一、泛型
? ? ??我们可以在类的声明处增加泛型列表,如:<T,E,V>。
? ? ??此处,字符可以是任何标识符,一般采用这3个字母。
【示例9-1】泛型类的声明
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | class?MyCollection<E>?{//?E:表示泛型;
????Object[]?objs?=?new?Object[5];
????public?E?get(int?index)?{//?E:表示泛型;
????????return?(E)?objs[index];
????}
????public?void?set(E?e,?int?index)?{//?E:表示泛型;
????????objs[index]?=?e;
????}
}
|
? ? ??泛型E像一个占位符一样表示“未知的某个数据类型”,我们在真正调用的时候传入这个“数据类型”。
【示例9-2】泛型类的应用
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | public?class?TestGenerics?{
????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{
????????//?这里的”String”就是实际传入的数据类型;
????????MyCollection<String>?mc?=?new?MyCollection<String>();
????????mc.set("aaa",?0);
????????mc.set("bbb",?1);
????????String?str?=?mc.get(1);?//加了泛型,直接返回String类型,不用强制转换;
????????System.out.println(str);
????}
}
|
二、Collection接口
? Collection 表示一组对象,它是集中、收集的意思。Collection接口的两个子接口是List、Set接口。
表9-1 Collection接口中定义的方法

? ? ??由于List、Set是Collection的子接口,意味着所有List、Set的实现类都有上面的方法。我们下一节中,通过ArrayList实现类来测试上面的方法。
三、List特点和常用方法
List是有序、可重复的容器。
? ? ??有序:List中每个元素都有索引标记。可以根据元素的索引标记(在List中的位置)访问元素,从而精确控制这些元素。
? ? ??可重复:List允许加入重复的元素。更确切地讲,List通常允许满足 e1.equals(e2) 的元素重复加入容器。
? ? ??除了Collection接口中的方法,List多了一些跟顺序(索引)有关的方法,参见下表:
表9-2List接口中定义的方法

? ? ??List接口常用的实现类有3个:ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector。
【示例9-4】List的常用方法
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | public?class?TestList?{
????/**
?????*?测试add/remove/size/isEmpty/contains/clear/toArrays等方法
?????*/
????public?static?void?test01()?{
????????List<String>?list?=?new?ArrayList<String>();
????????System.out.println(list.isEmpty());?//?true,容器里面没有元素
????????list.add("高淇");
????????System.out.println(list.isEmpty());?//?false,容器里面有元素
????????list.add("高小七");
????????list.add("高小八");
????????System.out.println(list);
????????System.out.println("list的大小:"?+?list.size());
????????System.out.println("是否包含指定元素:"?+?list.contains("高小七"));
????????list.remove("高淇");
????????System.out.println(list);
????????Object[]?objs?=?list.toArray();
????????System.out.println("转化成Object数组:"?+?Arrays.toString(objs));
????????list.clear();
????????System.out.println("清空所有元素:"?+?list);
????}
????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{
????????test01();
????}
}
|
? ? ??执行结果如图9-3所示:

【示例9-5】两个List之间的元素处理
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | public?class?TestList?{
????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{
????????test02();
????}
????/**
?????*?测试两个容器之间元素处理
?????*/
????public?static?void?test02()?{
????????List<String>?list?=?new?ArrayList<String>();
????????list.add("高淇");
????????list.add("高小七");
????????list.add("高小八");
????????List<String>?list2?=?new?ArrayList<String>();
????????list2.add("高淇");
????????list2.add("张三");
????????list2.add("李四");
????????System.out.println(list.containsAll(list2));?//false?list是否包含list2中所有元素
????????System.out.println(list);
????????list.addAll(list2);?//将list2中所有元素都添加到list中
????????System.out.println(list);
????????list.removeAll(list2);?//从list中删除同时在list和list2中存在的元素
????????System.out.println(list);
????????list.retainAll(list2);?//取list和list2的交集
????????System.out.println(list);
????}
}
|
? ? ? 执行结果如图9-4所示:
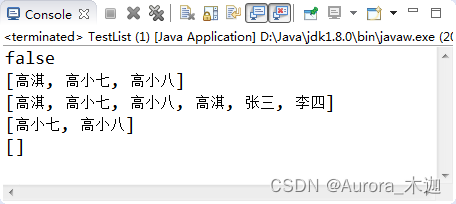
图9-4 示例9-5运行效果图
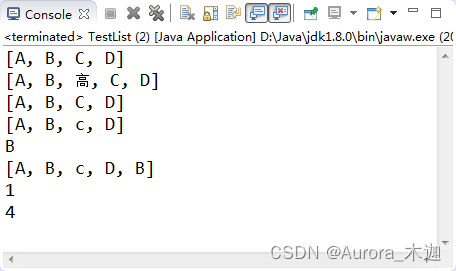
【示例9-6】List中操作索引的常用方法
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | public?class?TestList?{
????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{
????????test03();
????}
????/**
?????*?测试List中关于索引操作的方法
?????*/
????public?static?void?test03()?{
????????List<String>?list?=?new?ArrayList<String>();
????????list.add("A");
????????list.add("B");
????????list.add("C");
????????list.add("D");
????????System.out.println(list);?//?[A,?B,?C,?D]
????????list.add(2,?"高");
????????System.out.println(list);?//?[A,?B,?高,?C,?D]
????????list.remove(2);
????????System.out.println(list);?//?[A,?B,?C,?D]
????????list.set(2,?"c");
????????System.out.println(list);?//?[A,?B,?c,?D]
????????System.out.println(list.get(1));?//?返回:B
????????list.add("B");
????????System.out.println(list);?//?[A,?B,?c,?D,?B]
????????System.out.println(list.indexOf("B"));?//?1?从头到尾找到第一个"B"
????????System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("B"));?//?4?从尾到头找到第一个"B"
????}
}
|
? ? ??执行结果如图9-5所示:
三、Map接口-HashMap和HashTable
Map就是用来存储“键(key)-值(value) 对”的
Map类中存储的“键值对”通过键来标识,所以“键对象”不能重复(根据equals方法),否则新的会覆盖旧的
Map 接口的实现类有HashMap、TreeMap、HashTable、Properties等
HashMap底层实现采用了哈希表,这是一种非常重要的数据结构。希表的本质就是“数组+链表”
Entry[] table 就是HashMap的核心数组结构,我们也称之为“位桶数组”。一个Entry对象存储了:
- key:键对象,value:值对象
- next:下一个节点
- hash: 键对象的hash值
Entry[]数组的结构:
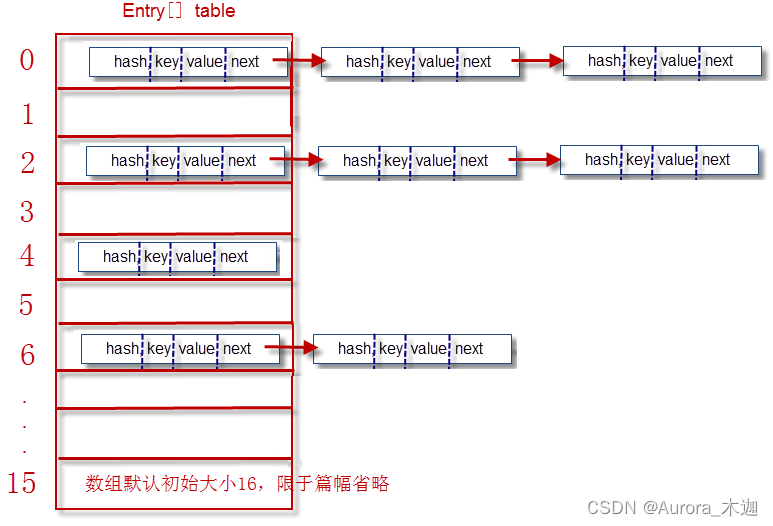
存储数据过程put(key,value)

? 当添加一个元素(key-value)时,首先计算key的hash值,以此确定插入数组中的位置,但是可能存在同一hash值的元素已经被放在数组同一位置了,这时就添加到同一hash值的元素的后面,他们在数组的同一位置,就形成了链表,同一个链表上的Hash值是相同的,所以说数组存放的是链表。
HashMap
?HashMap采用哈希算法实现,是Map接口最常用的实现类。 由于底层采用了哈希表存储数据,我们要求键不能重复,如果发生重复,新的键值对会替换旧的键值对。 HashMap在查找、删除、修改方面都有非常高的效率。
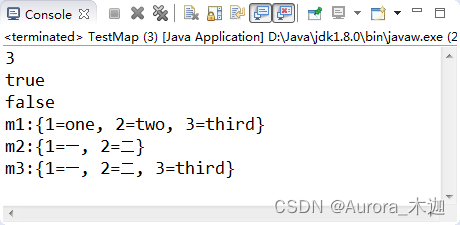
【示例9-7】Map接口中的常用方法
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | public?class?TestMap?{
????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{
????????Map<Integer,?String>?m1?=?new?HashMap<Integer,?String>();
????????Map<Integer,?String>?m2?=?new?HashMap<Integer,?String>();
????????m1.put(1,?"one");
????????m1.put(2,?"two");
????????m1.put(3,?"three");
????????m2.put(1,?"一");
????????m2.put(2,?"二");
????????System.out.println(m1.size());
????????System.out.println(m1.containsKey(1));
????????System.out.println(m2.containsValue("two"));
????????m1.put(3,?"third");?//键重复了,则会替换旧的键值对
????????Map<Integer,?String>?m3?=?new?HashMap<Integer,?String>();
????????m3.putAll(m1);
????????m3.putAll(m2);
????????System.out.println("m1:"?+?m1);
????????System.out.println("m2:"?+?m2);
????????System.out.println("m3:"?+?m3);
????}
}
|
? ? ??执行结果如图9-11所示:
HashTable
? ? ? HashTable类和HashMap用法几乎一样,底层实现几乎一样,只不过HashTable的方法添加了synchronized关键字确保线程同步检查,效率较低。
HashMap与HashTable的区别
? ? ??1. HashMap: 线程不安全,效率高。允许key或value为null。
? ? ??2. HashTable: 线程安全,效率低。不允许key或value为null。
四、Set接口-HashSet基本使用
大家在做下面练习时,重点体会“Set是无序、不可重复”的核心要点。
【示例9-9】HashSet的使用
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | public?class?Test?{
????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{
????????Set<String>?s?=?new?HashSet<String>();
????????s.add("hello");
????????s.add("world");
????????System.out.println(s);
????????s.add("hello");?//相同的元素不会被加入
????????System.out.println(s);
????????s.add(null);
????????System.out.println(s);
????????s.add(null);
????????System.out.println(s);
????}
}
|
? ? ??执行结果如图9-24所示:

五、Collections工具类
类 java.util.Collections 提供了对Set、List、Map进行排序、填充、查找元素的辅助方法。
? ? ??1. void sort(List) //对List容器内的元素排序,排序的规则是按照升序进行排序。
? ? ??2. void shuffle(List) //对List容器内的元素进行随机排列。
? ? ??3. void reverse(List) //对List容器内的元素进行逆续排列 。
? ? ??4. void fill(List, Object) //用一个特定的对象重写整个List容器。
? ? ??5. int binarySearch(List, Object)//对于顺序的List容器,采用折半查找的方法查找特定对象。
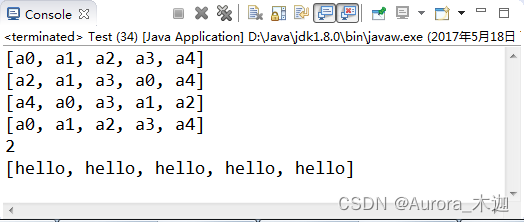
【示例9-23】Collections工具类的常用方法
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | public?class?Test?{
????public?static?void?main(String[]?args)?{
????????List<String>?aList?=?new?ArrayList<String>();
????????for?(int?i?=?0;?i?<?5;?i++){
????????????aList.add("a"?+?i);
????????}
????????System.out.println(aList);
????????Collections.shuffle(aList);?//?随机排列
????????System.out.println(aList);
????????Collections.reverse(aList);?//?逆续
????????System.out.println(aList);
????????Collections.sort(aList);?//?排序
????????System.out.println(aList);
????????System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(aList,?"a2"));?
????????Collections.fill(aList,?"hello");
????????System.out.println(aList);
????}
}
|
? ? ??执行结果如图9-31所示: