Linux shell编程学习笔记38:history命令

0?前言
使用DOS的朋友,都知道可以在命令行提示符中使用上下光标键来浏览最近执行过的命令,这是基于DOS提供的DosKey命令。
而在Unix和Linux的shell中,我们同样可以使用上下光标键来浏览最近执行过的命令历史纪录(history),这是因为有history命令。
bash可以保存的过去曾经执行过的命令。当某个用户登录到shell中,会读取该用户家目录中的~/.bash_history文件,并将历史命令列表保存到内存中。当用户退出当前shell时,会将内存中的历史命令列表覆盖至~/.bash_history文件。
?1? history命令的功能、格式和退出状态
我们可以使用 help history命令查看?history命令的帮助信息。
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $help history
history: history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or history -anrw [filename] or history -ps arg [arg...]
? ? Display or manipulate the history list.
? ??
? ? Display the history list with line numbers, prefixing each modified
? ? entry with a `*'. ?An argument of N lists only the last N entries.
? ??
? ? Options:
? ? ? -c ? ? ? ?clear the history list by deleting all of the entries
? ? ? -d offset delete the history entry at offset OFFSET.
? ??
? ? ? -a ? ? ? ?append history lines from this session to the history file
? ? ? -n ? ? ? ?read all history lines not already read from the history file
? ? ? -r ? ? ? ?read the history file and append the contents to the history
? ? ? ? list
? ? ? -w ? ? ? ?write the current history to the history file?
? ? ? ? and append them to the history list
? ??
? ? ? -p ? ? ? ?perform history expansion on each ARG and display the result
? ? ? ? without storing it in the history list
? ? ? -s ? ? ? ?append the ARGs to the history list as a single entry
? ??
? ? If FILENAME is given, it is used as the history file. ?Otherwise,
? ? if $HISTFILE has a value, that is used, else ~/.bash_history.
? ??
? ? If the $HISTTIMEFORMAT variable is set and not null, its value is used
? ? as a format string for strftime(3) to print the time stamp associated
? ? with each displayed history entry. ?No time stamps are printed otherwise.
? ??
? ? Exit Status:
? ? Returns success unless an invalid option is given or an error occurs.
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $

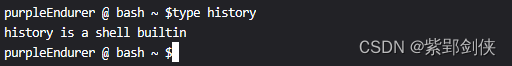
1.1?history命令的功能
history命令是一个内部命令,可以显示或操纵命令历史列表。
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $type history
history is a shell builtin
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $
1.2?history命令的格式
history [-c] [-d 偏移量] [历史记录数]
或
history -anrw [文件名]
或
history -ps?参数?[参数...]
| 选项 | 功能 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| -a | 将当前会话的命令行历史追加到历史文件~/.bash_history中 | append |
| -c | 删除所有条目从而清空历史列表内容。 | clear |
| -d?偏移量 | ?从指定位置删除历史列表内容。 | delete |
| 历史记录数 | 显示指定数量的历史命令纪录,应为正整数 | number |
| -n | 从历史文件中读取所有未被读取的行 | not |
| -p?参数 | 对每一个指定参数展开历史并显示结果而不存储到历史列表中 | perform |
| -r | 读取历史文件并将内容追加到历史列表中 | read |
| -s?命令 | 以单条记录将?指定命令 追加到历史列表中。如果指定了 文件名,则它将被作为历史文件。否则如果 $HISTFILE 变量有值的话使用之,不然使用 ~/.bash_history 文件。如果 $HISTTIMEFORMAT 变量被设定并且不为空,它的值会被用于 strftime(3) 的格式字符串来打印与每一个显示的历史条目想关联的时间戳,否则不打印时间戳。 | single |
| -w [文件] | 将当前历史写入到历史文件中,并追加到历史列表中 | write |
1.3退出状态
返回成功,除非使用了无效的选项或者发生错误。
2?命令应用实例
2.1?history:显示命令历史列表
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $?
?
?2.2 history -a:将当前会话的命令行历史追加到历史文件~/.bash_history中
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ cat ~/.bash_history
PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
history -2
echo $?
history
history -r
history
history
history -a
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history -a
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ cat ~/.bash_history
PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
history -2
echo $?
history
history -r
history
history
history -a
history -n
ls ~/.bash_history
cat ~/.bash_history
cat ~/.bash_history -a
cls
clear
cat ~/.bash_history -a
cls
clear
cat ~/.bash_history
history -a
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $?
我们先执行cat ~/.bash_history?命令查看文件~/.bash_history的内容
然后执行history -a?命令将当前会话的命令行历史追加到历史文件~/.bash_history中
接着再次执行cat ~/.bash_history?命令查看文件~/.bash_history的内容
可以看到文件~/.bash_history中确实增加了下面这些命令行:
history -n
ls ~/.bash_history
cat ~/.bash_history
cat ~/.bash_history -a
cls
clear
cat ~/.bash_history -a
cls
clear
cat ~/.bash_history
history -a2.3 history -c:删除所有条目从而清空历史列表
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?history 0
? ? 3 ?echo $?
? ? 4 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history -c
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history
? ? 1 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $?
我们先执行history?命令查看当前命令历史列表,内容如下:
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?history 0
? ? 3 ?echo $?
? ? 4 ?history然后执行history -c?命令将当前会话的命令行历史列表清空
接着再次执行history?命令查看当前命令历史列表,这时历史列表只有我们这次所输入的的命令:
? ? 1 ?history之前的命令历史列表都被清空了。
2.4?history -d?偏移量:从指定位置删除历史列表内容
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?history
? ? 3 ?history 0
? ? 4 ?echo $?
? ? 5 ?history 3
? ? 6 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history -d 2
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?history 0
? ? 3 ?echo $?
? ? 4 ?history 3
? ? 5 ?history
? ? 6 ?history -d 2
? ? 7 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $?

我们先执行history?命令查看当前命令历史列表,内容如下:
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?history
? ? 3 ?history 0
? ? 4 ?echo $?
? ? 5 ?history 3
? ? 6 ?history然后执行history -d 2?命令将第2行命令删除
接着再次执行history?命令查看当前命令历史列表,内容如下:
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?history 0
? ? 3 ?echo $?
? ? 4 ?history 3
? ? 5 ?history
? ? 6 ?history -d 2
? ? 7 ?history可以看到命令历史列表中之前的第2条纪录:
? ? 2 ?history被删除了。?
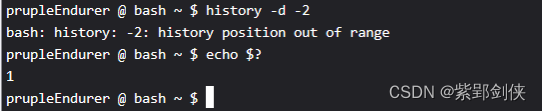
如果我指定的偏移量是负数,例如-2,命令将出错,退出状态码为1:
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history -d -2
bash: history: -2: history position out of range
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo $?
1
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $?
2.5?history?正整数:显示指定数量的历史命令纪录
?prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ history
? ? 1 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ history 1
? ? 2 ?history 1
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ history 0
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ history 2
? ? 3 ?history 0
? ? 4 ?history 2
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ history
? ? 1 ?history
? ? 2 ?history 1
? ? 3 ?history 0
? ? 4 ?history 2
? ? 5 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $?

如果我们指定的是负数,将提示出错,命令退出值为2。
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history -2
bash: history: -2: invalid option
history: usage: history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or history -anrw [filename] or history -ps arg [arg...]prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo $?
2

2.6?history -r:读取历史文件并将内容追加到历史列表中
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?cat ~/.bash_history
? ? 3 ?set | grep ?$HISTFILE
? ? 4 ?cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
? ? 5 ?history -w
? ? 6 ?cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
? ? 7 ?history -w c.log
? ? 8 ?cat c.log
? ? 9 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history -r
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?cat ~/.bash_history
? ? 3 ?set | grep ?$HISTFILE
? ? 4 ?cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
? ? 5 ?history -w
? ? 6 ?cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
? ? 7 ?history -w c.log
? ? 8 ?cat c.log
? ? 9 ?history
? ?10 ?history -r
? ?11 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ?12 ?cat ~/.bash_history
? ?13 ?set | grep ?$HISTFILE
? ?14 ?cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
? ?15 ?history -w
? ?16 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
cat ~/.bash_history
set | grep ?$HISTFILE
cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
history -w
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $?

我们先执行history?命令查看当前命令历史列表共有9条,内容如下:
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?cat ~/.bash_history
? ? 3 ?set | grep ?$HISTFILE
? ? 4 ?cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
? ? 5 ?history -w
? ? 6 ?cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
? ? 7 ?history -w c.log
? ? 8 ?cat c.log
? ? 9 ?history然后执行history -r?命令读取历史文件并将内容追加到历史列表中
接着再次执行history?命令查看当前命令历史列表,共有16条,内容如下:
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?cat ~/.bash_history
? ? 3 ?set | grep ?$HISTFILE
? ? 4 ?cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
? ? 5 ?history -w
? ? 6 ?cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
? ? 7 ?history -w c.log
? ? 8 ?cat c.log
? ? 9 ?history
? ?10 ?history -r
? ?11 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ?12 ?cat ~/.bash_history
? ?13 ?set | grep ?$HISTFILE
? ?14 ?cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
? ?15 ?history -w
? ?16 ?history我们用命令?cat /home/csdn/.bash_history 查看历史文件的内容:
PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
cat ~/.bash_history
set | grep ?$HISTFILE
cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
history -w可以看到,当前命令历史列表中的第10条-15条记录是从历史文件添加进来的。
2.7?history -s?命令 :将?指定命令 追加到历史列表
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ history
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?ls
? ? 3 ?cd Code
? ? 4 ?pwd
? ? 5 ?history
? ? 6 ?pwd
? ? 7 ?pwd
? ? 8 ?pwd
? ? 9 ?set | grep hist
? ?10 ?set | grep HIST
? ?11 ?export | grep HIST
? ?12 ?export
? ?13 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ history -s abcd
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ history
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?ls
? ? 3 ?cd Code
? ? 4 ?pwd
? ? 5 ?history
? ? 6 ?pwd
? ? 7 ?pwd
? ? 8 ?pwd
? ? 9 ?set | grep hist
? ?10 ?set | grep HIST
? ?11 ?export | grep HIST
? ?12 ?export
? ?13 ?history
? ?14 ?abcd
? ?15 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $

在上面的实例中,?我们执行命令?history -s abcd?将? abcd?加入到命令历史列表中。
2.8?history -w [文件]:将当前历史写入到历史文件中,并追加到历史列表中
?
2.8.1??将当前历史写入到默认历史文件中
系统默认历史文件说明符由环境变量?HISTFILE?指定。
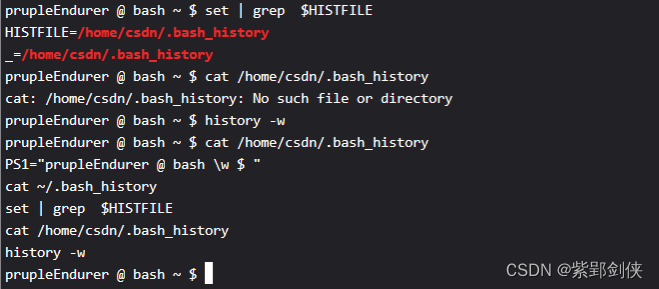
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ set | grep ?$HISTFILE
HISTFILE=/home/csdn/.bash_history
_=/home/csdn/.bash_history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
cat: /home/csdn/.bash_history: No such file or directory
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history -w
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
cat ~/.bash_history
set | grep ?$HISTFILE
cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
history -w
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $?
 ?
?
我们先执行?set | grep ?$HISTFILE?命令?查询环境变量?HISTFILE?的值为:/home/csdn/.bash_history。
然后我们执行? cat /home/csdn/.bash_history?命令查看?/home/csdn/.bash_history?的内容,结果这个文件不存在。
接着我们执行?history -w ?命令将命令行历史记录?保存到?/home/csdn/.bash_history。
最后我们再次执行 cat /home/csdn/.bash_history?命令查看?/home/csdn/.bash_history?的内容,这次文件不仅存在,而且文件内容就是我们之前输入的命令。
?
2.8.2? 将当前历史写入到指定文件中
我们将?命令行历史记录?保存到?到当前目录下的文件 c.log中。
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ history -w c.log
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ cat c.log
PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
cat ~/.bash_history
set | grep ?$HISTFILE
cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
history -w
cat /home/csdn/.bash_history
history -w c.log
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $?
 ??
??
首先,我们执行命令? history -w c.log?? 将?命令行历史记录?保存到?到当前目录下的文件 c.log中。
然后,我们执行命令? cat c.log? ?查看文件 c.log?的内容。
2.9?!:重复执行命令
2.9.1 !!?或 !-1:重复执行上一条命令
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ pwd
/home/csdn/Code
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ !!
pwd
/home/csdn/Code
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ !-1
pwd
/home/csdn/Code
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $?
?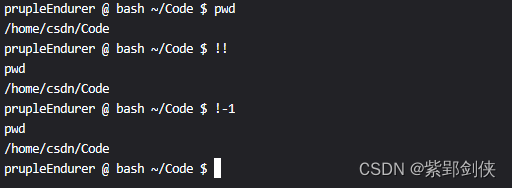
我们执行命令!!?或 !-1 ,均会重复执行上一条命令pwd
除了以上两种方法,还有两种方法 :
- 使用方向键↑选中命令,按↑↓调整,并回车执行
- 按Ctrl + p,调出命令,并回车执行
?
?2.9.2 !命令历史列表列号?:重复执行历史列表中指定行的命令
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ ls
Code
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ ls Code
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ cd Code
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ ls
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ history
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?ls
? ? 3 ?ls Code
? ? 4 ?cd Code
? ? 5 ?ls
? ? 6 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ !2
ls
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ ! 2
bash: 2: command not found

在上面的实例中,命令 !2?会执行命令历史列表中的?第2条命令 ls
由于?当前目录?下没有内容,所以ls命令没有显示。
如果?我们输入的命令是 ! 2,就会报错。
注意:
- ! 与?命令历史列表列号 之间不能有空格。
- 命令历史列表列号如果为正整数,则从头往下数;如果为负整数,则从下往上倒数,例如!-1执行的就是命令列表中最后一条命令
如果我们指定的命令历史列表列号?不在?命令历史列表实际列数中,会怎么样呢?
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ !0
bash: !0: event not found
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ echo $?
0
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ !100
bash: !100: event not found
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ echo $?
0
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $?
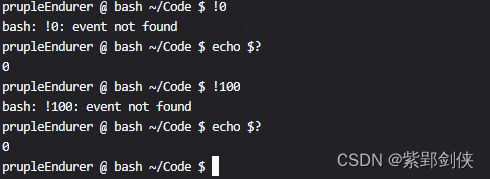
我们执行命令 !0?和 !100,系统都会提示:event not found
而命令返回值均为0。
?2.9.3?!字符串?:重复执行历史列表中以指定字符串开头的命令
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ history
? ? 1 ?PS1="prupleEndurer @ bash \w $ "
? ? 2 ?ls
? ? 3 ?ls Code
? ? 4 ?cd Code
? ? 5 ?ls
? ? 6 ?history
? ? 7 ?ls
? ? 8 ?! 2
? ? 9 ?cd Code
? ?10 ?ehco $?
? ?11 ?echo $?
? ?12 ?echo $?
? ?13 ?echo $?
? ?14 ?echo $?
? ?15 ?echo $?
? ?16 ?history
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ !cd
cd Code
bash: cd: Code: No such file or directory
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ ! cd
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ !ls
ls
Code
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ !ls Cod
ls Cod
ls: cannot access Cod: No such file or directory
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo $?
2
prupleEndurer @ bash ~ $?
我们行执行命令 history?查看当前命令历史列表
然后先后执行?了?!cd 、 ! cd 、!ls? 、!ls Cod?命令。从执行情况看,要注意两点:
- !?和 字符串?之间不能有空格
- 如果命令历史列表中不包括指定字符串的命令,系统会直接执行字符串,比如?!ls Cod
?
2.10 其它使用技巧
网上介绍的一些使用技巧,大家可以试试。
2.10.1? 重新执行或查看命令历史中的命令
- !:0?将前一条命令去除参数再执行
- Ctrl + n显示当前历史中的下一条命令,但不执行
- Ctrl + j执行当前命令
- !?string 重复前一个包含string字符串的命令
- !string:p ? 仅打印命令历史,而不执行
- !$:p 打印输出!$(上一条命令的最后一个参数)的内容
- !*:p 打印输出!*(上一条命令的所有参数)的内容
- ^string 删除上一条命令中的第一个string
- ^string1^string2将上一条命令中的第一个string1替换为string2
- !:gs/string1/srting2 将上一条命令中所有的string1都替换为string2
2.10.2?使用(reverse-i-search)模式
Crtl + r:在命令历史中搜索命令
Crtl + g:从历史搜索模式退出
?
2.10.3?使用命令历史记录中的参数
- ?重新调用前一个命令中最后一个参数
? ? ?有3种方法:
- !$
- Esc . (点击Esc键后松开,然后点击.键)
- Alt+. (按住Alt键的同时点击.键),在一些终端软件中屏蔽了Alt功能键,需要开启
- command !^ ???? 利用上一个命令的第一个参数做cmd的参数
- command !$ ???? 利用上一个命令的最后一个参数做cmd的参数
- command !*????? 利用上一个命令的全部参数做cmd的参数
- command !:n???? 利用上一个命令的第n个参数做cmd的参数
- command !n:^??? 调用第n条命令的第一个参数
- command !n:$??? 调用第n条命令的最后一个参数
- command !n:m??? 调用第n条命令的第m个参数
- command !n:*??? 调用第n条命令的所有参数
- command !srting:^?? 从命令历史中搜索string开头的命令,并获取它的第一个参数
- command !srting:$?? 从命令历史中搜索string开头的命令,并获取它的最后一个参数
- command !srting:n?? 从命令历史中搜索string开头的命令,并获取它的第n个参数
- command !srting:*?? 从命令历史中搜索string开头的命令,并获取它的所有参数
三、与history命令相关的环境变量
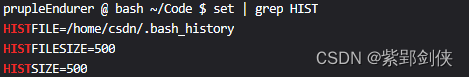
prupleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ set | grep HIST
HISTFILE=/home/csdn/.bash_history
HISTFILESIZE=500
HISTSIZE=500
 ?
?
- HISTFILE? ? ? ? :指定了默认命令历史文件说明符
- HISTFILESIZE:指定默认命令历史文件中保存命令的记录总数,即命令历史文件中最多只有HISTFILESIZE行
- HISTSIZE? ? ? ?:指定了 history 命令输出的记录数,即输出命令历史文件中的最后HISTSIZE行
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Jenkins创建maven项目
- 【响应式编程-02】Lambda的语法格式和使用
- 使用oled虚拟人主播,如何搭建场景
- 基于ChatGpt,Java,SpringBoot,Vue,Milvus向量数据库的定制化聊天Web demo
- [SAP] 解决程序提示被某用户使用或锁定的问题
- vue3安装vue-tools
- SpringCloud(17~21章):Alibaba入门简介、Nacos服务注册和配置中心、Sentinel实现熔断与限流、Seata处理分布式事务
- 力扣例题:分发糖果
- 防御式编程
- Ruff物联网数采网关助力工业企业数字化转型,降本增效