day13
1.多态的向上转型和向下转型
向上转型: 父类的引用指向子类的对象
Person person = new Man();
向下转型: 将父类的引用强转为子类的对象
Man man = (Man) person;
2.instanceof关键字的用法
引用 intanceof 运行类型
3.抽象类声明方式
abstract class Person {
}
4.接口的声明方式
interface 接口名字 {
}
5.继承的语法格式
class B extends A {
}
6.重写与重载
重写:
必须是继承关系,在子类中将父类的方法给覆盖
重载:
在一个类中,方法名字一样,参数列表不一样
7.final关键字用法
1.修饰成员变量
2.修饰局部变量
3.修饰成员方法
4.修饰类
5.修饰对象引用
回顾
1.父类的引用指向子类的对象(向上转型的)
真实的开发的时候 方法的参数是父类的引用。但是调用方法的时候,传参传的是子类的对象
2.向下转型 需要强转的。先向上转型再向下转型。
3.instanceof
今天的内容
1.static
2.异常
1.static关键字【重点】
static中文意思:静态的
static是和对象无关的。
1.1生活的角度来理解静态的资源
公共的资源的都属于静态的东西
? 对象可以使用静态的资源,但是和对象无关
? 厕所里面直饮机 就是静态资源
? 对象.name
1.2Java中的静态
1.修饰成员变量 静态属性
2.修饰成员方法 静态方法
3.修饰代码块 静态代码块
package com.qfedu.a_static;
class Man {
static String name;//静态的属性 和对象无关的
//静态方法
public static void eat () {
System.out.println("吃饭喝酒");
}
//静态代码块
static {
System.out.println("嘻嘻");
}
}
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//咋使用 类.静态的属性
Man.name = "狗蛋";
System.out.println(Man.name);
//使用 类.静态方法名字()
Man.eat();
}
}
1.2.1static修饰成员变量
静态成员变量:
static String name;
语法格式:
static 数据类型 变量名;注意事项:
? 1.使用static修饰的变量叫静态变量
? 2.代码中对象还没有创建的时候,如果加载了类,static修饰的属性已经存在了,和对象没有关系。
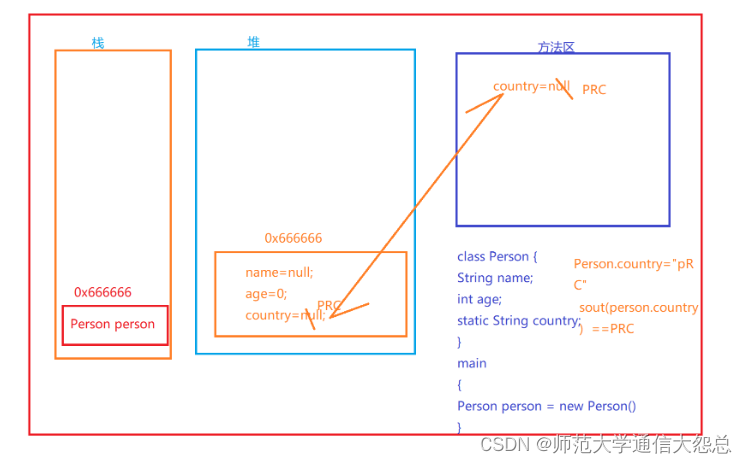
package com.qfedu.a_static;
class Person {
String name;
int age;
static String country;
}
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person sb = new Person();
sb.name = "张三";
sb.age = 23;
Person.country = "中国";
//The static field Person.country
//should be accessed in a static way
System.out.println(sb.country);//中国
System.out.println(Person.country);//in a static way
sb.country = "PRC";
System.out.println(Person.country);//PRC
}
}
总结:
以后记住:
类.静态属性即可
1.2.2static修饰成员方法
静态方法
语法格式:
public static 返回值 方法的名字 (参数列表) {}调用静态方法:
类.方法名字();
package com.qfedu.a_static;
class Dog {
public void eat () {
System.out.println("普通的成员方法");
}
public static void sleep () {
System.out.println("睡吧不用看家了");
}
}
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog.sleep();
//Dog.eat();只能拿对象来调用这个方法eat
Demo3.test();
}
public static void test () {
System.out.println("嘻嘻");
}
}
1.2.3static修饰代码块
语法格式: 静态代码块
static { 语句体 }只要这个类加载,那么静态代码块一定会执行
执行顺序: 静态代码块-》构造代码块-》构造方法
package com.qfedu.a_static;
class Cat {
public Cat () {
System.out.println("无参构造方法");
}
{
System.out.println("构造代码块");
}
static {
System.out.println("静态的代码块");
}
}
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat = new Cat();
}
}
2.异常
今天就给记语法格式和意思
2.1生活中的异常
人的一生 会经历伤病
医生会问?咋啦?
你头疼
脑部ct
医生诊断
完以后。治好这个病。
2.2Java中的异常
程序在自上而下执行的时候,发生了不可预期的事件,这个事件阻止程序的运行。这就是异常。
数组下标越界 类转换异常
Java给咱们封装很多的异常类,并且提供很优秀的异常处理机制。
Java提供了一个类Throwable
新学一个类,咋学?靠我教你吗?对的 你学会看API文档
https://www.matools.com/api/java8
2.3Throwable类
构造方法:
Throwable()构造一个新的可抛出的null作为其详细信息。Throwable(String message)构造一个具有指定的详细消息的新的throwable。
方法:
StringgetMessage()返回此throwable的详细消息字符串。voidprintStackTrace()将此throwable和其追溯打印到标准错误流。StringtoString()返回此可抛出的简短描述。
package com.qfedu.b_trhowable;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("嘻嘻");
System.err.println("哈哈");
Throwable throwable = new Throwable();
System.out.println(throwable.getMessage());
Throwable throwable2 = new Throwable("哈哈,我傻逼了");
System.out.println(throwable2.getMessage());
/**
* java.lang.Throwable: 哈哈,我傻逼了
at com.qfedu.b_trhowable.Demo1.main(Demo1.java:7)
*/
throwable2.printStackTrace();
//java.lang.Throwable: 哈哈,我傻逼了
//告知了这个错误信息
System.out.println(throwable2.toString());
}
}
2.4错误和异常
Throwable 下面有两个子类 一个叫Error 一个叫Exception
Error:是代表JVM本身的错误,咱们程序员是通过代码解决不了的。
Exception: 异常,代表程序在运行过程中,发生了不可预期的事件。可以使用Java来出来,让他继续执行下去。
? 异常分为两种:
? 编译时异常:
? FileNotFoundException
? SQLException
? ClassNotFoundException
? InterruptException
? 运行时异常:
? 数组下标越界 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException
? 类转换异常 ClassCastException
? 空指针异常 NullPointerException
2.5异常【重点】
代码有可能会出现异常。Java给咱们提供了两种解决方案
? 1.异常的捕捉
? 2.异常的抛出
2.5.1异常的捕捉
在程序运行过程中,代码难免有可能会遇到异常。如果没有异常,代码正常执行。
如果有异常,就捕捉异常
语法格式:
try { 有可能出现异常的代码 } catch (异常对象) { //针对于面异常的处理方案 }
package com.qfedu.c_Exception;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test(3, 0);
}
public static void test (int a, int b) {
int ret = 0;
try {
//有可能个出现异常的代码
ret = a / b;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("123");
//打印错误信息
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
//即使代码有异常,通过捕捉以后。是不会影响程序的接着执行的代码的
System.out.println(ret);
System.out.println( 4 + 4);
}
}
回顾上午的内容
1.static
static修饰成员变量
static修饰成员方法
static修饰代码块
2.异常
Exception
编译时异常
运行时异常
package com.qfedu.c_Exception;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[2];//数组的容量是2
test(1, 1, arr);
}
public static void test (int a, int b, int[] arr) {
int ret = 0;
try {
ret = a / b;//有可能出现的异常的代码
arr[2] = 89;//这个会有异常
//jvm造出来哪个异常对象,就去catch 到哪个异常然后去执行具体的catch
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("123");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("456");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println(4 + 8);
}
}
继续改进
package com.qfedu.c_Exception;
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[2];//数组的容量是2
test(1, 1, arr);
}
public static void test (int a, int b, int[] arr) {
int ret = 0;
try {
ret = a / b;//有可能出现的异常的代码
arr[2] = 89;//这个会有异常
//jvm造出来哪个异常对象,就去catch 到哪个异常然后去执行具体的catch
} catch (ArithmeticException | ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("123");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println(4 + 8);
}
}
改进的最终版本
package com.qfedu.c_Exception;
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[2];//数组的容量是2
test(1, 0, arr);
}
public static void test (int a, int b, int[] arr) {
int ret = 0;
try {
ret = a / b;//有可能出现的异常的代码
arr[2] = 89;//这个会有异常
//jvm造出来哪个异常对象,就去catch 到哪个异常然后去执行具体的catch
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("123");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println(4 + 8);
}
}
try-catch-finally
package com.qfedu.c_Exception;
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[2];//数组的容量是2
test(1, 0, arr);
}
public static void test (int a, int b, int[] arr) {
int ret = 0;
try {
ret = a / b;//有可能出现的异常的代码
arr[2] = 89;//这个会有异常
//jvm造出来哪个异常对象,就去catch 到哪个异常然后去执行具体的catch
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("123");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
//无论有没有异常,最终都要执行的
System.out.println(4 + 8);
}
}
}
2.5.2异常的抛出
在代码出现异常的地方进行异常的抛出
如果异常的抛出的话,一旦发生异常,从出现异常的地方会终止代码
使用两个关键字:
? throw: 在方法中抛出一个异常。自己造一个错
? throws: 在方法的声明处书写,告知当前调用者,此处有异常。要小心
package com.qfedu.c_Exception;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class Demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
test(0);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
public static void test (int a) throws FileNotFoundException{
if (a == 0) {
//编译时异常
throw new FileNotFoundException();
}
System.out.println("jvm xixi");
}
}
总结:
关于异常:一阶段和二阶段 只需要会咋抛的或者咋捕捉的即可
2.6自定义异常
Java给咱们提供了很多的异常对象,但是有的时候还是满足不了现实生活的需求,我自己造异常对象。
继承Exception
需求:
? 如果是单身 抛出一个异常 单身异常类
package com.qfedu.c_Exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
try {
test(score);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void test (int score) throws Exception {
if (score > 100 || score < 0) {
throw new Exception("输入的整数有误的。。。");
}
if (score >= 90 && score <= 100) {
System.out.println("优秀");
} else if (score >= 80) {
System.out.println("良好");
} else if (score >= 70) {
System.out.println("及格");
} else {
System.out.println("叫家长。。。");
}
}
}
3.String类
3.1String类型的两种的声明方式
package com.qfedu.d_string;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//声明字符串的两种方式
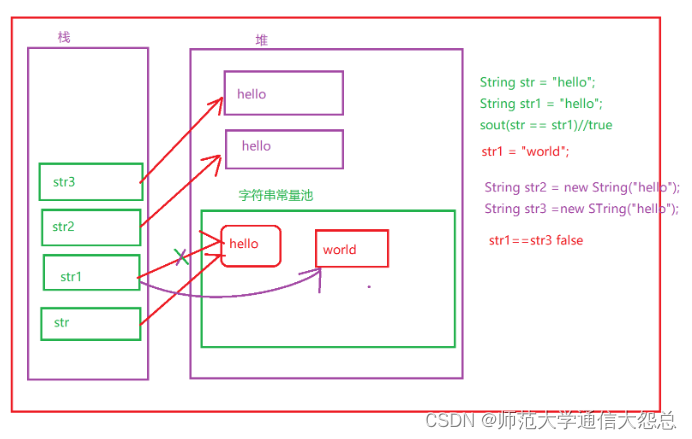
String str = "狗蛋";
String str2 = "狗蛋";
System.out.println(str);
String str1 = new String("狗蛋");
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str == str2);//true
//== 比较的是内存地址
System.out.println(str == str1);//false
//equal比较的是地址,如果地址不一样 再去比较内容。如果内容一样就是true
//开发中字符串的比较使用的是equals
System.out.println(str.equals(str1));//true
}
}
``
### 3.String类
#### 3.1String类型的两种的声明方式
```Java
package com.qfedu.d_string;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//声明字符串的两种方式
String str = "狗蛋";
String str2 = "狗蛋";
System.out.println(str);
String str1 = new String("狗蛋");
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str == str2);//true
//== 比较的是内存地址
System.out.println(str == str1);//false
//equal比较的是地址,如果地址不一样 再去比较内容。如果内容一样就是true
//开发中字符串的比较使用的是equals
System.out.println(str.equals(str1));//true
}
}
作业:
1.按照纲要去写今天的内容
2.博客坚持
3.String类下面方法 作业!!!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!