【图的应用四:关键路径】- 用 C 语言实现关键路径
目录
?
一、AOE-网
与 AOV-网相对应的是 AOE-网(Activity On Edge),即以边表示活动的网。AOE-网是一个带权的有向无环图,其中,顶点表示事件、弧表示活动,权表示活动持续的时间。通常,AOE-网可用来估算工程的完成时间。
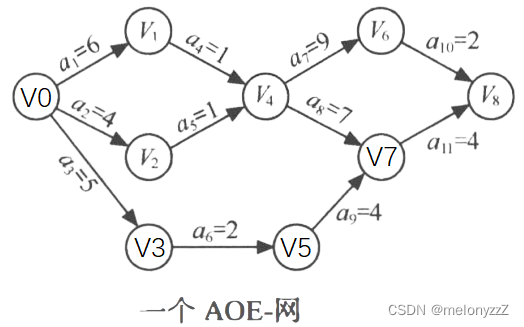
例如,下图所示为一个有 11 项活动的 AOE-网。其中有 9 个事件 v0, v1, ..., v8,每个事件表示在它之前的活动已经完成,在它之后的活动可以开始。例如,v0 表示整个工程开始,v8 表示整个过程结束,v4 表示 a4 和 a5 已经完成,a7 和 a8 可以开始了。与每个活动相联系的数是执行该活动所需的时间,比如,活动 a1 需要 6 天,a2 需要 4 天等。
AOE-网在工程计划和经营管理中有广泛的应用,针对实际的应用问题,通常需要解决以下两个问题:
-
估算完成整项工程至少需要多少时间。
-
判定哪些活动是影响工程进度的关键。
工程进度控制的关键在于抓住关键活动。在一定范围内,非关键活动的提前完成对于整个工程的进度没有直接的好处,它的稍许拖延也不会影响整个工程的进度。工程的指挥者可以把非关键活动的人力和物力资源暂时调给关键活动,加速其进展,以使整个工程提前完工。
由于整个工程只有一个开始点和一个完成点,故在正常的情况(无环)下,网中只有一个入度为零的点,称作源点,也只有一个出度为零的点,称作汇点。在 AOE-网中,一条路径各弧上的权值之和称为该路径的带权路径长度(后面简称路径长度)。要估算整项工程完成的最短时间,就是要找一条从源点到汇点的带权路径长度最长的路径,称为关键路径。关键路径上的活动叫做关键活动,这些活动是影响工程进度的关键,它们的提前或拖延使整个工程提前或拖延。
例如,在上图中,v0 是源点,v8 是汇点,关键路径有两条:(v0, v1, v4, v6, v8) 和 (v0, v1, v4, v7, v8),长度均为 18,关键活动为 (a1, a4, a7, a10) 和 (a1, a4, a8, a11)。比如,关键活动 a1 需要 6 天完成,如果 a1 提前 1 天,整个工程也可以提前 1 天完成。所以不论估算工期,还是研究如何加快工程进度,主要问题就在于要找到 AOE-网的关键路径。
如何确定关键路径,首先定义 4 个描述量。
-
事件 vi 的最早发生时间 ve(i):
进入事件 vi 的每一活动都结束,vi 才可发生,所以 ve(i) 是从源点到 vi 的最长路径长度。
求 ve(i) 的值,可根据拓扑顺序从源点开始向汇点递推。通常将工程的开始顶点事件 v0 的最早发生时间定义为 0,即:
其中,T 是所有以 vi 为头的弧的集合,
是弧 <vk, vi> 的权值,即对应活动 <vk, vi> 的持续时间。
-
事件 vi 的最迟发生事件 vl(i):
事件 vi 的发生不得延误 vi 的每一后继事件的最迟发生事件。为了不拖延工期,vi 的最迟发生时间不得迟于其后继事件 vk 的最迟发生事件减去活动 <vi, vk> 的持续事件。
求出 ve(i) 后,可根据逆拓扑顺序从汇点开始向源点递推,求出 vl(i)。
其中,S 是所有以 vi 为为的弧,
是弧 <vi, vk> 的权值。
-
活动 ai = <vj, vk> 的最早开始时间 ae(i):
只有事件 vj 发生了,活动 ai 才能开始,所以活动 ai 的最早开始时间等于事件 vj 的最早发生时间 ve(j),即:
-
活动 ai = <vj, vk> 的最晚开始时间 al(i):
活动 ai 的开始时间需保证不延误事件 vk 的最迟发生时间。所以活动 ai 的最晚开始时间 al(i) 等于事件 vk 的最迟发生时间 vl(k) 减去活动 ai 的持续时间
,即:
显然,对于关键活动而言,ae(i) = al(i)。对于非关键活动,al(i) - ae(i) 的值是该工程的期限余量,在此范围内的适度延误不会影响整个工程的工期。
二、算法的实现
由于每个事件的最早发生时间 ve(i) 和最迟发生时间 vl(i) 要在拓扑序列的基础上进行计算,所以关键路径算法的实现要基于拓扑排序算法,我们仍采用邻接表做有向图的存储结构。
2.1 - ALGraph.h
#pragma once
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int ArcType;
typedef char VertexType;
#define DEFAULT_CAPACITY 2
typedef struct ArcNode
{
int adjVexPos;
struct ArcNode* nextArc;
ArcType weight;
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VertexNode
{
VertexType vertex;
ArcNode* firstArc;
}VertexNode;
typedef struct ALGraph
{
VertexNode* vertices;
int vSize;
int aSize;
int capacity;
}ALGraph;
void ALGraphInit(ALGraph* pg);
void ShowAdjList(ALGraph* pg);
int GetVertexPos(ALGraph* pg, VertexType v);
void InsertVertex(ALGraph* pg, VertexType v);
void InsertArc(ALGraph* pg, VertexType v1, VertexType v2, ArcType weight);
void ALGraphDestroy(ALGraph* pg);
// 拓扑排序
bool TopologicalSort(ALGraph* pg, int* topo);
// 关键路径
void CriticalPath(ALGraph* pg);2.2 - ALGraph.c
#include "ALGraph.h"
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "Stack.h"
void ALGraphInit(ALGraph* pg)
{
assert(pg);
pg->vSize = pg->aSize = 0;
pg->capacity = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
pg->vertices = (VertexNode*)malloc(sizeof(VertexNode) * pg->capacity);
assert(pg->vertices);
for (int i = 0; i < pg->capacity; ++i)
{
pg->vertices[i].firstArc = NULL;
}
}
void ShowAdjList(ALGraph* pg)
{
assert(pg);
for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i)
{
printf("%d %c:>", i, pg->vertices[i].vertex);
ArcNode* cur = pg->vertices[i].firstArc;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d-->", cur->adjVexPos);
cur = cur->nextArc;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
}
int GetVertexPos(ALGraph* pg, VertexType v)
{
assert(pg);
for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i)
{
if (pg->vertices[i].vertex == v)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void InsertVertex(ALGraph* pg, VertexType v)
{
assert(pg);
if (pg->vSize == pg->capacity)
{
VertexNode* tmp = (VertexNode*)realloc(pg->vertices, sizeof(VertexNode) * 2 * pg->capacity);
assert(tmp);
pg->vertices = tmp;
for (int i = pg->capacity; i < 2 * pg->capacity; ++i)
{
pg->vertices[i].firstArc = NULL;
}
pg->capacity *= 2;
}
pg->vertices[pg->vSize++].vertex = v;
}
void InsertArc(ALGraph* pg, VertexType v1, VertexType v2, ArcType weight)
{
assert(pg);
int pos1 = GetVertexPos(pg, v1);
int pos2 = GetVertexPos(pg, v2);
if (pos1 == -1 || pos2 == -1)
return;
// 插入 <v1, v2>
ArcNode* p = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
assert(p);
p->adjVexPos = pos2;
p->weight = weight;
// 头插
p->nextArc = pg->vertices[pos1].firstArc;
pg->vertices[pos1].firstArc = p;
++pg->aSize;
}
void ALGraphDestroy(ALGraph* pg)
{
assert(pg);
for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i)
{
ArcNode* cur = pg->vertices[i].firstArc;
while (cur)
{
// 头删
pg->vertices[i].firstArc = cur->nextArc;
free(cur);
cur = pg->vertices[i].firstArc;
}
}
free(pg->vertices);
pg->vertices = NULL;
pg->vSize = pg->aSize = pg->capacity = 0;
}
// 拓扑排序
bool TopologicalSort(ALGraph* pg, int* topo)
{
assert(pg);
int* indegree = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * pg->vSize);
assert(indegree);
for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i)
{
indegree[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i)
{
ArcNode* cur = pg->vertices[i].firstArc;
while (cur)
{
++indegree[cur->adjVexPos];
cur = cur->nextArc;
}
}
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i)
{
if (indegree[i] == 0)
StackPush(&st, i);
}
int cnt = 0;
while (!StackEmpty(&st))
{
int i = StackTop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
topo[cnt++] = i;
ArcNode* cur = pg->vertices[i].firstArc;
while (cur)
{
if (--indegree[cur->adjVexPos] == 0)
StackPush(&st, cur->adjVexPos);
cur = cur->nextArc;
}
}
StackDestroy(&st);
if (cnt == pg->vSize)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// 关键路径
void CriticalPath(ALGraph* pg)
{
assert(pg);
int* topo = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * pg->vSize);
assert(topo);
if (!TopologicalSort(pg, topo))
{
printf("网中存在有向环!\n");
free(topo);
return;
}
int* ve = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * pg->vSize);
int* vl = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * pg->vSize);
assert(ve && vl);
for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i)
{
ve[i] = 0;
}
// 按照拓扑顺序求每个事件的最早发生时间
for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize - 1; ++i)
{
int k = topo[i];
ArcNode* cur = pg->vertices[k].firstArc;
while (cur)
{
if (ve[k] + cur->weight > ve[cur->adjVexPos])
ve[cur->adjVexPos] = ve[k] + cur->weight;
cur = cur->nextArc;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i)
{
vl[i] = ve[topo[pg->vSize - 1]];
}
// 按照逆拓扑顺序求每个事件的最迟发生时间
for (int i = pg->vSize - 2; i >= 0; --i)
{
int k = topo[i];
ArcNode* cur = pg->vertices[k].firstArc;
while (cur)
{
if (vl[cur->adjVexPos] - cur->weight < vl[k])
vl[k] = vl[cur->adjVexPos] - cur->weight;
cur = cur->nextArc;
}
}
// 判定每一活动是否为关键活动
for (int i = 0; i < pg->vSize; ++i)
{
ArcNode* cur = pg->vertices[i].firstArc;
while (cur)
{
int ae = ve[i];
int al = vl[cur->adjVexPos] - cur->weight;
if (ae == al)
printf("<%c, %c> 是关键活动\n", pg->vertices[i].vertex, pg->vertices[cur->adjVexPos].vertex);
cur = cur->nextArc;
}
}
free(topo);
free(ve);
free(vl);
}2.3 - Test.c
#include "ALGraph.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
ALGraph g;
ALGraphInit(&g);
InsertVertex(&g, 'A');
InsertVertex(&g, 'B');
InsertVertex(&g, 'C');
InsertVertex(&g, 'D');
InsertVertex(&g, 'E');
InsertVertex(&g, 'F');
InsertVertex(&g, 'G');
InsertVertex(&g, 'H');
InsertVertex(&g, 'I');
InsertArc(&g, 'A', 'B', 6);
InsertArc(&g, 'A', 'C', 4);
InsertArc(&g, 'A', 'D', 5);
InsertArc(&g, 'B', 'E', 1);
InsertArc(&g, 'C', 'E', 1);
InsertArc(&g, 'D', 'F', 2);
InsertArc(&g, 'E', 'G', 9);
InsertArc(&g, 'E', 'H', 7);
InsertArc(&g, 'F', 'H', 4);
InsertArc(&g, 'G', 'I', 2);
InsertArc(&g, 'H', 'I', 4);
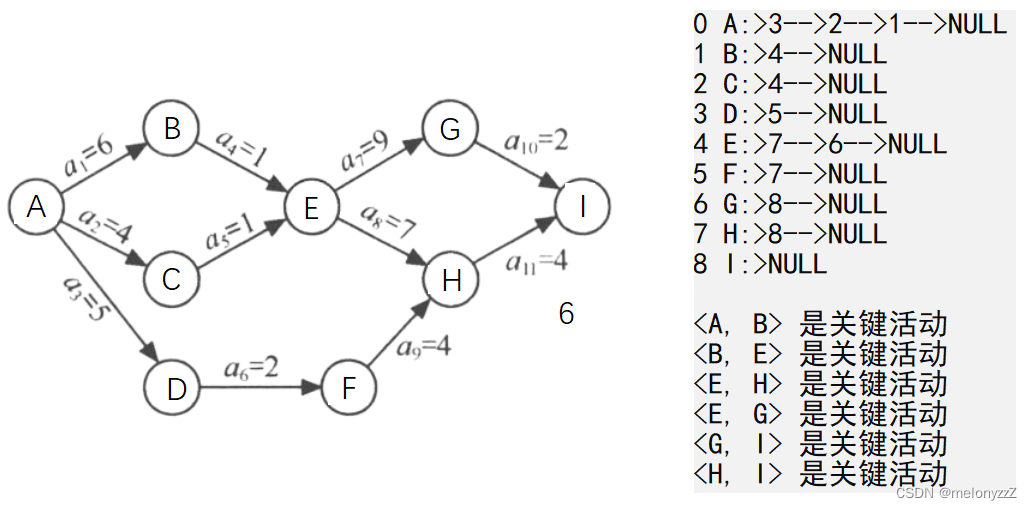
ShowAdjList(&g);
printf("\n");
CriticalPath(&g);
ALGraphDestroy(&g);
return 0;
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Windows下使用DOS命令上传文件到服务器
- 最新版git2.43安装以及tortoisegit2.15使用
- 云原生架构体系和重点概念解读
- linux下的strerror和perror处理错误函数
- 动态内存管理(补)
- 【已解决】如何用typedef简化函数指针
- 腾讯云最新优惠活动入口整理汇总
- 有私域和没私域的区别,有多么直观?
- 为什么AI数字人直播被判定为录播?
- 【随笔】程序员必备的面试技巧,如何成为那个令HR们心动的程序猿!