Java实现五子棋(保姆级教学)
发布时间:2024年01月15日
阶段项目 五子棋
需求说明
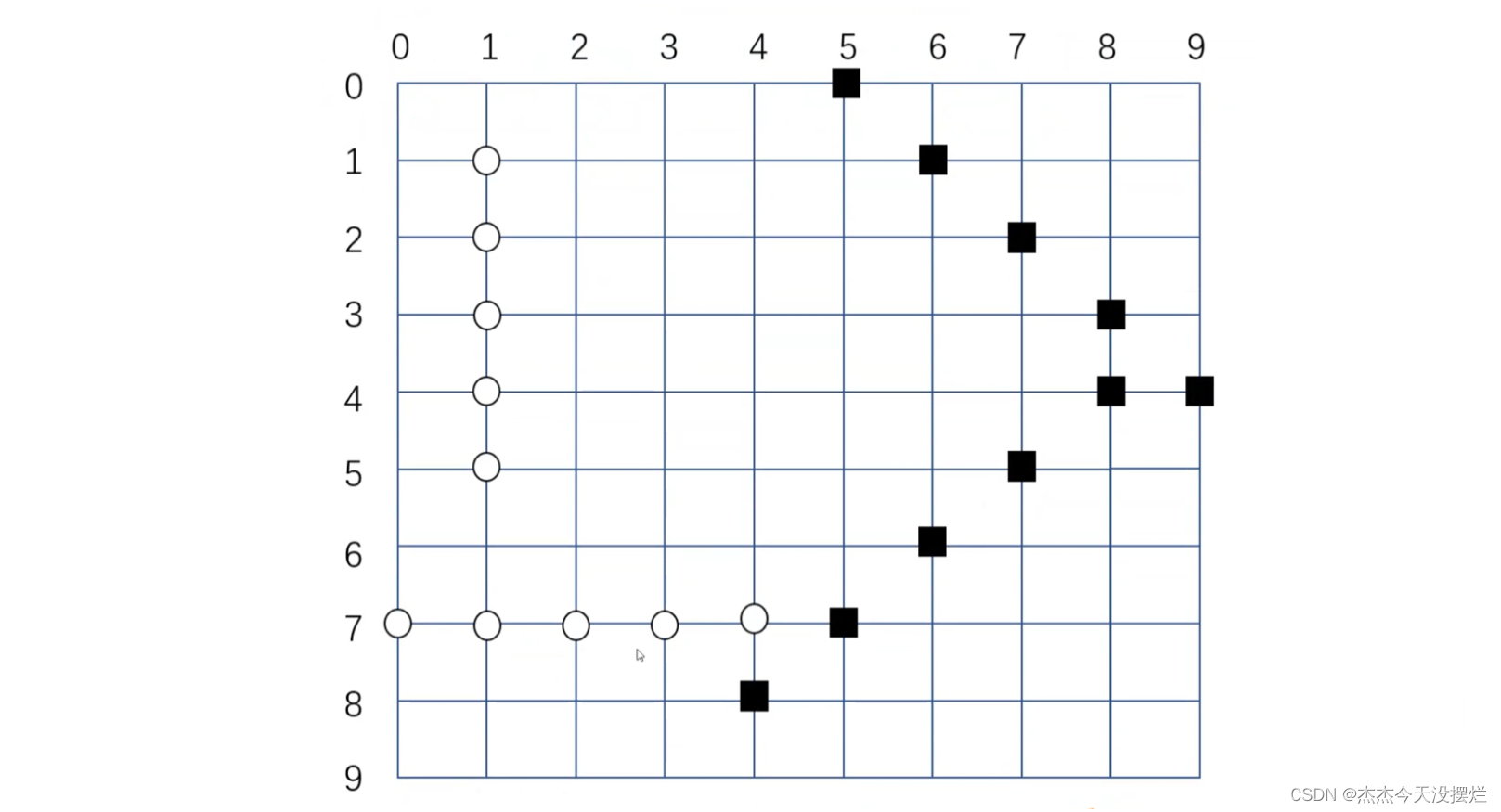
五子棋棋盘是一个10 X 10的棋盘,五子棋玩家共2个(这里分别称为A和B),A在棋盘上落子后,B再落子,以此往复,直到一方胜利或者棋盘空间用完为止。判断胜利的条件是一条直线或者任意斜线上同时存在A或B的连续5颗棋子(见下图)。
技术实现
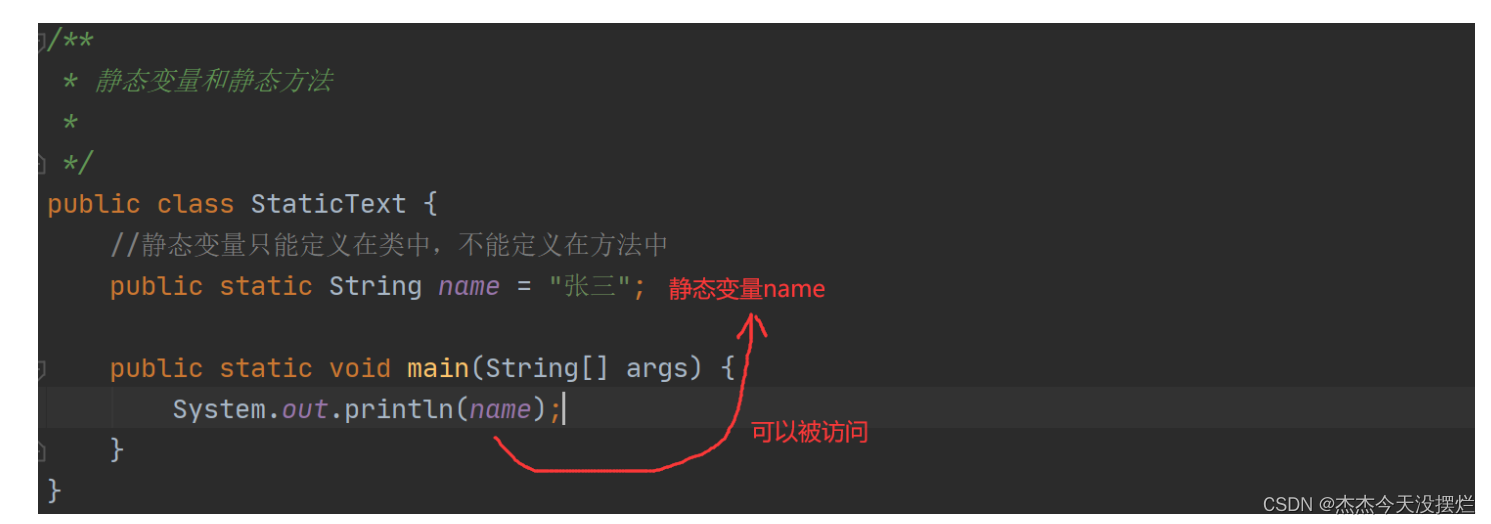
1.静态变量
语法
public static 数据类型 变量名 = 变量值;
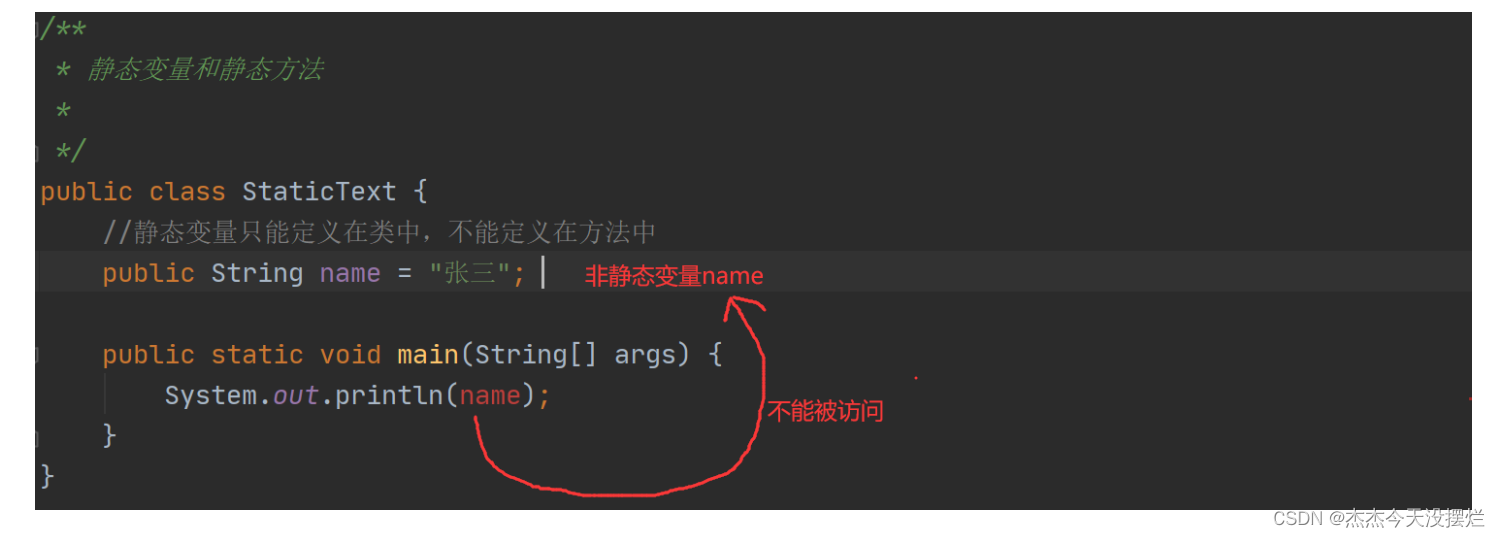
解释说明
静态变量只能定义在类中,不能定义在方法中。静态变量可以在static修饰的方法中使用,也可以在非静态的方法中访问。主要解决在静态方法中不能访问非静态的变量的问题。
2.静态方法
语法
public static 返回值类型 方法名(){
}
解释说明
静态方法就相当于一个箱子,只是这个箱子中装的是代码,需要使用这些代码的时候,就把这个箱子放在指定的位置即可。
示例
/**
* 静态变量和静态方法
*
*/
public class StaticText {
//静态变量只能定义在类中,不能定义在方法中
public static String name = "张三";
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(name);
show();//用下面定义的show方法来打印信息
}
public static void show() {
System.out.println("张三");
System.out.println("男");
System.out.println("20");
}
}
实现步骤分析
1.制作棋盘
a.使用输入法中的制表符在控制台直接打印出棋盘,然后寻找落子的特征
(制表图形作者用的是搜狗输入法—符号大全—制表符)
System.out.println("┌────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┬────┐");
System.out.println("│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
System.out.println("├────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┤");
System.out.println("│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
System.out.println("├────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┤");
System.out.println("│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
System.out.println("├────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┤");
System.out.println("│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
System.out.println("├────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┤");
System.out.println("│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
System.out.println("├────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┤");
System.out.println("│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
System.out.println("├────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┤");
System.out.println("│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
System.out.println("├────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┤");
System.out.println("│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
System.out.println("├────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┼────┤");
System.out.println("│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
System.out.println("└────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┴────┘");
b.利用二维数组重新制作棋盘
/**
* 五子棋
*
*/
public class Gobang {
public static char[][] chessboard = {
{'┌','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┐'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'└','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┘'}
};
public static String separator = "────";
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(" 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9");
for(int i=0; i<chessboard.length; i++){//外层循环控制行
System.out.print(i + " ");
for(int j=0; j<chessboard[i].length; j++){//内层循环控制列
if(j == chessboard[i].length - 1){//最后一列
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j]);
} else {
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j] + separator);//使用print打印,不换行
}
}
System.out.println();//打印完一行后换行
if(i < chessboard.length-1) {//排除最后一行
System.out.println(" │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
}
}
}
}
c.棋盘在玩家使用过程中会反复展示,需要使用方法来进行优化
public class Gobang {
public static char[][] chessboard = {
{'┌','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┐'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'└','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┘'}
};
public static String separator = "────";
public static void main(String[] args) {
showChessboard();
}
public static void showChessboard() {
System.out.println("========================================================");
System.out.println(" 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9");
for(int i=0; i<chessboard.length; i++){//外层循环控制行
System.out.print(i + " ");
for(int j=0; j<chessboard[i].length; j++){//内层循环控制列
if(j == chessboard[i].length - 1){//最后一列
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j]);
} else {
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j] + separator);//使用print打印,不换行
}
}
System.out.println();//打印完一行后换行
if(i < chessboard.length-1) {//排除最后一行
System.out.println(" │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
}
}
}
}
2.落子
a.玩家A、B会交替落子
int totalPosition = chessboard.length * chessboard[0].length;
for(int times=0; times < totalPosition; times++){
System.out.println(times % 2 == 0 ? "请玩家A落子" : "请玩家B落子");
}
b.落子位置必须是0~100之间的整数,且不能使用已经存在棋子的位置
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 五子棋
*
*/
public class Gobang {
public static char[][] chessboard = {
{'┌','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┐'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'└','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┘'}
};
public static String separator = "────";
public static char pieceA = '○';//玩家A的棋子
public static char pieceB = '■';//玩家B的棋子
public static void main(String[] args) {
showChessboard();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int totalPosition = chessboard.length * chessboard[0].length;
for(int times=0; times < totalPosition; times++){
System.out.println(times % 2 == 0 ? "请玩家A落子:" : "请玩家B落子:");
char currentPiece = (times % 2 == 0) ? pieceA : pieceB;//当前使用的棋子
while(true) {//保证落子成功才能够退出循环
//检测Scanner中是否有输入的数据并且判断数据是否为整数,如果没有数据,就需要从控制台输入
if(sc.hasNextInt()){
int position = sc.nextInt();
if (position >= 0 && position < totalPosition) {
//比如:position = 21在13 X 13的棋盘中,行号为21 / 13 = 1,列号为21 % 13 = 8
int row = position / chessboard.length;//位置除以棋盘数组的长度得到行号
int colo = position % chessboard[0].length;//位置取模棋盘总列数得到列号
if(chessboard[row][colo] == pieceA || chessboard[row][colo] == pieceB){
System.out.println("该位置已经有落子了,请重新选择落子位置");
continue;
} else {
chessboard[row][colo] = currentPiece;
break;
}
} else {
System.out.println("非法落子,请重新选择落子位置");
}
} else {
System.out.println("非法落子,请输入整数");
sc.next();//将Scanner中存储的非法数据取出来,防止死循环
}
}
//落子完成后,棋盘需重新展示
showChessboard();
}
}
public static void showChessboard() {
System.out.println("========================================================");
System.out.println(" 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9");
for(int i=0; i<chessboard.length; i++){//外层循环控制行
System.out.print(i + " ");
for(int j=0; j<chessboard[i].length; j++){//内层循环控制列
if(j == chessboard[i].length - 1){//最后一列
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j]);
} else {
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j] + separator);//使用print打印,不换行
}
}
System.out.println();//打印完一行后换行
if(i < chessboard.length-1) {//排除最后一行
System.out.println(" │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
}
}
}
}
c.落子完成后,需要校验是否获胜
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 五子棋
*
*/
public class Gobang {
public static char[][] chessboard = {
{'┌','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┐'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'└','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┘'}
};
public static String separator = "────";
public static char pieceA = '○';//玩家A的棋子
public static char pieceB = '■';//玩家B的棋子
public static void main(String[] args) {
showChessboard();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int totalPosition = chessboard.length * chessboard[0].length;
outer:
for(int times=0; times < totalPosition; times++){
System.out.println(times % 2 == 0 ? "请玩家A落子:" : "请玩家B落子:");
char currentPiece = (times % 2 == 0) ? pieceA : pieceB;//当前使用的棋子
while(true) {//保证落子成功才能够退出循环
//检测Scanner中是否有输入的数据并且判断数据是否为整数,如果没有数据,就需要从控制台输入
if(sc.hasNextInt()){
int position = sc.nextInt();
if (position >= 0 && position < totalPosition) {
//比如:position = 21在13 X 13的棋盘中,行号为21 / 13 = 1,列号为21 % 13 = 8
int row = position / chessboard.length;//位置除以棋盘数组的长度得到行号
int colo = position % chessboard[0].length;//位置取模棋盘总列数得到列号
if(chessboard[row][colo] == pieceA || chessboard[row][colo] == pieceB){
System.out.println("该位置已经有落子了,请重新选择落子位置");
continue;
} else {
chessboard[row][colo] = currentPiece;
break;
}
} else {
System.out.println("非法落子,请重新选择落子位置");
}
} else {
System.out.println("非法落子,请输入整数");
sc.next();//将Scanner中存储的非法数据取出来,防止死循环
}
}
//落子完成后,棋盘需重新展示
showChessboard();
//判断获胜情况:一共4种
for(int i=0; i<chessboard.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j<chessboard[i].length; j++){
//第一种:水平方向上存在同一玩家的连续5颗棋子
//(i,j) (i,j+1) (i,j+2) (i,j+3) (i,j+4)
boolean case1 = (j + 4 < chessboard[i].length)
&& chessboard[i][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i][j+1] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i][j+2] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i][j+3] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i][j+4] == currentPiece;
//第二种:垂直方向上存在同一玩家的连续5颗棋子
//(i,j)(i+1,j)(i+2,j)(i+3,j)(i+4,j)
boolean case2 = (i + 4 <chessboard.length)
&& chessboard[i][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+1][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+2][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+3][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+4][j] == currentPiece;
//第三种:135°角存在同一玩家的连续5颗棋子
//(i,j) (i+1,j+1) (i+2,j+2) (i+3,j+3) (i+4,j+4)
boolean case3 = (i + 4 <chessboard.length)
&& (j + 4 < chessboard[i].length)
&& chessboard[i][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+1][j+1] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+2][j+2] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+3][j+3] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+4][j+4] == currentPiece;
//第四种:45°角存在同一玩家的连续5颗棋子
//(i,j) (i-1,j+1) (i-2,j+2) (i-3,j+3) (i-4,j+4)
boolean case4 = (i - 4 >= 0)
&& (j + 4 < chessboard[i].length)
&& chessboard[i][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i-1][j+1] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i-2][j+2] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i-3][j+3] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i-4][j+4] == currentPiece;
if(case1 || case2 || case3 || case4){
System.out.println(times % 2 == 0 ? "玩家A获得胜利":"玩家B获得胜利");
break outer;
}
}
}
}
}
public static void showChessboard() {
System.out.println("========================================================");
System.out.println(" 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9");
for(int i=0; i<chessboard.length; i++){//外层循环控制行
System.out.print(i + " ");
for(int j=0; j<chessboard[i].length; j++){//内层循环控制列
if(j == chessboard[i].length - 1){//最后一列
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j]);
} else {
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j] + separator);//使用print打印,不换行
}
}
System.out.println();//打印完一行后换行
if(i < chessboard.length-1) {//排除最后一行
System.out.println(" │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
}
}
}
}
d.棋盘使用完毕还未分出胜负,需要提示(最终版)
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 五子棋
*
*/
public class Gobang {
public static char[][] chessboard = {
{'┌','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┐'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'└','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┘'}
};
public static String separator = "────";
public static char pieceA = '○';//玩家A的棋子
public static char pieceB = '■';//玩家B的棋子
public static int times = 0; //记录棋盘使用次数,偶数次玩家A落子,奇数次玩家B落子
public static void main(String[] args) {
showChessboard();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int totalPosition = chessboard.length * chessboard[0].length;
outer:
while(times < totalPosition){
System.out.println(times % 2 == 0 ? "请玩家A落子:" : "请玩家B落子:");
char currentPiece = (times % 2 == 0) ? pieceA : pieceB;//当前使用的棋子
while(true) {//保证落子成功才能够退出循环
//检测Scanner中是否有输入的数据并且判断数据是否为整数,如果没有数据,就需要从控制台输入
if(sc.hasNextInt()){
int position = sc.nextInt();
if (position >= 0 && position < totalPosition) {
//比如:position = 21在13 X 13的棋盘中,行号为21 / 13 = 1,列号为21 % 13 = 8
int row = position / chessboard.length;//位置除以棋盘数组的长度得到行号
int colo = position % chessboard[0].length;//位置取模棋盘总列数得到列号
if(chessboard[row][colo] == pieceA || chessboard[row][colo] == pieceB){
System.out.println("该位置已经有落子了,请重新选择落子位置");
continue;
} else {
chessboard[row][colo] = currentPiece;
break;
}
} else {
System.out.println("非法落子,请重新选择落子位置");
}
} else {
System.out.println("非法落子,请输入整数");
sc.next();//将Scanner中存储的非法数据取出来,防止死循环
}
}
//落子完成后,棋盘需重新展示
showChessboard();
//判断获胜情况:一共4种
for(int i=0; i<chessboard.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j<chessboard[i].length; j++){
//第一种:水平方向上存在同一玩家的连续5颗棋子
//(i,j) (i,j+1) (i,j+2) (i,j+3) (i,j+4)
boolean case1 = (j + 4 < chessboard[i].length)
&& chessboard[i][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i][j+1] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i][j+2] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i][j+3] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i][j+4] == currentPiece;
//第二种:垂直方向上存在同一玩家的连续5颗棋子
//(i,j)(i+1,j)(i+2,j)(i+3,j)(i+4,j)
boolean case2 = (i + 4 <chessboard.length)
&& chessboard[i][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+1][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+2][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+3][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+4][j] == currentPiece;
//第三种:135°角存在同一玩家的连续5颗棋子
//(i,j) (i+1,j+1) (i+2,j+2) (i+3,j+3) (i+4,j+4)
boolean case3 = (i + 4 <chessboard.length)
&& (j + 4 < chessboard[i].length)
&& chessboard[i][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+1][j+1] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+2][j+2] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+3][j+3] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i+4][j+4] == currentPiece;
//第四种:45°角存在同一玩家的连续5颗棋子
//(i,j) (i-1,j+1) (i-2,j+2) (i-3,j+3) (i-4,j+4)
boolean case4 = (i - 4 >= 0)
&& (j + 4 < chessboard[i].length)
&& chessboard[i][j] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i-1][j+1] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i-2][j+2] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i-3][j+3] == currentPiece
&& chessboard[i-4][j+4] == currentPiece;
if(case1 || case2 || case3 || case4){
System.out.println(times % 2 == 0 ? "玩家A获得胜利":"玩家B获得胜利");
break outer;
}
}
}
times++;
}
if(times == totalPosition){ //说明棋盘已经用完还未分出胜负
System.out.println("平局");
}
}
public static void showChessboard() {
System.out.println("========================================================");
System.out.println(" 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9");
for(int i=0; i<chessboard.length; i++){//外层循环控制行
System.out.print(i + " ");
for(int j=0; j<chessboard[i].length; j++){//内层循环控制列
if(j == chessboard[i].length - 1){//最后一列
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j]);
} else {
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j] + separator);//使用print打印,不换行
}
}
System.out.println();//打印完一行后换行
if(i < chessboard.length-1) {//排除最后一行
System.out.println(" │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
}
}
}
}
for(int j=0; j<chessboard[i].length; j++){//内层循环控制列
if(j == chessboard[i].length - 1){//最后一列
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j]);
} else {
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j] + separator);//使用print打印,不换行
}
}
System.out.println();//打印完一行后换行
if(i < chessboard.length-1) {//排除最后一行
System.out.println(" │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
}
}
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_80477286/article/details/135480949
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 数据结构_单链表-1.23
- 自动导入组件unplugin-auto-import和unplugin-vue-components
- LabVIEW开发自动驾驶的双目测距系统
- 跟我学C++编程中级篇——std::enable_if的使用
- 本地MinIO存储服务如何创建Buckets并实现公网访问上传文件
- 实现相对准时的setTimeout
- 什么是 XSS 攻击,如何避免?
- 失而复得!4年前的废柴,如今软件测试领域翻身成大咖!
- 基于Java SSM框架实现医院预约挂号系统项目【项目源码】
- shell脚本查看端口是否连通