Activity 栈管理
上一章笔记写的是Activity的启动流程
这章看下AMS的栈管理如何实现
Activity栈管理是AMS的另一个重要功能,栈管理又和Activity的启动模式和startActivity时所设置的Flag息息相关,Activity栈管理的主要处理逻辑是在ActivityStarter#startActivityUnchecked方法中
为什么要带Unchecked呢? Unchecked-不确定,是因为在执行这个方法时,我要启动哪个Activity还没决定呢,具体为什么,我想看过这篇文章你就明白了。
Activity栈管理相关类
ActivityStackSupervisor
Activity栈的管理人
ActivityDisplay
表示一个屏幕,Android支持三种屏幕,主屏幕,外接屏幕,虚拟屏幕(投屏)【这个介绍是从其他地方看来的,并不确定】。一般在手机上只有主屏幕,此时ActivityStackSupervisor与ActivityDisplay都是系统唯一的
TaskRecord
是ActivityTask的记录,TaskRecord是Activity栈的重要管理单元。形象一点理解,记得启动模式的 singleTask 吧?意思就是让这个Activity在单独的TaskRecord中启动。“Task":任务。
ActivityRecord
记录着每个Activity的信息,ActivityRecord和Activity一一对应。
ActivityStack
是ActivityRecord和TaskRecord两者的统一上司,记录着ActivityRecord和TaskRecord的状态。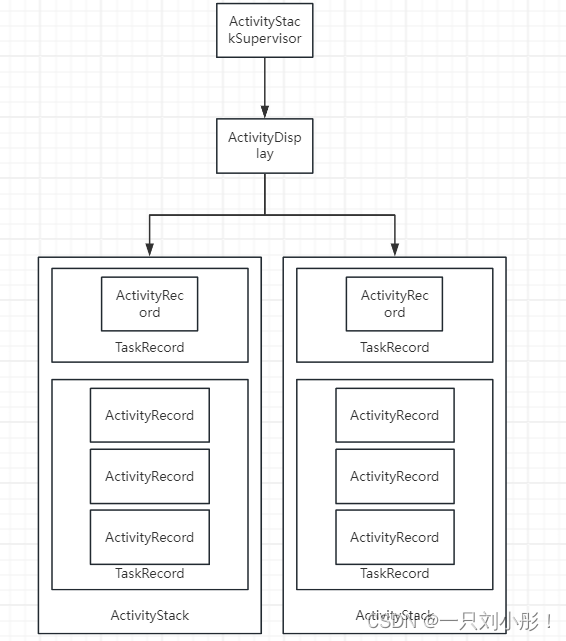
可以理解为一个屏幕上,可能会有很多个APP进程,每个APP进程对应一个ActivityStack,也就是activity栈,其中由于Activity的启动模式不同,又形成了若干个TaskRecord,其中包含着若干个ActivityRecord。
关于这段核心代码在?startActivityUnchecked 这个方法上,我们分析一下这段代码
private int startActivityUnchecked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int startFlags, boolean doResume, ActivityOptions options, TaskRecord inTask) {
//1. 初始化环境和lunchModeFlags
setInitialState(r, options, inTask, doResume, startFlags, sourceRecord, voiceSession,
voiceInteractor);
computeLaunchingTaskFlags();
computeSourceStack();
mIntent.setFlags(mLaunchFlags);
//2. 复用activity逻辑
mReusedActivity = getReusableIntentActivity();
......
if (mReusedActivity != null) {
......
mReusedActivity = setTargetStackAndMoveToFrontIfNeeded(mReusedActivity);
......
setTaskFromIntentActivity(mReusedActivity);
if (!mAddingToTask && mReuseTask == null) {
resumeTargetStackIfNeeded();
return START_TASK_TO_FRONT;
}
}
.......
//singleTop 或者singleInstance的处理
if (dontStart) {
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(AM_NEW_INTENT, top, top.task);
// For paranoia, make sure we have correctly resumed the top activity.
if (mDoResume) {
mSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
}
......
top.deliverNewIntentLocked(
mCallingUid, mStartActivity.intent, mStartActivity.launchedFromPackage);
......
return START_DELIVERED_TO_TOP;
}
//3. 设置对应task并带到前台
if (mStartActivity.resultTo == null && mInTask == null && !mAddingToTask
&& (mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0) {
newTask = true;
setTaskFromReuseOrCreateNewTask(taskToAffiliate);
......
} else if (mSourceRecord != null) {
......
final int result = setTaskFromSourceRecord();
......
} else if (mInTask != null) {
......
final int result = setTaskFromInTask();
if (result != START_SUCCESS) {
return result;
}
} else {
setTaskToCurrentTopOrCreateNewTask();
}
// 4. 启动Activity
mTargetStack.startActivityLocked(mStartActivity, newTask, mKeepCurTransition, mOptions);
// 5. 使Activity可见
if (mDoResume) {
if (!mLaunchTaskBehind) {
mService.setFocusedActivityLocked(mStartActivity, "startedActivity");
}
final ActivityRecord topTaskActivity = mStartActivity.task.topRunningActivityLocked();
if (!mTargetStack.isFocusable()
|| (topTaskActivity != null && topTaskActivity.mTaskOverlay
&& mStartActivity != topTaskActivity)) {
.... . .
mTargetStack.ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null, 0, !PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
mWindowManager.executeAppTransition();
} else {
mSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(mTargetStack, mStartActivity,
mOptions);
}
} else {
mTargetStack.addRecentActivityLocked(mStartActivity);
}
......
return START_SUCCESS;
}核心逻辑在startActivityUnchecked这个里面处理,分2类:
singleTask和singleInstance模式:处理在getReusableIntentActivity,不会重复创建Activity,然后reusedActivity.getTaskRecord()找到可以复用的Task
singleInstance模式:使用mRootActivityContainer.findActivity查找,因为在singleInstance模式下,只能存在一个Activity实例
singleTask模式:使用mRootActivityContainer.findTask找到最合适的Task,因为在singleTask模式下,可能在多个Task中存在Activity实例
standard和singleTop模式:singleTask和singleInstance模式处理完后,然后处理standard和singleTop模式。调用topStack.topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(mNotTop)获取当前top Activity,用作standard和singleTop分别处理
singleTop模式:如果非空且为mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP) != 0,调用deliverNewIntent,直接启动
standard模式:非以上3种场景,直接创建一个新的Activity
?
getReusableIntentActivity 处理singleTask和singleInstance模式
在此方法里面,使用isLaunchModeOneOf(LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE, LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK)判断 ,处理singleTask和singleInstance模式
方法里面的注释写的很清楚,不用单独作说明:
针对singleInstance模式,使用mRootActivityContainer.findActivity,因为在此模式下,只会存在一个Activity实例,通过Activity名称直接在ActivityStack里面查找
针对singleTask模式,mRootActivityContainer.findTask,因为在此模式下,可能在多个TaskRecord里面存在,所以需要找到合适的TaskRecord
从实现上来看,也体现了在singleTask和singleInstance模式里面的唯一差别
?
private ActivityRecord getReusableIntentActivity() {
// We may want to try to place the new activity in to an existing task. We always
// do this if the target activity is singleTask or singleInstance; we will also do
// this if NEW_TASK has been requested, and there is not an additional qualifier telling
// us to still place it in a new task: multi task, always doc mode, or being asked to
// launch this as a new task behind the current one.
boolean putIntoExistingTask = ((mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0 &&
(mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK) == 0)
|| isLaunchModeOneOf(LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE, LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK);
// If bring to front is requested, and no result is requested and we have not been given
// an explicit task to launch in to, and we can find a task that was started with this
// same component, then instead of launching bring that one to the front.
putIntoExistingTask &= mInTask == null && mStartActivity.resultTo == null;
ActivityRecord intentActivity = null;
if (mOptions != null && mOptions.getLaunchTaskId() != -1) {
final TaskRecord task = mSupervisor.anyTaskForIdLocked(mOptions.getLaunchTaskId());
intentActivity = task != null ? task.getTopActivity() : null;
} else if (putIntoExistingTask) {
if (LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE == mLaunchMode) {
// There can be one and only one instance of single instance activity in the
// history, and it is always in its own unique task, so we do a special search.
intentActivity = mSupervisor.findActivityLocked(mIntent, mStartActivity.info,
mStartActivity.isActivityTypeHome());
} else if ((mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_LAUNCH_ADJACENT) != 0) {
// For the launch adjacent case we only want to put the activity in an existing
// task if the activity already exists in the history.
intentActivity = mSupervisor.findActivityLocked(mIntent, mStartActivity.info,
!(LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK == mLaunchMode));
} else {
// Otherwise find the best task to put the activity in.
intentActivity = mSupervisor.findTaskLocked(mStartActivity, mPreferredDisplayId);
}
}
return intentActivity;
}在找到可以复用的Activity的时候,找到对应的TaskRecord,清除目标Task里面位于要启动的Activity之上的Activity
// 找到可以复用的Task
final TaskRecord task = reusedActivity.getTaskRecord();
// 清除目标Task里面位于要启动的Activity之上的Activity
final ActivityRecord top = task.performClearTaskForReuseLocked(mStartActivity,mLaunchFlags);
进行上面的操作后,目标Activity位于TaskRecord的栈顶,直接调用deliverNewIntent,调用top Activity的onNewIntent
if (top != null) {
if (top.frontOfTask) {
// Activity aliases may mean we use different intents for the top activity,
// so make sure the task now has the identity of the new intent.
top.getTaskRecord().setIntent(mStartActivity);
}
deliverNewIntent(top);
}
?
topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked 处理singleTop模式
getReusableIntentActivity方法返回非空时,把singleTask和singleInstance模式处理完。返回空时,先获取当前FocusStack,然后获取top Activity
在topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked方法里面,遍历ActivityStack里面的所有TaskRecord
ActivityRecord topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(ActivityRecord notTop) {
for (int taskNdx = mTaskHistory.size() - 1; taskNdx >= 0; --taskNdx) {
final TaskRecord task = mTaskHistory.get(taskNdx);
final ArrayList<ActivityRecord> activities = task.mActivities;
for (int activityNdx = activities.size() - 1; activityNdx >= 0; --activityNdx) {
ActivityRecord r = activities.get(activityNdx);
if (!r.finishing && !r.delayedResume && r != notTop && r.okToShowLocked()) {
return r;
}
}
}
return null;
}
如果当前要启动的Activity和当前Top Activity是一样的,通过dontStart变量来确认是否需要只启动一次
final boolean dontStart = top != null && mStartActivity.resultTo == null
&& top.mActivityComponent.equals(mStartActivity.mActivityComponent)
&& top.mUserId == mStartActivity.mUserId
&& top.attachedToProcess()
&& ((mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP) != 0
|| isLaunchModeOneOf(LAUNCH_SINGLE_TOP, LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK))
// This allows home activity to automatically launch on secondary display when
// display added, if home was the top activity on default display, instead of
// sending new intent to the home activity on default display.
&& (!top.isActivityTypeHome() || top.getDisplayId() == mPreferredDisplayId);
处理stander模式
前面3种模式处理完后,最后处理stander模式。判断是否需要创建一个newTask,来保存启动的Activity
// Should this be considered a new task?
int result = START_SUCCESS;
if (mStartActivity.resultTo == null && mInTask == null && !mAddingToTask
&& (mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0) {
newTask = true;
result = setTaskFromReuseOrCreateNewTask(taskToAffiliate);
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 记录2023年第3次重感冒
- Linux系统编程(十一):高级 IO
- Xcode编写基于C++的动态连接库(dylib)且用node-ffi-napi测试
- 链表的常见操作
- 提升办公效率用微服务快速开发平台怎么样?
- Lambda表达式与函数式接口
- Flink|《Flink 官方文档 - 部署 - 内存配置 - 配置 Flink 进程的内存》学习笔记
- Redis哨兵模式
- 新能源CRM系统功能解析,新能源CRM有什么用?
- 三张表看懂POE POE+ POE++ 三个协议的相关参数