DS|二叉树
题目一:DS二叉树 -- 二叉树构建与遍历
题目描述:
给定一颗二叉树的逻辑结构如下图,(先序遍历的结果,空树用字符‘#’表示,例如AB#C##D##),建立该二叉树的二叉链式存储结构,并输出该二叉树的先序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历结果。

输入要求:
第一行输入一个整数t,表示有t个二叉树
第二行起输入每个二叉树的先序遍历结果,空树用字符‘#’表示,连续输入t行。
输出要求:
输出每个二叉树的先序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历结果。
输入样例:
2
AB#C##D##
AB##C##
输出样例:
ABCD
BCAD
CBDA
ABC
BAC
BCA代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
struct BNode {
char data;
BNode* lChild;
BNode* rChild;
};
class BTree {
public:
BNode* root;
BTree() :root(NULL) {}
BNode* creatBTree() {
BNode* tmp;
char ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == '#') tmp = NULL;
else {
tmp = new BNode;
tmp->data = ch;
tmp->lChild = creatBTree();
tmp->rChild = creatBTree();
}
return tmp;
}
void Preorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
cout << cur->data;
Preorder(cur->lChild), Preorder(cur->rChild);
}
}
void Inorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Inorder(cur->lChild);
cout << cur->data;
Inorder(cur->rChild);
}
}
void Postorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Postorder(cur->lChild), Postorder(cur->rChild);
cout << cur->data;
}
}
};
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
BTree tree;
tree.root = tree.creatBTree();
tree.Preorder(tree.root);
cout << endl;
tree.Inorder(tree.root);
cout << endl;
tree.Postorder(tree.root);
cout << endl;
}
}题目二:DS二叉树 -- 叶子数量
题目描述:
计算一颗二叉树包含的叶子结点数量。
提示:叶子是指它的左右孩子为空。
建树方法采用“先序遍历+空树用0表示”的方法,即给定一颗二叉树的先序遍历的结果为AB0C00D00,其中空节点用字符‘0’表示。则该树的逻辑结构如下图。

输入要求:
第一行输入一个整数t,表示有t个测试数据
第二行起输入二叉树先序遍历的结果,空树用字符‘0’表示,输入t行
输出要求:
逐行输出每个二叉树的包含的叶子数量
输入样例:
3
AB0C00D00
AB00C00
ABC00D00E00
输出样例:
2
2
3代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
struct BNode {
char data;
BNode* lChild;
BNode* rChild;
};
class BTree {
public:
BNode* root;
BTree() :root(NULL) {}
BNode* creatBTree() {
BNode* tmp;
char ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == '0') tmp = NULL;
else {
tmp = new BNode;
tmp->data = ch;
tmp->lChild = creatBTree();
tmp->rChild = creatBTree();
}
return tmp;
}
void Preorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
cout << cur->data;
Preorder(cur->lChild), Preorder(cur->rChild);
}
}
void Inorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Inorder(cur->lChild);
cout << cur->data;
Inorder(cur->rChild);
}
}
void Postorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Postorder(cur->lChild), Postorder(cur->rChild);
cout << cur->data;
}
}
void countLeaves(BNode* cur, int& count) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild == NULL) count++;
countLeaves(cur->lChild, count), countLeaves(cur->rChild, count);
}
}
};
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int count = 0;
BTree tree;
tree.root = tree.creatBTree();
tree.countLeaves(tree.root, count);
cout << count << endl;
}
return 0;
}题目三:DS二叉树 -- 父子结点
题目描述:
给定一颗二叉树的逻辑结构如下图,(先序遍历的结果,空树用字符‘0’表示,例如AB0C00D00),建立该二叉树的二叉链式存储结构。
编写程序输出该树的所有叶子结点和它们的父亲结点

输入要求:
第一行输入一个整数t,表示有t个二叉树
第二行起,按照题目表示的输入方法,输入每个二叉树的先序遍历,连续输入t行
输出要求:
第一行按先序遍历,输出第1个示例的叶子节点
第二行输出第1个示例中与叶子相对应的父亲节点
以此类推输出其它示例的结果
输入样例:
3
AB0C00D00
AB00C00
ABCD0000EF000
输出样例:
C D
B A
B C
A A
D F
C E代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
struct BNode {
char data;
BNode* lChild;
BNode* rChild;
};
class BTree {
public:
BNode* root;
BTree() :root(NULL) {}
BNode* creatBTree() {
BNode* tmp;
char ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == '0') tmp = NULL;
else {
tmp = new BNode;
tmp->data = ch;
tmp->lChild = creatBTree();
tmp->rChild = creatBTree();
}
return tmp;
}
void Preorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
cout << cur->data;
Preorder(cur->lChild), Preorder(cur->rChild);
}
}
void Inorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Inorder(cur->lChild);
cout << cur->data;
Inorder(cur->rChild);
}
}
void Postorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Postorder(cur->lChild), Postorder(cur->rChild);
cout << cur->data;
}
}
void countLeaves(BNode* cur, int& count) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild == NULL) count++;
countLeaves(cur->lChild, count), countLeaves(cur->rChild, count);
}
}
void printLeaves(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild == NULL) cout << cur->data << " ";
printLeaves(cur->lChild), printLeaves(cur->rChild);
}
}
void printLeavesFather(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild != NULL && cur->lChild->lChild == NULL && cur->lChild->rChild == NULL) cout << cur->data << " ";
printLeavesFather(cur->lChild);
if (cur->rChild != NULL && cur->rChild->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild->rChild == NULL) cout << cur->data << " ";
printLeavesFather(cur->rChild);
}
}
};
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
BTree tree;
tree.root = tree.creatBTree();
tree.printLeaves(tree.root);
cout << endl;
tree.printLeavesFather(tree.root);
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}题目四:DS二叉树 -- 层次遍历
题目描述:
层次遍历二叉树,是从根结点开始遍历,按层次次序“自上而下,从左至右”访问树中的各结点。
建树方法采用“先序遍历+空树用0表示”的方法
建议使用队列结构实现,算法框架如下:
定义一个空白队列和一个树结点指针p
设T是指向根结点的指针变量,若二叉树为空,则返回;否则,令p=T,p入队,执行以下循环:
(1)队首元素出队到p;
(2)访问p所指向的结点;?
(3)p所指向的结点的左、右子结点依次入队。
(4)跳转步骤1循环,直到队列空为止
例如把上述算法中的访问操作定义为输出,算法结果就是把二叉树按层次遍历输出
输入要求:
第一行输入一个整数t,表示有t个测试数据
第二行起输入二叉树先序遍历的结果,空树用字符‘0’表示,输入t行
输出要求:
逐行输出每个二叉树的层次遍历结果
输入样例:
2
AB0C00D00
ABCD00E000FG00H0I00
输出样例:
ABDC
ABFCGHDEI代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct BNode {
char data;
BNode* lChild;
BNode* rChild;
};
class BTree {
public:
BNode* root;
BTree() :root(NULL) {}
BNode* creatBTree() {
BNode* tmp;
char ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == '0') tmp = NULL;
else {
tmp = new BNode;
tmp->data = ch;
tmp->lChild = creatBTree();
tmp->rChild = creatBTree();
}
return tmp;
}
void Preorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
cout << cur->data;
Preorder(cur->lChild), Preorder(cur->rChild);
}
}
void Inorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Inorder(cur->lChild);
cout << cur->data;
Inorder(cur->rChild);
}
}
void Postorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Postorder(cur->lChild), Postorder(cur->rChild);
cout << cur->data;
}
}
void countLeaves(BNode* cur, int& count) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild == NULL) count++;
countLeaves(cur->lChild, count), countLeaves(cur->rChild, count);
}
}
void printLeaves(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild == NULL) cout << cur->data << " ";
printLeaves(cur->lChild), printLeaves(cur->rChild);
}
}
void printLeavesFather(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild != NULL && cur->lChild->lChild == NULL && cur->lChild->rChild == NULL) cout << cur->data << " ";
printLeavesFather(cur->lChild);
if (cur->rChild != NULL && cur->rChild->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild->rChild == NULL) cout << cur->data << " ";
printLeavesFather(cur->rChild);
}
}
void levelDFSTree(BNode* cur) {
queue<BNode*> Q;
BNode* p = cur;
if (p) Q.push(p);
while (!Q.empty()) {
p = Q.front();
Q.pop();
if (p) {
cout << p->data;
Q.push(p->lChild), Q.push(p->rChild);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
};
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
BTree tree;
tree.root = tree.creatBTree();
tree.levelDFSTree(tree.root);
}
return 0;
}题目五:DS二叉树 -- 二叉树高度
题目描述:
给出一棵二叉树,求它的高度。
注意,二叉树的层数是从1开始
输出要求:
第一行输入一个整数t,表示有t个二叉树
第二行起输入每个二叉树的先序遍历结果,空树用字符‘0’表示,连续输入t行
输出要求:
每行输出一个二叉树的高度
输入样例:
1
AB0C00D00输出样例:
3代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct BNode {
char data;
BNode* lChild;
BNode* rChild;
};
class BTree {
public:
BNode* root;
BTree() :root(NULL) {}
BNode* creatBTree() {
BNode* tmp;
char ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == '0') tmp = NULL;
else {
tmp = new BNode;
tmp->data = ch;
tmp->lChild = creatBTree();
tmp->rChild = creatBTree();
}
return tmp;
}
void Preorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
cout << cur->data;
Preorder(cur->lChild), Preorder(cur->rChild);
}
}
void Inorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Inorder(cur->lChild);
cout << cur->data;
Inorder(cur->rChild);
}
}
void Postorder(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Postorder(cur->lChild), Postorder(cur->rChild);
cout << cur->data;
}
}
void countLeaves(BNode* cur, int& count) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild == NULL) count++;
countLeaves(cur->lChild, count), countLeaves(cur->rChild, count);
}
}
void printLeaves(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild == NULL) cout << cur->data << " ";
printLeaves(cur->lChild), printLeaves(cur->rChild);
}
}
void printLeavesFather(BNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild != NULL && cur->lChild->lChild == NULL && cur->lChild->rChild == NULL) cout << cur->data << " ";
printLeavesFather(cur->lChild);
if (cur->rChild != NULL && cur->rChild->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild->rChild == NULL) cout << cur->data << " ";
printLeavesFather(cur->rChild);
}
}
void levelDFSTree(BNode* cur) {
queue<BNode*> Q;
BNode* p = cur;
if (p) Q.push(p);
while (!Q.empty()) {
p = Q.front();
Q.pop();
if (p) {
cout << p->data;
Q.push(p->lChild), Q.push(p->rChild);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int TreeHeight(BNode* cur) {
if (cur == NULL) return 0;
else return max(TreeHeight(cur->lChild), TreeHeight(cur->rChild)) + 1;
}
};
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
BTree tree;
tree.root = tree.creatBTree();
cout << tree.TreeHeight(tree.root) << endl;
}
return 0;
}题目六:DS二叉树 -- 二叉树之数组存储
题目描述:
二叉树可以采用数组的方法进行存储,把数组中的数据依次自上而下,自左至右存储到二叉树结点中,一般二叉树与完全二叉树对比,比完全二叉树缺少的结点就在数组中用0来表示。如下图所示
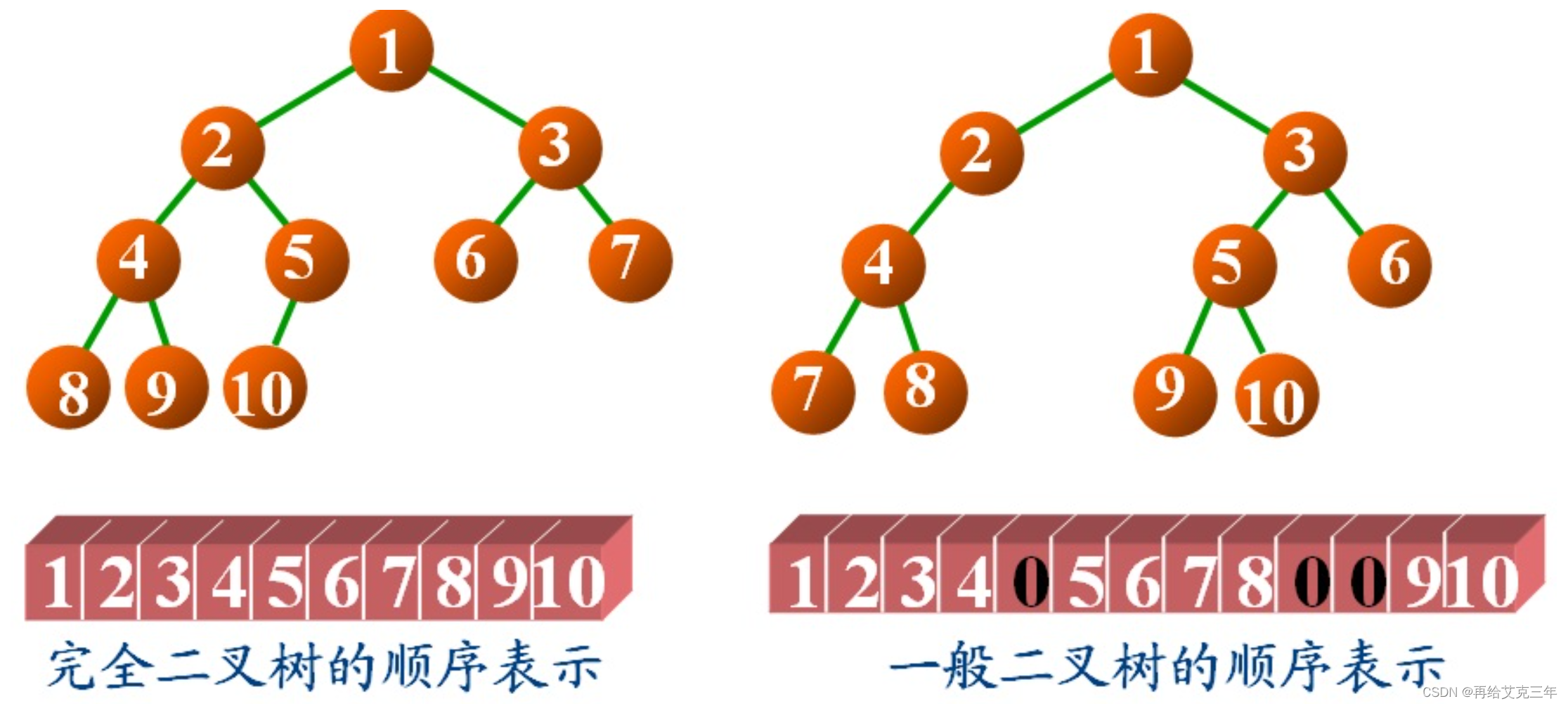
从上图可以看出,右边的是一颗普通的二叉树,当它与左边的完全二叉树对比,发现它比完全二叉树少了第5号结点,所以在数组中用0表示,同样它还少了完全二叉树中的第10、11号结点,所以在数组中也用0表示。
结点存储的数据均为非负整数
输入要求:
第一行输入一个整数t,表示有t个二叉树
第二行起,每行输入一个数组,先输入数组长度,再输入数组内数据,每个数据之间用空格隔开,输入的数据都是非负整数
连续输入t行
输出要求:
每行输出一个示例的先序遍历结果,每个结点之间用空格隔开
输入样例:
3
3 1 2 3
5 1 2 3 0 4
13 1 2 3 4 0 5 6 7 8 0 0 9 10
输出样例:
1 2 3
1 2 4 3
1 2 4 7 8 3 5 9 10 6 代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
class BTNode {
public:
int data;
BTNode* lChild;
BTNode* rChild;
BTNode() :lChild(NULL), rChild(NULL) {}
};
class BTree {
public:
BTNode* root;
BTree() :root(NULL) {}
~BTree() { DeleteTree(); }
BTNode* creatBTree() {
BTNode* tmp;
int ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == 0) tmp = NULL;
else {
tmp = new BTNode;
tmp->data = ch;
tmp->lChild = creatBTree();
tmp->rChild = creatBTree();
}
return tmp;
}
BTNode* creatBTree(queue<int> qint) {
BTNode* tmp = new BTNode;
BTNode* empty = new BTNode;
BTNode bridge;
queue<BTNode*> qnode;
if (!qint.front()) return NULL;
tmp->data = qint.front();
qint.pop();
qnode.push(tmp);
while (!qint.empty()) {
if (qint.front() == 0) {
qnode.front()->lChild = NULL;
qnode.push(empty);
}
else {
qnode.front()->lChild = new BTNode;
qnode.front()->lChild->data = qint.front();
qnode.push(qnode.front()->lChild);
}
qint.pop();
if (qint.front() == 0) {
qnode.front()->rChild = NULL;
qnode.push(empty);
}
else {
qnode.front()->rChild = new BTNode;
qnode.front()->rChild->data = qint.front();
qnode.push(qnode.front()->rChild);
}
qint.pop();
qnode.pop();
}
return tmp;
}
void Destory(BTNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Destory(cur->lChild), Destory(cur->rChild);
delete cur;
}
}
void DeleteTree() { Destory(root); root = NULL; }
void Preorder(BTNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
cout << cur->data << " ";
Preorder(cur->lChild), Preorder(cur->rChild);
}
}
void Inorder(BTNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Inorder(cur->lChild);
cout << cur->data;
Inorder(cur->rChild);
}
}
void Postorder(BTNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
Postorder(cur->lChild), Postorder(cur->rChild);
cout << cur->data;
}
}
void Countleaves(BTNode* cur, int& count) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild == NULL) count++;
Countleaves(cur->lChild, count), Countleaves(cur->rChild, count);
}
}
void Printleaves(BTNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild == NULL) cout << cur->data << " ";
Printleaves(cur->lChild), Printleaves(cur->rChild);
}
}
void PrintleavesFather(BTNode* cur) {
if (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->lChild != NULL && cur->lChild->lChild == NULL && cur->lChild->rChild == NULL) cout << cur->data << " ";
PrintleavesFather(cur->lChild), PrintleavesFather(cur->rChild);
if (cur->rChild != NULL && cur->rChild->lChild == NULL && cur->rChild->rChild == NULL) cout << cur->data << " ";
}
}
void levelDFSTree(BTNode* cur) {
queue<BTNode*> Q;
BTNode* p = cur;
if (p) Q.push(p);
while (!Q.empty()) {
p = Q.front();
Q.pop();
if (p) {
cout << p->data;
Q.push(p->lChild), Q.push(p->rChild);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int TreeHeight(BTNode* cur) {
if (cur == NULL) return 0;
else return max(TreeHeight(cur->lChild), TreeHeight(cur->rChild)) + 1;
}
};
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
queue<int> que;
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
int number;
cin >> number;
que.push(number);
}
BTree tree;
tree.root = tree.creatBTree(que);
tree.Preorder(tree.root);
cout << endl;
}
}本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【cmu15445c++入门】(2)c++中的std::move() 左值引用右值引用
- 全局变量跨线程的问题
- 点云从入门到精通技术详解100篇-基于几何特征增强和层次拓扑优化的大规模点云直线段提取
- 系统安全-WAF入侵防御系统测评指标
- C++中的引用详解
- 从0开始学mysql 第七课:MySQL 高级查询技巧
- FreeRTOS列表和列表项源码详解
- NATURE子刊 | IF:9.8,中科院2区水刊,审稿速度快!接收领域广!
- Docker之镜像上传和下载
- 一、数据结构