C++复习之构造函数调用规则
发布时间:2023年12月29日
1、创建一个类,C++会给每个类添加至少3个函数(默认(空实现),析构(空实现),拷贝构造(值拷贝))?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
int m_age;
// Person()
// {
// cout<<"Person的默认构造函数"<<endl;
//
// }
// Person(int age)
// {
// cout<<"Person的有参构造函数"<<endl;
// m_age=age;
// }
// Person(const Person &p)
// {
// cout<<"Person的拷贝构造函数"<<endl;
// m_age=p.m_age;
// }
~Person()
{
cout<<"Person的析构函数"<<endl;
}
};
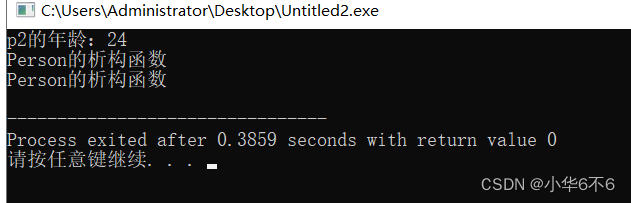
void test01()
{
Person p;
p.m_age=24;
Person p2(p);
cout<<"p2的年龄:"<<p2.m_age<<endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
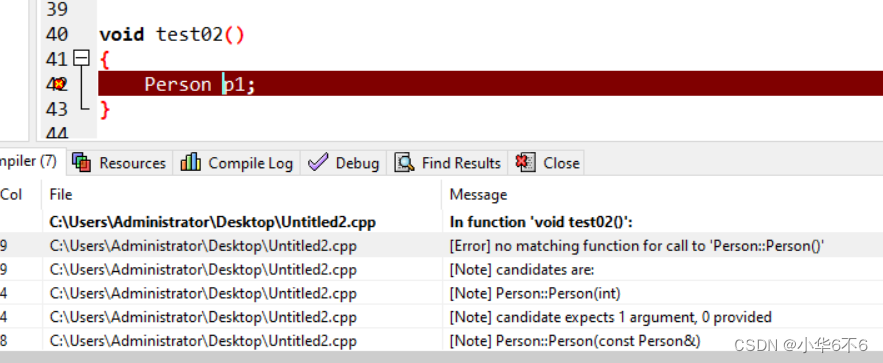
2、如果写了有参构造函数,编译器就不会提供无参构造函数 ,但依然提供拷贝构造函数
以下验证写了有参,既无无参:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
int m_age;
// Person()
// {
// cout<<"Person的默认构造函数"<<endl;
//
// }
Person(int age)
{
cout<<"Person的有参构造函数"<<endl;
m_age=age;
}
// Person(const Person &p)
// {
// cout<<"Person的拷贝构造函数"<<endl;
// m_age=p.m_age;
// }
~Person()
{
cout<<"Person的析构函数"<<endl;
}
};
void test02()
{
Person p1;
}
//void test01()
//{
// Person p;
// p.m_age=24;
// Person p2(p);
// cout<<"p2的年龄:"<<p2.m_age<<endl;
//
//}
int main()
{
// test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
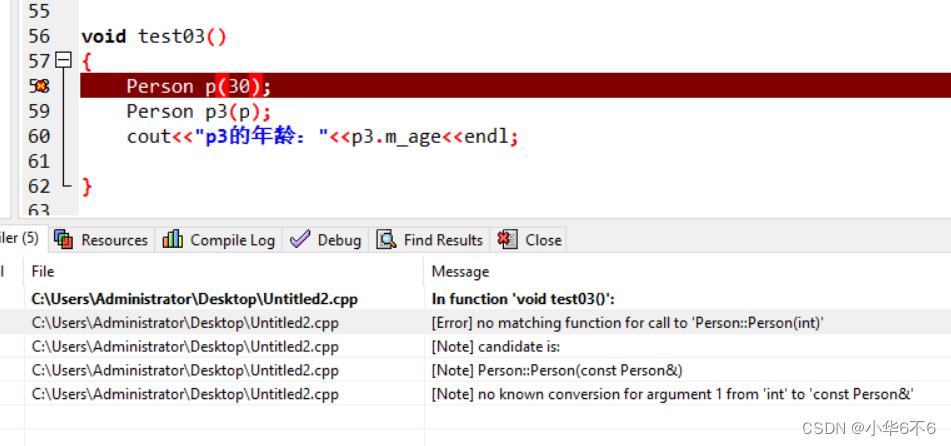
以下验证写了有参,仍有拷贝:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
int m_age;
// Person()
// {
// cout<<"Person的默认构造函数"<<endl;
//
// }
Person(int age)
{
cout<<"Person的有参构造函数"<<endl;
m_age=age;
}
// Person(const Person &p)
// {
// cout<<"Person的拷贝构造函数"<<endl;
// m_age=p.m_age;
// }
~Person()
{
cout<<"Person的析构函数"<<endl;
}
};
void test03()
{
Person p(30);
Person p3(p);
cout<<"p3的年龄:"<<p3.m_age<<endl;
}
int main()
{
test03();
return 0;
}

3、如果写了拷贝构造函数,编译器就不会提供其他的普通构造函数?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
int m_age;
// Person()
// {
// cout<<"Person的默认构造函数"<<endl;
//
// }
// Person(int age)
// {
// cout<<"Person的有参构造函数"<<endl;
// m_age=age;
// }
Person(const Person &p)
{
cout<<"Person的拷贝构造函数"<<endl;
m_age=p.m_age;
}
~Person()
{
cout<<"Person的析构函数"<<endl;
}
};
void test03()
{
Person p(30);
Person p3(p);
cout<<"p3的年龄:"<<p3.m_age<<endl;
}
int main()
{
test03();
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51615604/article/details/135273506
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!