10. Profile
发布时间:2024年01月24日
1. 区分环境的配置
1.1. properties 配置
假设,一个应用的工作环境有:dev、test、prod
那么,我们可以添加 4 个配置文件:
- applcation.properties - 公共配置
- application-dev.properties - 开发环境配置
- application-test.properties - 测试环境配置
- application-prod.properties - 生产环境配置
在 applcation.properties 文件中可以通过以下配置来激活 profile:
spring.profiles.active = test
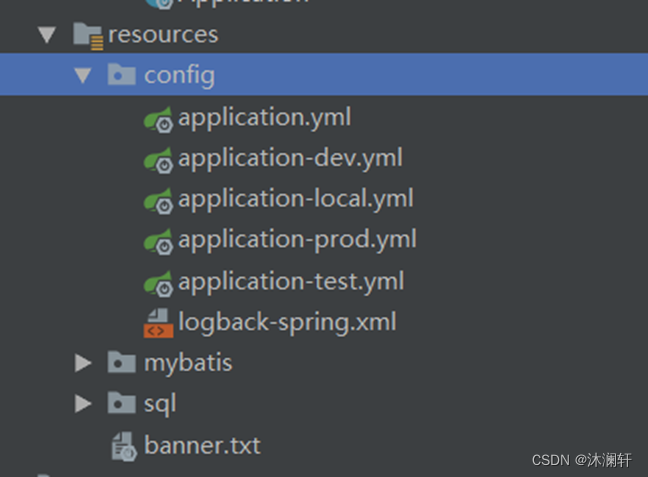
1.2. yml 配置
与 properties 文件类似,我们也可以添加 4 个配置文件:
- applcation.yml - 公共配置
- application-dev.yml - 开发环境配置
- application-test.yml - 测试环境配置
- application-prod.yml - 生产环境配置
在 applcation.yml 文件中可以通过以下配置来激活 profile:
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
此外,yml 文件也可以在一个文件中完成所有 profile 的配置:
# 激活 prod
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
# 也可以同时激活多个 profile
# spring.profiles.active: prod,proddb,prodlog
---
# dev 配置
spring:
profiles: dev
# 略去配置
---
spring:
profiles: test
# 略去配置
---
spring.profiles: prod
spring.profiles.include:
- proddb
- prodlog
---
spring:
profiles: proddb
# 略去配置
---
spring:
profiles: prodlog
# 略去配置
注意:不同 profile 之间通过 — 分割
2. 区分环境的代码
使用 @Profile 注解可以指定类或方法在特定的 Profile 环境生效。
2.1. 修饰类
@Configuration
@Profile("production")
public class JndiDataConfig {
@Bean(destroyMethod="")
public DataSource dataSource() throws Exception {
Context ctx = new InitialContext();
return (DataSource) ctx.lookup("java:comp/env/jdbc/datasource");
}
}
2.2. 修饰注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Profile("production")
public @interface Production {
}
2.3. 修饰方法
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean("dataSource")
@Profile("development")
public DataSource standaloneDataSource() {
return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder()
.setType(EmbeddedDatabaseType.HSQL)
.addScript("classpath:com/bank/config/sql/schema.sql")
.addScript("classpath:com/bank/config/sql/test-data.sql")
.build();
}
@Bean("dataSource")
@Profile("production")
public DataSource jndiDataSource() throws Exception {
Context ctx = new InitialContext();
return (DataSource) ctx.lookup("java:comp/env/jdbc/datasource");
}
}
3. 激活 profile
3.1. 插件激活 profile
spring-boot:run -Drun.profiles=prod
3.2. main 方法激活 profile
–spring.profiles.active=prod
3.3. jar 激活 profile
java -jar -Dspring.profiles.active=prod *.jar
3.4. 在 Java 代码中激活 profile
直接指定环境变量来激活 profile:
System.setProperty("spring.profiles.active", "test");
在 Spring 容器中激活 profile:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
ctx.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("development");
ctx.register(SomeConfig.class, StandaloneDataConfig.class, JndiDataConfig.class);
ctx.refresh();
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/muLanlh/article/details/135571733
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 前端框架的单文件组件(Single File Component)
- 我是如何零基础就能制作电子杂志的
- Java NIO (二)NIO Buffer类的重要方法
- 阿里云大模型数据存储解决方案,为 AI 创新提供推动力
- ros2基础学习13 DDS 通信得学习
- 购买腾讯云服务器需要多少钱?购买腾讯云服务器方法教程
- 增加SOC优化函数过程中,出现程序跑飞现象
- Qt/QML编程之路:QWidget和QOBJECT的不同之处(37)
- 无人机集群反制与对抗技术探讨
- 【elfboard linux开发板】7.i2C工具应用与aht20温湿度寄存器读取