【c++】——栈or队列or优先级队列
目录
🎓容器适配器
?容器适配器是一个封装了序列容器的一个类模板,它在一般的序列容器的基础上提供了一些不同的功能。之所以称为容器适配器,是因为它是适配容器来提供其它不一样的功能。通过对应的容器和成员函数来实现我们需要的功能。
? ? ? ? 下面介绍了三个容器适配器:statk<T>,queue<T>,priority_queue<T>。
?注意:容器适配器都不存在迭代器。
????????如果没有为stack,queue指定容器,默认使用deque作为默认容器。priority_queue容器默认使用vector作为默认容器。
🎓Stack栈
🚩Stack的介绍


以下是stack的成员函数?
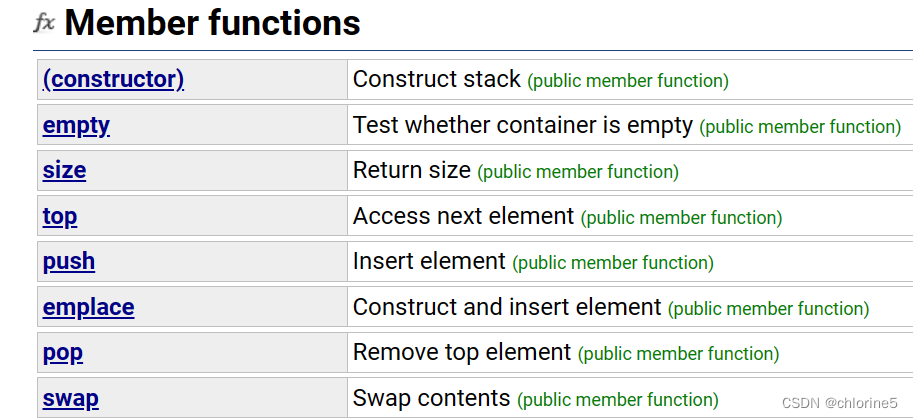
string、vector、list都是容器,而stack和queue 是容器适配器,发现stack和queue都没有迭代器,因为stack要保证后进先出(LIFO),queue要保证先进先出(FIFO)所以其实它们不需要迭代器。
🚩Stack的基本使用?
这下面是stack接口函数,使用是简单的,主要应用的场景。

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stack>//记得包头文件
int main()
{
stack<int> st;
st.push(1);
st.push(2);
st.push(3);
st.push(4);
st.push(5);
st.push(6);
while (!st.empty())
{
cout << st.top() << " ";
st.pop();
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
🚩Stack底层实现
stack就是我们数据结构学的栈,是一种操作受限制的线性表,所以它可以用链表实现,也可以用顺序表(数组)实现,不过当时C语言只实现了数组栈,因为相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入删除数据的代价比较小。那传统的写法就是用一个数组或链表去写.若按C++STL库里的方式来写,就可以用适配器(配接器)模式来实现。

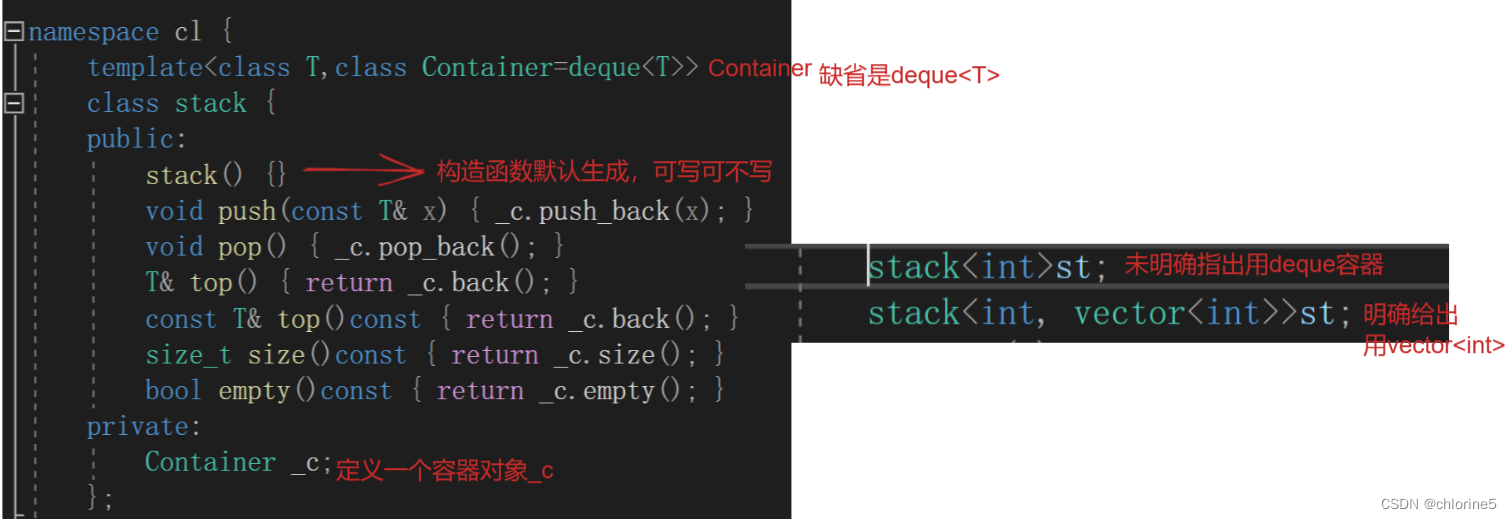
#pragma once
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<deque>
namespace cl {
template<class T,class Container=deque<T>>//Container缺省用deque容器
class stack {
public:
stack() {}
void push(const T& x) { _c.push_back(x); }
void pop() { _c.pop_back(); }
T& top() { return _c.back(); }
const T& top()const { return _c.back(); }
size_t size()const { return _c.size(); }
bool empty()const { return _c.empty(); }
private:
Container _c;
};
void test_stack1()
{
//stack<int>st;
stack<int, vector<int>>st;//明确给出用vector容器
st.push(1);
st.push(2);
st.push(3);
st.push(4);
while (!st.empty())
{
cout << st.top() << " ";
st.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_stack2()
{
stack<int, list<int>>st;//明确给出用list容器
st.push(1);
st.push(2);
st.push(3);
st.push(4);
while (!st.empty())
{
cout << st.top() << " ";
st.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
🎓queue队列
🚩queue的介绍

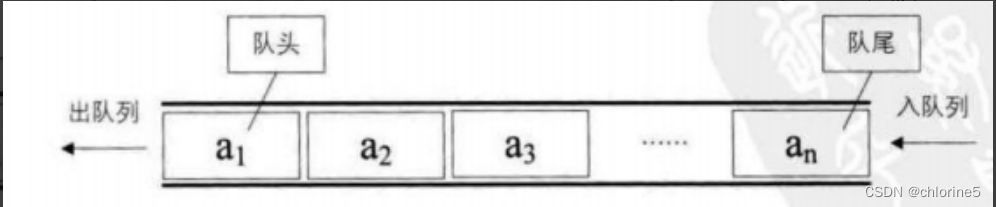
元素从队尾入队列,从对头出队列。
🚩queue的基本使用
这下面是queue接口函数,使用是简单的,主要应用的场景。
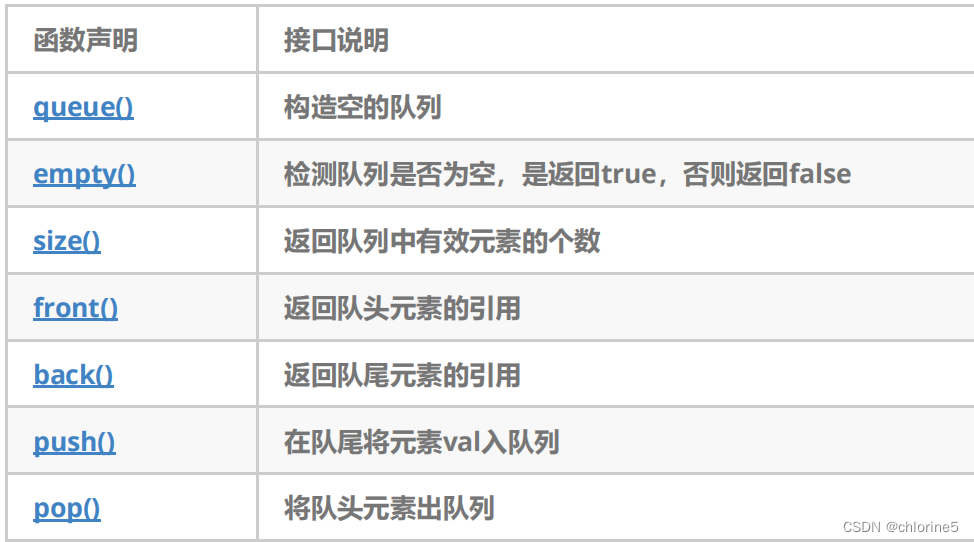
使用queue需要包含头文件#include<queue>,queue容器适配器没有迭代器
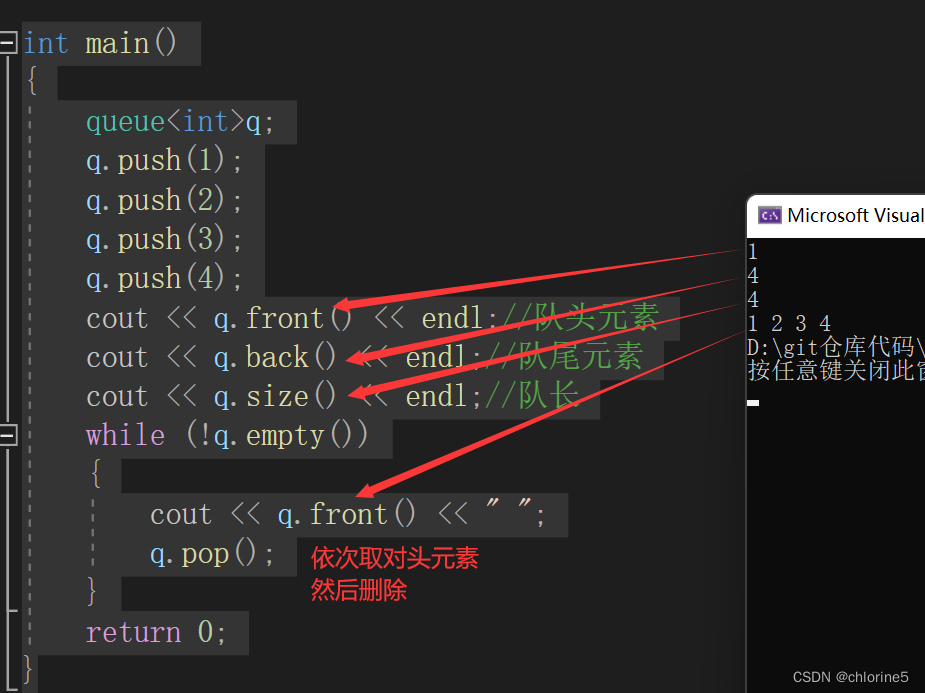
int main()
{
queue<int>q;
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
cout << q.front() << endl;//队头元素
cout << q.back() << endl;//队尾元素
cout << q.size() << endl;//队长
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
return 0;
}
🚩queue的底层实现
因为queue存在头删和尾插,因此使用vector容器来封装效率太低,头删需要挪动数据,并且vector并没有提供pop_front(),因为效率太低。
#pragma once
#include<queue>
#include<list>
namespace cl {
template <class T,class Container=deque<T>>
class queue {
public:
queue(){}
void push(const T& x) { _c.push_back(x); }//尾插
void pop() { _c.pop_front(); }//头删
T& back() { return _c.back(); }//队尾值
const T& back()const { return _c.back(); }//取队尾值
T& front() { return _c.front(); }//队头值
const T& front()const { return _c.front(); }//取队头值
size_t size()const { return _c.size(); }//队长
bool empty()const { return _c.empty(); }//判空
private:
Container _c;
};
void test_queue()
{
queue<int>q;
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_queue2()
{
queue<int,list<int>>q;
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
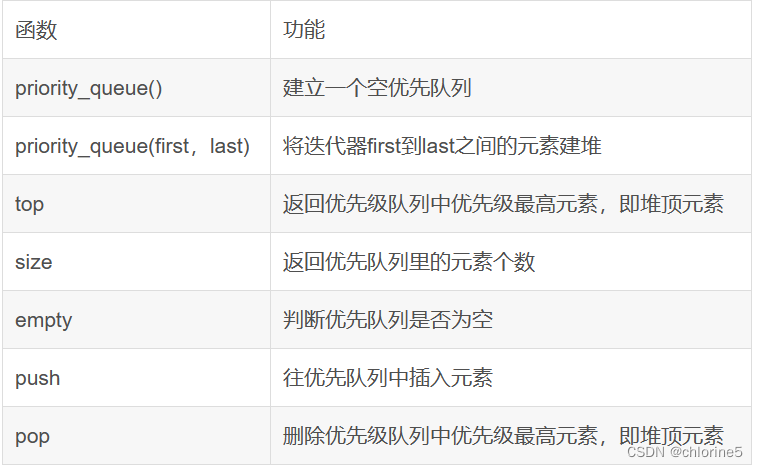
🎓priority_queue优先级队列
🚩priority_queue的介绍

默认形成大堆。优先队列使用仿函数来控制生成大根堆还是生成小根堆。
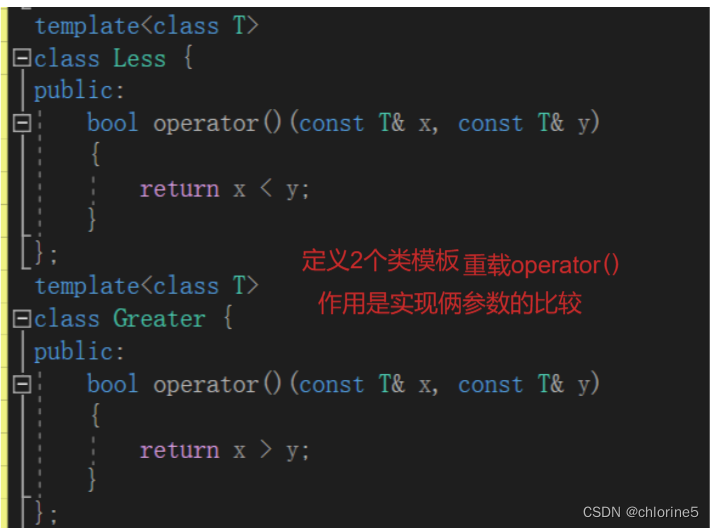
?简单介绍一下仿函数
?仿函数(Functor)又称为函数对象(Function Object)是一个能行使函数功能的类。仿函数的语法几乎和我们普通的函数调用一样,不过作为仿函数的类,都必须重载 operator() 运算符。因为调用仿函数,实际上就是通过类对象调用重载后的 operator() 运算符。仿函数是一个类,只是使用起来像函数。等下模拟实现时就知道了。
?🚩priority_queue的基本使用
优先队列默认使用vector作为存储数据的容器,在容器的基础上使用堆算法,将vector中的元素调整成一个堆结构。
注意:优先队列就是一个堆,在使用堆的地方都可以使用优先队列。默认生成大根堆,头文件也是#include<queue>
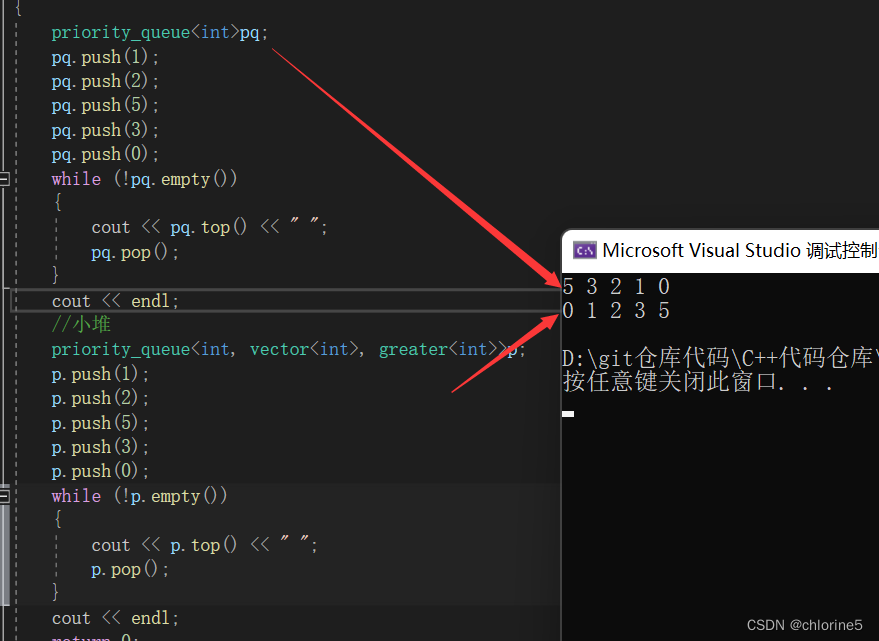
//默认调整大堆
int main()
{
priority_queue<int>pq;
pq.push(1);
pq.push(2);
pq.push(5);
pq.push(3);
pq.push(0);
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
//小堆
int main()
{
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>>pq;
pq.push(1);
pq.push(2);
pq.push(5);
pq.push(3);
pq.push(0);
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
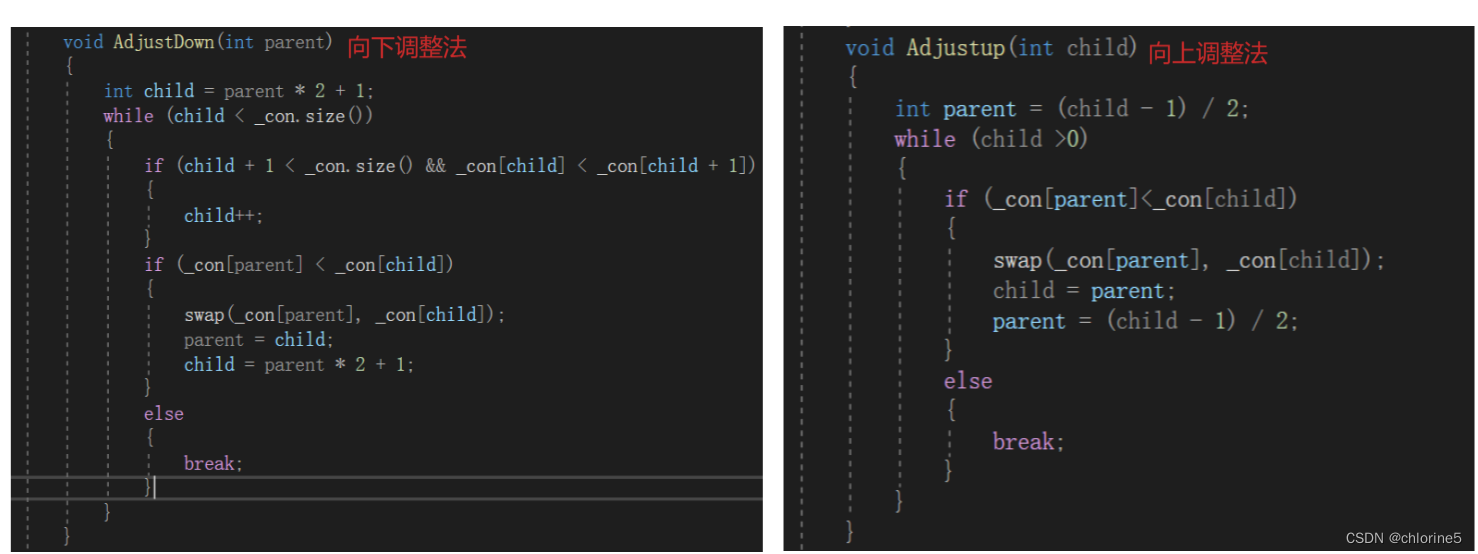
🚩priority_queue的底层实现
?? 回顾一下堆的插入与删除操作。
- ? ? ? ? 堆的插入:在堆尾插入数据,再向上调整成堆。
- ? ? ? ? 堆的删除:将堆顶元素和对尾元素交换,再向下调整成堆。
#pragma once
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
namespace cl {
template <class T,class Container=vector<T>>
class priority_queue {
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child] < _con[child + 1])
{
child++;
}
if (_con[parent] < _con[child])
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void Adjustup(int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child >0)
{
if (_con[parent]<_con[child])
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
public:
priority_queue() {}
template <class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
++first;
}
//建堆
for (int i = (_con.size - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(i);
}
}
bool empty() {
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size() {
return _con.size();
}
T& top() {
return _con.front();
}
const T& top()const {
return _con.front();
}
void push(const T& val) {
_con.push_back(val);
Adjustup(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop() {
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
//少一个元素是size减减,交换后,直接删除最后一个元素
_con.pop_back();
AdjustDown(0);
}
private:
Container _con;
};
void priority_queue1()
{
priority_queue<int>pq;
pq.push(1);
pq.push(3);
pq.push(4);
pq.push(5);
while(!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}?仿函数的使用
仿函数:优先队列通过仿函数来实现建立大根堆还是小根堆。
调整建立大根堆还是小根堆,只需要改变调整函数。父亲结点与孩子结点比较时的大于小于号。怎么通过仿函数来实现呢?

调整函数如何修改

#pragma once
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
template<class T>
class Less {
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
template<class T>
class Greater {
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
namespace cl {
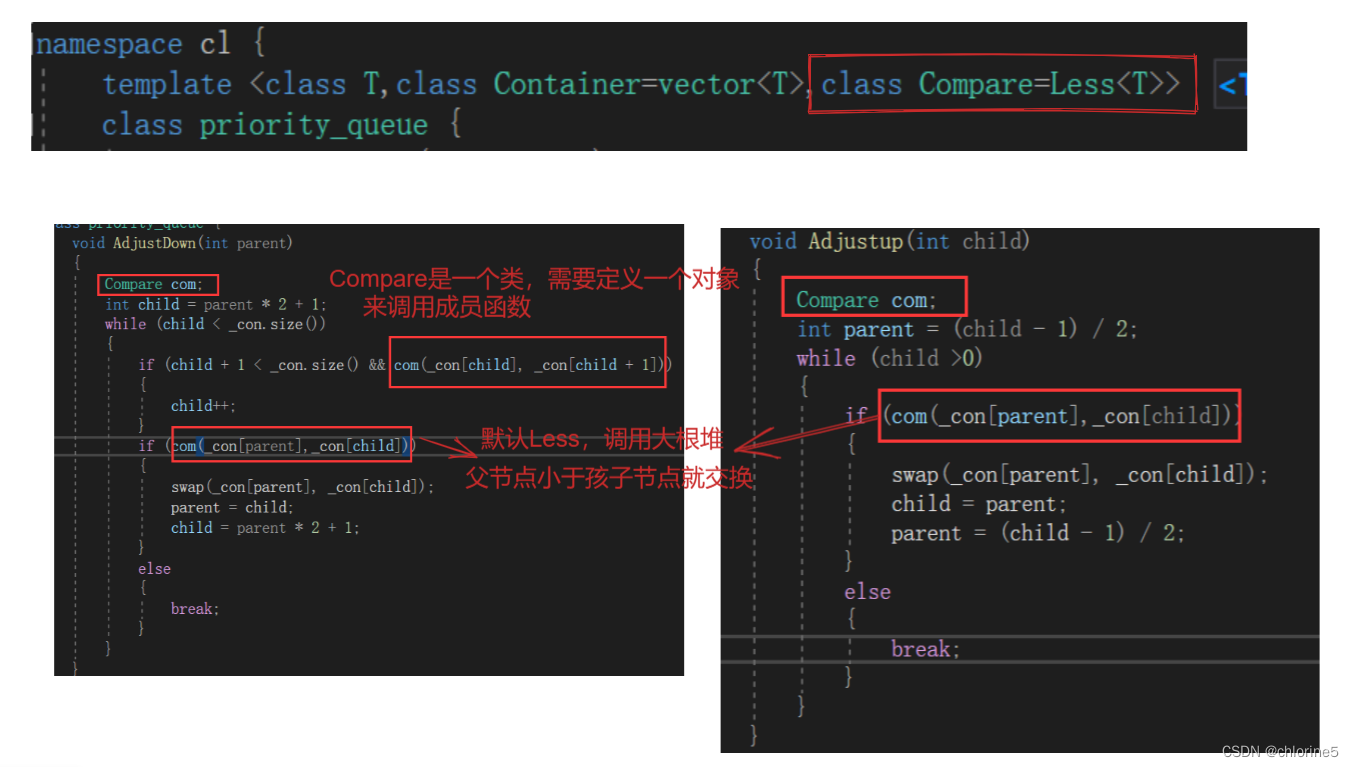
template <class T,class Container=vector<T>,class Compare=Less<T>>
class priority_queue {
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
Compare com;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]))
{
child++;
}
if (com(_con[parent],_con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void Adjustup(int child)
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child >0)
{
if (com(_con[parent],_con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
public:
priority_queue() {}
template <class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
++first;
}
//建堆
for (int i = (_con.size - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(i);
}
}
bool empty() {
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size() {
return _con.size();
}
T& top() {
return _con.front();
}
const T& top()const {
return _con.front();
}
void push(const T& val) {
_con.push_back(val);
Adjustup(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop() {
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
//少一个元素是size减减,交换后,直接删除最后一个元素
_con.pop_back();
AdjustDown(0);
}
private:
Container _con;
};
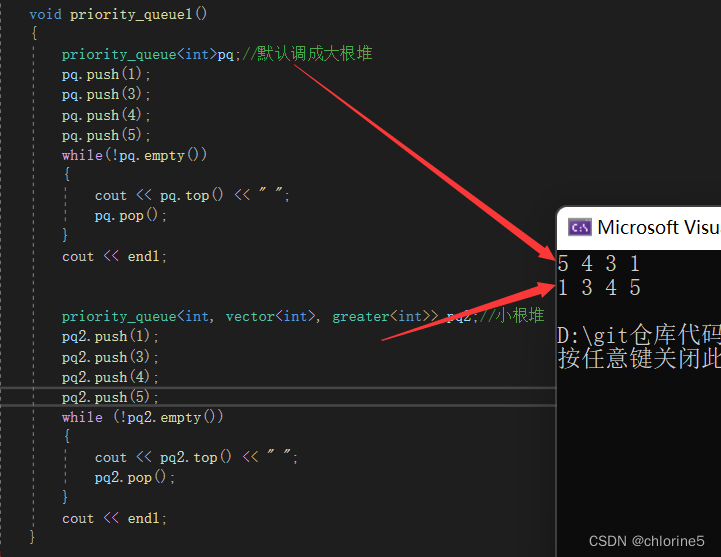
void priority_queue1()
{
priority_queue<int>pq;//默认调成大根堆
pq.push(1);
pq.push(3);
pq.push(4);
pq.push(5);
while(!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq2;//小根堆
pq2.push(1);
pq2.push(3);
pq2.push(4);
pq2.push(5);
while (!pq2.empty())
{
cout << pq2.top() << " ";
pq2.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
一帆风顺不现实,祝你挫折少一点。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 文字的baseLine算法
- java 常?的线程池模式以及不同线程池的使?场景
- UE5 C++ Slate独立程序的打包方法
- Codeforces Round 916 (Div. 3)补题
- 力扣刷题——两两交换链表的节点:24题
- k8s网络类型
- 图片编辑软件有哪些?哪个更加得心应手?
- Android学习之路(22) ARouter原理解析
- 40. 组合总和 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
- AcWing--翻转-->思维
