JAVA多线程
发布时间:2023年12月17日
目录
_______________________________________________________________________
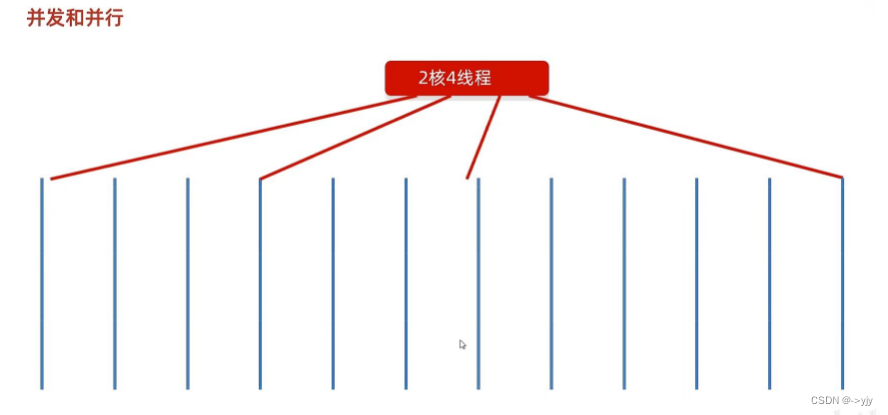
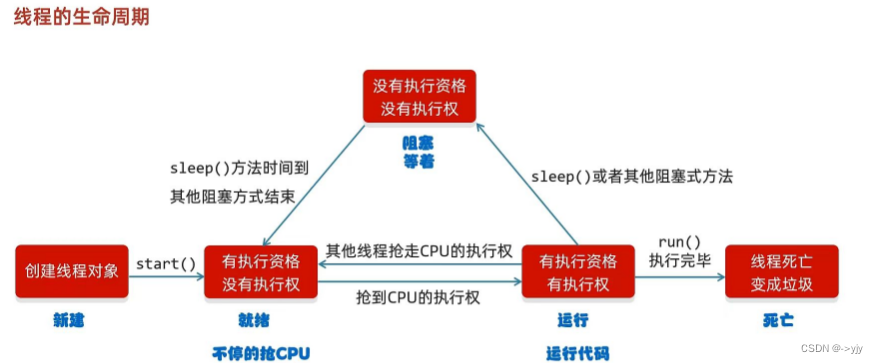
什么是多线程?

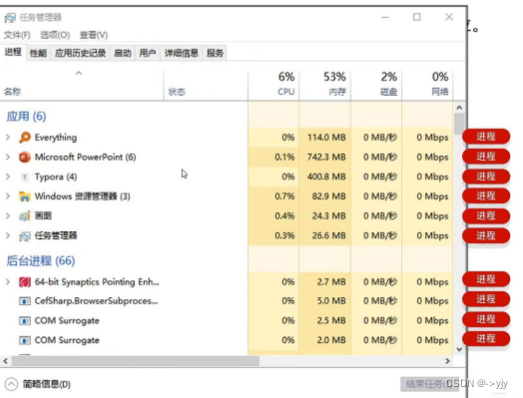

 ?
?

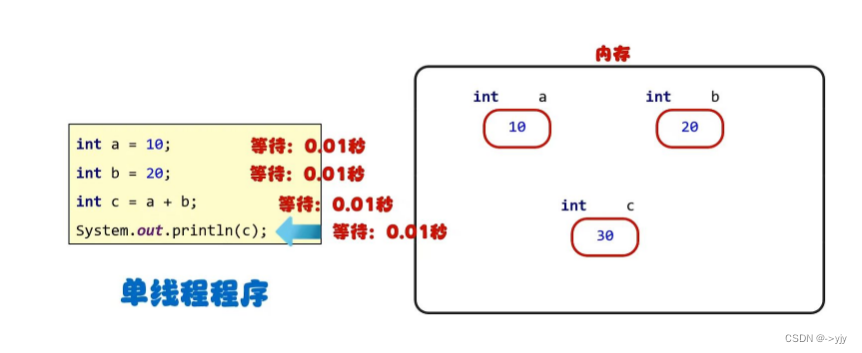
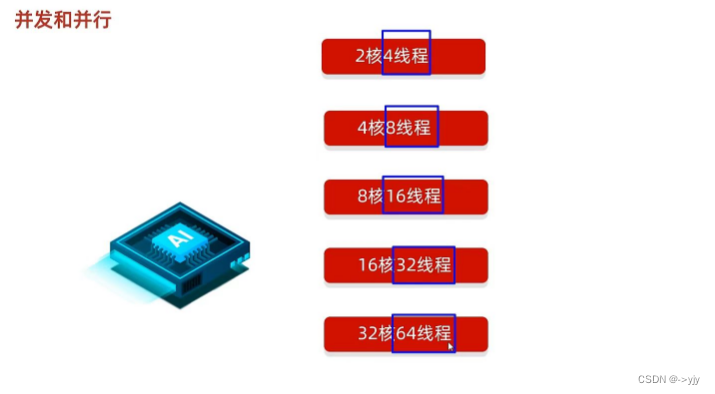
多线程的两个概念

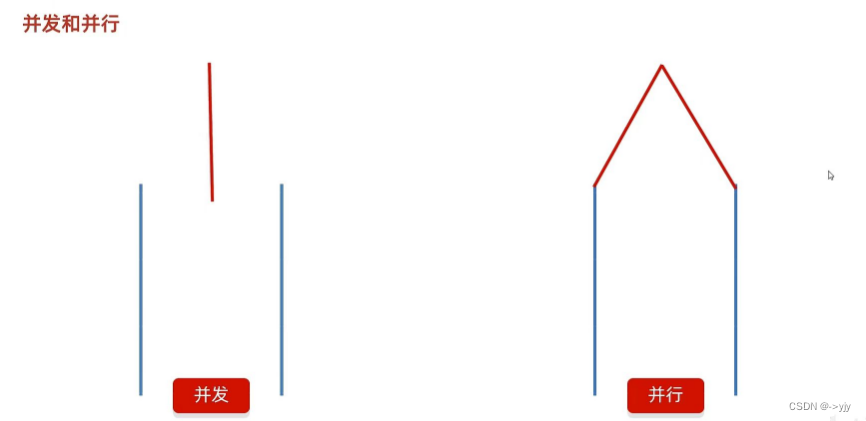 ?
?
 ?
?
多线程的实现方式


package Day22;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demoo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//多线程的第一种实现方式
/*1.自己定义一个类继承Thread
* 2.重写run方法
* 3.创建子类的对象,并启动线程*/
MyThread t1 = new MyThread();
MyThread t2 = new MyThread();
t1.setName("线程一");
t2.setName("线程二");
//开启线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}package Day22;
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
//书写线程要执行的代码
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(getName()+"Hello World");
}
}
}package Day22;
public class MyRun implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
//书写线程要执行的代码
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
//获取到当前线程的对象
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(t.getName()+"Hello World!");
}
}
}
package Day22;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demoo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* 多线程的第二种启动方式:
* 1.自己实现一个类实现Runable接口
* 2.重写里面的run方法
* 3.创建自己的类的对象
* 4.创建Thread的类的对象,并开启线程
* */
//创建MyRun的对象
//表示多线程要执行的任务
MyRun mr =new MyRun();
//创建线程对象
Thread t1 =new Thread(mr);
Thread t2 =new Thread(mr);
//给线程设置名字
t1.setName("线程一");
t2.setName("线程二");
//开启线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
package Day22;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class Demoo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
/*
* 多线程的第三种多线程实现方式:
* 特点:可以获取到多线程运行的结果
* 1.创建一个类MyCallable实现Callable接口
* 2.重写call(是有返回值的,表示多线程运行的结果)
* 3.创建MyCallable对象(表示多线程要执行的任务)
* 4.创建Futuretask对象(作用管理多线程运行的结果)
* 5.创建Thread类的对象,并启动(表示线程)
* */
MyCallable mc =new MyCallable();
FutureTask<Integer>ft =new FutureTask<>(mc);
Thread t1 =new Thread(ft);
t1.start();
//获取多线程运行的结果
Integer result = ft.get();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
package Day22;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
//求1-100之间的和
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum= sum+i;
}
return sum;
}
}
常见的成员方法

 ?
?
package Day23;
public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//
// MyThread t1 =new MyThread("飞机");
// MyThread t2 = new MyThread("坦克");
//
//
//
// t1.start();
// t2.start();
/*String getName() 返回此线程的名称
void setName(String name) 设置线程的名字(构造方法也可以)
细节:1.如果我们没有给线程设置名字,线程也是有默认的名字的
格式:Thread-X(X序号,从0开始的)
2.如果我们要给线程设置名字,可以用set方法进行设置 也可以构造方法进行设置
static Thread currentThread()获取当前线程的对象
细节:当JVM虚拟机启动之后,会自动的启动多条线程
其中有一条线程叫做main线程
他的作用就是去调用main方法,并执行里面的代码
在以前我们写的所有的代码,其实都是运行在main线程当中的
static void sleep(long time)毫秒
1秒=1000毫秒
* */
//那条线程执行到这个方法,此时获取的就是那条线程的对象
// Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// String name = t.getName();
// System.out.println(name);//main
System.out.println("1111111");
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("7777");
}
}
public class MyThread extends Thread{
public MyThread() {
}
public MyThread(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(getName()+"@"+i);
}
}
}
public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//线程的优先级
//抢占式调度---随机
//非抢占式调度---轮流
//创建线程要执行的参数对象
MyRunnable mr =new MyRunnable();
//创建线程对象
Thread t1 =new Thread("飞机");
Thread t2 =new Thread("坦克");
// System.out.println(t1.getPriority());
// System.out.println(t2.getPriority());//5
//
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getPriority());//5
//
//优先级越高执行的概率越高
t1.setPriority(1);
t2.setPriority(10);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"----"+i);
}
}
}public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//守护线程
//final void setDaemon(boolean on)设置为守护线程
//细节:当其他的非守护线程执行完毕之后,守护线程会陆续结束
//通俗易懂:当女神线程结束了,那么备胎也没有存在的必要了
MyThread1 t1 =new MyThread1();
MyThread2 t2 =new MyThread2();
t1.setName("女神");
t2.setName("备胎");
//把第二个线程设置为守护线程(备胎线程)
t2.setDaemon(true);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
public class MyThread2 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(getName()+"@"+i);
}
//表示出让当前cpu的执行权
Thread.yield();//让结果尽可能的均匀一点
}
} //public static void yield() 出让线程
MyThread2 t1 =new MyThread2();
MyThread2 t2 =new MyThread2();
t1.setName("飞机");
t2.setName("坦克");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//public static void join() 插入线程/插队线程
MyThread2 t =new MyThread2();
t.setName("土豆");
t.start();
t.join();
//执行在main线程当中的
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main线程"+i);
}
}
}?
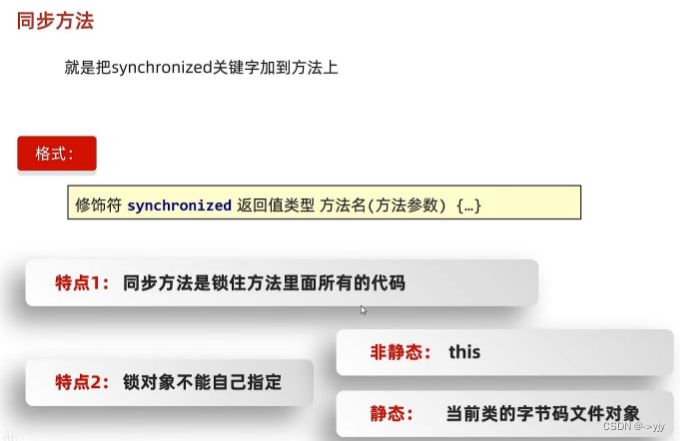
线程安全的问题

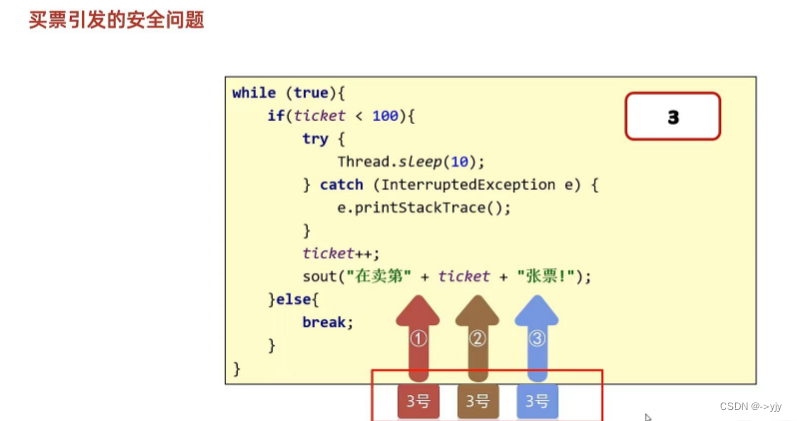 ?
?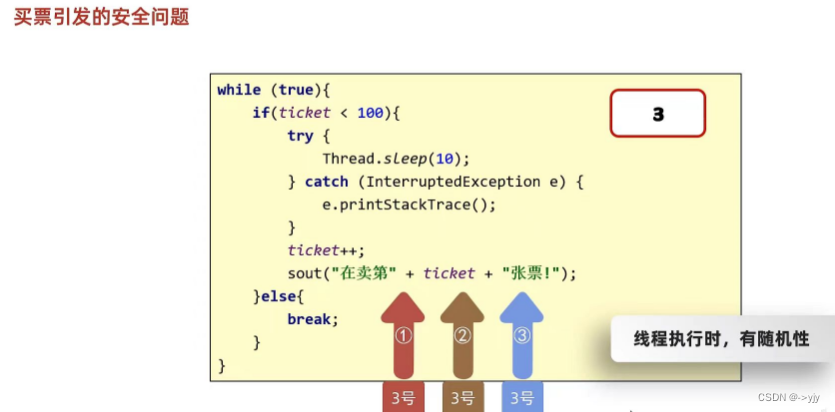
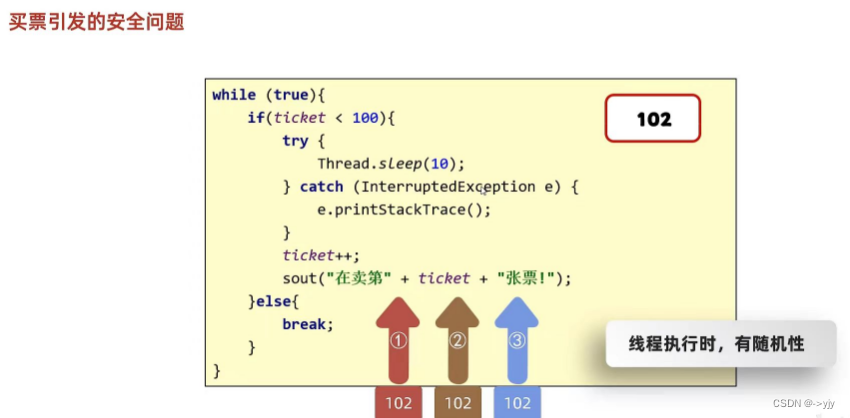
 ?
?
public class MyThread extends Thread{
static int ticket = 0;//0~99
//锁对象,一定是唯一的
//static Object obj = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
//同步代码块 字节码对象
synchronized (MyThread.class){
if(ticket<100){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
ticket++;
System.out.println(getName()+"正在卖第"+ticket+"张票!!!");
}else{
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//需求
//某电源目前正在上映国产大片,共有100张电影票
//而且它有3个窗口买票,
//请设计一个程序模拟该电影院卖票
MyThread t1 = new MyThread();
MyThread t2 = new MyThread();
MyThread t3 = new MyThread();
//起名字
t1.setName("窗口1");
t2.setName("窗口2");
t3.setName("窗口3");
//开启线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//需求
//某电源目前正在上映国产大片,共有100张电影票
//而且它有3个窗口买票,
//请设计一个程序模拟该电影院卖票
//同步方法完成
MyRunnable mr = new MyRunnable();
Thread t1 =new Thread(mr);
Thread t2 =new Thread(mr);
Thread t3 =new Thread(mr);
t1.setName("窗口1");
t2.setName("窗口2");
t3.setName("窗口3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
//StringBuffer用在多线程中更安全 相比StringBuilder
//因为StringBuffer底层全部都用了synchronized
}
}public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
int ticket =0;
@Override
public void run() {
//1.循环
//2.同步代码(同步方法)
//3.判断共享数据是否到了末尾,如果到了末尾
//4.判断共享数据是否到了末尾,如果没有到末尾
while(true){
if (method()) break;
}
}
//非静态 this -->测试类的mr
private synchronized boolean method() {
if(ticket==100){
return true;
}else{
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
ticket++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"在卖第"+ticket+"张票!!!");
}
return false;
}
}?
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
static int ticket = 0;//0~99
static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//锁对象,一定是唯一的
//static Object obj = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
//同步代码块 字节码对象
//synchronized (MyThread.class){
lock.lock();
try {
if (ticket == 100) {
break;
//break直接出循环 最后一次元素带着锁对象出循环
} else {
Thread.sleep(100);
ticket++;
System.out.println(getName() + "正在卖第" + ticket + "张票!!!");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
//}
}
}
}
public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//需求
//某电源目前正在上映国产大片,共有100张电影票
//而且它有3个窗口买票,
//请设计一个程序模拟该电影院卖票
MyThread t1 = new MyThread();
MyThread t2 = new MyThread();
MyThread t3 = new MyThread();
//起名字
t1.setName("窗口1");
t2.setName("窗口2");
t3.setName("窗口3");
//开启线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
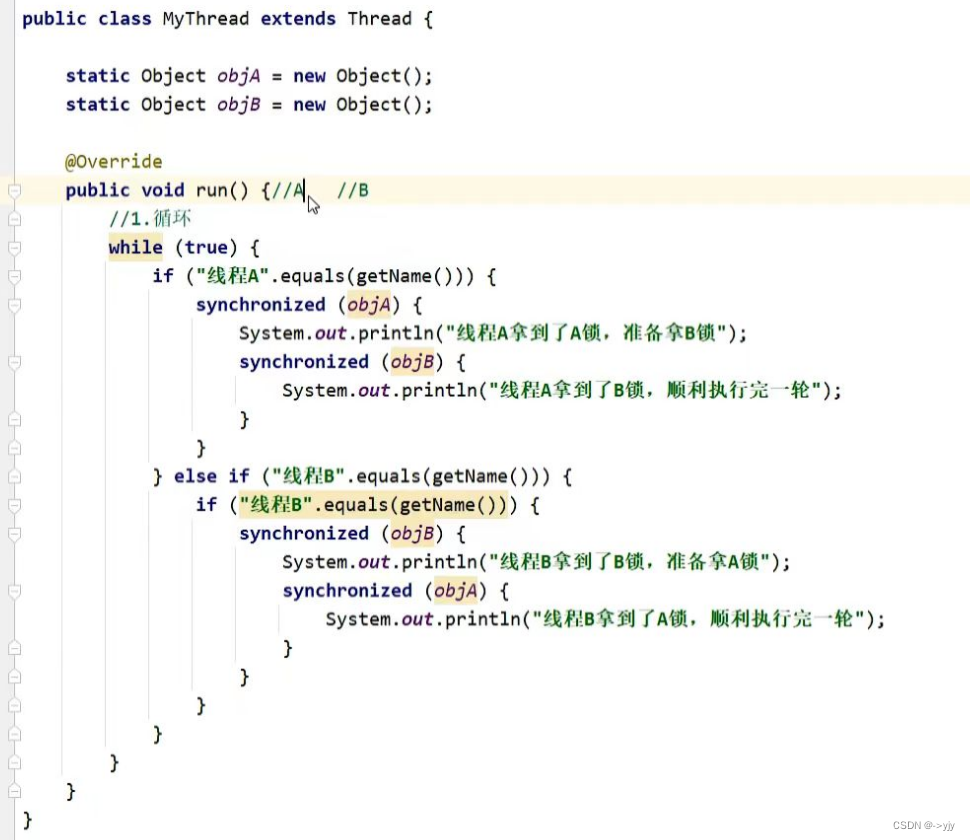
}死锁(是一个错误,避免写死锁)
核心:不要让锁嵌套

 ?
?
 ?
?
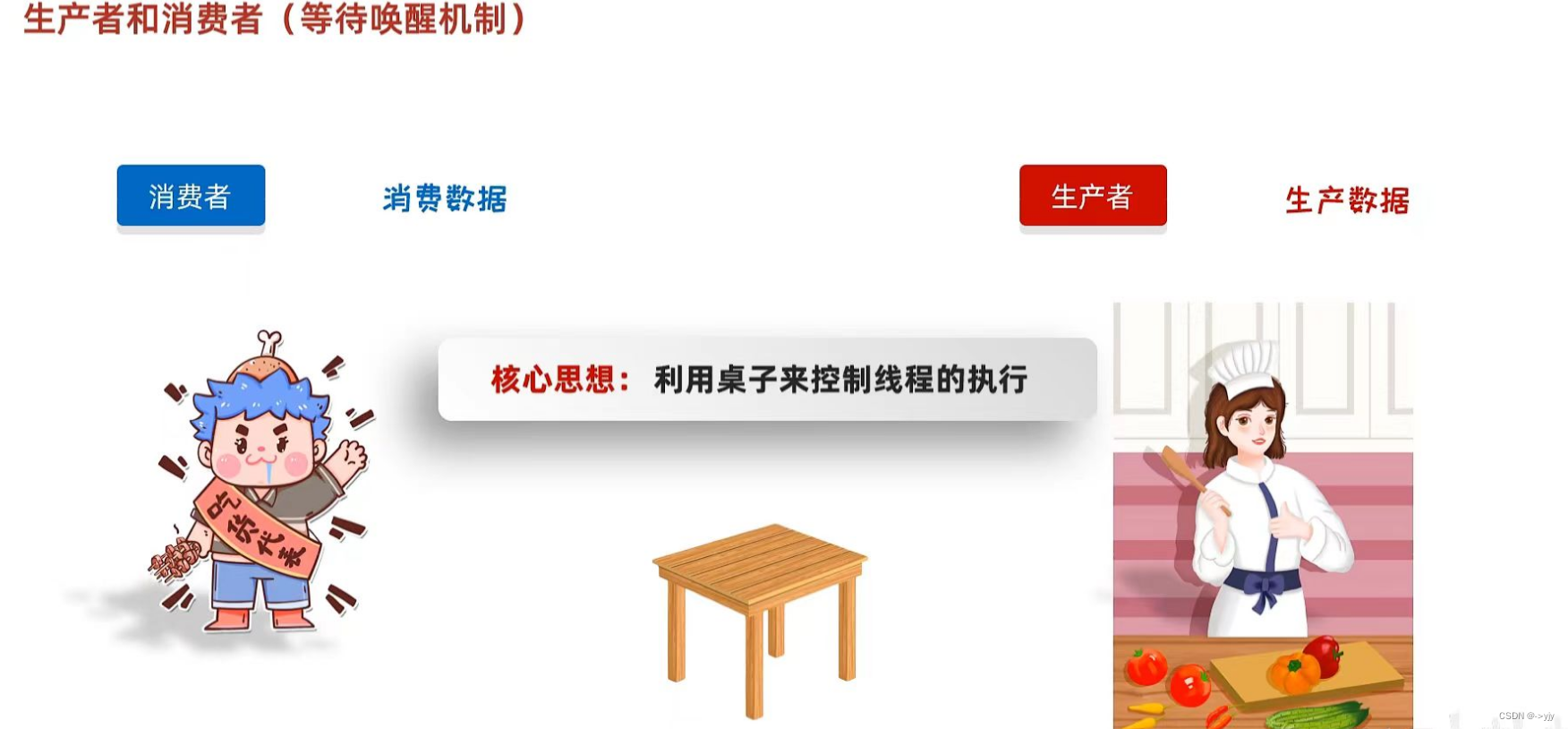
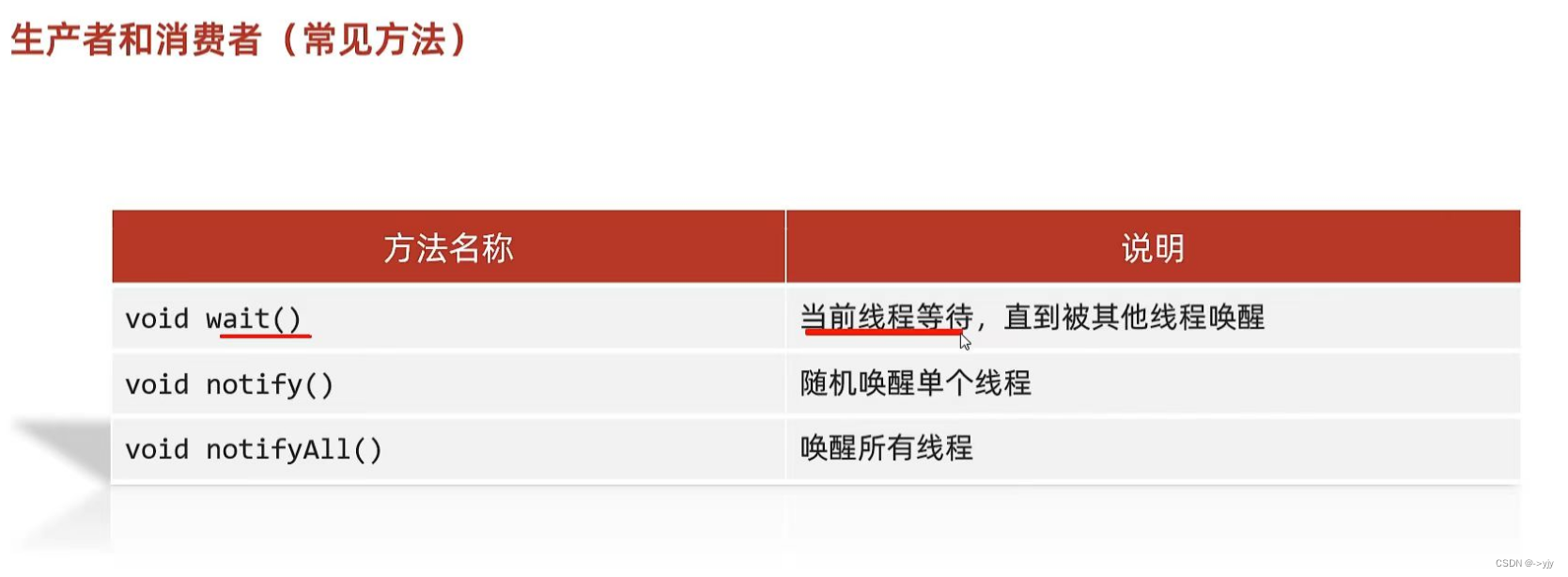
生产者和消费者
 ?
?
 ?
?
 ?
?
 ?
?
public class Foodie extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
/*
* 1. 循环
* 2. 同步代码块
* 3. 判断共享数据是否到了末尾(到了末尾)
* 4. 判断共享数据是否到了末尾(没有到末尾,执行核心逻辑)
* */
while(true){
synchronized (Desk.lock){
if(Desk.count == 0){
break;
}else{
//先判断桌子上是否有面条
if(Desk.foodFlag == 0){
//如果没有,就等待
try {
Desk.lock.wait();//让当前线程跟锁进行绑定
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
//把吃的总数-1
Desk.count--;
//如果有,就开吃
System.out.println("吃货在吃面条,还能再吃" + Desk.count + "碗!!!");
//吃完之后,唤醒厨师继续做
Desk.lock.notifyAll();
//修改桌子的状态
Desk.foodFlag = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
public class Desk {
/*
* 作用:控制生产者和消费者的执行
*
* */
//是否有面条 0:没有面条 1:有面条
public static int foodFlag = 0;
//总个数
public static int count = 10;
//锁对象
public static Object lock = new Object();
}public class Cook extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
/*
* 1. 循环
* 2. 同步代码块
* 3. 判断共享数据是否到了末尾(到了末尾)
* 4. 判断共享数据是否到了末尾(没有到末尾,执行核心逻辑)
* */
while (true){
synchronized (Desk.lock){
if(Desk.count == 0){
break;
}else{
//判断桌子上是否有食物
if(Desk.foodFlag == 1){
//如果有,就等待
try {
Desk.lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
//如果没有,就制作食物
System.out.println("厨师做了一碗面条");
//修改桌子上的食物状态
Desk.foodFlag = 1;
//叫醒等待的消费者开吃
Desk.lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}
}
}
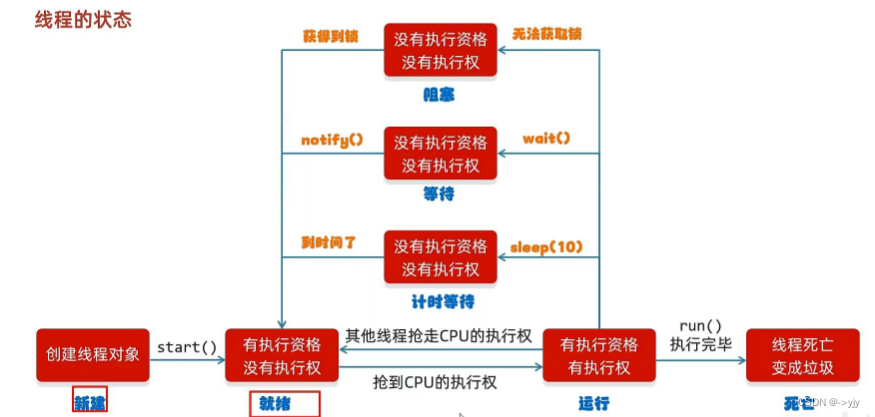
?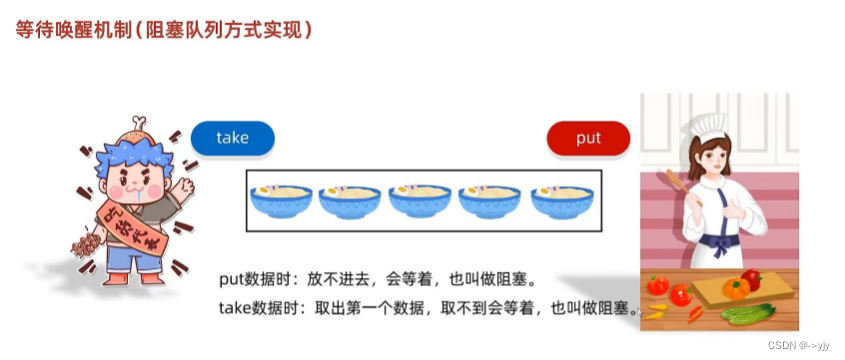
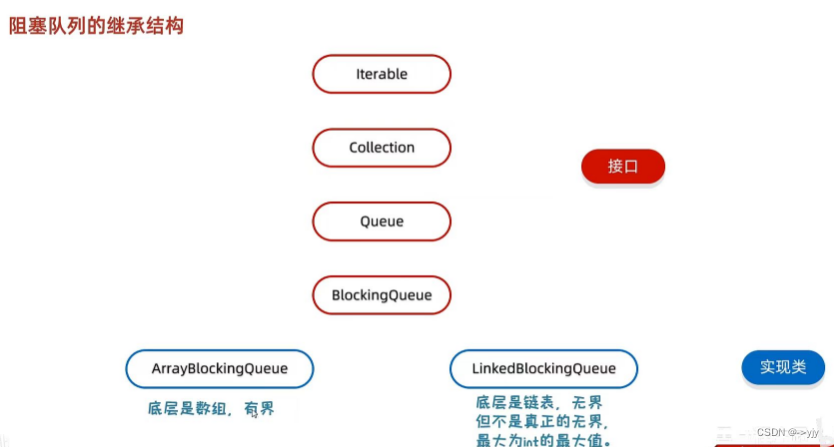 ?
?
 ?
?
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
*
* 需求:利用阻塞队列完成生产者和消费者(等待唤醒机制)的代码
* 细节:
* 生产者和消费者必须使用同一个阻塞队列
*
* */
//1.创建阻塞队列的对象
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1);
//2.创建线程的对象,并把阻塞队列传递过去
Cook c = new Cook(queue);
Foodie f = new Foodie(queue);
//3.开启线程
c.start();
f.start();
}
}import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Cook extends Thread{
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue;
public Cook(ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
//不断的把面条放到阻塞队列当中
try {
queue.put("面条");
System.out.println("厨师放了一碗面条");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Foodie extends Thread{
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue;
public Foodie(ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
//不断从阻塞队列中获取面条
try {
String food = queue.take();
System.out.println(food);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
static int ticket = 0;//0~999
static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();//实现类
//锁对象,一定是唯一的
//static Object obj = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
//同步代码块 字节码对象
//synchronized (MyThread.class){
lock.lock();
try {
if (ticket == 1000) {
break;
//break直接出循环 最后一次元素带着锁对象出循环
} else {
Thread.sleep(3000);
ticket++;
System.out.println(getName() + "正在卖第" + ticket + "张票!!!");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/*一个有1000张电影票,可以在两个窗口领取,假设每次领取的时间为3000毫秒
* 要求:请用户多线程模拟买票的过程并打印剩余电影票的数量*/
MyThread t1 =new MyThread();
MyThread t2 =new MyThread();
t1.setName("窗口一");
t2.setName("窗口二");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
 ?
?
public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread t1 = new MyThread();
MyThread t2 = new MyThread();
t1.setName("星光");
t2.setName("流星");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
static int gifts =100;
static Lock lock =new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
if(gifts<10){
break;
}else{
lock.lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
gifts--;
System.out.println(getName()+"礼物还剩下"+gifts+"份");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
}

?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
同时开启两个线程,共同获取1-100之间的所有数字。
要求:将输出所有的奇数。
*/
//创建参数对象
MyRunable mr = new MyRunable();
//创建线程对象
Thread t1 = new Thread(mr,"线程A");
Thread t2 = new Thread(mr,"线程B");
//启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}?
public class MyRunable implements Runnable {
//第二种方式实现多线程,测试类中MyRunable只创建一次,所以不需要加static
int number = 1;
@Override
public void run() {
//1.循环
while (true) {
//2.同步代码块
synchronized (MyThread.class) {
//3.判断共享数据(已经到末尾)
if (number > 100) {
break;
} else {
//4.判断共享数据(没有到末尾)
if(number % 2 == 1){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "打印数字" + number);
}
number++;
}
}
}
}
} ?
?
import java.util.Random;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
//共享数据
static double money =100;
static int count =3;
//最小的金额
static final double MIN =0.01;
@Override
public void run() {
//循环
//同步代码块
synchronized (MyThread.class){
if(count==0){
//判断,共享数据是否到了末尾(已经到末尾)
System.out.println(getName()+"没有抢到红包!");
}else{
//判断,共享数据(没有到末尾)
//不能直接随机
//定义一个变量,表示中奖的金额
double prize=0;
if(count==1){
//表示此时是最后一个红包
//就无序随机 剩余所有的钱都是中奖金额
prize = money;
}else{
//表示第一第二次的中奖情况
Random r = new Random();
//100元 3个包
//第一个红包 99.98
//100-(3-1)*0.01
double bounds = money - (count - 1) * MIN;
prize = r.nextDouble(bounds);//JDK17
if(prize<MIN){
prize = MIN;
}
}
//从money中,去掉当前中奖的金额
money = money-prize;
//红包个数--
count--;
//本次红包的信息进行打印
System.out.println(getName()+"抢到了"+prize+"元");
}
}
}
}
public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建线程的对象
MyThread t1 =new MyThread();
MyThread t2 =new MyThread();
MyThread t3 =new MyThread();
MyThread t4 =new MyThread();
MyThread t5 =new MyThread();
//给线程设置名字
t1.setName("小A");
t2.setName("小B");
t3.setName("小C");
t4.setName("小D");
t5.setName("小E");
//启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
t5.start();
}
}?

?
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
//共享数据
//集合
ArrayList<Integer>list;
public MyThread(ArrayList<Integer> list) {
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
synchronized (MyThread.class){
if(list.size()==0){
break;
}else{
Collections.shuffle(list);
Integer integer = list.get(0);
Integer prize = list.remove(0);
System.out.println(getName()+"又产生了一个"+prize+"元的大奖");
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
?
public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//抽奖箱抽奖
//创建奖池
ArrayList<Integer>list =new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,10,5,20,50,100,200,500,800,2,80,300,700);
//创建线程
MyThread t1 =new MyThread(list);
MyThread t2 =new MyThread(list);
t1.setName("抽奖箱1");
t2.setName("抽奖箱2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//抽奖箱抽奖
//创建奖池
ArrayList<Integer>list =new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,10,5,20,50,100,200,500,800,2,80,300,700);
//创建线程
MyThread t1 =new MyThread(list);
MyThread t2 =new MyThread(list);
t1.setName("抽奖箱1");
t2.setName("抽奖箱2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
?
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
//共享数据
//集合
ArrayList<Integer>list;
public MyThread(ArrayList<Integer> list) {
this.list = list;
}
//线程一所使用的集合
static ArrayList<Integer>list1=new ArrayList<>();
//线程二所使用的集合
static ArrayList<Integer>list2=new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
synchronized (MyThread.class){
if(list.size()==0){
if("抽奖箱1".equals(getName())){
System.out.println("抽奖箱1"+list1);
}else{
System.out.println("抽奖箱2"+list2);
}
break;
}else{
Collections.shuffle(list);
int prize = list.remove(0);
// System.out.println(getName()+"又产生了一个"+prize+"元的大奖");
if("抽奖箱1".equals(getName())){
list1.add(prize);
}else{
list2.add(prize);
}
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
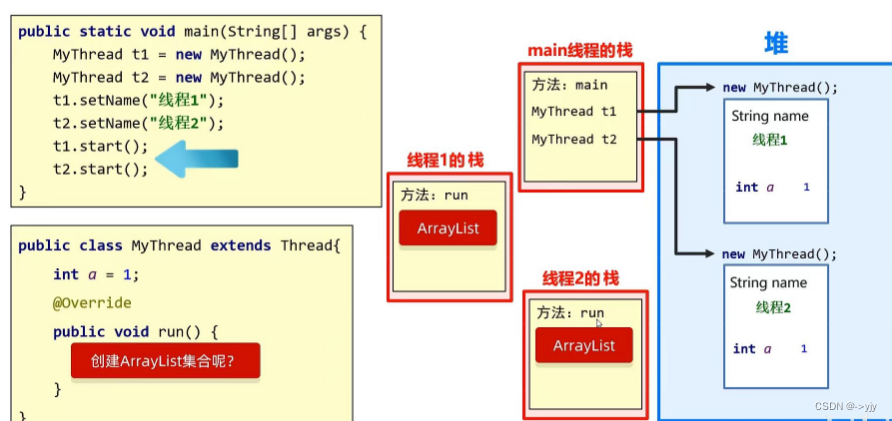 ?
?
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class DUOXIANCHENG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//抽奖箱抽奖
//创建奖池
ArrayList<Integer>list =new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,10,5,20,50,100,200,500,800,2,80,300,700);
//创建多线程要运行的参数对象
MyCallable mc =new MyCallable(list);
//创建多线程运行结果的管理者对象
//线程一
FutureTask<Integer>ft1 =new FutureTask<>(mc);
//线程二
FutureTask<Integer>ft2 =new FutureTask<>(mc);
//创建线程
Thread t1 =new Thread(ft1);
Thread t2 =new Thread(ft2);
//设置名字
t1.setName("抽奖箱1");
t2.setName("抽奖箱2");
//开启线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
Integer max1 = ft1.get();
Integer max2 = ft2.get();
System.out.println(max1);
System.out.println(max2);
}
}?
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
//核心逻辑:线程获取的最大值(看成是线程运行的结果)
public class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer> {
//共享数据
//集合
ArrayList<Integer> list;
public MyCallable(ArrayList<Integer> list) {
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
ArrayList<Integer> boxList = new ArrayList<>();//每个线程都有自己的集合
while (true) {
synchronized (MyCallable.class) {
if (list.size() == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + boxList);
break;
} else {
Collections.shuffle(list);
int prize = list.remove(0);
boxList.add(prize);
}
}
Thread.sleep(10);//因为call方法可以抛出异常
}
// 把集合中的最大值返回
if(boxList.size()==0){
return null;
}else{
return Collections.max(boxList);
}
}
}线程池

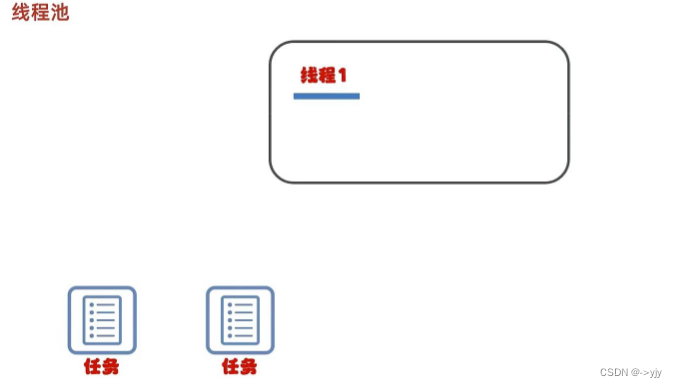 ?
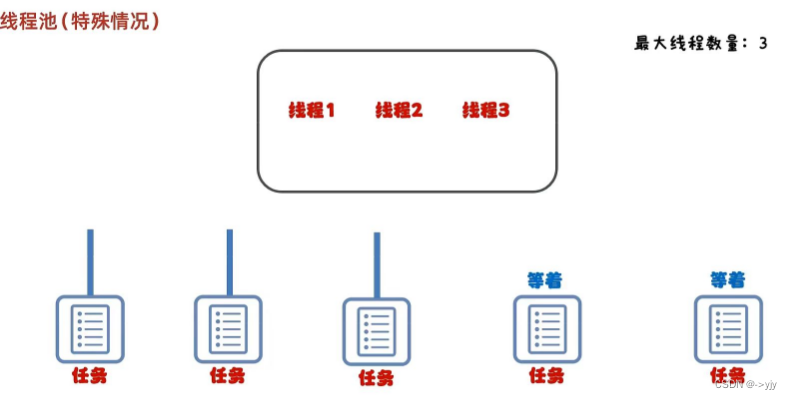
?
 ?
?
 ?
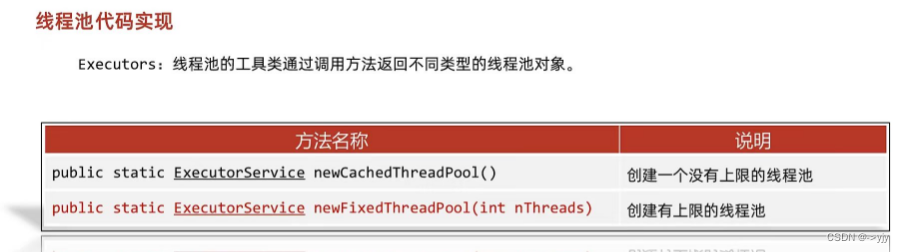
?
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---" + i);
}
}
}public class MyThreadPoolDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/*
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() 创建一个没有上限的线程池
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool (int nThreads) 创建有上限的线程池
*/
//1.获取线程池对象
ExecutorService pool1 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
//2.提交任务
pool1.submit(new MyRunnable());
pool1.submit(new MyRunnable());
pool1.submit(new MyRunnable());
pool1.submit(new MyRunnable());
pool1.submit(new MyRunnable());
pool1.submit(new MyRunnable());
//3.销毁线程池
//pool1.shutdown();
}
}
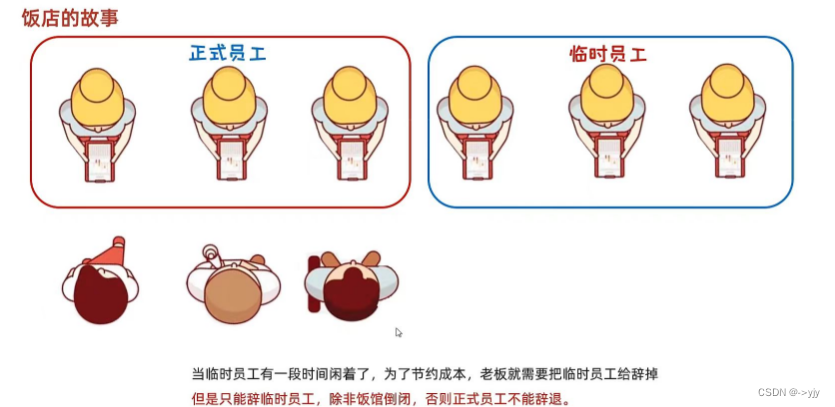
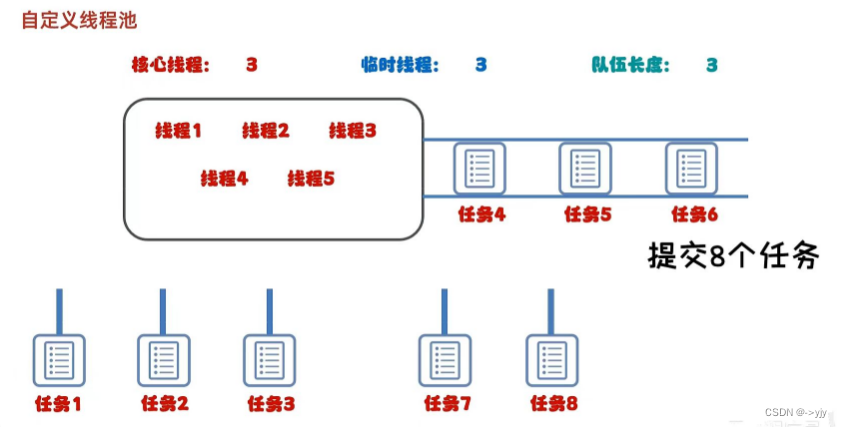
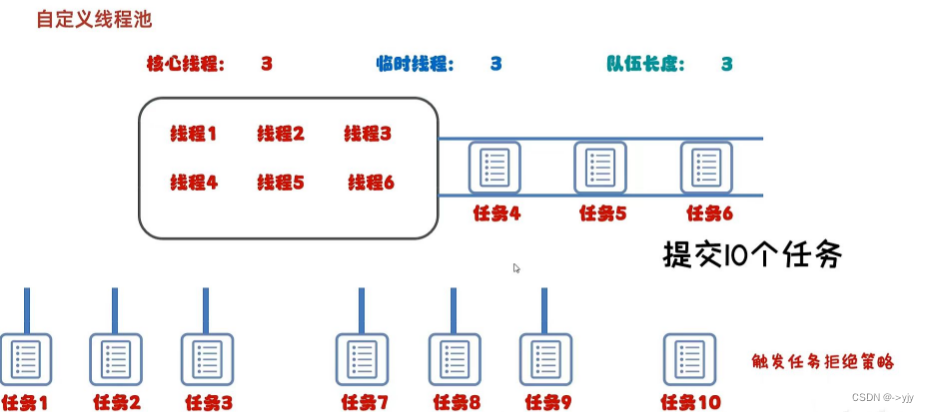
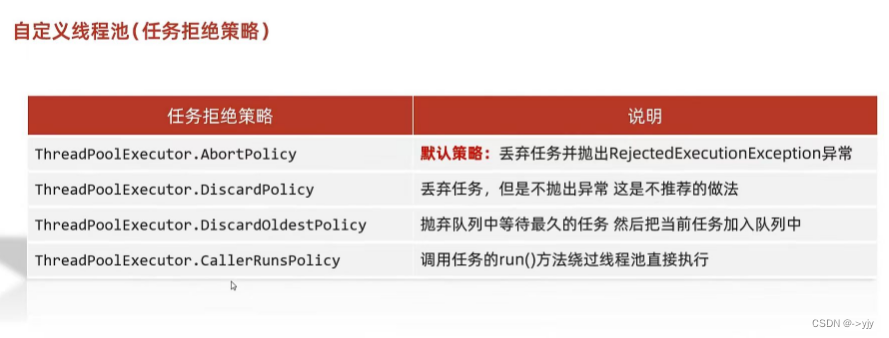
自定义线程池

 ?
?
 ?
?
 ?
?
 ?
?
 ?
?
?
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class MyThreadPoolDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
/*
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor
(核心线程数量,最大线程数量,空闲线程最大存活时间,任务队列,创建线程工厂,任务的拒绝策略);
参数一:核心线程数量 不能小于0
参数二:最大线程数 不能小于0,最大数量 >= 核心线程数量
参数三:空闲线程最大存活时间 不能小于0
参数四:时间单位 用TimeUnit指定
参数五:任务队列 不能为null
参数六:创建线程工厂 不能为null
参数七:任务的拒绝策略 不能为null
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
3, //核心线程数量,不能小于0
6, //最大线程数,不能小于0,最大数量 >= 核心线程数量
60,//空闲线程最大存活时间
TimeUnit.SECONDS,//时间单位
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3),//任务队列
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),//创建线程工厂
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()//任务的拒绝策略
);
pool.submit()
}
}?
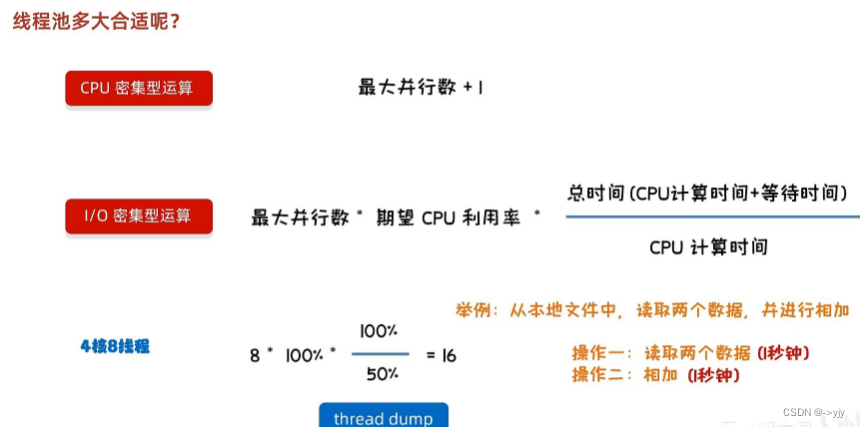
public class MyThreadPoolDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//向Java虚拟机返回可用处理器的数目
int count = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
System.out.println(count);
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_79602614/article/details/135038064
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 开发常用的核验类API,含免费次数
- 力扣hot100 多数元素 摩尔投票
- 【Spring-Securty】安全框架使用详解
- Vue.js轻量级框架:快速搭建可扩展的管理系统
- 静态网页设计实践(HTML+CSS)
- 重磅发布|2023年度中国可观测性现状调研报告发布
- SwiftUI 打造一款可收缩的 HStack(二):对齐+ZStack
- Vue3 中 ref和reactive的区别是什么?
- streamlit设置sidebbar和页面背景
- “SRP模型+”多技术融合在生态环境脆弱性评价模型构建、时空格局演变分析与RSEI 指数的生态质量评价及拓展应用