scrapy爬虫实战
scrapy爬虫实战
Scrapy 简介
Scrapy 是一个强大的开源网络爬虫框架,用于从网站上提取数据。它以可扩展性和灵活性为特点,被广泛应用于数据挖掘、信息处理和历史数据抓取等领域。官网链接(外)
主要特性
-
模块化结构:Scrapy 的设计采用了模块化结构,包括引擎、调度器、下载器、爬虫和管道等组件。这使得用户能够根据需要选择性地使用或扩展不同的功能。
-
选择器:Scrapy 提供了灵活强大的选择器,可以通过 CSS 或 XPath 表达式轻松地提取网页中的数据。
-
中间件支持:用户可以通过中间件自定义处理请求和响应,例如修改请求头、实现代理、或者处理异常情况。
-
自动限速:Scrapy 具备自动限速功能,避免对目标网站造成过大的负担,同时支持自定义的下载延迟。
-
并发控制:支持异步处理和并发请求,提高爬取效率。
-
扩展性:Scrapy 提供了丰富的扩展接口,用户可以通过编写扩展插件实现定制化的功能。
-
数据存储:通过管道(Pipeline)机制,Scrapy 支持将抓取到的数据存储到多种格式,如 JSON、CSV、数据库等。
-
用户友好的命令行工具:Scrapy 提供了一套直观易用的命令行工具,方便用户创建、运行和管理爬虫项目。
示例代码
import scrapy
class MySpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'my_spider' # 爬虫名字,后续是根据这个名字运行相关代码,而不是类名
start_urls = ['http://example.com'] # 爬虫的入口网站
def parse(self, response):
# 使用选择器提取数据
title = response.css('h1::text').get()
body = response.css('p::text').get()
# 返回抓取到的数据
yield {
'title': title,
'body': body,
}
这是一个简单的爬虫示例,通过定义爬虫类、指定起始 URL 和解析方法,用户可以快速创建一个基本的爬虫。
以上是 Scrapy 的简要介绍,它的灵活性和强大功能使其成为网络爬虫领域的瑞士军刀。
安装scrapy,并创建项目
使用python包管理工具pip安装scrapy
pip install scrapy
安装完成后使用scrapy创建项目
scrapy startproject sw
创建完成后,我的目录格式如下:
sw/
│
├── sw/
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── items.py
│ ├── middlewares.py
│ ├── pipelines.py
│ ├── settings.py
│ └── spiders/
│ └── __init__.py
│
├── scrapy.cfg
└── README.md
解释一下各个目录和文件的作用:
-
sw/sw/: 项目的 Python 模块,包含了爬虫项目的主要代码。
- init.py: 空文件,用于指示该目录是一个 Python 包。
- items.py: 定义用于存储爬取数据的数据模型。
- middlewares.py: 包含自定义中间件的文件,用于处理请求和响应。
- pipelines.py: 包含自定义管道的文件,用于处理抓取到的数据的存储和处理。
- settings.py: 包含项目的设置和配置信息。
(如果要链接数据库,记得在这个文件里填写相应信息) - spiders/: 存放爬虫代码的目录。
- init.py: 空文件,用于指示该目录是一个 Python 包。
-
scrapy.cfg: Scrapy 项目的配置文件,包含有关项目的元数据和设置。
-
README.md: 项目的说明文档,可以包含有关项目的描述、使用说明等信息。
这是一个标准的 Scrapy 项目结构,您可以根据实际需求和项目规模进行调整和扩展。
运行单个脚本
代码示例
配置
先配置相关信息
item
item.py中的内容如下:
# Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
import scrapy
class SwItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
url = scrapy.Field()
title = scrapy.Field()
time = scrapy.Field()
content = scrapy.Field()
scrapy_time = scrapy.Field()
trans_title = scrapy.Field()
trans_content = scrapy.Field()
org = scrapy.Field()
trans_org = scrapy.Field()
setting
setting.py中的内容如下:
# Scrapy settings for sw project
#
# For simplicity, this file contains only settings considered important or
# commonly used. You can find more settings consulting the documentation:
#
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html
BOT_NAME = "sw"
SPIDER_MODULES = ["sw.spiders"]
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = "sw.spiders"
DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 3
RANDOMIZE_DOWNLOAD_DELAY = True
USER_AGENT = 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36'
COOKIES_ENABLED = True
# Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent
#USER_AGENT = "sw (+http://www.yourdomain.com)"
# Obey robots.txt rules
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = True
# Configure maximum concurrent requests performed by Scrapy (default: 16)
#CONCURRENT_REQUESTS = 32
# Configure a delay for requests for the same website (default: 0)
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html#download-delay
# See also autothrottle settings and docs
#DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 3
# The download delay setting will honor only one of:
#CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_DOMAIN = 16
#CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_IP = 16
# Disable cookies (enabled by default)
#COOKIES_ENABLED = False
# Disable Telnet Console (enabled by default)
#TELNETCONSOLE_ENABLED = False
# Override the default request headers:
#DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = {
# "Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8",
# "Accept-Language": "en",
#}
# Enable or disable spider middlewares
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html
#SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES = {
# "sw.middlewares.SwSpiderMiddleware": 543,
#}
# Enable or disable downloader middlewares
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html
#DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
# "sw.middlewares.SwDownloaderMiddleware": 543,
#}
# Enable or disable extensions
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/extensions.html
#EXTENSIONS = {
# "scrapy.extensions.telnet.TelnetConsole": None,
#}
# Configure item pipelines
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
#ITEM_PIPELINES = {
# "sw.pipelines.SwPipeline": 300,
#}
# ITEM_PIPELINES = {
# "sw.pipelines.SwPipeline": 300,
# }
# 数据库的相关配置
# DB_SETTINGS = {
# 'host': '127.0.0.1',
# 'port': 3306,
# 'user': 'root',
# 'password': '123456',
# 'db': 'scrapy_news_2024_01_08',
# 'charset': 'utf8mb4',
# }
# Enable and configure the AutoThrottle extension (disabled by default)
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/autothrottle.html
#AUTOTHROTTLE_ENABLED = True
# The initial download delay
#AUTOTHROTTLE_START_DELAY = 5
# The maximum download delay to be set in case of high latencies
#AUTOTHROTTLE_MAX_DELAY = 60
# The average number of requests Scrapy should be sending in parallel to
# each remote server
#AUTOTHROTTLE_TARGET_CONCURRENCY = 1.0
# Enable showing throttling stats for every response received:
#AUTOTHROTTLE_DEBUG = False
# Enable and configure HTTP caching (disabled by default)
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html#httpcache-middleware-settings
#HTTPCACHE_ENABLED = True
#HTTPCACHE_EXPIRATION_SECS = 0
#HTTPCACHE_DIR = "httpcache"
#HTTPCACHE_IGNORE_HTTP_CODES = []
#HTTPCACHE_STORAGE = "scrapy.extensions.httpcache.FilesystemCacheStorage"
# Set settings whose default value is deprecated to a future-proof value
REQUEST_FINGERPRINTER_IMPLEMENTATION = "2.7"
TWISTED_REACTOR = "twisted.internet.asyncioreactor.AsyncioSelectorReactor"
FEED_EXPORT_ENCODING = "utf-8"
# REDIRECT_ENABLED = False
爬虫脚本
过程非常简单,只需要在spiders/目录下,创建自己的代码即可。示例代码p3_new_39.py (tips: 直接把这个代码放到spiders/目录下) 如下:
"""
Created on 2024/01/06 14:00 by Fxy
"""
import scrapy
from sw.items import SwItem
import time
from datetime import datetime
class SWSpider(scrapy.Spider):
'''
scrapy变量
'''
# 爬虫名称(自己定义)
name = "p3_new_39"
# 允许爬取的域名
allowed_domains = ["www.meduniwien.ac.at"]
# 爬虫的起始链接
start_urls = ["https://www.meduniwien.ac.at/web/en/about-us/news/"]
# 创建一个VidoItem实例
item = SwItem()
'''
自定义变量
'''
# 机构名称
org = "奥地利维也纳医科大学病毒学中心"
# 机构英文名称
org_e = "Med Univ Vienna, Ctr Virol"
# 日期格式
site_date_format = '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M' # 网页的日期格式
date_format = '%d.%m.%Y %H:%M:%S' # 目标日期格式
# 网站语言格式
language_type = "zh2zh" # 中文到中文的语言代码, 调用翻译接口时,使用
#爬虫的主入口,这里是获取所有的归档文章链接
def parse(self,response):
achieve_links = response.xpath('//*[@id="c4345"]//div[@class="news-teaser__caption"]/h2/a/@href').extract()
print("achieve_links",achieve_links)
for achieve_link in achieve_links:
if "http" in achieve_link:
continue
full_achieve_link = "https://www.meduniwien.ac.at" + achieve_link
print("full_achieve_link", full_achieve_link)
# 进入每个归档链接
yield scrapy.Request(full_achieve_link, callback=self.parse_item, dont_filter=True)
#翻页逻辑
xpath_expression = f'//*[@id="c4345"]//ul[@class="pagination"]/li[@class="next"]/a/@href'
next_page = response.xpath(xpath_expression).extract_first()
print("next_page = ", next_page)
# 翻页操作
if next_page != None:
print(next_page)
print('next page')
full_next_page = "https://www.meduniwien.ac.at" + next_page
print("full_next_page",full_next_page)
yield scrapy.Request(full_next_page, callback=self.parse, dont_filter=True)
#获取每个文章的内容,并存入item
def parse_item(self,response):
source_url = response.url
print("source_url:", source_url)
title_o = response.xpath('//*[@id="main"]/header/div/div[2]/div[1]/h1/text()').extract_first().strip()
# title_t = my_tools.get_trans(title_o, "de2zh") *[@id="c4342"]/div/div/div[2]/span
print("title_o:", title_o) #//*[@id="c4342"]/div/div/div[2]/span
year_string = response.xpath('//div[@class="news-detail__meta"]/span/@data-year').extract_first().strip()
month_string = response.xpath('//div[@class="news-detail__meta"]/span/@data-month').extract_first().strip()
day_string = response.xpath('//div[@class="news-detail__meta"]/span/@data-day').extract_first().strip()
hour_string = response.xpath('//div[@class="news-detail__meta"]/span/@data-hour').extract_first().strip()
minute_string = response.xpath('//div[@class="news-detail__meta"]/span/@data-minute').extract_first().strip()
publish_time = f'{year_string}-{month_string}-{day_string} {hour_string}:{minute_string}'
print("publish_time:", publish_time)
date_object = datetime.strptime(publish_time, self.site_date_format) # 先读取成网页的日期格式
date_object = date_object.strftime(self.date_format) # 转换成目标的日期字符串
publish_time = datetime.strptime(date_object, self.date_format) # 从符合格式的字符串,转换成日期
content_o = [content.strip() for content in response.xpath('//div[@class="content__block"]//text()').extract()]
content_o = ' '.join(content_o) # 这个content_o提取出来是一个字符串数组,所以要拼接成字符串
# content_t = my_tools.get_trans(content_o, "de2zh")
print("source_url:", source_url)
print("title_o:", title_o)
# print("title_t:", title_t)
print("publish_time:", publish_time) #15.01.2008
print("content_o:", content_o)
# print("content_t:", content_t)
print("-" * 50)
page_data = {
'source_url': source_url,
'title_o': title_o,
# 'title_t' : title_t,
'publish_time': publish_time,
'content_o': content_o,
# 'content_t': content_t,
'org' : self.org,
'org_e' : self.org_e,
}
self.item['url'] = page_data['source_url']
self.item['title'] = page_data['title_o']
# self.item['title_t'] = page_data['title_t']
self.item['time'] = page_data['publish_time']
self.item['content'] = page_data['content_o']
# self.item['content_t'] = page_data['content_t']
# 获取当前时间
current_time = datetime.now()
# 格式化成字符串
formatted_time = current_time.strftime(self.date_format)
# 将字符串转换为 datetime 对象
datetime_object = datetime.strptime(formatted_time, self.date_format)
self.item['scrapy_time'] = datetime_object
self.item['org'] = page_data['org']
self.item['trans_org'] = page_data['org_e']
yield self.item
代码解析
接下来我们来分析,上面p3_new_39.py代码中的response.xpath()中的参数如何确定。
1、首先进入网页: https://www.meduniwien.ac.at/web/en/about-us/news/(外):
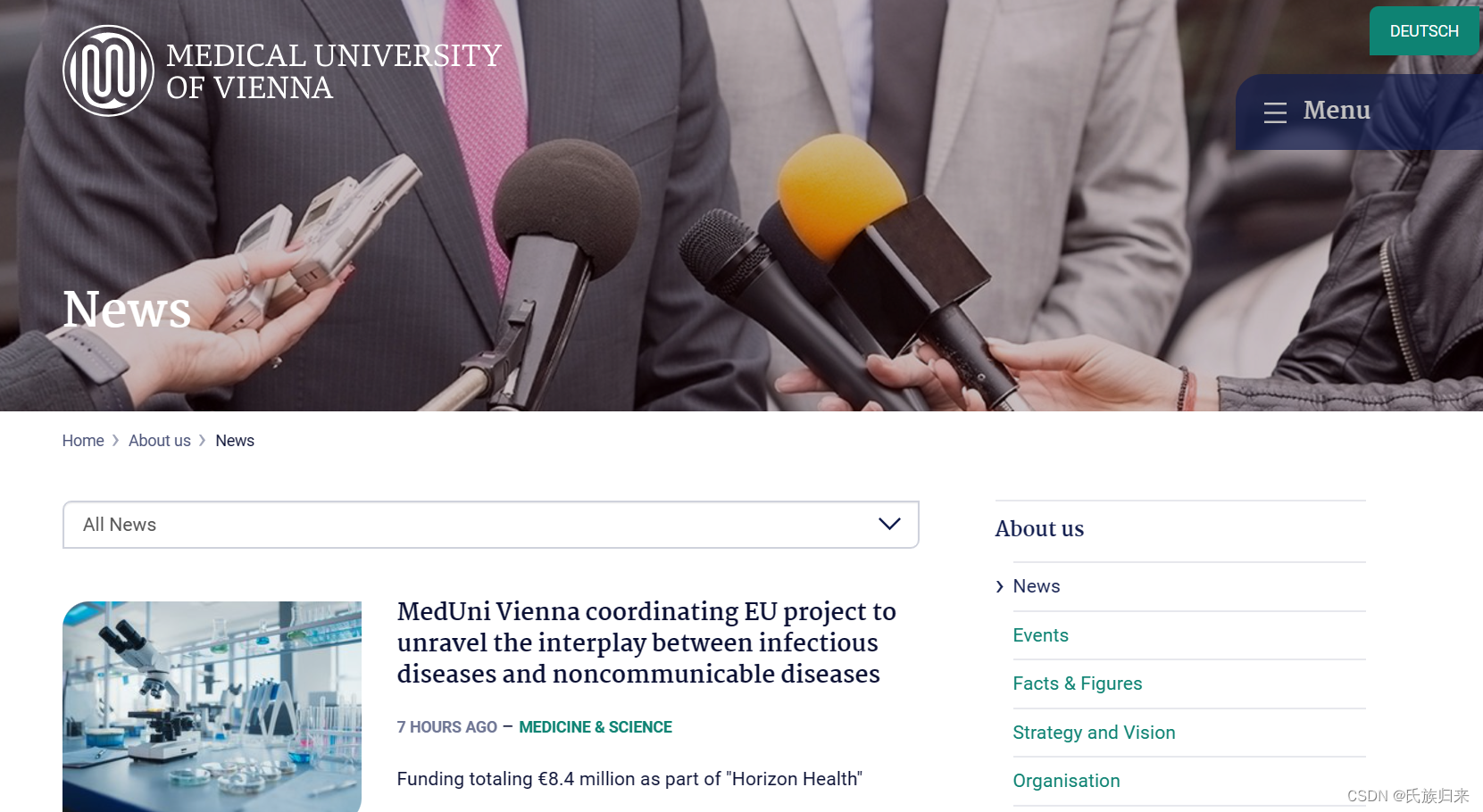
2、确定自己要爬取的数据,这里我假定为每一条新闻。

3、打开浏览器的调试工具(默认f12)找到跳转的链接。
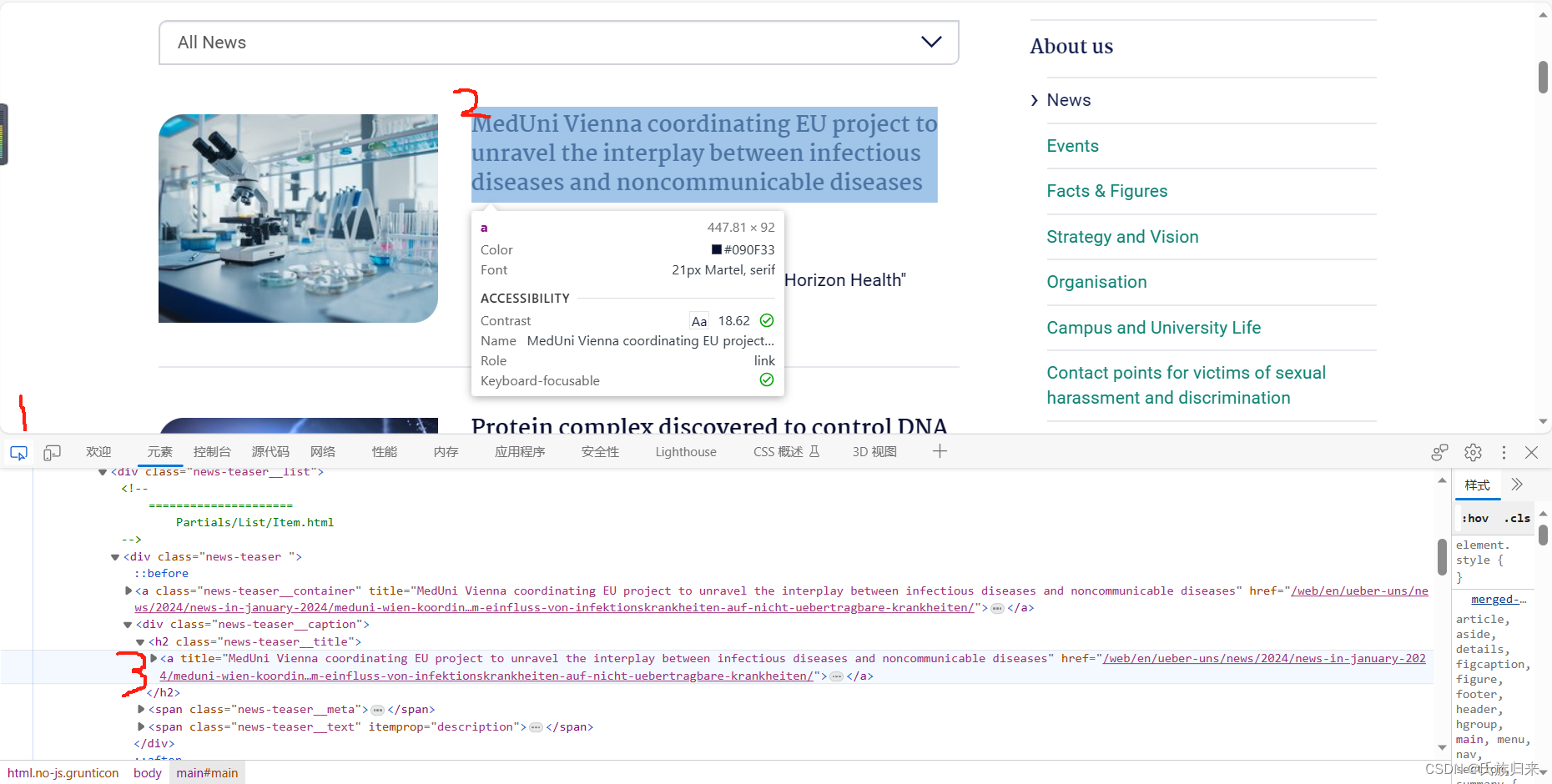
4、右键元素,复制xpath即可。

我的复制结果如下://*[@id="c4345"]/div/div[1]/div/h2/a
xpath基本语法:
XPath(XML Path Language)是一种用于在 XML 文档中定位和选择节点的查询语言。它不仅可以用于 XML,还可以用于 HTML 和其他标记语言。以下是XPath的主要语法和一些常见用法:
-
节点选择:
/: 从根节点开始选择。//: 选择节点,不考虑它们的位置。.: 选取当前节点。..: 选取当前节点的父节点。
-
节点名称:
elementName: 选取所有名称为elementName的节点。*: 选取所有子节点。
-
谓语:
[condition]: 通过添加条件筛选节点。- 例如:
//div[@class='example']选取所有 class 属性为 ‘example’ 的 div 节点。
- 例如:
路径表达式示例:
/bookstore/book[1]: 选取第一个<book>元素。/bookstore/book[last()]: 选取最后一个<book>元素。/bookstore/book[position()<3]: 选取前两个<book>元素。//title[@lang='en']: 选取所有带有 lang 属性为 ‘en’ 的<title>元素。//title[@lang='en']/text(): 选取所有带有 lang 属性为 ‘en’ 的<title>元素的文本内容。//title[not(@lang='en')]/text(): 选取所有 lang 属性不为 ‘en’ 的<title>元素的文本内容。//title[@lang='en' or @lang='zh']/text(): 选取所有带有 lang 属性为 ‘en’ 或 ‘zh’ 的<title>元素的文本内容。//title[contains(@lang, 'en')]/text()选取所有带有 lang 属性包含 'en’子串 的<title>元素的文本内容。
通配符和多路径:
*: 通配符,匹配任何元素节点。@*: 匹配任何属性节点。//book/title | //book/price: 选取所有<book>元素的<title>和<price>子元素。
函数:
XPath 还支持一些内置函数,例如:
text(): 获取节点的文本内容。contains(str1, str2): 判断一个字符串是否包含另一个字符串。
示例:
考虑以下 XML 结构:
<bookstore>
<book>
<title lang="en">Introduction to XPath</title>
<price>29.95</price>
</book>
<book>
<title lang="fr">XPath et ses applications</title>
<price>39.99</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
使用 XPath 可以选择如下:
/bookstore/book: 选取所有<book>元素。/bookstore/book/title[@lang='en']: 选取所有带有 lang 属性为 ‘en’ 的<title>元素。
这是XPath的基本语法和用法示例,它允许您灵活而精确地定位和提取 XML 或 HTML 文档中的数据。
批量运行
在sw项目目录下可以创建一个mian.py
from scrapy.crawler import CrawlerProcess
from scrapy.utils.project import get_project_settings
settings = get_project_settings()
crawler = CrawlerProcess(settings)
bot_list = ["p3_new_39"] # 把要运行的通通放进去
for bot in bot_list:
crawler.crawl(bot)
crawler.start()
附录1,持久化存入数据库
scrapy有个非常好的特点,就是支持自动存入数据库。我们只要将代码写好,然后每次scrapy都会自动调用该代码,不需要自己显示的调用,非常省心。我的piplines.py代码如下:
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
# useful for handling different item types with a single interface
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
import pymysql
class SwPipeline:
def __init__(self, db_settings):
self.db_settings = db_settings
@classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
db_settings = crawler.settings.get("DB_SETTINGS")
return cls(db_settings)
def open_spider(self, spider):
self.connection = pymysql.connect(**self.db_settings)
self.cursor = self.connection.cursor()
def close_spider(self, spider):
self.connection.close()
def process_item(self, item, spider):
# Assuming your item keys match the column names in your database table
keys = ', '.join(item.keys())
values = ', '.join(['%s'] * len(item))
query = f"INSERT INTO org_news ({keys}) VALUES ({values})" #这里记得确认我们item.py中定义的类型名字,是否和数据库中的一样,不一样,这个查询语句需要进行相应的修改,我这里就不一样,所以没法直接运行哦,我懒得改了!!!!哈哈哈
# Check if the record already exists based on a combination of fields, 如果记录已经存在则取消插入,如果有键的话直接用键就行,我这里没有键
unique_fields = ["title_o", "source_url"] # Replace with the actual field names you want to use
check_query = f"SELECT * FROM org_news WHERE {' AND '.join(f'{field} = %s' for field in unique_fields)}"
check_values = tuple(item.get(field) for field in unique_fields)
try:
# Check if the record already exists
self.cursor.execute(check_query, check_values)
existing_record = self.cursor.fetchone()
if existing_record:
spider.logger.warning("Record already exists. Skipping insertion.")
else:
# If the record doesn't exist, insert it into the database
self.cursor.execute(query, tuple(item.values()))
self.connection.commit()
except Exception as e:
self.connection.rollback()
spider.logger.error(f"Error processing item and inserting data into database: {e}")
return item
我创建数据库的代码如下:
/*
Navicat Premium Data Transfer
Source Server : 172.16.6.165
Source Server Type : MySQL
Source Server Version : 80035
Source Host : 172.16.6.165:3306
Source Schema : swaq
Target Server Type : MySQL
Target Server Version : 80035
File Encoding : 65001
Date: 08/01/2024 10:01:57
*/
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for org_news
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `org_news`;
CREATE TABLE `org_news` (
`id` int(0) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`title_t` varchar(1000) CHARACTER SET utf8mb3 COLLATE utf8mb3_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '翻译标题名称',
`title_o` varchar(1000) CHARACTER SET utf8mb3 COLLATE utf8mb3_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '原消息标题',
`content_t` longtext CHARACTER SET utf8mb3 COLLATE utf8mb3_general_ci NULL COMMENT '翻译',
`publish_time` datetime(0) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '发布时间',
`content_o` longtext CHARACTER SET utf8mb3 COLLATE utf8mb3_general_ci NULL COMMENT '原文',
`site` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb3 COLLATE utf8mb3_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '新闻源',
`tag` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb3 COLLATE utf8mb3_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '标签',
`author` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb3 COLLATE utf8mb3_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '作者',
`create_time` datetime(0) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '爬取时间',
`source_url` varchar(1000) CHARACTER SET utf8mb3 COLLATE utf8mb3_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'url',
`country` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8mb3 COLLATE utf8mb3_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '国家/地区',
`imgurl` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb3 COLLATE utf8mb3_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '图片存放地址',
`org` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb3 COLLATE utf8mb3_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '机构名称',
`org_e` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb3 COLLATE utf8mb3_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '机构英文名称',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 314 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb3 COLLATE = utf8mb3_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
附录2,如何在本地启动数据库
1、先安装mysql
2、配置好?(我电脑的mysql几年前安装的,下载了一个navicat)
3、windows控制台输入mysqld --console应该就能启动了。
注意: mysqld 是服务端程序 ,mysql是命令行客户端程序
4、然后应该就能够连接了
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【华为OD真题 Python】精准核酸检测
- 客户需求分析常用的ChatGPT通用提示词模板
- 深度学习记录--偏差/方差(bias/variance)
- 数据结构——树
- 【PostgreSQL内核学习(十九)—— 存储管理(元组操作)】
- 项目管理进阶之序言
- E - Envious Exponents——二进制
- 百度地图再vue中的引入方式
- 2024年【广东省安全员A证第四批(主要负责人)】考试内容及广东省安全员A证第四批(主要负责人)复审考试
- 大模型的研究新方向:混合专家模型(MoE)