-level: 设置日志级别,以控制输出详细程度。可选值为”debug”、”info”、”warning”、”error”和”critical”。
????–log-file: 将日志输出到指定的文件中,而不是标准输出。
????–version: 显示stressapptest版本信息并退出。
四、实例
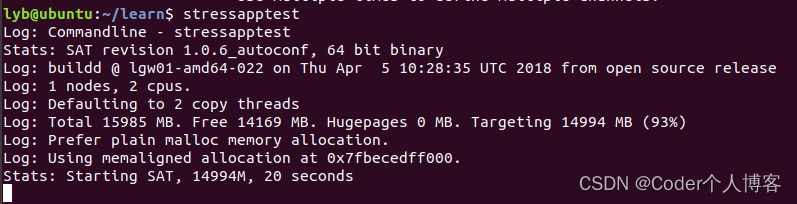
4.1、随机测试(默认模式)
??随机模式是stressapptest的默认模式,它会随机访问系统内存中的所有部分来测试系统的稳定性。可以通过以下命令启动:
stressapptest
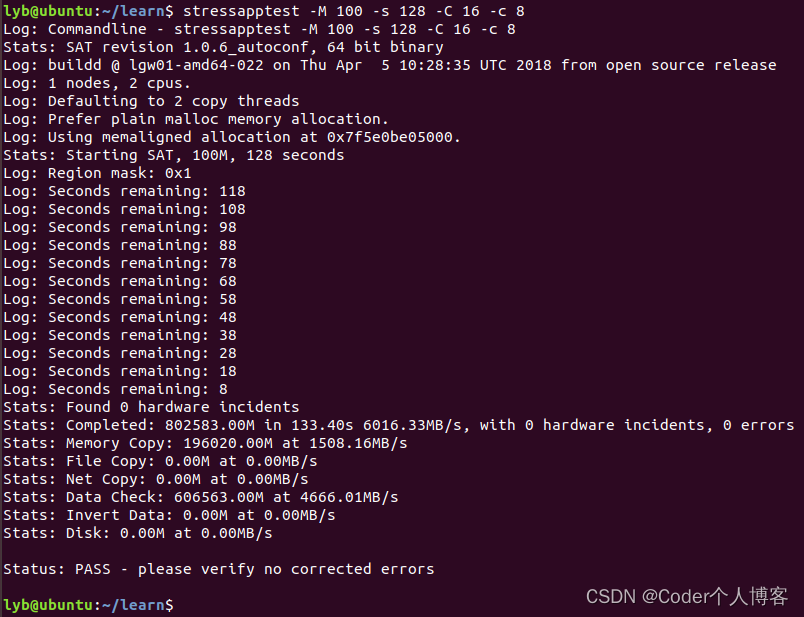
4.2、循环测试
??循环模式是stressapptest的另一种模式,它会在指定的时间内不断迭代相同的内存模式。可以使用以下命令启动:
stressapptest -M 100 -s 128 -C 16 -c 8
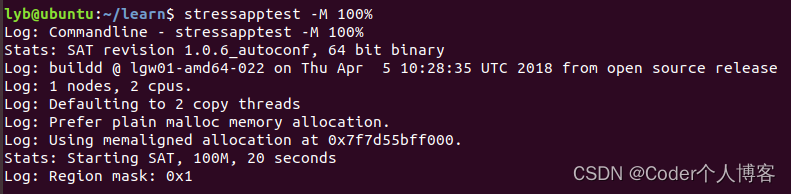
4.2、全内存测试
??全内存模式会尝试占用所有可用的空闲内存。可以使用以下命令启动:
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- net8 golang python性能比较
- 【音视频 | H.264】H.264视频编码及NALU详解
- Linux系统服务器日常巡检脚本
- Postman基本使用、测试环境(Environment)配置
- Wireshark插件开发
- 前端性能优化-重绘与回流
- 1.C++程序的内存模型
- 全球数据隐私相关专业薪酬趋势
- java与大数据:Hadoop与MapReduce
- 【shell脚本实战案例】awk将科学计数法数字转为实数数字