GDPU 数据结构 天码行空14
发布时间:2023年12月18日
实验十四 查找算法的实现
一、【实验目的】
1、掌握顺序排序,二叉排序树的基本概念
2、掌握顺序排序,二叉排序树的基本算法(查找算法、插入算法、删除算法)
3、理解并掌握二叉排序数查找的平均查找长度。
二、【实验内容】
1、已知如下11个元素的有序表:
{ 5, 13, 19, 21, 37, 56, 64, 75, 80, 88, 92 }
请设计完成二分查找法查找关键字为64的数据元素的程序。
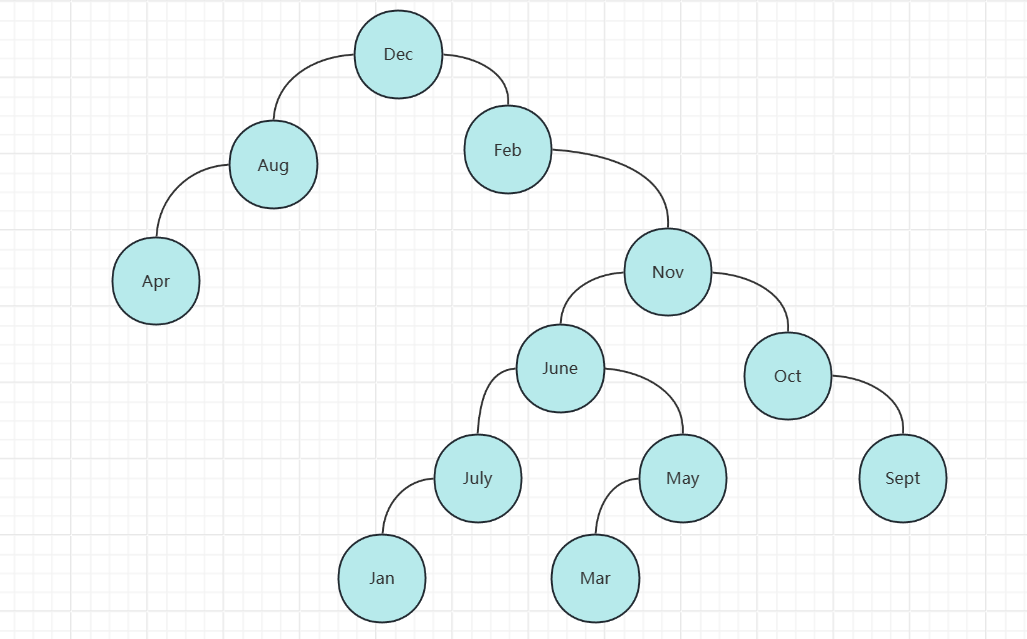
2、已知一个个数为12的数据元素序列为 { “Dec”, “Feb”, “Nov”, “Oct”, “June”, “Sept”, “Aug”, “Apr”, “May”, “July”, “Jan”, “Mar” },
要求:
(1)按各数据元素的顺序(字母大小顺序)构造一棵二叉排序数,并中序打印排序结果。
(2)查找数据”Sept”是否存在。
三、【实验源代码】
📕 CPP版
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Node // 定义二叉树节点
{
public:
string data; // 存储节点的数据
Node* left; // 指向左子节点
Node* right; // 指向右子节点
Node(string data) // 构造函数
{
this->data = data; // 初始化数据
this->left = nullptr; // 左子节点指向空
this->right = nullptr; // 右子节点指向空
}
};
// 在长度为 n 的 a 数组中找 x,找到返回下标,找不到返回 -1
int binarySearch(int a[], int x, int n)
{
int l = 0; // 左端点
int r = n - 1; // 右端点
while (l < r) // 当左端点小于右端点时循环
{
int mid = (l + r) >> 1; // 取中间点(右移一位相当于除以2)
if (x > a[mid]) // 如果要查找的数在中间点的右边
l = mid + 1; // 左端点移到中间点的右侧
else
r = mid; // 右端点移到中间点或中间点的左侧
}
if (a[l] == x) // 如果查到了要找的数
return l; // 返回下标
cout << "没找到!!" << x << endl; // 否则输出没找到的消息
return -1; // 返回-1
}
void insert(Node* root, string s) // 向二叉搜索树中插入一个节点
{
if (root == nullptr) // 如果根节点为空
{
root = new Node(s); // 创建一个新节点作为根节点
return;
}
Node* t = root; // 定义指针t指向根节点
while (t != nullptr) // 循环直到找到合适的位置插入新节点
{
int com = s.compare(t->data); // 比较节点的数据与要插入的数据的大小关系
if (com == 0) // 如果相等,说明已经存在该节点
return; // 直接返回
else if (com > 0) // 如果要插入的数据大于节点的数据,说明要插入右子树
{
if (t->right == nullptr) // 如果右子树为空
t->right = new Node(s); // 创建一个新节点作为右子节点
else
t = t->right; // 否则继续向右子树查找
}
else if (com < 0) // 如果要插入的数据小于节点的数据,说明要插入左子树
{
if (t->left == nullptr) // 如果左子树为空
t->left = new Node(s); // 创建一个新节点作为左子节点
else
t = t->left; // 否则继续向左子树查找
}
}
}
Node* initBiTree(string ss[], int n) // 初始化二叉搜索树
{
Node* root = new Node(ss[0]); // 创建根节点
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) // 循环插入其余的节点
insert(root, ss[i]);
return root; // 返回根节点
}
void inOrder(Node* root) // 中序遍历二叉搜索树
{
if (root != nullptr) // 如果节点不为空
{
if (root->left != nullptr) // 如果有左子节点,先中序遍历左子树
inOrder(root->left);
cout << root->data << " "; // 输出节点的数据
if (root->right != nullptr) // 如果有右子节点,后中序遍历右子树
inOrder(root->right);
}
}
void search(Node* root, string s) // 在二叉搜索树中查找一个节点
{
while (root != nullptr) // 如果节点不为空
{
int com = s.compare(root->data); // 比较节点的数据与要查找的数据的大小关系
if (com == 0) // 如果相等,说明找到了
{
cout << "找到了" << s << endl; // 输出找到的消息
return;
}
else if (com > 0) // 如果要查找的数据大于节点的数据,说明要查找右子树
root = root->right; // 继续向右子树查找
else // 否则要查找左子树
root = root->left; // 继续向左子树查找
}
cout << "没找到" << s << endl; // 输出没找到的消息
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 5, 13, 19, 21, 37, 56, 64, 75, 80, 88, 92 }; // 定义一个有序数组
int x = 64; // 要查找的数
int idx = binarySearch(a, x, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0])); // 在数组中查找要查找的数
if (idx != -1) // 如果找到了
cout << x << "在数组中的下标是" << idx << endl; // 输出结果
string ss[] = { "Dec", "Feb", "Nov", "Oct", "June", "Sept", "Aug", "Apr", "May", "July", "Jan", "Mar" }; // 定义一个字符串数组
Node* root = initBiTree(ss, sizeof(ss) / sizeof(ss[0])); // 初始化二叉搜索树
cout << "中序遍历序列为:";
inOrder(root); // 中序遍历二叉搜索树
cout << endl;
string s = "Sept"; // 要查找的字符串
search(root, s); // 在二叉搜索树中查找节点
return 0;
}
📕 java版
class Main
{
static class Node
{
String data;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(String data)
{
this.data = data;
}
}
// 在长度为 n 的 a 数组中找 x,找到返回下标,找不到返回 -1
static int binarySearch(int[] a, int x, int n)
{
int l = 0;
int r = n - 1;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (x > a[mid]) // x在 mid 的右边
l = mid + 1;
else
r = mid;
}
if (a[l] == x)
return l;
System.out.println("没找到!!" + x);
return -1;
}
static void insert(Node root, String s)
{
if (root == null)
{
root = new Node(s);
return;
}
Node t = root;
while (t != null)
{
int com = s.compareTo(t.data);
if (com == 0)
return;
else if (com > 0)// 右子树
{
if (t.right == null)
t.right = new Node(s);
else
t = t.right;
} else if (com < 0)
{
if (t.left == null)
t.left = new Node(s);
else
t = t.left;
}
}
}
static Node initBiTree(String[] ss, int n)
{
Node root = new Node(ss[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
insert(root, ss[i]);
return root;
}
static void inOrder(Node root)
{
if (root != null)
{
if (root.left != null)
inOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
if (root.right != null)
inOrder(root.right);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] a = { 5, 13, 19, 21, 37, 56, 64, 75, 80, 88, 92 };
int x = 64;
int idx = binarySearch(a, x, a.length);
if (idx != -1)
System.out.println(x + "在数组中的下标是" + idx);
String[] ss = { "Dec", "Feb", "Nov", "Oct", "June", "Sept", "Aug", "Apr", "May", "July", "Jan", "Mar" };
Node root = initBiTree(ss, ss.length);
inOrder(root);
System.out.println();
String s = "Sept";
boolean search = search(root, s);
if (search)
System.out.println("找到了" + s);
else
{
System.out.println("没找到" + s);
}
}
private static boolean search(Node root, String s)
{
while (root != null)
{
int com = s.compareTo(root.data);
if (com == 0)
return true;
else if (com > 0)
root = root.right;
else
{
root = root.left;
}
}
return false;
}
}
四、【实验结果】
64在数组中的下标是6
中序遍历序列为:Apr Aug Dec Feb Jan July June Mar May Nov Oct Sept
找到了Sept
五、【实验总结】
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/lt6666678/article/details/135006616
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 华为设备vlan下配置MSTP,STP选举
- 在做题中学习(33):只出现一次的数字 II
- React面试题:React.Component和React.PureComponent的区别?
- 学习python仅此一篇就够了(使用python操作数据库)
- 前端知识笔记(三十七)———Django与Ajax
- VSCode 正则表达式 匹配多行
- 时序分解 | Matlab实现DBO-VMD基于蜣螂优化算法优化VMD变分模态分解时间序列信号分解
- 南京观海微电子---时序分析基本概念(二)——保持时间
- L1-069:胎压监测
- 5-7 各门课程平均分(列的计算)——python