双指针算法
发布时间:2023年12月31日
目录
双指针算法
常见的两种样式:
-
双指针指向两个不同的区间
-
双指针指向一个区间的左右两端,这种方式更加常见
双指针算法思想
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
O(n^2) 时间复杂度我们要把这个思想优化,一般利用一些单调性的方式
需求 asd qwe zxc 去掉空格,每个字符串单独一行
要求输出:
asd
qwe
zxc
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[100];
gets(str);
int n = strlen(str);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int j=i;
while(j<n && str[i]!=" ") j++;
for(int k=i;k<j;k++) cout<<str[k];
cout<<endl;
//令i直接移到j的位置,利用的是发现题目中单调性来优化,降低时间复杂度
i=j;
}
return 0;
}双指针算法模板
for(int i=0,j=0;i<n;i++)
{
while(j<i && check(i,j)) j++;
//每道题目的具遗体逻辑
}
for循环遍历i,while依据题意定下j停下的位置,之后题目的具体代码,之后利用i,j之间关系进行优化最长连续不重复子序列
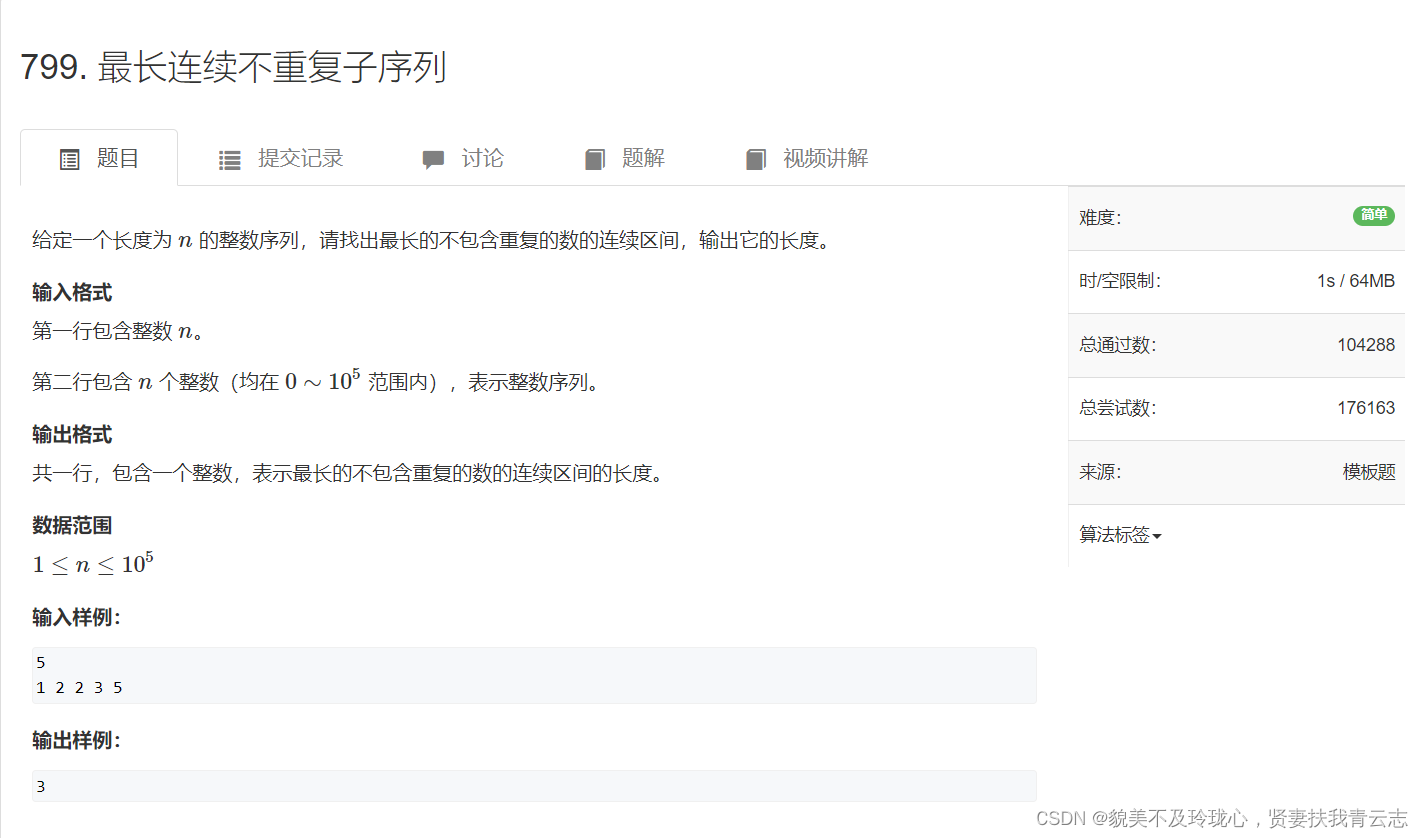
解题代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n;
int q[N], s[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &q[i]);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
s[q[i]] ++ ;
while (j < i && s[q[i]] > 1) s[q[j ++ ]] -- ;
res = max(res, i - j + 1);
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}数组元素的目标和
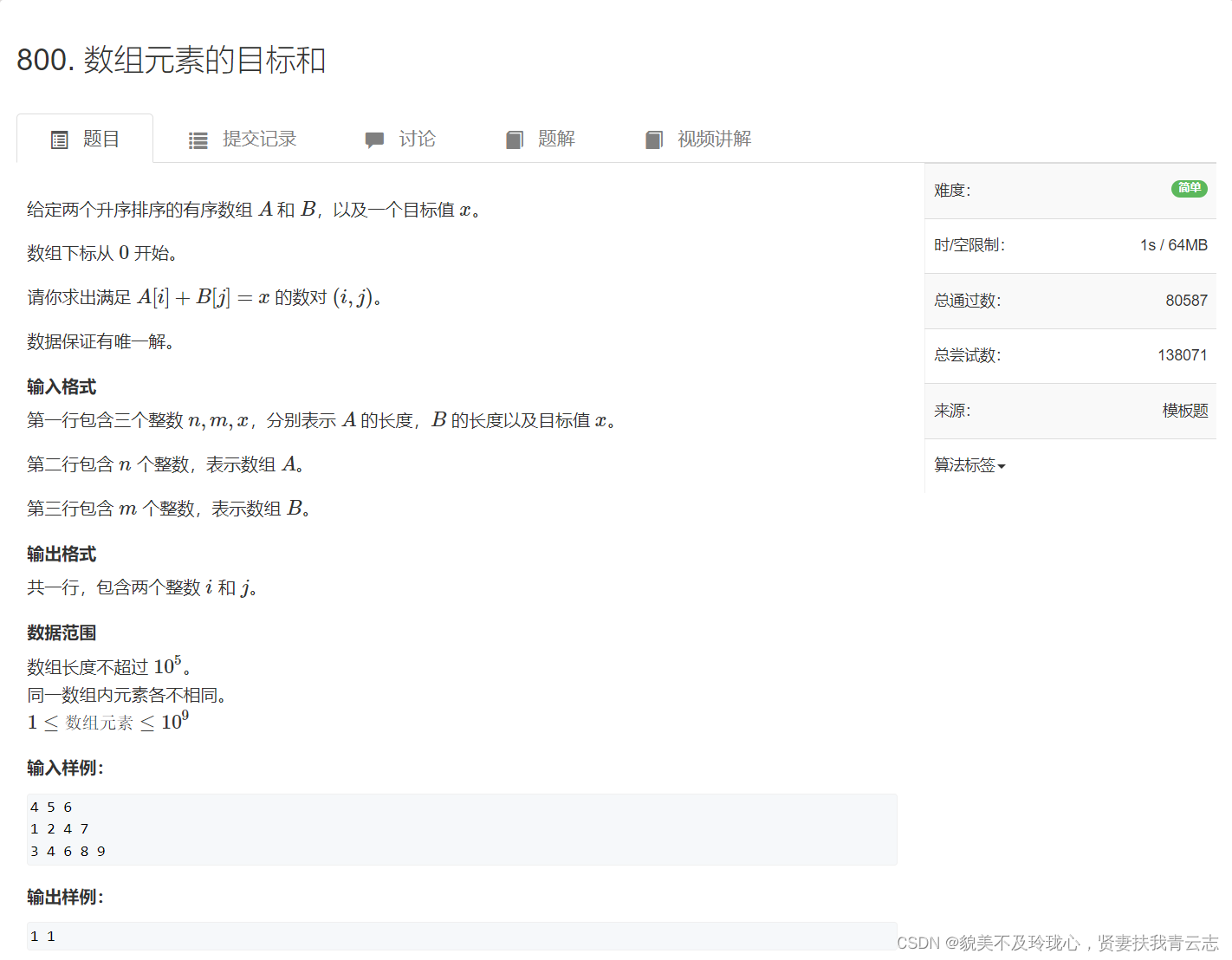
解题代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m, x;
int a[N], b[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &x);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &b[i]);
for (int i = 0, j = m - 1; i < n; i ++ )
{
while (j >= 0 && a[i] + b[j] > x) j -- ;
if (j >= 0 && a[i] + b[j] == x) cout << i << ' ' << j << endl;
}
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61553520/article/details/135320592
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 重生奇迹MU中需要组队的地方
- 【网站项目】基于SSM的271楚师师生健康管理系统
- Linux第8步_USB设置
- 海康visionmaster流程 ID:通过流程名获取流程 ID 的方法
- CMake入门教程【实战篇】使用CURL网络库
- chromium通信系统-ipcz系统(九)-ipcz系统代码实现-跨Node通信-代理和代理消除
- 文件包含检测工具汇总
- 神奇的代码——可随意修改复制页面内容
- 工厂设计模式看这一篇就够了
- 【Java基础】BIO/NIO/AIO的详细介绍与比较区分