IPQ6010 vs. IPQ4019: The battle of Qualcomm chips and WIFI 6 vs WIFI 5
In the field of wireless communications, Qualcomm's IPQ6010 and IPQ4019 chips are engaged in a fierce technical duel, representing leading technologies for high-performance networks and mid-range connections respectively. Let’s dig deeper into their technical features to reveal the true pinnacle of this battle for future connectivity.
IPQ6010: High-performance network engine
1. Excellent processing capabilities:
IPQ6010 uses a quad-core 64-bit ARM Cortex-A53 processor with a maximum CPU frequency of up to 1.8GHz. It has excellent processing performance and can easily handle highly complex network tasks.
2. Wi-Fi 6 support:
As a leader in Wi-Fi 6, IPQ6010 supports the latest 802.11ax standard, providing users with high-throughput wireless connections, especially suitable for enterprise-level routers and advanced Wi-Fi access points.
3. Rich physical interfaces:
Multiple high-speed Ethernet ports and USB interfaces are designed to provide flexible deployment options for complex network topologies and support a variety of network interfaces and protocols.
4. Strong security:
Built-in hardware encryption and authentication functions ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data transmission, providing reliable security for enterprise-level networks.
5. Advanced wireless connection technology:
It integrates 802.11ax Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.0 wireless connection functions, supports MU-MIMO technology and OFDMA technology, providing users with high-speed and reliable wireless connection performance.
6. Wide range of applications:
High performance and flexibility enable IPQ6010 to play a key role in the Internet of Things, enterprise-level networks and advanced communication equipment, and is suitable for scenarios such as smart homes, smart cities and industrial automation.
IPQ4019: The smart choice for mid-range connectivity
1. Energy-saving design:
Known for its low-power design, it is suitable for devices that need to run for a long time, especially for smart home devices and small business networks, helping to extend battery life.
2. Reliable 802.11ac standard support:
Supports the 802.11ac standard, providing users with reliable wireless connections, suitable for home and small business networks, and providing a stable connection experience.
3. Simplified physical interface:
Provides an appropriate but sufficient number of physical interfaces, simplifies device deployment and management, and reduces the complexity of network devices.
4. Wide application fields:
The design of IPQ4019 makes it widely used in home networks, small business-level routers and smart home devices. It is suitable for building smart home systems, small business networks and other scenarios.
The result of the showdown: the battle for the pinnacle of future connectivity
Although IPQ6010 and IPQ4019 each have their own strengths and serve different markets, the battle for the pinnacle of future connections has yet to be revealed. This technology battle will be verified in actual market applications and user feedback. As technology continues to evolve, it remains to be seen which party will become the true king of connectivity. Stay tuned to witness this fierce showdown between technology giants and jointly unveil the future network.
And Comparing WiFi 6 and WiFi 5, the difference lies in these three items
WiFi 5 is the original 802.11ac wireless protocol, and WiFi 6 is the latest 802.11ax wireless protocol. In 2019, when the 802.11ax protocol was officially certified, the WiFi Alliance officially named the 802.11ax wireless protocol as the WiFi 6 wireless protocol. Moreover, the previous generations of wireless protocols can be extrapolated in order, namely WiFi 5 (802.11ac), WiFi 4 (802.11n)...

First, let's take a look at the features of WiFi 6. Compared with the most popular WiFi 5, WiFi 6 is faster, supports more concurrent devices, has lower latency and lower power consumption. WiFi 6 uses the same OFDMA technology as 5G, combined with 1024-QAM high-order modulation, which can support a maximum bandwidth of 160MHz and is nearly three times faster than WiFi 5. Intelligent frequency division technology can support more devices concurrently and increase access device capacity by 4 times. Multiple concurrent access devices can reduce queuing and proactively avoid interference coloring, reducing latency by two-thirds. When the terminal device is in standby, it supports on-demand wake-up function, reducing terminal power consumption by 30%.
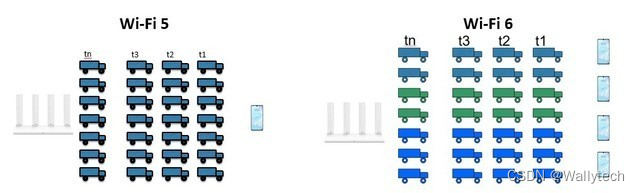
We can compare the scene where the router transmits to the device to a fleet. Under the WiFi i5 standard, the fleet can only deliver to one customer at the same time. Even if there are empty vehicles, it will still depart as usual. If there is a vehicle failure (interference), the entire The teams were unable to start. Under the WiFi 6 standard, a fleet starting at the same time can form a team of at least 26 adjacent vehicles. Each team can be dispatched to different customers. If a vehicle fails (is interfered with), it will only affect the vehicle where it is located. squad.
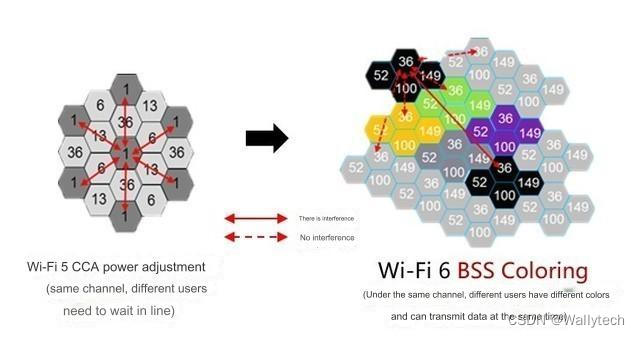
Usually when we are at home, we often search for neighbor’s WiFi signals, and these signals will interfere with our own WiFi transmission. The interference coloring technology used by WiFi 6 can mark neighbor network signal frames passing through the wall so that the user's router can ignore them. WiFi signals between neighbors can transmit data simultaneously on the same channel without interfering with each other, reducing the interference rate by 30%.
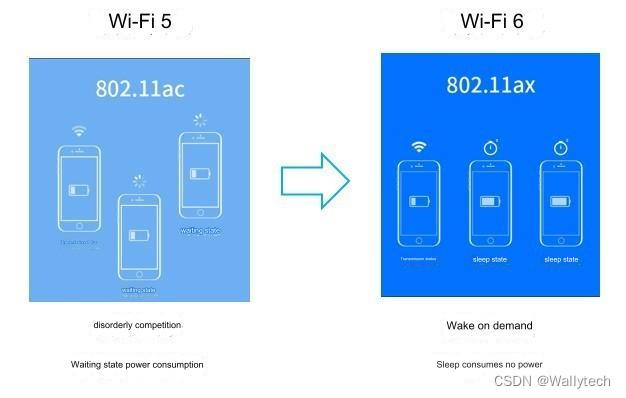
The power consumption comparison between WiFi 6 and WiFi 5 is huge. WiFi 6 will negotiate the WiFi wake-up time with the terminal to wake up on demand and consume no power during other sleep times. WiFi 5 can only communicate with one device at the same time. All terminals connected to the same route are either in the transmitting state or in the waiting state, and are disordered. The waiting state still consumes power.
It can be seen that compared to WiFi 5, WiFi 6’s technical transcendence is all-round. If users upgrade their home routers to WiFi 6 routing, they can enjoy a faster WiFi Internet experience.
By:Wallystech
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 开发电子商务网站/APP如何对接淘宝/天猫商品详情的API接口来丰富自建商城的产品展示
- 【MIdjourney】关于图像中人物视角的关键词
- 突发!大众集团「降价」救市
- 【动态规划】C++ 算法458:可怜的小猪
- LLM增强LLM;通过预测上下文来提高文生图质量;Spikformer V2;同时执行刚性和非刚性编辑的通用图像编辑框架
- 典型的无人机打击技术
- CloudCompare 二次开发(24)——欧式聚类分割
- 在Docker上使用Portainer轻松管理容器 - 安装与配置指南
- 【lesson16】进程控制之进程替换(2)
- 使用双异步后,从 191s 优化到 2s