NVIDIA NCCL 源码学习(十二)- double binary tree
上节我们以ring allreduce为例看到了集合通信的过程,但是随着训练任务中使用的gpu个数的扩展,ring allreduce的延迟会线性增长,为了解决这个问题,NCCL引入了tree算法,即double binary tree。
double binary tree
朴素的tree算法将所有机器节点构造成一棵二叉树,支持broadcast,reduce,前缀和。假设root节点要broadcast一个消息M给所有节点,root会将M发送给他的子节点,其他所有的节点收到消息M后再发送给子节点,叶节点因为没有子节点,所以叶结点只会接收M。这个过程可以将M切分为k个block,从而可以流水线起来。
但这个朴素算法有一个问题,叶节点只接收数据,不发送,因此只利用了带宽的一半,为了解决这个问题,MPI提出了double binary tree算法,假设一共有N个节点,MPI会构建两个大小为N的树T1和T2,T1的中间节点在T2中是叶节点,T1和T2同时运行,各自负责消息M的一半,这样每个节点的双向带宽可以都被利用到。以十台机器为例,构建出的结构如下:
?
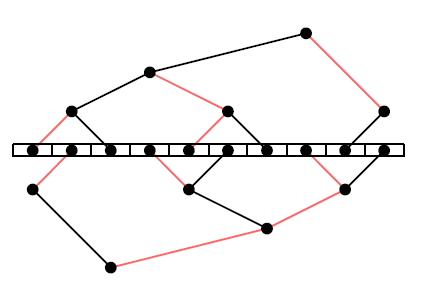
T1的构建方式下边会介绍,T2的构造有两种方式,一种是shift,将rank向左shift一位,比如rank10变成rank9,然后通过和T1一样的方式构造,这种构造方式下T1和T2的树结构完全一致;另外一种是mirror,将rank号镜像一下,比如rank0镜像为rank9,这种构造方式下T1和T2树结构是镜像对称的,不过mirror的方式只能用于机器数为偶数的场景,否则会存在节点在两棵树中都是叶节点。
如图一,T1和T2的边可以被染成红色或者黑色,从而有如下很好的性质:
- 不会有节点在T1和T2中连到父节点的边的颜色相同,比如node A在T1中通过红色的边连到父节点,那T2中A一定通过黑色的边连到父节点。
- 不会有节点连到子节点的边颜色相同,比如node A在T1中是中间节点,如果A通过红色的边连到左子节点,那么A一定通过黑色的边连到右子节点
根据上述性质,就有了两棵树的工作流程,在每一步中从父节点中收数据,并将上一步中收到的数据发送给他的一个子节点,比如在偶数步骤中使用红色边,奇数步骤中使用黑色边,这样的话在一个步骤中可以同时收发,从而利用了双向带宽。
nccl tree
nccl中的tree只用于节点之间,节点内是一条链,2.7.8版本使用的pattern为NCCL_TOPO_PATTERN_SPLIT_TREE,假设为4机32卡,对于T2后边再介绍,T1如下所示:
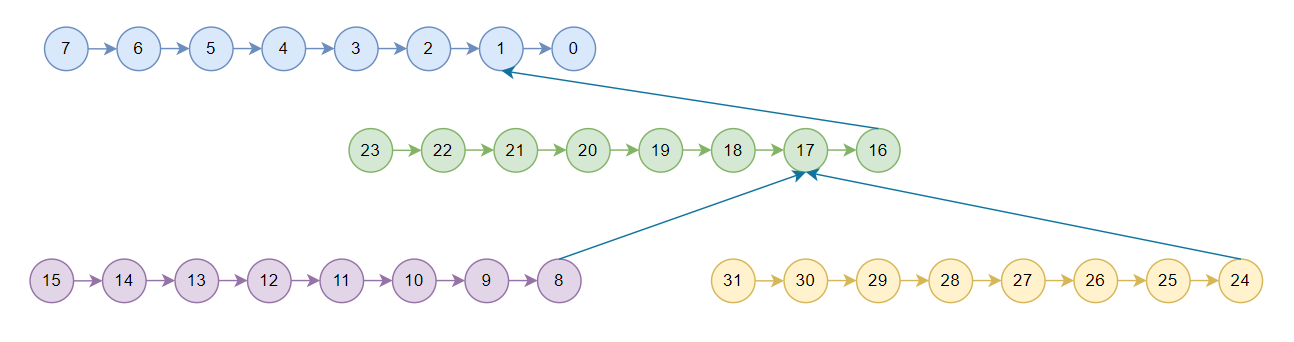
由于allreduce可以拆分为reduce和broadcast两个过程,所以nccl tree allreduce先执行reduce,数据按照图中箭头方向流动,称为上行阶段,从rank15,rank31,rank23,rank7开始一直reduce到rank 0,rank0拿到全局reduce的结果之后再按照箭头反方向开始流动,称为下行阶段,broadcast到所有卡。
tree搜索
如上所述,节点内为链,因此机内tree搜索的过程和ring搜索很像,指定pattern为NCCL_TOPO_PATTERN_SPLIT_TREE,然后执行ncclTopoCompute。
struct ncclTopoGraph treeGraph;
treeGraph.id = 1;
treeGraph.pattern = NCCL_TOPO_PATTERN_SPLIT_TREE;
treeGraph.crossNic = ncclParamCrossNic();
treeGraph.collNet = 0;
treeGraph.minChannels = 1;
treeGraph.maxChannels = ringGraph.nChannels;
NCCLCHECK(ncclTopoCompute(comm->topo, &treeGraph));
NCCLCHECK(ncclTopoPrintGraph(comm->topo, &treeGraph));
ncclTopoCompute中会设置搜索参数,对于NCCL_TOPO_PATTERN_SPLIT_TREE会设置backToFirstRank = -1,backToNet = 1
ncclResult_t ncclTopoSearchParams(struct ncclTopoSystem* system, int pattern, int* backToNet, int* backToFirstRank) {
if (system->nodes[NET].count) {
if (pattern == NCCL_TOPO_PATTERN_RING) *backToNet = system->nodes[GPU].count-1;
else if (pattern == NCCL_TOPO_PATTERN_TREE) *backToNet = 0;
else *backToNet = 1;
if (pattern == NCCL_TOPO_PATTERN_SPLIT_TREE_LOOP) *backToFirstRank = system->nodes[GPU].count-1;
else *backToFirstRank = -1;
} else {
*backToNet = -1;
if (pattern == NCCL_TOPO_PATTERN_RING || pattern == NCCL_TOPO_PATTERN_SPLIT_TREE_LOOP) *backToFirstRank = system->nodes[GPU].count-1;
else *backToFirstRank = -1;
}
return ncclSuccess;
}
因此会搜索出如下的tree,为方便介绍,假设只搜出了这一个tree
NET/0 GPU/0 GPU/1 GPU/2 GPU/3 GPU/4 GPU/5 GPU/6 GPU/7 NET/0
连接tree
ncclResult_t ncclTopoPreset(struct ncclComm* comm,
struct ncclTopoGraph* treeGraph, struct ncclTopoGraph* ringGraph, struct ncclTopoGraph* collNetGraph,
struct ncclTopoRanks* topoRanks) {
int rank = comm->rank;
int localRanks = comm->localRanks;
int nChannels = comm->nChannels;
for (int c=0; c<nChannels; c++) {
struct ncclChannel* channel = comm->channels+c;
channel->treeUp.up = -1;
for (int i=0; i<NCCL_MAX_TREE_ARITY; i++) channel->treeUp.down[i] = -1;
channel->treeDn.up = -1;
for (int i=0; i<NCCL_MAX_TREE_ARITY; i++) channel->treeDn.down[i] = -1;
}
...
}
然后执行ncclTopoPreset,上文提到,tree allreduce过程分为上行和下行阶段,因此这里可以看到每个channel有两个tree,一个是treeUp,另一个为treeDn,表示上行和下行,treeUp和treeDn其实对应一个树,比如都对应T1。但是treeUp和treeDn完全一样,新版的nccl只保留了一个数据结构,因此后边介绍中,我们只需要关注treeUp即可。
treeDn.up表示父节点,这里初始化为-1,treeDn.down[i]表示子节点,这里初始化为-1,NCCL_MAX_TREE_ARITY表示最多有几个子节点,因为为二叉树,再加上机内的一个子节点,因此最多有三个子节点,NCCL_MAX_TREE_ARITY即等于3。
ncclResult_t ncclTopoPreset(struct ncclComm* comm,
struct ncclTopoGraph* treeGraph, struct ncclTopoGraph* ringGraph, struct ncclTopoGraph* collNetGraph,
struct ncclTopoRanks* topoRanks) {
int rank = comm->rank;
int localRanks = comm->localRanks;
int nChannels = comm->nChannels;
for (int c=0; c<nChannels; c++) {
...
int* ringIntra = ringGraph->intra+c*localRanks;
int* treeIntra = treeGraph->intra+c*localRanks;
int* collNetIntra = collNetGraph->intra+c*localRanks;
for (int i=0; i<localRanks; i++) {
...
if (treeIntra[i] == rank) {
int recvIndex = 0, sendIndex = treeGraph->pattern == NCCL_TOPO_PATTERN_TREE ? 0 : 1;
int prev = (i-1+localRanks)%localRanks, next = (i+1)%localRanks;
// Tree loop always flows in the same direction. Other trees are symmetric, i.e.
// up/down go in reverse directions
int sym = treeGraph->pattern == NCCL_TOPO_PATTERN_SPLIT_TREE_LOOP ? 0 : 1;
// Down tree is common
topoRanks->treeDnRecv[c] = treeIntra[recvIndex];
topoRanks->treeDnSend[c] = treeIntra[sendIndex];
channel->treeDn.up = treeIntra[prev];
channel->treeDn.down[0] = treeIntra[next];
// Up tree depends on the pattern
topoRanks->treeUpRecv[c] = sym ? topoRanks->treeDnSend[c] : topoRanks->treeDnRecv[c];
topoRanks->treeUpSend[c] = sym ? topoRanks->treeDnRecv[c] : topoRanks->treeDnSend[c];
channel->treeUp.down[0] = sym ? channel->treeDn.down[0] : channel->treeDn.up ;
channel->treeUp.up = sym ? channel->treeDn.up : channel->treeDn.down[0];
}
...
}
...
}
// Duplicate channels rings/trees
struct ncclChannel* channel0 = comm->channels;
struct ncclChannel* channel1 = channel0+nChannels;
memcpy(channel1, channel0, nChannels*sizeof(struct ncclChannel));
return ncclSuccess;
}
然后根据机内搜索出的链初始化treeUp,up设置为prev,down[0]设置为next,treeUpRecv为1,表示当前机器会使用localrank为1的rank执行recv,treeUpSend为0,表示当前节点会使用localrank为0的rank执行send,此时结构如下所示,箭头指向的是up,黄色为treeUpSend,绿色为treeUpRecv
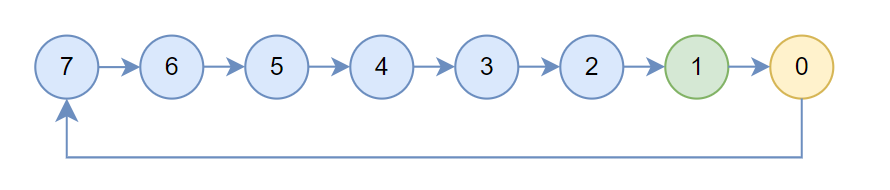
Preset之后执行全局allgather拿到所有节点的信息,然后执行Postset以完成全局tree的连接。
首先将每个rank的treeUpRecv和treeUpSend打平到同一个数组中。
ncclResult_t ncclTopoPostset(struct ncclComm* comm, int* firstRanks, struct ncclTopoRanks** allTopoRanks, int* rings) {
// Gather data from all ranks
int *ringRecv, *ringSend, *ringPrev, *ringNext, *treeUpRecv, *treeUpSend, *treeDnRecv,*treeDnSend;
int nranks = comm->nRanks;
int nChannels = comm->nChannels;
...
NCCLCHECK(ncclCalloc(&treeUpRecv, nranks*MAXCHANNELS));
NCCLCHECK(ncclCalloc(&treeUpSend, nranks*MAXCHANNELS));
NCCLCHECK(ncclCalloc(&treeDnRecv, nranks*MAXCHANNELS));
NCCLCHECK(ncclCalloc(&treeDnSend, nranks*MAXCHANNELS));
for (int i=0; i<nranks; i++) {
for (int c=0; c<nChannels;c++) {
...
treeUpRecv[c*nranks+i] = allTopoRanks[i]->treeUpRecv[c];
treeUpSend[c*nranks+i] = allTopoRanks[i]->treeUpSend[c];
...
}
}
NCCLCHECK(connectTrees(comm, treeUpRecv, treeUpSend, treeDnRecv, treeDnSend, firstRanks));
...
}
然后执行connectTrees
static ncclResult_t connectTrees(struct ncclComm* comm, int* treeUpRecv, int* treeUpSend, int* treeDnRecv, int* treeDnSend, int* firstRanks) {
const int nChannels = comm->nChannels, nNodes = comm->nNodes, node = comm->node;
int* indexesSend, *indexesRecv;
NCCLCHECK(ncclCalloc(&indexesSend, nNodes));
NCCLCHECK(ncclCalloc(&indexesRecv, nNodes));
// Compute tree depth. Not an exact value but a good approximation in most
// cases
int depth = comm->nRanks/nNodes - 1 + log2i(nNodes);
int u0, d0_0, d0_1, u1, d1_0, d1_1;
NCCLCHECK(ncclGetDtree(nNodes, node, &u0, &d0_0, &d0_1, &u1, &d1_0, &d1_1));
...
}
首先通过ncclGetDtree根据节点数建立double binary tree结构,u0是当前node在T1中的父节点,d0_0和d0_1是当前node在T1中的左右子节点,同理u1,d1_0,d1_1是当前node在T2中的父节点和左右子节点。
ncclGetDtree中首先通过ncclGetBtree建立T1的结构,然后通过shift或者mirror来得到T2,不过2.7.8版本中这里似乎有一些问题,机器数为偶数的时候这里通过shift,奇数这里使用了mirro,前边有说到mirro的方式只适用于机器数为偶数的场景,否则会有节点在两棵树中都是叶节点,导致性能较差,新版本中已经修复了这点。后续逻辑我们按照偶数节点镜像,奇数节点shift的方式介绍。
ncclResult_t ncclGetDtree(int nranks, int rank, int* s0, int* d0_0, int* d0_1, int* s1, int* d1_0, int* d1_1) {
// First tree ... use a btree
ncclGetBtree(nranks, rank, s0, d0_0, d0_1);
// Second tree ... mirror or shift
if (nranks % 2 == 0) {
// shift
int shiftrank = (rank-1+nranks) % nranks;
int u, d0, d1;
ncclGetBtree(nranks, shiftrank, &u, &d0, &d1);
*s1 = u == -1 ? -1 : (u+1) % nranks;
*d1_0 = d0 == -1 ? -1 : (d0+1) % nranks;
*d1_1 = d1 == -1 ? -1 : (d1+1) % nranks;
} else {
// mirror
int u, d0, d1;
ncclGetBtree(nranks, nranks-1-rank, &u, &d0, &d1);
*s1 = u == -1 ? -1 : nranks-1-u;
*d1_0 = d0 == -1 ? -1 : nranks-1-d0;
*d1_1 = d1 == -1 ? -1 : nranks-1-d1;
}
return ncclSuccess;
}
然后通过ncclGetBtree构建T1,这里注释写的很详细,首先找到当前node编号在二进制上最低的非0 bit,即lowbit,以注释的14机为例:
- 对于父节点:
- 如果node二进制形如xx01[0],其中1表示lowbit,列表表示连续的0,xx为任意的高位,如果xx10[0]小于nranks,那么父节点为xx10[0]
- 根据1.1,如果xx10[0]大于等于nranks,那么父节点为xx00[0]
- 如果node二进制形如xx11[0],那么父节点为xx10[0]
- 对于子节点,当前节点形如xx10[0]:
- 对于左子节点,因为当前node的左子节点一定是小于node的,所以一定是规则1.1变换过来的,这种场景只需要逆回去即可,即xx01[0],如果lowbit为0,那么左子节点为-1
- 对于右子节点,右子节点大于当前node,对于情况1.3比较好找,直接lowbit-1位设置为1即可,即xx11[0];如果xx11[0]大于等于nranks,说明他是1.2的场景,这种场景并不知道右子节点的lowbit是多少,所以只能从左往右逐位判断
然后通过shift或者mirror的方式构造T2,不再赘述。
/* Btree which alternates leaves and nodes.
* Assumes root is 0, which conveniently builds a tree on powers of two,
* (because we have pow2-1 ranks) which lets us manipulate bits.
* Find first non-zero bit, then :
* Find the parent :
* xx01[0] -> xx10[0] (1,5,9 below) or xx00[0] if xx10[0] is out of bounds (13 below)
* xx11[0] -> xx10[0] (3,7,11 below)
* Find the children :
* xx10[0] -> xx01[0] (2,4,6,8,10,12) or -1 (1,3,5,7,9,11,13)
* xx10[0] -> xx11[0] (2,4,6,8,10) or xx101[0] (12) or xx1001[0] ... or -1 (1,3,5,7,9,11,13)
*
* Illustration :
* 0---------------8
* ______/ \______
* 4 12
* / \ / \
* 2 6 10 \
* / \ / \ / \ \
* 1 3 5 7 9 11 13
*/
ncclResult_t ncclGetBtree(int nranks, int rank, int* u, int* d0, int* d1) {
int up, down0, down1;
int bit;
for (bit=1; bit<nranks; bit<<=1) {
if (bit & rank) break;
}
if (rank == 0) {
*u = -1;
*d0 = nranks > 1 ? bit >> 1 : -1;
*d1 = -1;
return ncclSuccess;
}
up = (rank ^ bit) | (bit << 1);
if (up >= nranks) up = (rank ^ bit);
*u = up;
int lowbit = bit >> 1;
// down0 is always within bounds
down0 = lowbit == 0 ? -1 : rank-lowbit;
down1 = lowbit == 0 ? -1 : rank+lowbit;
// Make sure down1 is within bounds
while (down1 >= nranks) {
down1 = lowbit == 0 ? -1 : rank+lowbit;
lowbit >>= 1;
}
*d0 = down0; *d1 = down1;
return ncclSuccess;
}
到这里就完成了double binary tree的构建,以4机场景为例,构造出的tree如下所示,蓝色为T1,绿色为T2,这里和原始论文不一样的地方在于T2树结构应该和T1是对称的,不过没有什么影响。
?
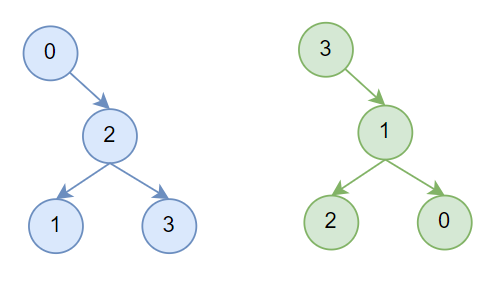
现在有了图3的机内连接,也有了图4的机间结构,connectTrees接下来会完成图2的机间连接。
这里channel0就是搜索出来的channel,channel1就是复制的channel0,channel0对应T1,channel1对应T2。treeUpSend保存了每个rank搜索出来的channel的send rank,即图3的黄色节点,通过getIndexes获取到每个节点send rank到indexsSend中。
static ncclResult_t connectTrees(struct ncclComm* comm, int* treeUpRecv, int* treeUpSend, int* treeDnRecv, int* treeDnSend, int* firstRanks) {
...
for (int c=0; c<nChannels; c++) {
struct ncclChannel* channel0 = comm->channels+c;
struct ncclChannel* channel1 = channel0+nChannels;
NCCLCHECK(getIndexes(treeUpSend+c*comm->nRanks, indexesSend, nNodes, firstRanks));
NCCLCHECK(getIndexes(treeUpRecv+c*comm->nRanks, indexesRecv, nNodes, firstRanks));
NCCLCHECK(openRing(&channel0->treeUp, comm->rank, indexesSend[node]));
NCCLCHECK(openRing(&channel1->treeUp, comm->rank, indexesSend[node]));
int root = indexesSend[node];
if (indexesSend[node] == comm->rank) NCCLCHECK(setTreeUp(&channel0->treeUp, &channel1->treeUp, indexesRecv, u0, u1));
if (indexesRecv[node] == comm->rank) NCCLCHECK(setTreeDown(&channel0->treeUp, &channel1->treeUp, indexesSend, d0_0, d0_1, d1_0, d1_1));
...
channel0->treeUp.depth = channel1->treeUp.depth = depth;
}
free(indexesSend);
free(indexesRecv);
return ncclSuccess;
}
static ncclResult_t openRing(struct ncclTree* tree, int rank, int upRank) {
if (tree->down[0] == upRank) tree->down[0] = -1;
if (rank == upRank) tree->up = -1;
return ncclSuccess;
}
然后执行openRing,就从图3变成了图5,。如果当前rank的子节点为sendrank,就断掉这个链,如图5的rank 7,如果当前rank就是sendrank,那么断掉up这个链,如图5的rank 0。
如果当前节点是sendrank,然后执行setTreeUp,设置sendrank的父节点,其实channel0就是indexesRecv[u0],channel1就是ndexesRecv[u1],同理再通过setTreeDown设置recvrank的子节点,执行完成后就得到了图2。
到这里就完成了ncclTopoPostset,然后建立tree的通信链接,当前rank从treeUp.down接收数据,向treeUp.up发数据;如前所述treeDn和treeUp一样,所以也建立了从treeUp.up收数据,向treeUp.down发数据的链接。
for (int c=0; c<comm->nChannels; c++) {
struct ncclChannel* channel = comm->channels+c;
...
NCCLCHECKGOTO(ncclTransportP2pSetup(comm, &treeGraph, channel, NCCL_MAX_TREE_ARITY, channel->treeUp.down, 1, &channel->treeUp.up), ret, affinity_restore);
NCCLCHECKGOTO(ncclTransportP2pSetup(comm, &treeGraph, channel, 1, &channel->treeDn.up, NCCL_MAX_TREE_ARITY, channel->treeDn.down), ret, affinity_restore);
}
enqueue
enqueue的过程和ring allreduce完全一样,直接看ncclSaveKernel的computeColl
static ncclResult_t computeColl(struct ncclInfo* info /* input */, struct ncclColl* coll, struct ncclProxyArgs* proxyArgs /* output */) {
coll->args.sendbuff = info->sendbuff;
coll->args.recvbuff = info->recvbuff;
coll->args.comm = info->comm->devComm;
...
// Set nstepsPerLoop and nchunksPerLoop
NCCLCHECK(getAlgoInfo(info));
NCCLCHECK(getPatternInfo(info));
NCCLCHECK(getLoopInfo(info));
...
}
首先通过getAlgoInfo选取协议和算法,假设算法为NCCL_ALGO_TREE,协议为NCCL_PROTO_SIMPLE。
然后通过getPatternInfo选pattern,得到的pattern为ncclPatternTreeUpDown。
case ncclCollAllReduce:
info->pattern = info->algorithm == NCCL_ALGO_COLLNET ? ncclPatternCollTreeUp : info->algorithm == NCCL_ALGO_TREE ? ncclPatternTreeUpDown : ncclPatternRingTwice; break;
然后通过getLoopInfo计算nstepsPerLoop和nchunksPerLoop,tree的每个循环只需要reduce然后发送即可,所以都是1。
info->nstepsPerLoop = info-> nchunksPerLoop = 1;
stepSize为buffer中一个slot的大小,chunkSteps和sliceSteps均为1,因此chunkSize初始化为stepSize*chunkSteps,也就是stepSize。
然后开始根据树的高度调整chunkSize,因为当nsteps比较小的时候,整个树无法流水线起来,这里的三种情况猜测可能是针对每个机器上使用8卡,4卡和单卡这三种场景对应的流水线深度。
然后设置proxy的参数,因为一次循环就能处理一个chunkSize大小的数据,一共有nChannels个channel,所以一次性能处理的数据量为(info->nChannels))info->nchunksPerLoopchunkEffectiveSize,然后去除nBytes就得到了总循环数nLoops。然后开始计算一共需要多少个slot,即nsteps,一共有nLoops个循环,一个循环里会执行nstepsPerLoop个chunk,一个chunk有chunkSteps个step,所以nsteps为nstepsPerLoop * nLoops * chunkSteps,不过tree的场景下,nsteps就等于nLoops。
static ncclResult_t computeColl(struct ncclInfo* info /* input */, struct ncclColl* coll, struct ncclProxyArgs* proxyArgs /* output */) {
...
coll->args.coll.root = info->root;
coll->args.coll.count = info->count;
coll->args.coll.nChannels = info->nChannels;
coll->args.coll.nThreads = info->nThreads;
coll->funcIndex = FUNC_INDEX(info->coll, info->op, info->datatype, info->algorithm, info->protocol);
int stepSize = info->comm->buffSizes[info->protocol]/NCCL_STEPS;
int chunkSteps = (info->protocol == NCCL_PROTO_SIMPLE && info->algorithm == NCCL_ALGO_RING) ? info->chunkSteps : 1;
int sliceSteps = (info->protocol == NCCL_PROTO_SIMPLE && info->algorithm == NCCL_ALGO_RING) ? info->sliceSteps : 1;
int chunkSize = stepSize*chunkSteps;
// Compute lastChunkSize
if (info->algorithm == NCCL_ALGO_TREE && info->protocol == NCCL_PROTO_SIMPLE) {
if (info->pattern == ncclPatternTreeUpDown) {
// Optimize chunkSize / nSteps
while (info->nBytes / (info->nChannels*chunkSize) < info->comm->channels[0].treeUp.depth*8 && chunkSize > 131072) chunkSize /= 2;
while (info->nBytes / (info->nChannels*chunkSize) < info->comm->channels[0].treeUp.depth*4 && chunkSize > 65536) chunkSize /= 2;
while (info->nBytes / (info->nChannels*chunkSize) < info->comm->channels[0].treeUp.depth && chunkSize > 32768) chunkSize /= 2;
}
// Use lastChunkSize as chunkSize
coll->args.coll.lastChunkSize = chunkSize / ncclTypeSize(info->datatype);
} else if (info->algorithm == NCCL_ALGO_COLLNET && info->protocol == NCCL_PROTO_SIMPLE) {
...
} else if (info->protocol == NCCL_PROTO_LL) {
...
} else if (info->algorithm == NCCL_ALGO_TREE && info->protocol == NCCL_PROTO_LL128) {
...
}
int chunkEffectiveSize = chunkSize;
...
int nLoops = (int)(DIVUP(info->nBytes, (((size_t)(info->nChannels))*info->nchunksPerLoop*chunkEffectiveSize)));
proxyArgs->nsteps = info->nstepsPerLoop * nLoops * chunkSteps;
proxyArgs->sliceSteps = sliceSteps;
proxyArgs->chunkSteps = chunkSteps;
proxyArgs->protocol = info->protocol;
proxyArgs->opCount = info->comm->opCount;
proxyArgs->dtype = info->datatype;
proxyArgs->redOp = info->op;
TRACE(NCCL_NET,"opCount %lx slicesteps %d spl %d cpl %d nbytes %zi -> protocol %d nchannels %d nthreads %d, nloops %d nsteps %d comm %p",
coll->args.opCount, proxyArgs->sliceSteps, info->nstepsPerLoop, info->nchunksPerLoop, info->nBytes, info->protocol, info->nChannels, info->nThreads,
nLoops, proxyArgs->nsteps, info->comm);
return ncclSuccess;
}
kernel执行
之后的流程和ring allreduce很像,直接看kernel launch,这里kernel为ncclAllReduceTreeKernel。
其中count为用户数据长度,loopSize为所有channel一次循环能处理的数据量,thisInput和thisOutput为用户传入的输入输出。
template<int UNROLL, class FUNC, typename T>
__device__ void ncclAllReduceTreeKernel(struct CollectiveArgs* args) {
const int tid = threadIdx.x;
const int nthreads = args->coll.nThreads-WARP_SIZE;
const int bid = args->coll.bid;
const int nChannels = args->coll.nChannels;
struct ncclDevComm* comm = args->comm;
struct ncclChannel* channel = comm->channels+blockIdx.x;
const int stepSize = comm->buffSizes[NCCL_PROTO_SIMPLE] / (sizeof(T)*NCCL_STEPS);
int chunkSize = args->coll.lastChunkSize;
const ssize_t minChunkSize = nthreads*8*sizeof(uint64_t) / sizeof(T);
const ssize_t loopSize = nChannels*chunkSize;
const ssize_t size = args->coll.count;
...
const T * __restrict__ thisInput = (const T*)args->sendbuff;
T * __restrict__ thisOutput = (T*)args->recvbuff;
...
}
然后开始reduce阶段,即树的上行阶段,创建prims,从treeUp的down收数据,往treeUp的up发送数据。然后开始遍历整个数据,如果up为-1,表示为根节点,那么执行recvReduceCopy将数据从子节点接收过来和自己的数据reduce然后拷贝到用户的输出。如果down[0]为-1,说明为叶节点,那么通过send将数据从用户的输入拷贝到父节点的buffer中。对于中间节点,执行recvReduceSend将数据从子节点收到的数据和自己的用户输入执行reduce,然后发送给父节点。
do {
struct ncclTree* tree = &channel->treeUp;
// Reduce : max number of recv is 3, max number of send is 1 (binary tree + local)
ncclPrimitives<UNROLL/2, 1, 1, T, NCCL_MAX_TREE_ARITY, 1, 0, FUNC> prims(tid, nthreads, tree->down, &tree->up, NULL, stepSize, channel, comm);
for (ssize_t gridOffset = 0; gridOffset < size; gridOffset += loopSize) {
// Up
ssize_t offset = gridOffset + bid*chunkSize;
int nelem = min(chunkSize, size-offset);
if (tree->up == -1) {
prims.recvReduceCopy(thisInput+offset, thisOutput+offset, nelem);
} else if (tree->down[0] == -1) {
prims.send(thisInput+offset, nelem);
} else {
prims.recvReduceSend(thisInput+offset, nelem);
}
}
} while(0);
执行结束之后就完成了reduce,此时根节点已经有了全局的reduce结果,然后开始执行allgather。创建prim,如上所述treeDn其实就是treeUp,因此prim将从treeUp的up rank收数据然后发送给treeUp的down rank。如果up为-1,说明为根节点,那么通过directSend直接将数据从用户输出发送给子节点的buffer。如果down[0]为-1,说明为子节点,那么通过directRecv将数据从父节点的buffer拷贝到用户输出。如果是中间节点,那么通过directRecvCopySend从父节点的buffer接收数据,拷贝到自己的用户输出,并发送到子节点的buffer。
do {
struct ncclTree* tree = &channel->treeDn;
// Broadcast : max number of recv is 1, max number of send is 3 (binary tree + local)
ncclPrimitives<UNROLL/2, 1, 1, T, 1, NCCL_MAX_TREE_ARITY, 1, FUNC> prims(tid, nthreads, &tree->up, tree->down, thisOutput, stepSize, channel, comm);
for (ssize_t gridOffset = 0; gridOffset < size; gridOffset += loopSize) {
// Down
ssize_t offset = gridOffset + bid*chunkSize;
int nelem = min(chunkSize, size-offset);
if (tree->up == -1) {
prims.directSend(thisOutput+offset, offset, nelem);
} else if (tree->down[0] == -1) {
prims.directRecv(thisOutput+offset, offset, nelem);
} else {
prims.directRecvCopySend(thisOutput+offset, offset, nelem);
}
}
} while(0);
proxy
到这里,我们看到了kernel的执行过程,然后再看下proxy的流程。可以看到会保存到treeUp子节点的recv args,到treeUp父节点的send args。同时会保存到treeDn子节点的send args,到treeDn父节点的recv args。
ncclResult_t ncclProxySaveColl(struct ncclProxyArgs* args, int pattern, int root, int nranks) {
...
if (pattern == ncclPatternTreeUp || pattern == ncclPatternTreeUpDown) {
// Tree up
struct ncclTree* tree = &args->channel->treeUp;
for (int i=0; i<NCCL_MAX_TREE_ARITY; i++) NCCLCHECK(SaveProxy<proxyRecv>(tree->down[i], args));
NCCLCHECK(SaveProxy<proxySend>(tree->up, args));
}
if (pattern == ncclPatternTreeDown || pattern == ncclPatternTreeUpDown) {
// Tree down
struct ncclTree* tree = &args->channel->treeDn;
for (int i=0; i< NCCL_MAX_TREE_ARITY; i++) NCCLCHECK(SaveProxy<proxySend>(tree->down[i], args));
NCCLCHECK(SaveProxy<proxyRecv>(tree->up, args));
}
...
return ncclSuccess;
}
ring和tree的选择
主体思想很简单,对于用户传入的nBytes长度数据,总耗时time = latency + nBytes / algo_bw,其中algo_bw为算法带宽,基础总线带宽为busBw,就是每个channel的带宽乘channel数,然后会根据实测的数据对带宽进行一些修正,比如tree场景会乘0.9。然后计算算法带宽,tree的话会除以2,因为上行一次,下行一次相当于发送了两倍的数据量,ring的话会除以2 * (nranks - 1) / nranks,原因见第十一节。latency计算不再赘述,最后将计算出的每种协议和算法的带宽延迟保存到bandwidths和latencies。
当用户执行allreduce api的时候会通过getAlgoInfo计算出每种算法和协议组合的执行时间,选出最优的。
ncclResult_t ncclTopoTuneModel(struct ncclComm* comm, int minCompCap, int maxCompCap, struct ncclTopoGraph** graphs) {
int simpleDefaultThreads = (graphs[NCCL_ALGO_RING]->bwIntra*graphs[NCCL_ALGO_RING]->nChannels <= PCI_BW) ? 256 : NCCL_SIMPLE_MAX_NTHREADS;
...
for (int coll=0; coll<NCCL_NUM_FUNCTIONS; coll++) {
int nsteps = coll == ncclFuncAllReduce ? 2*(nRanks-1) :
coll == ncclFuncReduceScatter || coll == ncclFuncAllGather ? nRanks-1 :
nRanks;
int nInterSteps = coll == ncclFuncAllReduce ? (nNodes > 1 ? 2*nNodes :0) :
coll == ncclFuncReduceScatter || coll == ncclFuncAllGather ? nNodes-1 :
nNodes;
for (int a=0; a<NCCL_NUM_ALGORITHMS; a++) {
if (coll == ncclFuncBroadcast && a != NCCL_ALGO_RING) continue;
if (coll == ncclFuncReduce && a != NCCL_ALGO_RING) continue;
if (coll == ncclFuncReduceScatter && a != NCCL_ALGO_RING && a != NCCL_ALGO_NVLS) continue;
if (coll == ncclFuncAllGather && a != NCCL_ALGO_RING && a != NCCL_ALGO_NVLS) continue;
for (int p=0; p<NCCL_NUM_PROTOCOLS; p++) {
...
float busBw = graphs[a]->nChannels * bw;
// Various model refinements
if (a == NCCL_ALGO_RING && p == NCCL_PROTO_LL) { busBw = std::min(llMaxBw, busBw * ((nNodes > 1 || coll == ncclFuncAllReduce || coll == ncclFuncReduce) ? 1.0/4.0 : 1.0/3.0)); }
if (a == NCCL_ALGO_RING && p == NCCL_PROTO_LL128) busBw = std::min(busBw * (ppn < 2 ? 0.7 : 0.92 /*120.0/128.0*/), graphs[a]->nChannels*perChMaxRingLL128Bw);
if (a == NCCL_ALGO_TREE) busBw = std::min(busBw*.92, graphs[a]->nChannels*perChMaxTreeBw);
if (a == NCCL_ALGO_TREE && p == NCCL_PROTO_LL) busBw = std::min(busBw*1.0/3.8, llMaxBw);
if (a == NCCL_ALGO_TREE && p == NCCL_PROTO_LL128) busBw = std::min(busBw * (nNodes == 1 ? 7.0/9.0 : 120.0/128.0), graphs[a]->nChannels*perChMaxTreeLL128Bw);
if (a == NCCL_ALGO_TREE && graphs[a]->pattern == NCCL_TOPO_PATTERN_TREE) busBw *= .85;
...
// Convert bus BW to algorithm BW
float ratio;
if (a == NCCL_ALGO_RING) ratio = (1.0 * nRanks) / nsteps;
else if (a == NCCL_ALGO_NVLS || a == NCCL_ALGO_NVLS_TREE) ratio = 5.0/6.0;
else ratio = .5;
comm->bandwidths[coll][a][p] = busBw * ratio;
...
}
}
参考
Two-Tree Algorithms for Full Bandwidth Broadcast, Reduction and Scan
massively-scale-deep-learning-training-nccl-2-4/
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【Java SE】java中继承详解
- 【Python】Python编程技能比较实用的技巧和建议
- Shell脚本③条件语句、if命令和case命令
- 2024自动化控制与信息技术国际会议(ICACIT2024)
- 脆皮大学生“拯救”方案——智慧高校智能视频监控系统的建设
- Python之random模块详解
- 054:vue工具 --- BASE64加密解密互相转换
- 集成电路模拟设计——【基于Serdes 应用的 串化/解串器 & 时钟与数据恢复电路CDR】
- Mac AE 报错 “无法获取动态链路服务器”
- 小孩暑寒假北京游学计划 结合学习和娱乐,让孩子在寒假期间有充实而有趣的体验 比上学还快乐