数据结构栈实现(赋完整代码)
发布时间:2024年01月15日
1、结构及定义
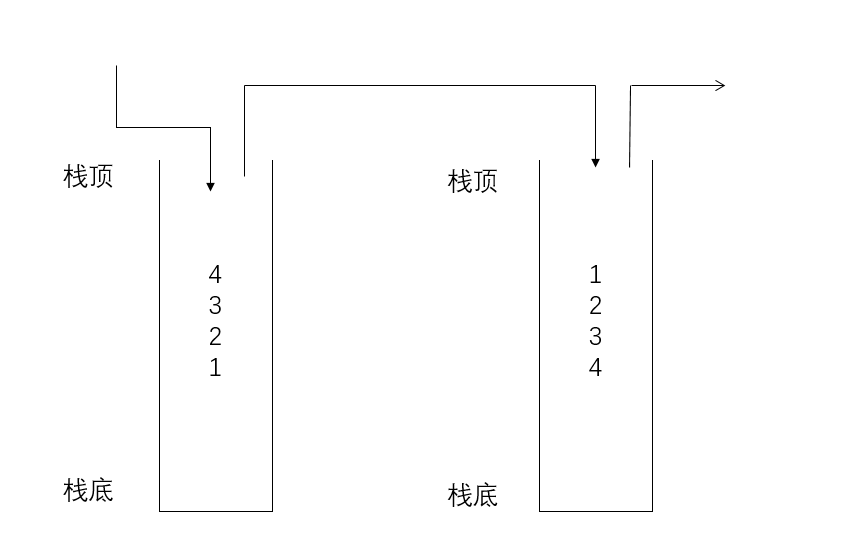
1.栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。
2.进行数据插入和删除操作的一端 称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
3.压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。 出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶
2、栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小,此处我们就使用动态开辟的数组来为大家举例。
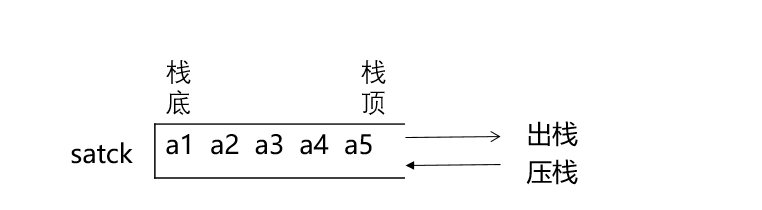
1)结构定义:栈的结构中,动态开辟位置指针与栈容量都与动态开辟顺序表的类似。设置一个栈顶变量是因为栈中数据的压账和出账都是在栈顶进行,便于操作。
typedef struct Stack {
//动态空间开辟位置
STDataType* a;
//栈顶
int top;
//容量,检查是否需要扩容
int capacity;
}ST;
2)初始化
//初始化
void StackInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
//动态开辟空间,初始化空间大小为4个数据类型空间
pst->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (pst->a == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
//容量
pst->capacity = 4;
//栈中无元素,栈顶初始化为0
pst->top = 0;
}
3)压栈
//压栈
void StackPush(ST* pst,STDataType x) {
assert(pst);
//判满
if (pst->capacity == pst->top) {
//判断初始空间是否为0,为0赋值4,不为0则在原基础山乘2
int newCapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* temp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a,sizeof(STDataType)*newCapacity);
if (temp == NULL) {
perror("relloc");
return;
}
pst->a = temp;
pst->capacity = newCapacity;
}
//修改栈顶处元素,与光标类似,在栈顶出是无元素的,是一个等待输入区,所以可以直接修改
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
//栈顶位置后移一位
pst->top++;
}
4)出栈
//出栈
void StackPop(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
//栈中有值才能出栈
assert(pst->top > 0);
pst->top--;
}
5)获取栈顶元素
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
//栈顶处无元素,栈顶前一位才是元素存放处
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
6)获取栈中元素个数
//获取栈中有效数据个数
int StackSize(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
7)判断栈空
//判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
//双等号是条件判断语句,满足返回True,不满足返回False
return pst->top == 0;
}
8)清空栈
//清空栈
void StackClear(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
pst->top = 0;
}
9)销毁栈
//销毁
void StackDestory(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
//释放栈空间
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
}
10)显示栈中元素
//显示栈中元素
void StackPrint(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
for (int i = 0; i < pst->top;i++) {
printf("%d ",pst->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
3、完整代码
1.Stack.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack {
//动态空间开辟位置
STDataType* a;
//栈顶
int top;
//容量,检查是否需要扩容
int capacity;
}ST;
//初始化
void StackInit(ST* pst);
//压栈
void StackPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
//出栈
void StackPop(ST* pst);
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* pst);
//获取栈中有效数据个数
int StackSize(ST* pst);
//判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(ST* pst);
//清空栈
void StackClear(ST* pst);
//销毁
void StackDestory(ST* pst);
//显示栈中元素
void StackPrint(ST* pst);
2.Stack.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"Stack.h"
//初始化
void StackInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
//动态开辟空间,初始化空间大小为4个数据类型空间
pst->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (pst->a == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
//容量
pst->capacity = 4;
//栈中无元素,栈顶初始化为0
pst->top = 0;
}
//压栈
void StackPush(ST* pst,STDataType x) {
assert(pst);
//判满
if (pst->capacity == pst->top) {
//判断初始空间是否为0,为0赋值4,不为0则在原基础山乘2
int newCapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* temp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a,sizeof(STDataType)*newCapacity);
if (temp == NULL) {
perror("relloc");
return;
}
pst->a = temp;
pst->capacity = newCapacity;
}
//修改栈顶处元素,与光标类似,在栈顶出是无元素的,是一个等待输入区,所以可以直接修改
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
//栈顶位置后移一位
pst->top++;
}
//出栈
void StackPop(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
//栈中有值才能出栈
assert(pst->top > 0);
pst->top--;
}
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
//栈顶处无元素,栈顶前一位才是元素存放处
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
//获取栈中有效数据个数
int StackSize(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
//判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
//双等号是条件判断语句,满足返回True,不满足返回False
return pst->top == 0;
}
//清空栈
void StackClear(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
pst->top = 0;
}
//销毁
void StackDestory(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
//释放栈空间
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
}
//显示栈中元素
void StackPrint(ST* pst) {
assert(pst);
for (int i = 0; i < pst->top;i++) {
printf("%d ",pst->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
3.Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"stack.h"
int main() {
ST stack;
StackInit(&stack);
StackPush(&stack, 1);
StackPush(&stack, 4);
StackPush(&stack, 2);
StackPush(&stack, 3);
StackPop(&stack);
int top = StackTop(&stack);
printf("%d\n",top);
StackPrint(&stack);
int size = StackSize(&stack);
printf("%d\n",size);
bool ret1 =StackEmpty(&stack);
if (ret1 == true) {
printf("为空\n");
}
else {
printf("不为空\n");
}
StackClear(&stack);
bool ret2 = StackEmpty(&stack);
if (ret2 == true) {
printf("为空\n");
}
else {
printf("不为空\n");
}
StackDestory(&stack);
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/wjfwonderful/article/details/135602694
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Flask和Vue框架实现WebSocket消息通信
- dragonfly 加 harbor 实现镜像预热
- 2分钟了解syscall系统调用|详细易懂的流程
- resetlogs失败故障恢复-ORA-01555---惜分飞
- 2024 1.9 Spark_SQL , 数据清洗API , 写出操作
- layui 自定义日期选择器今日、昨日 、本周、本月、上个月等
- 10 款顶级的免费U盘数据恢复软件(2024 年 更新)
- 数据结构学习 days2
- 51系列--数码管显示的4X4矩阵键盘设计
- C# 提取PDF中指定文本、图片的坐标