vue-property-decorator 源码解析
前言
在使用 vue-class-components 构建 Vue 组件时,像 watch 、props 等属性还是需要写在 @Component 中。
@Component({
watch: {
postId(id: string) {
// To fetch post data when the id is changed.
this.fetchPost(id) // -> Property 'fetchPost' does not exist on type 'Vue'.
},
},
})
class Post extends Vue {
postId: string
fetchPost(postId: string): Promise<void> {
// ...
}
}
这相当于还是 options api的写法。为了风格统一,一般会配合 vue-property-decorator 使用装饰器去实现 watch 等功能。
@Component
export default class Post extends Vue {
postId: string
fetchPost(postId: string): Promise<void> {
// ...
}
@Watch('postId')
onPostIdWatcher(val: string) {
// ...
}
}
本文将详细讲解 vue-property-decorator 中 Api 的实现。
createDecorator
在此之前,先介绍一下 createDecorator 这个函数。它会将所有的装饰器存储到构造函数的 __decorators__ 属性中。 在实例化的时候,在进行统一调度从而对 options 的值进行修饰。
以下是 createDecorator 的实现源码:
export function createDecorator(
factory: (options: ComponentOptions<Vue>, key: string, index: number) => void
): VueDecorator {
return (target: Vue | typeof Vue, key?: any, index?: any) => {
// 获取构造函数
const Ctor =
typeof target === 'function'
? (target as DecoratedClass)
: (target.constructor as DecoratedClass)
// 如果没有__decorators__属性,就创建一个
if (!Ctor.__decorators__) {
Ctor.__decorators__ = []
}
if (typeof index !== 'number') {
index = undefined
}
// 将装饰器函数添加到__decorators__数组中
Ctor.__decorators__.push((options) => factory(options, key, index))
}
}
在 vue 实例化的时候,会执行这样的操作:
// decorate options
const decorators = (Component as DecoratedClass).__decorators__
if (decorators) {
// 这里的options 会含有 prop mixins computed 等相关的属性,也是 vue 实例化所需要的属性
// 因此在 createDecorator中,可以拿到 在实例化期间的options 并且进行修饰
decorators.forEach((fn) => fn(options))
delete (Component as DecoratedClass).__decorators__
}
VModel
VModel 装饰器主要用于在 props 中声明 value,并且在 value 改变的时候 emit 一个 input 事件。(参考 v-model)
🌰 如下:
<template>
<!-- Child.vue -->
<div>
<input v-model="val" />
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { Component, Vue, VModel } from 'vue-property-decorator'
@Component
export default class Child extends Vue {
@VModel({ type: String }) public val!: string
}
</script>
<template>
<!-- App.vue -->
<div id="app">
<Child v-model="msg" />
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { Component, Vue } from 'vue-property-decorator'
import Child from './components/Child.vue'
@Component({
components: {
Child,
},
})
export default class App extends Vue {
msg = 'hello word'
}
</script>
可以看到使用了 VModel 修饰了 val 属性,在它改变的时候会触发 input 事件,并且注册了 value 属性在 props 中。
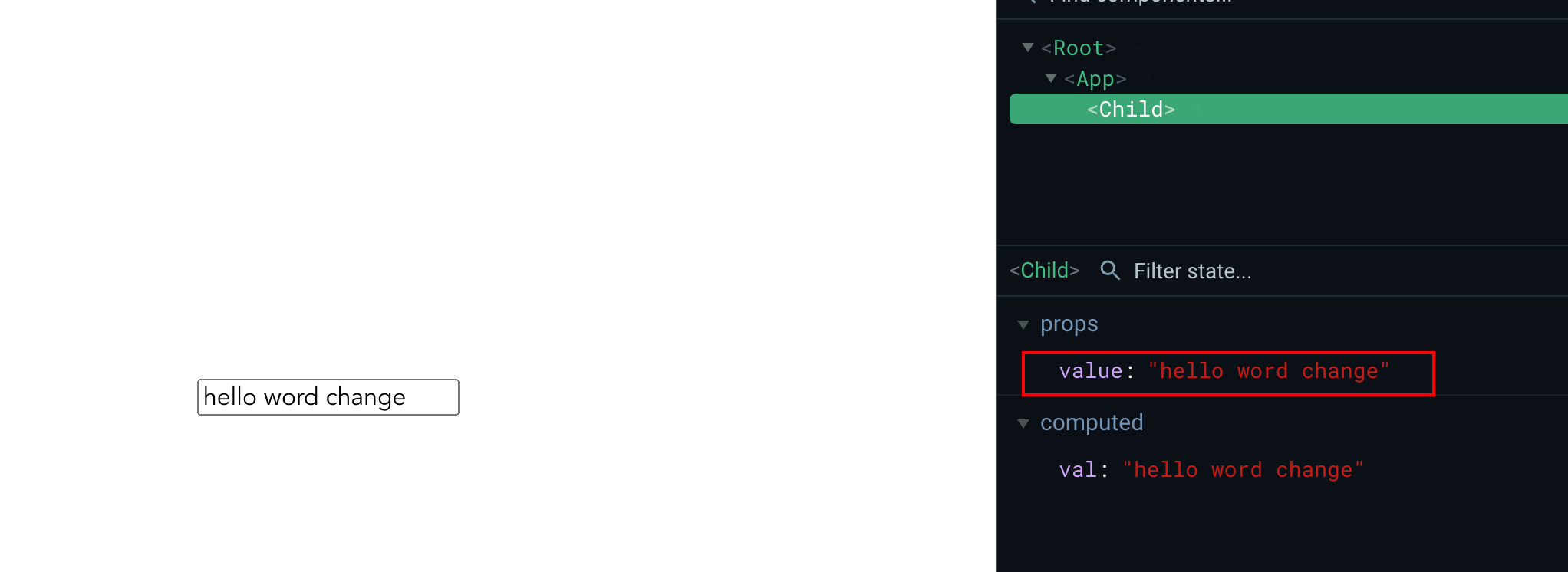
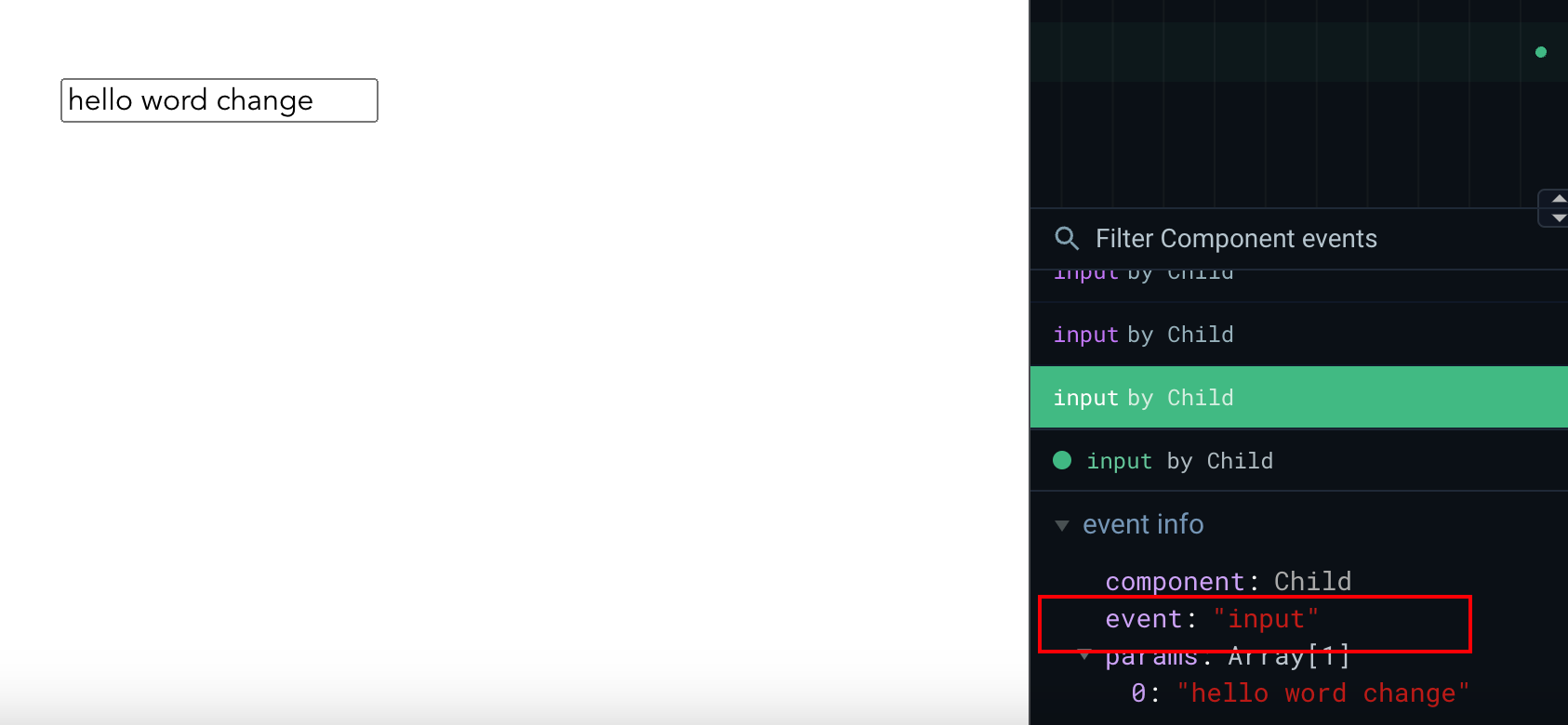
下面将探究一下 VModel 的实现:
import { PropOptions } from 'vue'
import { createDecorator } from 'vue-class-component'
export const vModal = function (options: PropOptions) {
// 设置到 props 中的 key
const valueKey = 'value'
return createDecorator((componentOptions, key) => {
// 判断是否有 props 没有则初始化
;(componentOptions.props || ((componentOptions.props = {}) as any))[
valueKey
] = options
// 将当前 VModel 修饰的属性值定义到 computed 中。
// get的时候取 props.value
// set的时候 emit input 事件
;(componentOptions.computed || (componentOptions.computed = {}))[key] = {
get() {
return Reflect.get(this, valueKey)
},
set(this: Vue, value: any) {
this.$emit('input', value)
},
}
})
}
拓展 VModel 实现 async 语法糖
可以对 VModel 进行深层次的拓展,使其支持 :visible.sync 的写法
这也是
PropsSync装饰器的功能。
// VSync.ts
import { PropOptions } from 'vue'
import { createDecorator } from 'vue-class-component'
export const VSync = (options: PropOptions, propsKey: string) => {
return createDecorator((componentOptions, key) => {
;(componentOptions.props || ((componentOptions.props = {}) as any))[
propsKey
] = options
;(componentOptions.computed || (componentOptions.computed = {}))[key] = {
get() {
return Reflect.get(this, propsKey)
},
set(this: Vue, value: any) {
this.$emit(`update:${propsKey}`, value)
},
}
})
}
<template>
<!-- App.vue -->
<div id="app">
<Child v-model="msg" :visible.sync="visible" />
App visible : {{ visible }}
</div>
</template>
<template>
<!-- Child.vue -->
<div>
<!-- 现在可以通过改变 vis 的值 去emit `update:visible` 事件 -->
<button @click="vis = !vis">click</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { Component, Vue } from 'vue-property-decorator'
import { VSync } from '@/decorator/vSync'
@Component
export default class Child extends Vue {
@VSync({ type: Boolean }, 'visible') public vis!: boolean
}
</script>
Prop
Prop 装饰器用于声明哪些属性是需要父组件传递的。
基本用法:
@Component
class Test extends Vue {
@Prop({ default: value }) [propertyName]!: string
}
实现原理:
通过
createDecorator将修改的函数注册到Ctor.__decorators__中,通过修饰的key的属性 将他设置到props上。
// 简略实现过程如下
import { PropOptions } from 'vue'
import { createDecorator } from 'vue-class-component'
export const Props = (options: PropOptions) => {
// 这里需要拿到修饰的 key
return (target: Vue, key: string) => {
createDecorator((componentOptions, k) => {
// 处理option 将 key 绑定到 props 属性中
;(componentOptions.props || ((componentOptions.props = {}) as any))[k] =
options
})(target, key)
}
}
Watch
基本使用:
@Component
export default class Child extends Vue {
@VProps({ type: Boolean, default: true }) visible!: boolean
public dataSource = { total: 0 }
handleAdd() {
this.dataSource.total++
}
@Watch('dataSource.total', { immediate: true })
totalWatcher(total: number) {
console.log(total)
}
}
实现原理:
/**
* @param path 需要监听的路径属性 e.g: dataSource.total
* @param watchOptions e.g: { deep: true, immediate: true }
*/
export function Watch(path: string, watchOptions: WatchOptions = {}) {
// 由于修饰的是方法 因此第二个参数会是方法名,是一个 string
return createDecorator((componentOptions, handler) => {
componentOptions.watch ||= Object.create(null)
const watch: any = componentOptions.watch
// 修改 watch[path] 的方式 使用数组存储
if (typeof watch[path] === 'object' && !Array.isArray(watch[path])) {
watch[path] = [watch[path]]
} else if (typeof watch[path] === 'undefined') {
watch[path] = []
}
watch[path].push({ handler, ...watchOptions })
})
}
Ref
Ref 也是通过将属性设置在 computed 中来通过 getter 获取值
export function Ref(refKey?: string) {
return createDecorator((options, key) => {
options.computed = options.computed || {}
options.computed[key] = {
cache: false,
get(this: Vue) {
return this.$refs[refKey || key]
},
}
})
}
Provide/Inject
provide 的实现如下:
export function Provide(key?: string | symbol) {
return createDecorator((componentOptions, k) => {
let provide: any = componentOptions.provide
// 初始化 inject 属性
inheritInjected(componentOptions)
// 判断是否存在 managed managedReactive 以及 provide 是否是一个 function
// 若果不是 则构造provide 并且此函数上还含有managed managedReactive 属性
if (needToProduceProvide(provide)) {
provide = componentOptions.provide = produceProvide(provide)
}
// 需要provide的属性值 使用 value 存储
provide.managed[k] = key || k
})
}
而 ProvideReactive 与 provide 的实现基本一摸一样,只是将 存储的属性从managed 改成了 managedReactive
export function ProvideReactive(key?: string | symbol) {
return createDecorator((componentOptions, k) => {
let provide: any = componentOptions.provide
inheritInjected(componentOptions)
if (needToProduceProvide(provide)) {
provide = componentOptions.provide = produceProvide(provide)
}
- provide.managed[k] = key || k
+ provide.managedReactive[k] = key || k
})
}
这里的写法与 provide 的初始化有关, 在 vue 源码中,provide 支持 Function 初始化
源代码在 vue 仓库的 src/core/instance/inject.ts
export function initProvide(vm: Component) {
const provideOption = vm.$options.provide
if (provideOption) {
// provide = componentOptions.provide = produceProvide(provide) 这一步已经会将 provide修改成一个 Function,因此这里会走 provideOption.call(vm)
const provided = isFunction(provideOption)
? provideOption.call(vm)
: provideOption
if (!isObject(provided)) {
return
}
const source = resolveProvided(vm)
const keys = hasSymbol ? Reflect.ownKeys(provided) : Object.keys(provided)
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
const key = keys[i]
Object.defineProperty(
source,
key,
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(provided, key)!
)
}
}
provideOption 实际就是 produceProvide(provide) 所产生的返回值。
接下来看下 produceProvide 的函数的执行过程:
源代码在 vue-property-decorator 的 src/helpers/provideInject.ts
// provideOption 实际就是 pro
export function produceProvide(original: any) {
// 这里的 this 就是 上面的 provideOption.call(vm) 的 vm
let provide: ProvideFunc = function (this: any) {
let rv = typeof original === 'function' ? original.call(this) : original
// 如果不是通过装饰器创建的 而是原 provide 声明的, 这里使用 原型链的方式去实现整合 provider
rv = Object.create(rv || null)
// 这里设置响应式的provider的属性
// set reactive services (propagates previous services if necessary)
rv[reactiveInjectKey] = Object.create(this[reactiveInjectKey] || {})
for (let i in provide.managed) {
// 将 provide.managed[k] = key || k 存储的key 和 vm实例上的值存储到 rv 中
rv[provide.managed[i]] = this[i]
}
// 这里是响应式的转换过程
for (let i in provide.managedReactive) {
rv[provide.managedReactive[i]] = this[i] // Duplicates the behavior of `@Provide`
Object.defineProperty(rv[reactiveInjectKey], provide.managedReactive[i], {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: () => this[i],
})
}
// 最后 将 rv 返回 作为 provide 的值
return rv
}
provide.managed = {}
provide.managedReactive = {}
return provide
}
因此总体的执行顺序就是:
- 使用装饰器改变 vue 实例化的时 provide 的属性时,替换
options.provider为一个函数,并且设置managed、managedReactive两个静态属性以供装饰器实现 provide - 在 vue
initProvider的过程中,调用了options.provider函数,将装饰器设置的provider与原有写法的provider进行一个整合实现最终的provider。
而 inject 的实现就是常规使用 createDecorator 实现即可。
export function Inject(options?: InjectOptions | InjectKey) {
return createDecorator((componentOptions, key) => {
if (typeof componentOptions.inject === 'undefined') {
componentOptions.inject = {}
}
if (!Array.isArray(componentOptions.inject)) {
componentOptions.inject[key] = options || key
}
})
}
而 InjectReactive 的代码会比较多一点,因为 Provide装饰器在执行时还调用了 inheritInjected 这个方法。
// 这里进行了
// options.inject['__reactiveInject__'] = {from: "__reactiveInject__", default:{}}
// 这样的初始化操作
export function inheritInjected(componentOptions: ComponentOptions<Vue>) {
// inject parent reactive services (if any)
if (!Array.isArray(componentOptions.inject)) {
componentOptions.inject = componentOptions.inject || {}
componentOptions.inject[reactiveInjectKey] = {
from: reactiveInjectKey,
default: {},
}
}
}
因此相较于 inject,injectReactive的实现:
关于
inject的from以及default属性,文档中有介绍:https://v2.cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#provide-inject
export function InjectReactive(options?: InjectOptions | InjectKey) {
return createDecorator((componentOptions, key) => {
if (typeof componentOptions.inject === 'undefined') {
componentOptions.inject = {}
}
if (!Array.isArray(componentOptions.inject)) {
- componentOptions.inject[key] = options || key
+ const fromKey = !!options ? (options as any).from || options : key
+ const defaultVal = (!!options && (options as any).default) || undefined
+ if (!componentOptions.computed) componentOptions.computed = {}
+ // 获取 需要 Inject 的 key 的值 和 defaultValue 使用 computed 去通过 getter 的方式 获取 Inject 的 值
+ componentOptions.computed![key] = function () {
+ const obj = (this as any)[reactiveInjectKey]
+ return obj ? obj[fromKey] : defaultVal
+ }
+ componentOptions.inject[reactiveInjectKey] = reactiveInjectKey
}
})
}
Emit
Emit 装饰器则是通过对函数进行进一步封装实现。
const hyphenateRE = /\B([A-Z])/g
const hyphenate = (str: string) => str.replace(hyphenateRE, '-$1').toLowerCase()
export function Emit(event?: string) {
return function (_target: Vue, propertyKey: string, descriptor: any) {
// propertyKey 函数名
const key = hyphenate(propertyKey)
// 存储原有的方法
const original = descriptor.value
// 对原方法进行进一步加工
descriptor.value = function emitter(...args: any[]) {
const emit = (returnValue: any) => {
const emitName = event || key
// 根据 原有方法的返回值以及 传入的参数值进行 emit 不同的参数
if (returnValue === undefined) {
if (args.length === 0) {
this.$emit(emitName)
} else if (args.length === 1) {
this.$emit(emitName, args[0])
} else {
this.$emit(emitName, ...args)
}
} else {
args.unshift(returnValue)
this.$emit(emitName, ...args)
}
}
// 调用原有方法 获取返回值
const returnValue: any = original.apply(this, args)
// 如果是 Promise then之后再调用 emit 否则直接调用 emit
if (isPromise(returnValue)) {
returnValue.then(emit)
} else {
emit(returnValue)
}
return returnValue
}
}
}
function isPromise(obj: any): obj is Promise<any> {
return obj instanceof Promise || (obj && typeof obj.then === 'function')
}
参考文章
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- JavaScript 深度剖析:克服常见陷阱
- ROS-ID?总活性氧/超氧化物检测试剂盒
- python超实用插件REST Client、autoDocstring、Better Comments
- java基础知识点系列——数据输入(五)
- 1071:菲波那契数 ------ 信息学奥赛高级题库
- Python 面向对象之多态
- 【年终总结系列 2023】新起点,同时追寻更高的起点
- 第八章 Gateway网关
- HTML5期末大作业:HTML+CSS茶叶官网网页设计实例 企业网站制作
- python:检查是否有重复的库文件