Java基础进阶(学习笔记)
注:本篇的代码和PPT图片来源于黑马程序员,本篇仅为学习笔记
static
static 是静态的意思,可以修饰成员变量,也可以修饰成员方法
修饰成员的特点:
被其修饰的成员, 被该类的所有对象所共享
多了一种调用方式, 可以通过类名调用
随着类的加载而加载, 优先于对象存在
class User {
??? String name;
??? int age;
??? static int onLineNumber;
}
public class StaticTest1 {
??? public static void main(String[] args) {
??????? User.onLineNumber++;
??????? User u1 = new User();
??????? u1.name = "张三";
??????? u1.age = 23;
??????? sout(u1.name + "---" + u1.age
? + "---" + u1.onLineNumber);
??????? User.onLineNumber++;
??????? User u2 = new User();
??????? u2.name = "李四";
??????? u2.age = 24;
??????? sout(u2.name + "---" + u2.age
? + "---" + u2.onLineNumber);
??? }
}张三﹣--23---1
李四﹣--24---2
注意事项:
static 方法中,? 只能访问静态成员 (直接访问)
static 中不允许使用 this 关键字
重新认识main方法
public class HelloWorld {
??? public static void main(String[] args) {
? System.out.println("HelloWorld");
??? }
}public:? 被 JVM 调用,访问权限足够大static :? 被 JVM 调用,不用创建对象? 因为main方法是静态的,所以测试类中其他方法也需要是静态的
void :? 被 JVM 调用,不需要给 JVM 返回值main :? 一个通用的名称,虽然不是关键字,但是被 JVM 识别String[] args : ? 以前用于接收键盘录入数据的,现在没用
继承
让类与类之间产生关系(子父类关系),子类可以直接使用父类中非私有的成员
成员变量
public class Fu {
??? int num = 10;
}class Zi extends Fu {
??? int num = 20;
??? public void method(){
??????? int num = 30;
??????? System.out.println(num); ???????????// 30
??????? System.out.println(this.num); ??????// 20
??????? System.out.println(super.num);????? // 10
??? }
}成员方法
子类重写父类方法,需要保证方法声明完全一致(方法名,参数,返回值类型需要保持一致)
目标1: 能够独立识别出, 方法是不是重写的方法
- @Override
目标2: 清楚方法重写的使用场景
- 当子类需要父类的方法, 但是觉得父类的方法逻辑不好 (修改 | 增强)
? 就可以对父类的方法进行重写
注意
父类中私有方法不能被重写
子类重写父类方法时,访问权限必须大于等于父类

继承特点:
Java只支持单继承,不支持多继承,但支持多层继承
public static void main(String[] args) {
??? Student stu = new Student("钢门吹雪", 23, 100);
??? sout(stu.getName() + "---" + stu.getAge() +
???????? "---" + stu.getScore());
}public class Student extends Person{
??? private int score;
??? public Student(String name, int age, int score) {
??????? super(name, age);
??????? this.score = score;
??? }
}public class Person {
??? private String name;
??? private int age;
??? public Person(String name, int age) {
??????? this.name = name;
??????? this.age = age;
??? }
}final关键字
final 关键字是最终的意思,可以修饰(方法,类,变量)
final 修饰的特点
修饰方法:表明该方法是最终方法,不能被重写
修饰类:表明该类是最终类,不能被继承
修饰变量:表明该变量是常量,不能再次被赋值
public class Test {
public static final String schoolName="au";
private final String name="c";//无意义
public static void main(String[] args) {
//final只能赋值一次
final int a;
a=12;
final double r=3.14;
}
public static void buy(final double z){
}
}
final class A{}
class C{
public void test(){
}
}
class D extends C{
}
final 修饰变量的细节补充
变量是基本类型:final 修饰指的是基本类型的数据值不能发生改变
变量是引用类型:final 修饰指的是引用类型的地址值不能发生改变,但是地址里面的内容是可以发生改变的
成员变量如果被 final 修饰,需要在构造方法结束之前完成赋值
抽象类
抽象类是一种特殊的父类,内部可以编写方法
抽象方法:将共性的行为(方法)抽取到父类之后,发现该方法的实现逻辑,无法在父类中给出具体明确,该方法就可以定义为抽象方法。
抽象类:如果一个类中存在抽象方法,那么该类就必须声明为抽象类
抽象方法的定义格式:
public abstract 返回值类型 方法名(参数列表);
抽象类的定义格式:
public abstract class 类名{}
注意:
抽象类不能实例化
抽象类存在构造方法
抽象类中可以存在普通方法
抽象类的子类
要么重写抽象类中的所有抽象方法
要么是抽象类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Teacher t=new Teacher();
t.write();
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
Student s=new Student();
s.write();
}
}
public abstract class People {
public final void write(){
System.out.println("\t\t\t\t\t\t《GGB》");
System.out.println("\t\t哦GGB童话里做英雄");
System.out.println(writeMain());
System.out.println("GGGGGBBBB!");
}
public abstract String writeMain();
}
public class Student extends People {
@Override
public String writeMain() {
return "啊啊啊啊啊啊啊";
}
}public class Teacher extends People {
@Override
public String writeMain() {
return "啦啦啦啦啦啦啦";
}
}
接口
接口用关键字interface来定义
public interface 接口名 {}
接口不能实例化
接口和类之间是实现关系,通过implements关键字表示
public class 类名 implements 接口名 {}
接口的子类(实现类)
要么重写接口中的所有抽象方法
要么是抽象类
接口
综合案例:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassManager clazz=new ClassManager();
clazz.printInfo();
clazz.printScore();
}
}public class Student {
private String name;
private char sex;
public Student() {
}
private double score;
public Student(String name, char sex, double score) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.score = score;
}import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ClassManager {
private ArrayList<Student> students=new ArrayList<>();
private StudentOperator studentOperator=new StudentOperator1();
public ClassManager(){
students.add(new Student("迪丽热巴",'女',99));
students.add(new Student("古力娜扎",'女',99));
students.add(new Student("马儿扎哈",'女',80));
students.add(new Student("卡尔扎巴",'女',60));
}
public void printInfo(){
studentOperator.printAllInfo((students));
}
public void printScore(){
studentOperator.printAverageScore(students);
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public interface StudentOperator {
void printAllInfo(ArrayList<Student> students);
void printAverageScore(ArrayList<Student> students);
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class StudentOperator1 implements StudentOperator{
@Override
public void printAllInfo(ArrayList<Student> students) {
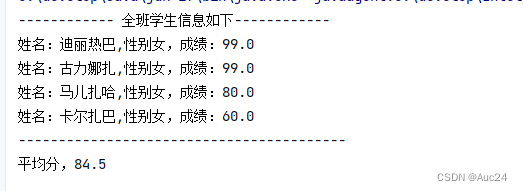
System.out.println("------------ 全班学生信息如下------------");
for (int i = 0; i < students.size(); i++) {
Student s=students.get(i);
System.out.println("姓名:"+s.getName()+",性别"+s.getSex()+",成绩:"+s.getScore());
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
}
@Override
public void printAverageScore(ArrayList<Student> students) {
double allScore=0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < students.size(); i++) {
Student s=students.get(i);
allScore+=s.getScore();
}
System.out.println("平均分,"+(allScore)/ students.size());
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class StudentOperator2 implements StudentOperator{
@Override
public void printAllInfo(ArrayList<Student> students) {
System.out.println("------------ 全班学生信息如下------------");
int count1=0;
int count2=0;
for (int i = 0; i < students.size(); i++) {
Student s=students.get(i);
System.out.println("姓名:"+s.getName()+",性别"+s.getSex()+",成绩:"+s.getScore());
if(s.getSex()=='男'){
count1++;
}else {
count2++;
}
}
System.out.println("男生人数是:"+count1+",女生人数是:"+count2);
System.out.println("班级总人数是:"+students.size());
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
}
@Override
public void printAverageScore(ArrayList<Student> students) {
double allScore=0.0;
double max=students.get(0).getScore();
double min=students.get(0).getScore();
for (int i = 0; i < students.size(); i++) {
Student s=students.get(i);
if(s.getScore()>max) max=s.getScore();
if(s.getScore()<min) min=s.getScore();
allScore+=s.getScore();
}
System.out.println("学生的最高分是:"+max);
System.out.println("学生的最低分是:"+min);
System.out.println("平均分,"+(allScore-max-min)/ (students.size()-2));
}
}
多态
多态的成员访问特点
成员变量:编译看左边(父类),执行看左边(父类)
成员方法:编译看左边(父类),执行看右边(子类)
多态的好处 :提高了程序的扩展性
对象多态 : 将方法的形参定义为父类类型, 这个方法可以接收该父类的任意子类对象
行为多态 : 同一个行为, 具有多个不同表现形式或形态的能力
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
People p1=new Teacher();
p1.run();
System.out.println(p1.name);
People p2=new Student();
p2.run();
System.out.println(p2.name);
}
}public class People {
public String name="父类Peoplet的名称";
public void run(){
System.out.println("人可以跑~");
}
}public class Student extends People{
public String name="子类Student的名称";
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("学生跑得快~~");
}
}public class Teacher extends People{
public String name="Teacher的名称";
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("跑的气喘吁吁~~");
}
}
多态的转型问题
概述:如果被转的引用类型变量,对应的实际类型和目标类型不是同一种类型,那么在转换的时候就会出现ClassCastException
关键字 instanceof
使用格式:
对象名 instanceof 类型
判断一个对象是否是一个类的实例
通俗的理解:判断关键字左边的对象,是否是右边的类型,返回boolean类型结果
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
People p1=new Student();
p1.run();
if(p1 instanceof Student){
Student s1=(Student) p1;
s1.test();
}else {
Teacher t2=(Teacher) p1;
t2.teach();
}
}
}public class Student extends People{
public String name="子类Student的名称";
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("学生跑得快~~");
}
public void test(){
System.out.println("学生需要考试");
}
}
public class Teacher extends People{
public String name="Teacher的名称";
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("跑的气喘吁吁~~");
}
public void teach(){
System.out.println("老师需要教书");
}
}
接口新特性
JDK8的新特性:接口中可以定义有方法体的方法。(默认、静态)
JDK9的新特性:接口中可以定义私有方法。
JDK8 接口特性
允许在接口中定义非抽象方法,但是需要使用关键字 default 修饰,这些方法就是默认方法
作用:解决接口升级的问题
接口中默认方法的定义格式:
格式:public default 返回值类型 方法名(参数列表) {}
范例:public default void show() {}
注意:
1.默认方法不是抽象方法,所以不强制被重写? (但是可以被重写,重写的时候去掉default关键字)
2.public可以省略,default不能省略
3.如果实现了多个接口,多个接口中存在相同的方法声明,子类就必须对该方法进行重写
接口中允许定义 static 静态方法
接口中静态方法的定义格式:
格式:public static 返回值类型 方法名(参数列表) {}
范例:public static void show() {}
注意:
1.静态方法只能通过接口名调用,不能通过实现类名或者对象名调用
2.public可以省略,static不能省略
JDK9 接口特性
接口中允许定义 private 私有方法
接口中静态方法的定义格式:
格式1:private 返回值类型 方法名(参数列表) {}
范例1:private void show() {}
格式2:private static 返回值类型 方法名(参数列表) {}
范例2:private static void method() {}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b=new B();
b.test1();
A.test3();
}
}
public interface A {
public default void test1(){
System.out.println("==默认方法==");
test2();
}
private void test2(){
System.out.println("==私有方法==");
}
public static void test3(){
System.out.println("==静态方法==");
}
}public class B implements A{
}

接口的多继承
作用:便于实现类去实现
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
interface A{
void test1();
}
interface B{
void test2();
}
interface C{}
interface D extends C,B,A{
}
class E implements D{
@Override
public void test1() {
}
@Override
public void test2() {
}
}注意:
1.一个接口继承多个接口,如果多个接口存在方法签名冲突,则此时不支持多继承
2.一个类实现多个接口,如果多个接口存在方法签名冲突,则此时不支持多实现
3.一个类继承了父类,又同时实现接口,父类和接口中有同名的默认方法,会优先使用父类
4.一个类实现多个接口,多个接口中存在同名的默认方法。可以不冲突,这个类重写该方法即可
内部类
创建对象的格式 :
格式:外部类名.内部类名 对象名 = new 外部类对象().new 内部类对象();
范例:Outer.Inner in = new Outer().new Inner();
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Outer.Inner in=new Outer().new Inner();
in.test();
}
}public class Outer {
public class Inner{
private String name;
public static String schoolName;
public void test(){
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
}内部类成员访问
内部类中, 访问外部类成员 : 直接访问, 包括私有
外部类中, 访问内部类成员 : 需要创建对象访问
class Outer {
??? int num = 150;
??? class Inner {
??????? int num = 110;
??????? public void show(){
??????????? int num = 78;
??????????? System.out.println(num); // 78
??????????? System.out.println(this.num); // 110
??????????? System.out.println(Outer.this.num); // 150
??????? }
??? }
}匿名内部类
概述:匿名内部类本质上是一个特殊的局部内部类(定义在方法内部)
前提:需要存在一个接口或类
new 类名 / 接口 () {
???
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Animal a=new Cat();
// a.cry();
Animal a=new Animal(){
@Override
public void cry() {
System.out.println("喵喵喵喵的叫~~~");
}
};
a.cry();
}
}
//class Cat extends Animal{
//
// @Override
// public void cry() {
// System.out.println("喵喵喵喵的叫~~~");
// }
//}
abstract class Animal{
public abstract void cry();
}枚举
枚举是一种特殊的类
特点:
●枚举类的第一行只能罗列一些名称,这些名称都是常量,并且每个常量记住的都是枚举类的一个对象。
●枚举类的构造器都是私有的(写不写都只能是私有的),因此,枚举类对外不能创建对象。
●枚举都是最终类,不可以被继承。
●枚举类中,从第二行开始,可以定义类的其他各种成员。
●编译器为枚举类新增了几个方法,并且枚举类都是继承:?java?.?lang?.?Enum?类的,从?enum?类也会继承到一些方法。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a1=A.X;
System.out.println(a1);
B y=B.Y;
y.go();
}
}
public enum B {
X(){
public void go(){
}
},Y(){
@Override
public void go() {
}
};
public abstract void go();
}public enum A {
X,Y,Z;
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}枚举的应用场景:做信息标志和分类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
check(Constant2.BOY);
}
public static void check(Constant2 sex){
switch (sex){
case BOY:
System.out.println("游戏信息");
break;
case GIRL:
System.out.println("土豪信息");
break;
}
}
}
public enum Constant2 {
BOY,GIRL;
}
泛型
作用:提供了在编译阶段约束所能操作的数据类型,并自动进行检查的能力!这样可以避免强制类型转换,及可能出现异常
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();
list.add("kava");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String e= (String) list.get(i);
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("----------------------------");
ArrayList<String> list1=new ArrayList<String>();
list1.add("java1");
//list1.add(new Cat())
for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) {
String e=list1.get(i);
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
class Cat{}
泛型类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList<String> list=new MyArrayList<>();
list.add("java1");
list.add("java2");
String ele= list.get(1);
System.out.println(ele);
}
}public class MyArrayList<E> {
public boolean add(E e){
return true;
}
public E get(int index){
return null;
}
}
泛型接口
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}public class Teacher {
}public class Student {
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public interface Data<T> {
void add(T t);
ArrayList<T> getByName(String name);
}public class StudentData implements Data<Student>{
@Override
public void add(Student student) {
}
@Override
public ArrayList<Student> getByName(String name) {
return null;
}
}public class TeacherData implements Data<Teacher>{
@Override
public void add(Teacher teacher) {
}
@Override
public ArrayList<Teacher> getByName(String name) {
return null;
}
}泛型方法、泛型的通配符和上下限
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String rs=test("java");
System.out.println(rs);
Dog d=test(new Dog());
System.out.println(d);
ArrayList<CAr> cars=new ArrayList<>();
cars.add(new BENZ());
cars.add(new BMW());
go(cars);
// ArrayList<Dog> dogs=new ArrayList<>();
}
public static void go(ArrayList<? extends CAr> cars){
}
public static <T> T test(T t){
return t;
}
}通配符:?,代表一切类型
API
API(Application Programming interface)? 应用程序编程接口。
简单来说:就是 Java 帮我们已经写好的一些类和方法,我们直接拿过来用就可以了
Object类
所有的类,都直接或者间接的继承了 Object 类 (祖宗类)
Object类的方法是一切子类都可以直接使用的,所以我们要学习Object类的方法。

toString存在的意义
父类 toString() 方法存在的意义就是为了被子类重写,以便返回对象的内容信息,而不是地址信息!!
equals存在的意义
父类equals方法存在的意义就是为了被子类重写,以便子类自己来定制比较规则。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1=new Student("au",23);
//System.out.println(s1.toString());
System.out.println(s1);
Student s2=new Student("au",23);
System.out.println(s2.equals(s1));
}
}import java.util.Objects;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//eq
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
protected Object clone() 对象克隆
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
User u1=new User(1,"zhangsan","wo666",new double[]{99.0,99.5});
System.out.println(u1.getId());
System.out.println(u1.getUsername());
System.out.println(u1.getPassword());
System.out.println(u1.getScores());
User u2=(User)u1.clone();
System.out.println(u2.getId());
System.out.println(u2.getUsername());
System.out.println(u2.getPassword());
System.out.println(u2.getScores());
}
}//Cloneable是一个标记接口
public class User implements Cloneable{
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private double[] scores;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String username, String password, double[] scores) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.scores = scores;
}
//clone
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public double[] getScores() {
return scores;
}
public void setScores(double[] scores) {
this.scores = scores;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1="auc";
String s2=null;
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//错误
System.out.println(Objects.equals(s1,s2));
System.out.println(Objects.isNull(s1));//false
System.out.println(Objects.nonNull(s2));//true
}
}包装类
包装类就是吧基本类型的数据包装成对象
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a2=Integer.valueOf(12);
System.out.println(a2);
Integer a3=12;
int a4=a3;
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(12);
int rs= list.get(1);
}
} System.out.println("---------------------------");
Integer a=23;
String rs1=Integer.toString(a);
System.out.println(rs1+1);
String rs2=a.toString();
System.out.println(rs2+1);
String agsStr="29";
int ageI=Integer.parseInt(agsStr);
System.out.println(ageI+1);
String scoreStr="99.5";
// double score=Double.parseDouble(scoreStr);
double score=Double.valueOf(scoreStr);
System.out.println(score+0.5);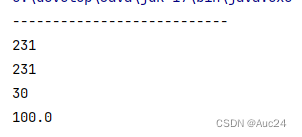
StringBuilder
●?StringBuilder?代表可变字符串对象,相当于是一个容器,它里面装的字符串是可以改变的,就是用来操作字符串的。
●好处:?StringBuilder?比?String?更适合做字符串的修改操作,效率会更高,代码也会更简洁。
?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder s=new StringBuilder("auc");
//拼接内容
s.append(12);
s.append("n");
s.append(true);
s.append(666).append("xxx").append(2323);
System.out.println(s);
//反转
s.reverse();
System.out.println(s);
//长度
System.out.println(s.length());
//把对象转成String类型
String rs=s.toString();
System.out.println(rs);
}
}
StringBuffer
线性安全,同StringBuffer功能相同
案例:用于返回任意整形数组的内容,要求返回的数组内容格式如:【11,22,33】
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getArrayData(new int[]{11, 22, 33}));
}
public static String getArrayData(int[] arr){
if(arr==null){
return null;
}
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(i==arr.length-1){
sb.append(arr[i]);
}else {
sb.append(arr[i]).append(",");
}
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}

StringJoiner
提供字符串的操作效率,代码更简洁
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringJoiner s=new StringJoiner(",","[","]");
s.add("java1");
s.add("java2");
s.add("java3");
System.out.println(s);
}
}
Math、System、Runtime

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.abs(-12));
System.out.println(Math.abs(-3.14));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(4.00000001));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(4.0));
System.out.println(Math.floor(4.9999999));
System.out.println(Math.floor(4.0));
System.out.println(Math.round(3.4999));
System.out.println(Math.round(4.50001));
System.out.println(Math.max(10, 20));
System.out.println(Math.min(10, 20));
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 3));
System.out.println(Math.pow(3, 2));
System.out.println(Math.random());//{0.0,1.0)
}
}

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// System.exit(0);
System.out.println("--------------------");
long time=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(time);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("输出了"+i);
}
long time2=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((time2-time)/1000.0+"s");
}
}

Runtime

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Runtime r=Runtime.getRuntime();
System.out.println(r.availableProcessors());
System.out.println(r.totalMemory()/1024.0/1024.0+"MB");
System.out.println(r.freeMemory()/1024.0/1024.0+"MB");
}
}
BigDecimal
解决浮点运算问题

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
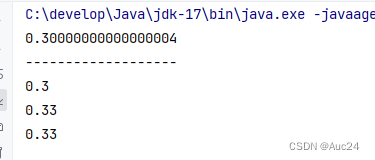
double a=0.1;
double b=0.2;
double c=a+b;
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println("-------------------");
//
// BigDecimal a1=new BigDecimal(Double.toHexString(a));
// BigDecimal b1=new BigDecimal(Double.toHexString(b));
BigDecimal a1=BigDecimal.valueOf(a);
BigDecimal b1=BigDecimal.valueOf(b);
BigDecimal c1=a1.add(b1);
System.out.println(c1);
BigDecimal i=BigDecimal.valueOf(0.1);
BigDecimal j=BigDecimal.valueOf(0.3);
BigDecimal k=i.divide(j,2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);
System.out.println(k);
double rs=k.doubleValue();
System.out.println(rs);
}
}
Date

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Date d=new Date();
System.out.println(d);
long time=d.getTime();
System.out.println(time);
time+=2*1000;//把时间毫秒值转换成日期对象,2s之后时间是多少
Date d2=new Date(time);
System.out.println(d2);
Date d3=new Date();
d3.setTime(time);
System.out.println(d3);
}
}
SimpleDateFormat

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ParseException {
Date d=new Date();
System.out.println(d);
long time=d.getTime();
System.out.println(time);
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss EEE a");
String rs=sdf.format(d);
System.out.println(rs);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
//解析字符串时间
String dateStr="2022-12-12 12:12:11";
SimpleDateFormat sdf2=new SimpleDateFormat("YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date d2=sdf2.parse(dateStr);
System.out.println(d2);
}
}
1、SimpleDateFormat 代表什么,有什么作用?
可以把日期对象格式化成我们想要的形式;
可以把字符串的时间形式解析成Date日期对象。
2、SimpleDateFormat 的对象如何创建?
public SimpleDateFormat?(String pattern)
3、SimpleDateFormat 格式化,以及解析时间的方法是哪些?
public final String format(Date d):格式化日期对象
public Date parse?(String source):解析字符串时间
案例:时间秒杀活动
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ParseException {
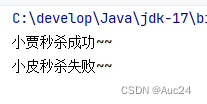
String start="2023年11月11日 0:0:0";
String end="2023年11月11日 0:10:0";
String xj="2023年11月11日 0:01:18";
String xp="2023年11月11日 0:10:57";
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
Date startDt=sdf.parse(start);
Date endDt=sdf.parse(end);
Date xjDt=sdf.parse(xj);
Date xpDt=sdf.parse(xp);
long startTime=startDt.getTime();
long endTime= endDt.getTime();
long xjTime= xjDt.getTime();
long xpTime= xpDt.getTime();
if(xjTime>=startTime && xjTime<=endTime){
System.out.println("小贾秒杀成功~~");
}else {
System.out.println("小贾秒杀失败~~");
}
if(xpTime>=startTime && xpTime<=endTime){
System.out.println("小皮秒杀成功~~");
}else {
System.out.println("小皮秒杀失败~~");
}
}
}
Calendar
代表的是系统此刻时间对应的日历,通过它可以单独获取、修改时间中的年、月、日、时、分、秒等。


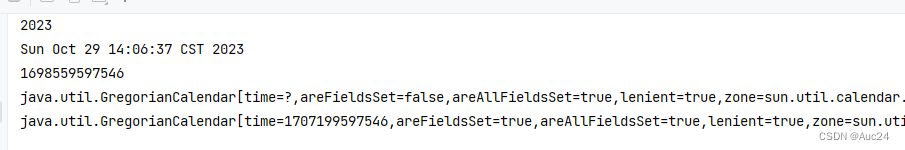
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar now=Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(now);
int year=now.get(Calendar.YEAR);
System.out.println(year);
Date d=now.getTime();
System.out.println(d);
long time=now.getTimeInMillis();
System.out.println(time);
now.set(Calendar.MONTH,9);
System.out.println(now);
now.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR,100);
System.out.println(now);
}
}
JDK8新增时间API




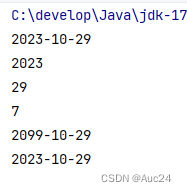
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDate ld=LocalDate.now();
System.out.println(ld);
int year=ld.getYear();
int month=ld.getMonthValue();
int day=ld.getDayOfMonth();
int dayOfyear=ld.getDayOfYear();//一年中的第几天
int dayOfWeek=ld.getDayOfWeek().getValue();
System.out.println(year);
System.out.println(day);
System.out.println(dayOfWeek);
LocalDate ld2=ld.withYear(2099);
System.out.println(ld2);
System.out.println(ld);
LocalDate ld4=ld.plusYears(2);
LocalDate ld6=LocalDate.of(2099,12,12);
}
}




public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zoneId=ZoneId.systemDefault();
System.out.println(zoneId.getId());
System.out.println(ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds());
ZoneId zoneId1=ZoneId.of("America/El_Salvador");
ZonedDateTime now=ZonedDateTime.now(zoneId1);
System.out.println(now);
ZonedDateTime now1=ZonedDateTime.now(Clock.systemUTC());
System.out.println(now1);
ZonedDateTime now2=ZonedDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now2);
}
}?

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Instant now=Instant.now();
long second=now.getEpochSecond();
System.out.println(second);
int nano=now.getNano();
System.out.println(nano);
System.out.println(now);
Instant instant=now.plusNanos(111);
}
}?



public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DateTimeFormatter formatter=DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime now=LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now);
String rs= formatter.format(now);
System.out.println(rs);
String rs2=now.format(formatter);
System.out.println(rs2);
String dateStr="2029年12月12日 12:12:12";
LocalDateTime ldt=LocalDateTime.parse(dateStr,formatter);
System.out.println(ldt);
}
}


public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDate start=LocalDate.of(2029,8,10);
LocalDate end=LocalDate.of(2029,8,15);
Period period=Period.between(start,end);
System.out.println(period.getYears());
System.out.println(period.getMonths());
System.out.println(period.getDays());
}
}

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime start=LocalDateTime.of(2025,11,11,11,10,10);
LocalDateTime end=LocalDateTime.of(2025,11,11,11,11,11);
Duration duration=Duration.between(start,end);
System.out.println(duration.toDays());
System.out.println(duration.toHours());
System.out.println(duration.toMinutes());
System.out.println(duration.toSeconds());
}
}
Arrays

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
int[] arr2=Arrays.copyOfRange(arr,1,4);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
int[] arr3=Arrays.copyOf(arr,10);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr3));
double[] prices={99.8,128,100};
Arrays.setAll(prices, new IntToDoubleFunction() {
@Override
public double applyAsDouble(int value) {
return prices[value]*0.8;
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(prices));
}
}
Lambda表达式

public class Lambda {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Swimming s=() -> {
System.out.println("学生快乐的游泳~~~");
};
s.swim();
}
}
interface Swimming{
void swim();
}



方法引用



算法
冒泡排序

public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] arr={5,2,3,1};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length-i-1; j++) {
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
int temp=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
选择排序
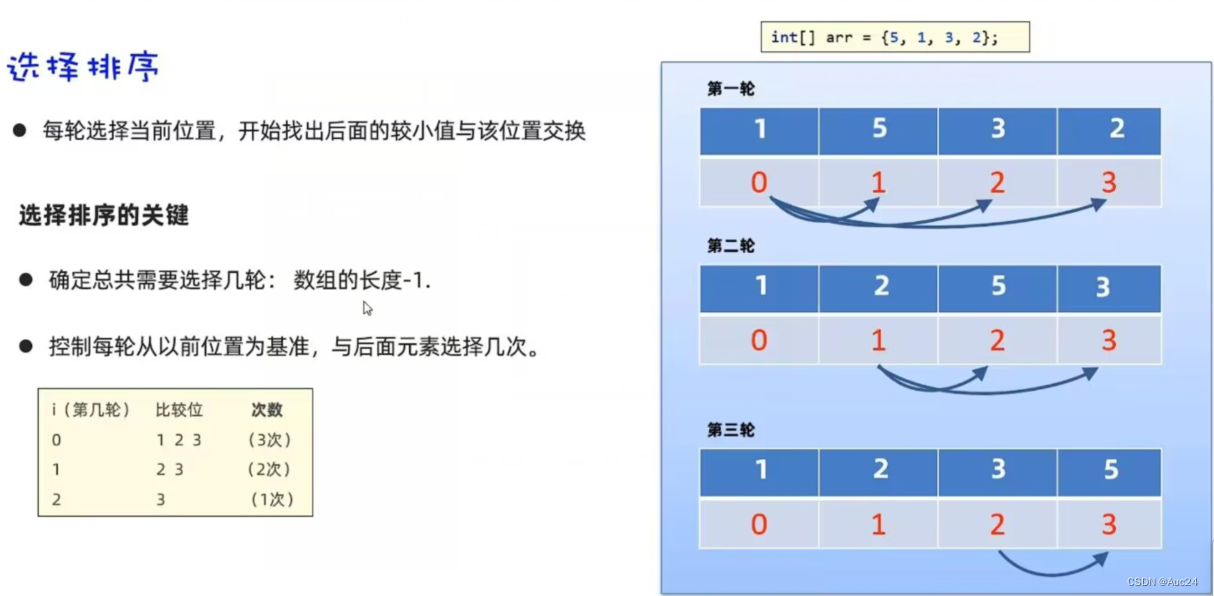
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] arr={5,2,3,1};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if(arr[i]>arr[j]){
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
二分查找
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={7,23,79,81,103,127,131,147};
System.out.println(binarySearch(arr,81));
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr,int data){
int left=0;
int right=arr.length-1;
while (left<=right){
int middle=(left+right)/2;
if(data<arr[middle]){
right=middle-1;
} else if (data>arr[middle]) {
left=middle+1;
}else {
return middle;
}
}
return -1;
}
}

正则表达式
校验数据是否合法
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(checkQQ(null));
System.out.println(checkQQ("3435556545"));
}
public static boolean checkQQ(String qq){
return qq!=null && qq.matches("[1-9]\\d{5,19}");
}
}

应用案例
校验用户输入的电话,邮箱,时间是否合法
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
checkPhone();
}
public static void checkPhone() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入您的电话号码(手机|座机):");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String phone = sc.nextLine();
if (phone.matches("(1[3-9]\\d{9})|(0\\d{2,7}-?[1-9]\\d{4,19})")) {
System.out.println("您输入的号码格式正确~~~");
break;
} else {
System.out.println("你输入的号码格式不正确~~~");
}
}
}
public static void checkEmail() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入您的邮箱:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String emial = sc.nextLine();
if (emial.matches("\\w{2,}@\\w{2,20}(\\.\\w{2,10}){1,2}")) {
System.out.println("您输入的邮箱格式正确~~~");
break;
} else {
System.out.println("你输入的邮箱格式不正确~~~");
}
}
}


public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
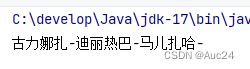
String s1="古力娜扎ai888888迪丽热巴999a876马儿扎哈4345434rf";
System.out.println(s1.replaceAll("\\w+", "-"));
}
}
异常
异常体系
 1.异常是什么?
1.异常是什么?
异常是代码在编译或者执行的过程中可能出现的错误。
2.异常的体系结构 ?
Throwable
?Error : 严重级别问题, 通常跟系统有关
Exception : 异常类, 程序常见的错误
3.Exception的分类 ?
l编译时异常、运行时异常。
l编译时异常:没有继承 RuntimeExcpetion 的异常,编译阶段就会出错。
l运行时异常:继承自 RuntimeException的 异常或其子类
编译阶段不报错,运行可能报错
异常的处理方式
异常的默认处理流程
①虚拟机会在出现异常的代码那里自动的创建一个异常对象:ArithmeticException
②异常会从方法中出现的点这里抛出给调用者,调用者最终抛出给JVM虚拟机
③虚拟机接收到异常对象后,先在控制台直接输出异常信息数据
④终止 Java 程序的运行
⑤后续代码没有机会执行了,因为程序已经噶了


自定义异常
自定义异常的分类
1、自定义编译时异常??????
定义一个异常类继承Exception.
重写构造器
2、自定义运行时异常
定义一个异常类继承RuntimeException.
重写构造器。

public class ExceptionTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
saveAge(160);
System.out.println("底层执行成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("底层执行失败");
}
}
public static void saveAge(int age){
if(age>0 && age<150){
System.out.println("年龄被成功保存:"+age);
}else {
throw new AgellegalRuntimeException("/age is illegal,your age is "+age);
}
}
}public class AgellegalRuntimeException extends RuntimeException{
public AgellegalRuntimeException() {
}
public AgellegalRuntimeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println(getMoney());
break;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("请您输入合法的数字!");
}
}
}
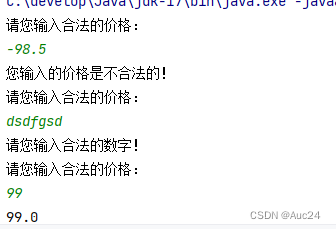
public static double getMoney(){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while (true){
System.out.println("请您输入合法的价格:");
double money=sc.nextDouble();
if(money>=0){
return money;
}else {
System.out.println("您输入的价格是不合法的!");
}
}
}
}
集合

ublic class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("java1");
list.add("java2");
list.add("java1");
list.add("java2");
System.out.println(list);
HashSet<String> set=new HashSet<>();
set.add("java1");
set.add("java2");
set.add("java1");
set.add("java2");
set.add("java3");
System.out.println(set);
}
}
?collection的常用方法

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c=new ArrayList<>();
c.add("java1");
c.add("java2");
c.add("java1");
c.add("java2");
c.add("java3");
System.out.println(c);
// c.clear();
// System.out.println(c);
System.out.println(c.isEmpty());
System.out.println(c.size());
System.out.println(c.contains("java1"));
System.out.println(c.remove("java2"));
System.out.println(c);
Object[] arr=c.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
String[] arr2=c.toArray(new String[c.size()]);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
System.out.println("------------------------");
Collection<String> c1=new ArrayList<>();
c1.add("java1");
c1.add("java2");
Collection<String> c2=new ArrayList<>();
c2.add("java3");
c2.add("java4");
c1.addAll(c2);
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
}
}
Collection的遍历方式
迭代器

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c=new ArrayList<>();
c.add("ad");
c.add("ac");
c.add("au");
c.add("aq");
Iterator<String> it=c.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
String ele=it.next();
System.out.println(ele);
}
}
}
增强for循环
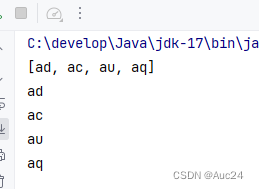
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c=new ArrayList<>();
c.add("ad");
c.add("ac");
c.add("au");
c.add("aq");
System.out.println(c);
for (String ele : c){
System.out.println(ele);
}
}
}
Lambda表达式
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c=new ArrayList<>();
c.add("ad");
c.add("ac");
c.add("au");
c.add("aq");
System.out.println(c);
c.forEach(new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
});
c.forEach((String s) ->{
System.out.println(s);
});
c.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
List集合
特点和方法?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("蜘蛛精");
list.add("至尊宝");
list.add("至尊宝");
list.add("牛夫人");
System.out.println(list);
list.add(2,"紫霞仙子");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.remove(2));
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.get(3));
System.out.println(list.set(3, "牛魔王"));
System.out.println(list);
}
}
遍历方式
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("蜘蛛精");
list.add("至尊宝");
list.add("牛夫人");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String s=list.get(i);
System.out.println(s);
}
Iterator<String> it=list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
list.forEach(s-> {
System.out.println(s);
});
}
}底层原理


队列
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> queue=new LinkedList<>();
//入队
queue.addLast("1hao");
queue.addLast("2hao");
queue.addLast("3hao");
queue.addLast("4hao");
System.out.println(queue);
//出队
System.out.println(queue.removeFirst());
System.out.println(queue.removeFirst());
System.out.println(queue.removeFirst());
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
队列:先进先出,后进后出。
栈
LinkedList<String> stack=new LinkedList<>();
//压栈
stack.addFirst("ike");
stack.addFirst("2ke");
stack.push("3ke");
stack.addFirst("4ke");
System.out.println(stack);
//出栈
System.out.println(stack.removeFirst());
System.out.println(stack.removeFirst());
System.out.println(stack);
栈:后进先出,先进后出。
Set集合

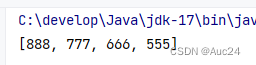
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
set.add(666);
set.add(555);
set.add(555);
set.add(888);
set.add(777);
System.out.println(set);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set=new TreeSet<>();
set.add(666);
set.add(555);
set.add(555);
set.add(888);
set.add(777);
System.out.println(set);
}
}
HashSet底层原理

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1=new Student("蜘蛛精",25,169.5);
Student s2=new Student("紫霞",22,166.5);
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());
System.out.println(s2.hashCode());
}
}


若想去除重复项,则需重写hashCode()和equals()方法
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return age == student.age && Double.compare(height, student.height) == 0 && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age, height);
}
LinkedHashSet底层原理

TreeSet集合底层原理
Set<Integer> set1=new TreeSet<>();
set1.add(6);
set1.add(5);
set1.add(5);
set1.add(7);
System.out.println(set1);

Set<Student> students=new TreeSet<>();
students.add(new Student("蜘蛛精",25,169.5));
students.add(new Student("紫霞",22,166.5));
students.add(new Student("至尊宝",26,165.5));
System.out.println(students);public class Student implements Comparator<Student> {
private String name;
private int age;
private double height;
public int compareTo(Student o){
return this.age-o.age;
}
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return 0;
} Set<Student> students=new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(),o2.getHeight());
}
});
 并发异常问题
并发异常问题
Iterator<String> it=list.iterator;
while (it.hasNext()){
String name=it.next();
if(name.contains("李")){
it.remove();
}
}
集合(二)
前置知识
可变参数

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
test(10);
test(10,20,30);
test(new int[]{10,20,30,40});
}
public static void test(int...nums){
System.out.println(nums.length);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
System.out.println("----------------------------");
}
}
Collestions

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> names=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names,"小明","小红","小芳");
System.out.println(names);
Collections.shuffle(names);
System.out.println(names);
List<Student> students=new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student("蜘蛛精",25,169.5));
students.add(new Student("紫霞",22,166.5));
students.add(new Student("至尊宝",26,165.5));
//Collections.sort(students);
Collections.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(),o2.getHeight());
}
});
System.out.println(students);
}
}

综合案例斗地主

public class GameDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Room m=new Room();
m.start();
}
}
package collection_d1;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class Room {
private List<Card> allCards=new ArrayList<>();
public Room(){
String[] numbers={"3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10","J","Q","K","A","2"};
String[] colors={"?","?","?","?"};
int size=0;
for (String number : numbers) {
size++;
for (String color : colors) {
Card c=new Card(number,color,size);
allCards.add(c);
}
}
Card c1=new Card("","🃏",++size);
Card c2=new Card("","😡",++size);
Collections.addAll(allCards,c1,c2);
System.out.println("新牌:"+allCards);
}
public void start(){
Collections.shuffle(allCards);
System.out.println("洗牌后:"+allCards);
List<Card> Keberan=new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> Jorden=new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> LebulanJim=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < allCards.size(); i++) {
Card c=allCards.get(i);
if(i%3==0){
Keberan.add(c);
} else if (i%3==1) {
Jorden.add(c);
}else if (i%3==2){
LebulanJim.add(c);
}
}
sortCards(Keberan);
sortCards(Jorden);
sortCards(LebulanJim);
System.out.println("Kobe:"+Keberan);
System.out.println("Jorden:"+Jorden);
System.out.println("Zmusi:"+LebulanJim);
List<Card> lastThreeCards=allCards.subList(allCards.size()-3,allCards.size());
System.out.println("底牌:"+lastThreeCards);
Keberan.addAll(lastThreeCards);
sortCards(Keberan);
System.out.println("Kebe抢到地主后:"+Keberan);
}
private void sortCards(List<Card> cards) {
Collections.sort(cards, new Comparator<Card>() {
@Override
public int compare(Card o1, Card o2) {
return o2.getSize()-o1.getSize();
}
});
}
}package collection_d1;
public class Card {
private String number;
private String color;
private int size;
public Card() {
}
public Card(String number, String color, int size) {
this.number = number;
this.color = color;
this.size = size;
}
public String getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public void setSize(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return color+number;
}
}
Map集合


public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("手表",100);
map.put("手表",220);
map.put("手机",2);
map.put("Java",2);
map.put(null,null);
System.out.println(map);
}![]()
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map=new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("手表",100);
map.put("手表",220);
map.put("手机",2);
map.put("Java",2);
map.put(null,null);
System.out.println(map);
}
常用方法
public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("手表",100);
map.put("手表",220);
map.put("手机",2);
map.put("Java",2);
map.put(null,null);
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.size());
map.clear();
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
System.out.println(map.get("手机"));
System.out.println(map.remove("手表"));
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.containsKey("手表"));
System.out.println(map.containsKey("手机"));
System.out.println(map.containsValue(2));
Set<String> keys= map.keySet();
System.out.println(keys);
Collection<Integer> values=map.values();
System.out.println(values);
Map<String,Integer> map1=new HashMap<>();
map1.put("java1",10);
map1.put("java2",20);
Map<String,Integer> map2=new HashMap<>();
map2.put("java3",10);
map2.put("java2",222);
map1.putAll(map2);
System.out.println(map1);
System.out.println(map2);
}
}
遍历方式

public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//键找值
Map<String,Double> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("蜘蛛精",162.5);
map.put("蜘蛛精",169.8);
map.put("紫霞",165.8);
map.put("至尊宝",169.5);
map.put("牛魔王",183.6);
System.out.println(map);
Set<String> keys=map.keySet();
System.out.println(keys);
for (String key : keys) {
double value=map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"====>"+value);
}
}
}

public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//键找值
Map<String,Double> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("蜘蛛精",162.5);
map.put("蜘蛛精",169.8);
map.put("紫霞",165.8);
map.put("至尊宝",169.5);
map.put("牛魔王",183.6);
System.out.println(map);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Double> entry : entries) {
String key=entry.getKey();
double value=entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"====>"+value);
}
}
}

public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//键找值
Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("蜘蛛精", 162.5);
map.put("蜘蛛精", 169.8);
map.put("紫霞", 165.8);
map.put("至尊宝", 169.5);
map.put("牛魔王", 183.6);
System.out.println(map);
map.forEach((k,v) -> {
System.out.println(k+"-->"+v);
});
}
}
综合案例

public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> data=new ArrayList<>();
String[] selects={"A","B","C","D"};
Random r=new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 80; i++) {
int index=r.nextInt(4);
data.add(selects[index]);
}
System.out.println(data);
Map<String,Integer> result=new HashMap<>();
for (String s : data) {
if(result.containsKey(s)){
result.put(s,result.get(s)+1);
}else {
result.put(s,1);
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}

HashMap


LinkedHashMap

TreeMap

集合的嵌套

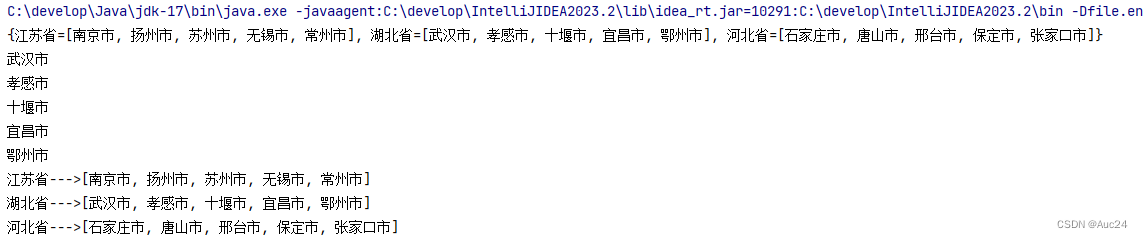
package collection_d1;
import java.util.*;
public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,List<String>> map=new HashMap<>();
List<String> cities1=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(cities1,"南京市","扬州市","苏州市","无锡市","常州市");
map.put("江苏省",cities1);
List<String> cities2=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(cities2,"武汉市","孝感市","十堰市","宜昌市","鄂州市");
map.put("湖北省",cities2);
List<String> cities3=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(cities3,"石家庄市","唐山市","邢台市","保定市","张家口市");
map.put("河北省",cities3);
System.out.println(map);
List<String> cities = map.get("湖北省");
for (String city : cities) {
System.out.println(city);
}
map.forEach((p,c) -> {
System.out.println(p+"--->"+c);
});
}
}
stream流


public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> names=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names,"1科比","2詹姆斯","1库里");
System.out.println(names);
List<String> list2=names.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("1")).filter(a -> a.length()==3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list2);
}
}
常用方法


public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> names=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names,"张三丰","张无忌","周芷若","赵敏","张强");
Stream<String> stream = names.stream();
Set<String> set=new HashSet<>();
Collections.addAll(set,"刘德华","张曼玉","蜘蛛精","马德","德玛西亚");
Stream<String> stream1 = names.stream();
stream1.filter(s -> s.contains("德")).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
Map<String,Double> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("古力娜扎",172.3);
map.put("迪丽热巴",168.3);
map.put("马儿扎哈",166.3);
map.put("卡尔扎巴",168.3);
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
Stream<String> ks=keys.stream();
Collection<Double> values=map.values();
Stream<Double> vs=values.stream();
Set<Map.Entry<String,Double>> entries=map.entrySet();
Stream<Map.Entry<String, Double>> kvs = entries.stream();
kvs.filter(e ->e.getKey().contains("巴"))
.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getKey()+"-->"+e.getValue()));
String[] names2={"张翠山","东方不败","唐大山","孤独求败"};
Stream<String> s1 = Arrays.stream(names2);

public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> students=new ArrayList<>();
Student s1=new Student("zzj",26,172.5);
Student s2=new Student("zzj",26,172.5);
Student s3=new Student("zx",23,167.6);
Student s4=new Student("bjj",25,169.0);
Student s5=new Student("nmw",35,183.3);
Student s6=new Student("nfr",34,168.3);
Collections.addAll(students,s1,s2,s3,s4,s5,s6);
students.stream().filter(s->s.getAge()>=23 && s.getAge()<=30)
.sorted((o1, o2) -> o2.getAge()-o1.getAge())
.forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("---------------");
students.stream().sorted((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o2.getHeight(),o1.getHeight()))
.limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("---------------");
students.stream().sorted((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o2.getHeight(),o1.getHeight()))
.skip(students.size()-3).forEach(System.out::println);
Stream<String> st1 = Stream.of("张三", "李四");
Stream<String> st2 = Stream.of("张三2", "李四2","王五");
Stream<String> allSt = Stream.concat(st1, st2);
allSt.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}

public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> students=new ArrayList<>();
Student s1=new Student("zzj",26,172.5);
Student s2=new Student("zzj",26,172.5);
Student s3=new Student("zx",23,167.6);
Student s4=new Student("bjj",25,169.0);
Student s5=new Student("nmw",35,183.3);
Student s6=new Student("nfr",34,168.3);
Collections.addAll(students,s1,s2,s3,s4,s5,s6);
long size=students.stream().filter(s-> s.getHeight()>168).count();
System.out.println(size);
Student s=students.stream().max((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o1.getHeight(),o2.getHeight())).get();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
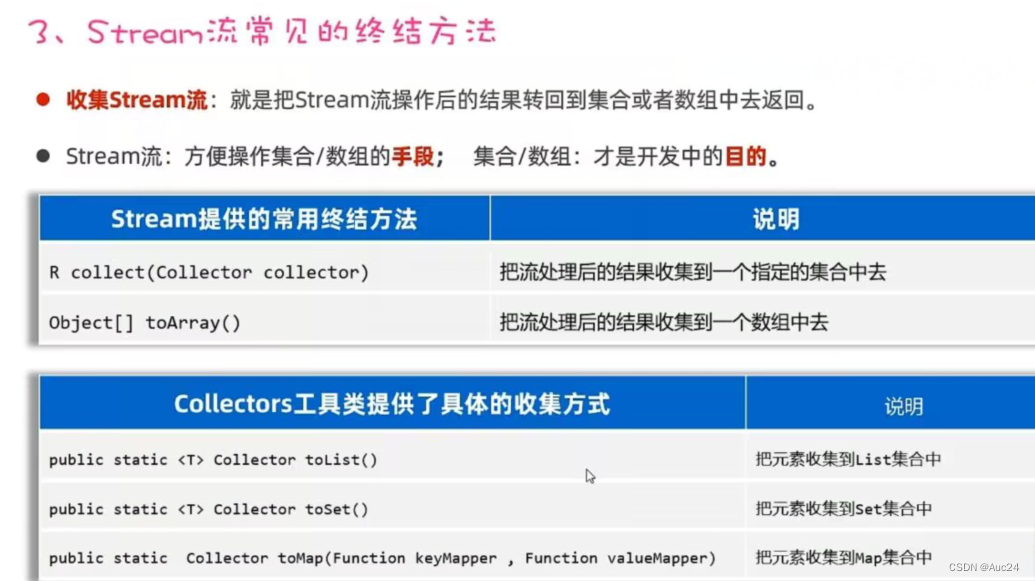
List<Student> students1=students.stream().filter(a->a.getHeight()>170).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(students1);
// Map<String,Double> map=students.stream().filter(a->a.getHeight()>170).distinct()
// .collect(Collectors.toMap(a->a.getName(),a->a.getHeight()));
// System.out.println(map);![]()
IO流(一)
File
创建对象


public class FileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f1=new File("C:\\Users\\Auc\\Pictures\\Saved Pictures\\pexels-asad-photo-maldives-3601425.jpg");
System.out.println(f1.length());
System.out.println(f1.exists());
}
}
判断文件类型、获取文件信息

public class FileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f1=new File("C:\\Users\\Auc\\Pictures\\Saved Pictures\\pexels-asad-photo-maldives-3601425.jpg");
System.out.println(f1.exists());
System.out.println(f1.isFile());
System.out.println(f1.isDirectory());
System.out.println(f1.getName());
System.out.println(f1.length());
long time = f1.lastModified();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(sdf.format(time));
File f2=new File("D:\\study\\ab.txt");
System.out.println(f2.getPath());
System.out.println(f2.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
创建文件和删除文件

public class FileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f1=new File("D:\\study\\auc.txt");
System.out.println(f1.createNewFile());
File f2=new File("D:\\study\\acc\\bcc");
System.out.println(f2.mkdirs());
System.out.println(f1.delete());
System.out.println(f2.delete());
}
}
遍历文件夹

public class FileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f1=new File("D:\\study\\auc.txt");
String[] names = f1.list();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
File[] files = f1.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}方法递归
认识递归的形式

public class FileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
}
//直接方法递归
public static void test1(){
System.out.println("--test1--");
test1();
}
//间接方法递归
public static void test2(){
System.out.println("--test2--");
test3();
}
public static void test3(){
test2();
}
}算法思想

public class FileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("5的阶乘:"+f(5));
}
public static int f(int n){
if(n==1){
return 1;
}else {
return f(n-1)*n;
}
}
}


public class FileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(f(1));
}
public static int f(int n){
if(n==10){
return 1;
}else {
return 2*f(n+1)+2;
}
}
}
文件搜索

public class FileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
searchFile(new File("c:/"),"QQ.exe");
}
/**
* 去目录下搜素某个文件
* @param dir 目录
* @param fileName
*/
public static void searchFile(File dir,String fileName) throws IOException {
if(dir==null|| !dir.exists() || dir.isFile()){
return;
}
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if(files!=null && files.length>0){
for (File f : files) {
if(f.isFile()){
if(f.getName().contains(fileName)){
System.out.println("找到了"+f.getAbsolutePath());
Runtime runtime=Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.exec(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}else {
searchFile(f,fileName);
}
}
}
}
}


public class FileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File dir=new File("E:\\resource");
deleteDir(dir);
}
public static void deleteDir(File dir){
if(dir==null || !dir.exists()){
return;
}
if(dir.isFile()){
dir.delete();
return;
}
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if(files==null){
return;
}
if(files.length==0){
dir.delete();
return;
}
for (File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()){
file.delete();
}else {
deleteDir(file);
}
}
dir.delete();
}
}字符集


public class FileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String data="a我b";
byte[] bytes = data.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
byte[] bytes1 = data.getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes1));
String s1 = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(s1);
String s2=new String(bytes1,"GBK");
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
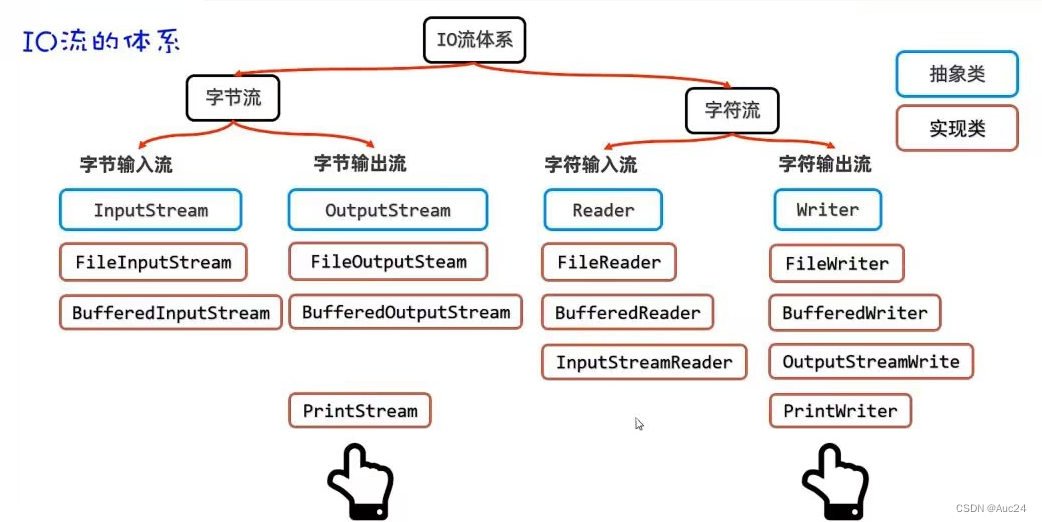
IO流


public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is=new FileInputStream(("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\itauc"));
int b1=is.read();
System.out.println(b1);
int b2=is.read();
System.out.println((char)b2);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is=new FileInputStream(("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\itauc"));
int b;
while ((b=is.read())!=-1){
System.out.printf((char)b);
}
is.close();
}文件字节输入流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is=new FileInputStream(("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\itauc"));
byte[] buffer=new byte[3];
int len=is.read(buffer);
String s = new String(buffer);
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("当前的读取字节数:"+len);
int len1=is.read(buffer);
String s1 = new String(buffer,0,len1);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println("当前的读取字节数:"+len1);
is.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is=new FileInputStream(("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\itauc"));
byte[] buffer=new byte[3];
int len;
while ((len= is.read())!=-1){
String rs = new String(buffer,0,len);
System.out.println(rs);
}
is.close();
}一次读完全部字节

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is=new FileInputStream(("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\itauc"));
File f=new File("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\itauc");
long size=f.length();
byte[] buffer=new byte[(int) size];
int len = is.read(buffer);
System.out.println(new String(buffer));
System.out.println(size);
System.out.println(len);
is.close();
}byte[] buffer=is.readAllBytes();
System.out.println(new String(buffer));写字节输出

public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream(("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\auc.cc"),true);
os.write(97);
os.write('b');
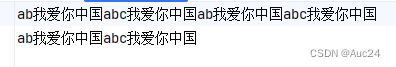
byte[] bytes="我爱你中国abc".getBytes();
os.write(bytes);
os.write(bytes,0,15);
os.write("\r\n".getBytes());
os.close();
}
}
文件复制
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is=new FileInputStream("d:/resource/pictures.png");
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream("c:/data/pcitures.png");
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
os.close();
is.close();
}释放资源的方式
try {
System.out.println(10/0);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("===finally执行了一次===");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is =null;
OutputStream os=null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream("d:/resource/pictures.png");
os = new FileOutputStream("c:/data/pcitures.png");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
if(os!=null)os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(is!=null)is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("d:/resource/pictures.png");
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("c:/data/pcitures.png");
){
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}IO流(二)
字符流
文件字符输入流
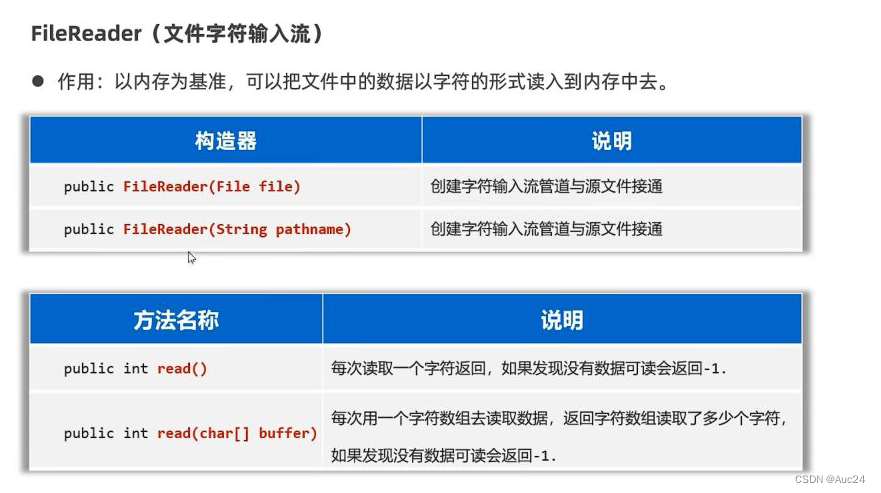
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (
FileReader fr = new FileReader("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\auc.cc");
){
// int c;
// while ((c=fr.read())!=-1){
// System.out.print((char) c);
// }
char[] buffer=new char[3];
int len;
while ((len=fr.read(buffer))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}文件字符输入流

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\auc.cc",true);
){
fw.write('a');
fw.write("我爱你");
fw.write("我爱你abcde",0,5);
fw.write("\r\n");
char[] buffer={'A','u','c',24};
fw.write(buffer);
fw.write(buffer,0,2);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
fw.flush();
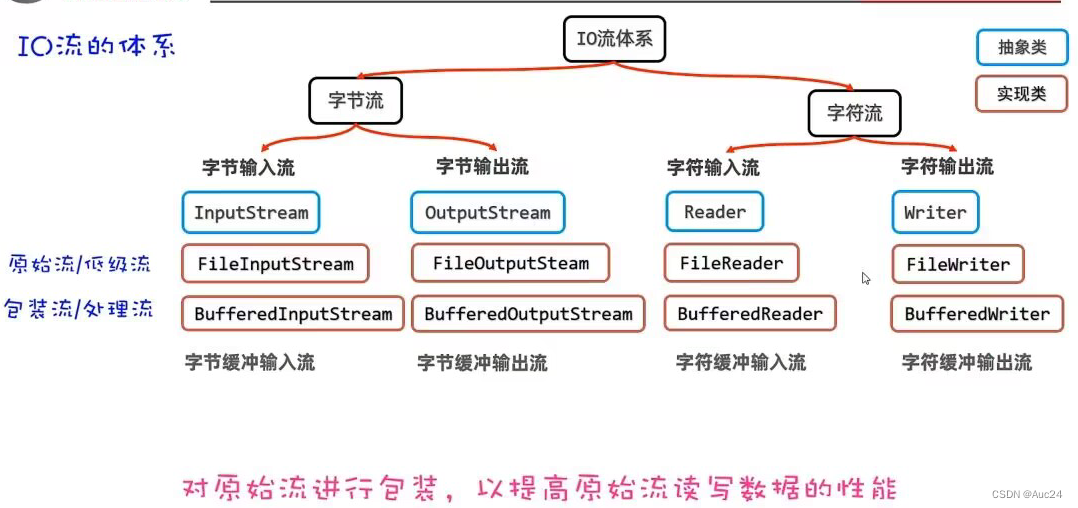
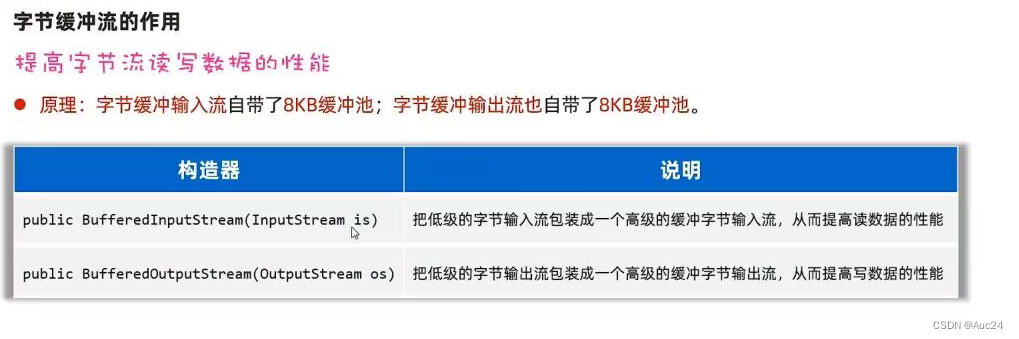
fw.close();缓冲流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (
InputStream fr = new FileInputStream("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\auc.cc");
InputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fr);
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\itauc");
OutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(os);
){
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=fr.read(buffer))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
System.out.println("复制完成");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try (
Reader fr = new FileReader("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\auc.cc");
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(fr);
){
char[] buffer=new char[3];
int len;
while ((len=br.read(buffer))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
//System.out.println(br.readLine());
// String line;
// while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){
// System.out.println(line);
// }
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\auc.cc",true);
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(fw);
){
bw.write('a');
bw.write("我爱你");
bw.write("我爱你abcde",0,5);
// fw.write("\r\n");
bw.newLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}转换流


public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(
InputStream is=new FileInputStream("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\auc.cc");
Reader isr=new InputStreamReader(is,"GBK");
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr);
) {
String line;
while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream("\"D:\\\\study\\\\java\\\\src\\\\pra\\\\adc.cc\"");
Writer osw=new OutputStreamWriter(os,"GBK");
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(osw);
) {
bw.write("我爱你中国");
bw.write("abcd");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}打印流

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(
PrintStream ps=new PrintStream("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\auc.cc", Charset.forName("GBK"));
) {
ps.println("我爱你中国");
ps.println(97);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(
PrintWriter ps=new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream("\"D:\\\\study\\\\java\\\\src\\\\pra\\\\auc.cc\"",true));
) {
ps.println("我爱你中国");
ps.println(97);
ps.write(97);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
数据流

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\auc.cc"));
) {
dos.writeInt(97);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\auc.cc"));
) {
int i=dis.readInt();
System.out.println(i);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}序列化流
public class User implements Serializable {
private String loginName;
private String userName;
private int age;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(String loginName, String userName, int age, String password) {
this.loginName = loginName;
this.userName = userName;
this.age = age;
this.password = password;
}
public String getLoginName() {
return loginName;
}
public void setLoginName(String loginName) {
this.loginName = loginName;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\auc.cc"));
){
User u=new User("admin","张三",32,"6688xyz");
oos.writeObject(u);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (
ObjectInputStream oos = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\auc.cc"));
){
User u=(User) oos.readObject();
System.out.println(u);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}IO框架

特殊文件
Properties属性文件

public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Properties properties=new Properties();
System.out.println(properties);
properties.load(new FileReader("D:\\study\\java\\src\\sac\\src\\users.properties"));
System.out.println(properties);
System.out.println(properties.getProperty("张无忌"));
}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.setProperty("张无忌","minmin");
properties.store(new FileWriter("D:\\study\\java\\src\\pra\\itauc"),"i saved many users!");
}XML文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!--注释:放在第一行-->
<users>
<users id="1">
<name>张无忌</name>
<password>minmin</password>
<data>3<2&&5>4</data>
</users>
<users id="2">
<name>小明</name>
<password>1234</password>
</users>
</users>
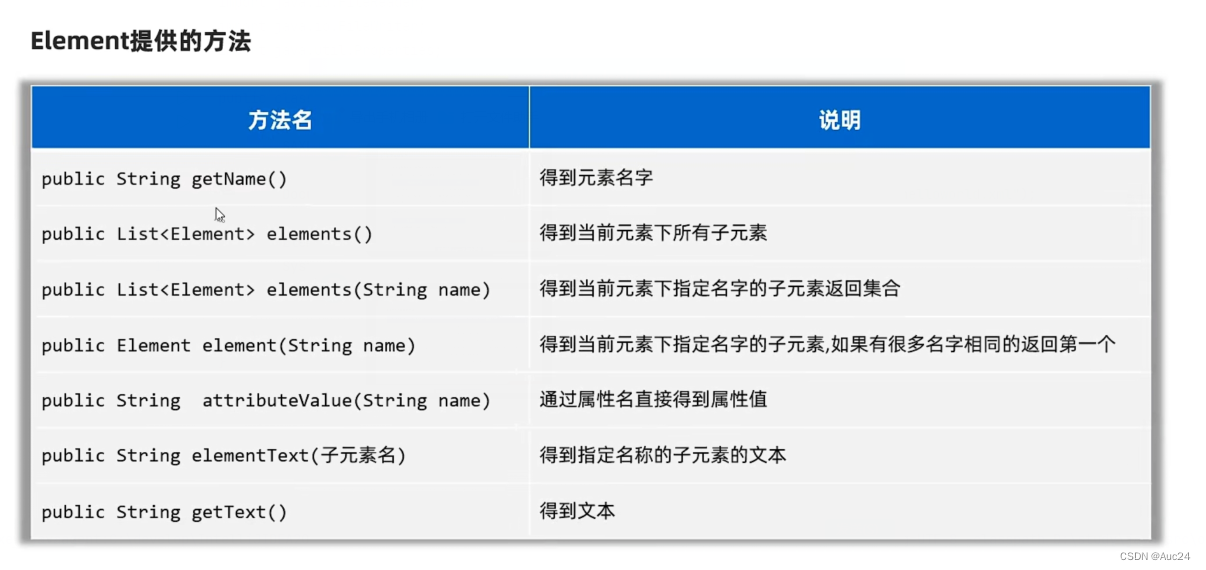
public class Tesd {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
SAXReader saxReader=new SAXReader();
Document document = saxReader.read("D:\\study\\java\\src\\sac\\src\\helloworld.xml");
Element root = document.getRootElement();
System.out.println(root.getName());
List<Element> elements = root.elements();
for (Element element : elements) {
System.out.println(element.getName());
}
Element people = root.element("people");
System.out.println(people.getText());
Element user = root.element("user");
System.out.println(user.elementText("name"));
System.out.println(user.elementText("password"));
}
}
读取数据?
public class Tesd {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
sb.append("<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\" ?>");
sb.append("<name>").append("点点点").append("</name>");
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("properties=app/src/book"));
}
}日志技术


public static final Logger LOGGER= LoggerFactory.getLogger("Tesd");
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
try {
LOGGER.info("方法开始执行");
}catch (Exception e){
LOGGER.error(bug);
}
?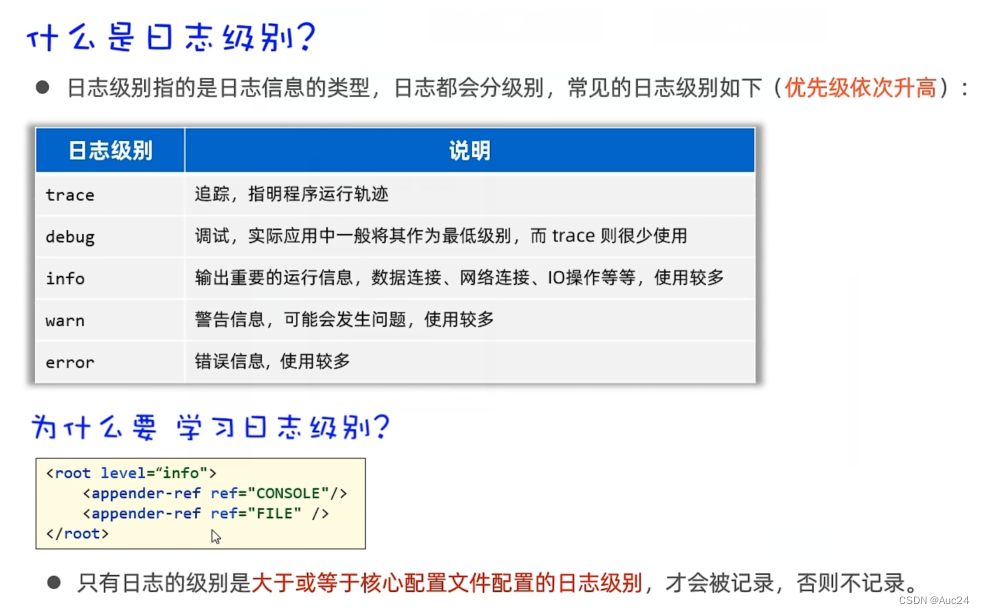
<root level="debug">
<appender-ref ref="CONSOLE"/>
<appender-ref ref="FILE" />
</root>多线程
继承Thread类

public class Tesd {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t=new MyThread();
t.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程输出:"+i);
}
}
}public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("子线程MyThread输出:"+i);
}
}
}
实现Runnable接口

public class Tesd {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable target=new MyRunnable();
new Thread(target).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程输出:"+i);
}
}
}public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("子线程输出:"+i);
}
}
}
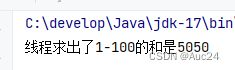
Callable接口

public class Tesd {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Callable<String> call = new MyCallable(100);
FutureTask<String> f1 = new FutureTask<>(call);
new Thread(f1).start();
String rs = f1.get();
System.out.println(rs);
}
}public class MyCallable implements Callable<String> {
private int n;
public MyCallable(int n) {
this.n = n;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
int sum=0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
sum+=i;
}
return "线程求出了1-"+n+"的和是"+sum;
}
}

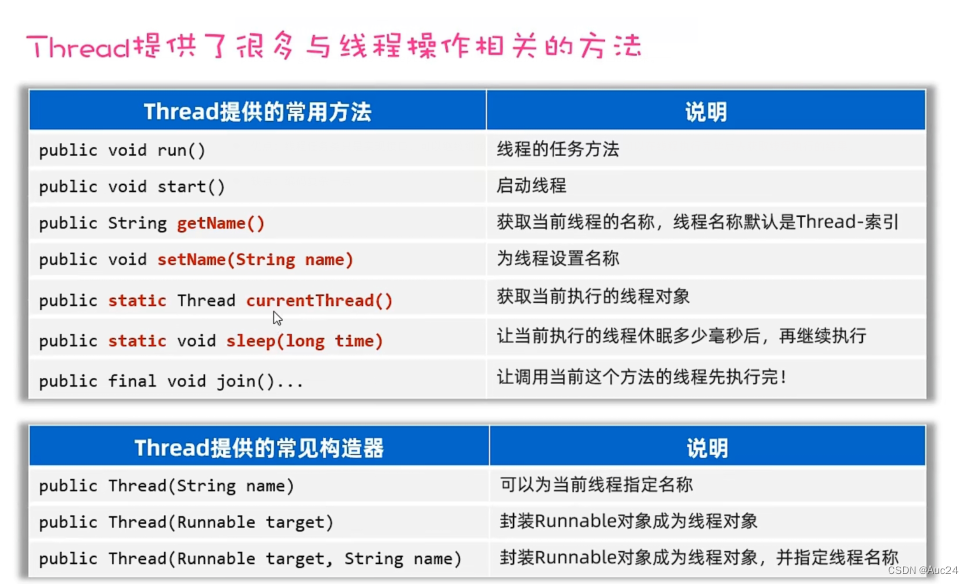
线程安全

public class Tesd {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException{
Account acc=new Account(100000,"ICBC-110");
new DrawThread(acc,"小明").start();
new DrawThread(acc,"小红").start();
}
}
public class DrawThread extends Thread{
private Account acc;
public DrawThread(Account acc,String name){
super(name);
this.acc=acc;
}
public void run(){
acc.drawMoney(100000);
}
}public class Account {
private double money;
private String cardId;
public double getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(double money) {
this.money = money;
}
public String getCardId() {
return cardId;
}
public void setCardId(String cardId) {
this.cardId = cardId;
}
public Account() {
}
public Account(double money, String cardId) {
this.money = money;
this.cardId = cardId;
}
public void drawMoney(double money) {
String name=Thread.currentThread().getName();
if(this.money>=money){
System.out.println(name+"来取钱"+money+"成功!");
this.money-=money;
System.out.println(name+"来取钱后,余额剩余:"+this.money);
}else {
System.out.println(money+"来取钱,余额不足");
}
}
}
线程同步
同步代码块

synchronized (this) {
if(this.money>=money){
System.out.println(name+"来取钱"+money+"成功!");
this.money-=money;
System.out.println(name+"来取钱后,余额剩余:"+this.money);
}else {
System.out.println(name+"来取钱,余额不足");
}
}
同步方法

public synchronized void drawMoney(double money) {
String name=Thread.currentThread().getName();
if(this.money>=money){
System.out.println(name+"来取钱"+money+"成功!");
this.money-=money;
System.out.println(name+"来取钱后,余额剩余:"+this.money);
}else {
System.out.println(name+"来取钱,余额不足");
}
}Lock锁
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Account {
private double money;
private String cardId;
private final Lock lk=new ReentrantLock();
public double getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(double money) {
this.money = money;
}
public String getCardId() {
return cardId;
}
public void setCardId(String cardId) {
this.cardId = cardId;
}
public Account() {
}
public Account(double money, String cardId) {
this.money = money;
this.cardId = cardId;
}
public void drawMoney(double money) {
String name=Thread.currentThread().getName();
lk.lock();
try {
if(this.money>=money){
System.out.println(name+"来取钱"+money+"成功!");
this.money-=money;
System.out.println(name+"来取钱后,余额剩余:"+this.money);
}else {
System.out.println(name+"来取钱,余额不足");
}
} finally {
lk.unlock();
}
}
}
线程池
创建线程池

public class Tesd {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException{
//public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
// int maximumPoolSize,
// long keepAliveTime,
// TimeUnit unit,
// BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
// ThreadFactory threadFactory,
// RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
ExecutorService pool=new ThreadPoolExecutor(3,5,8, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(4),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
}
}
线程池处理Runnable任务
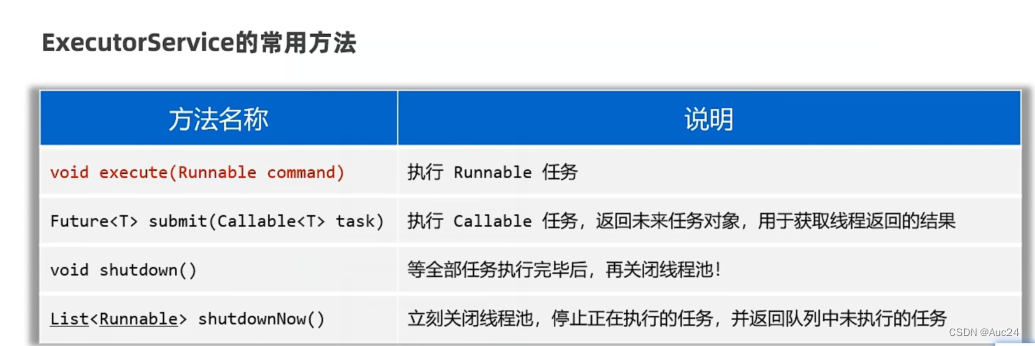
public class Tesd {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException{
ExecutorService pool=new ThreadPoolExecutor(3,5,8, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(4),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
Runnable target=new MyRunnable();
pool.execute(target);
pool.execute(target);
pool.execute(target);
pool.execute(target);
pool.execute(target);
pool.shutdown();
}
}public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==>输出666");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}

线程池处理Callable任务

public class Tesd {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool=new ThreadPoolExecutor(3,5,8, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(4),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
Future<String> f1 = pool.submit(new Mycallable(100));
Future<String> f2 = pool.submit(new Mycallable(200));
Future<String> f3 = pool.submit(new Mycallable(300));
Future<String> f4 = pool.submit(new Mycallable(400));
System.out.println(f1.get());
System.out.println(f2.get());
System.out.println(f3.get());
System.out.println(f4.get());
}
}import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class Mycallable implements Callable<String> {
private int n;
public Mycallable(int n) {
this.n = n;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
int sum=0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
sum+=i;
}
return Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程求出了1-"+n+"的和是"+sum;
}
}
Executors工具类实现线程池

ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);网络通信
网络通信三要素

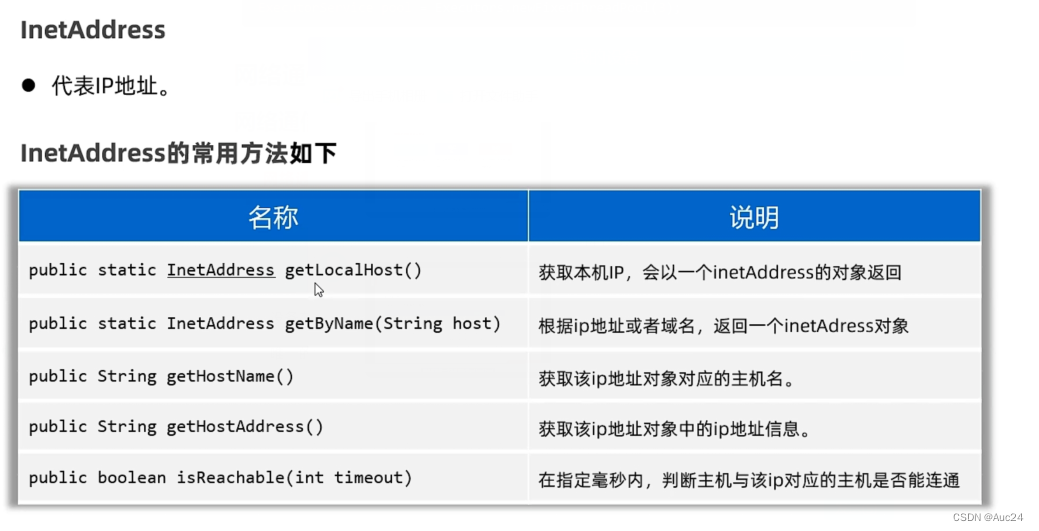
public class Tesd {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InetAddress ip1 = Inet4Address.getLocalHost();
System.out.println(ip1.getHostName());
System.out.println(ip1.getHostAddress());
InetAddress ip2 = Inet4Address.getByName("www.baidu.com");
System.out.println(ip2.getHostName());
System.out.println(ip2.getHostAddress());
System.out.println(ip2.isReachable(6000));
}
}UDP通信
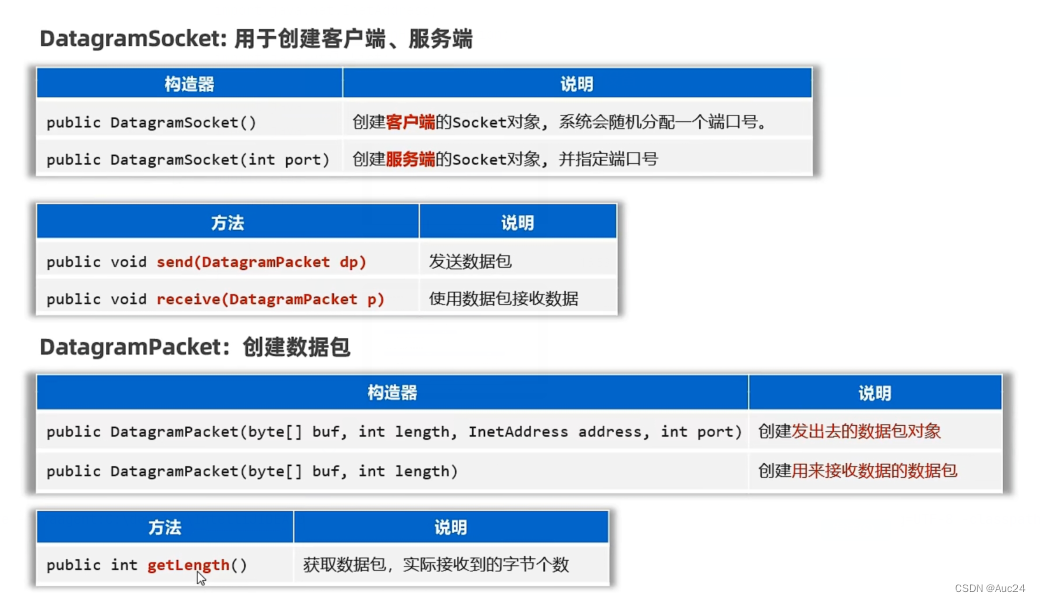
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.Inet4Address;
import java.net.InetAddress;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1、创建客户端对象
DatagramSocket socket=new DatagramSocket();
//2、创建数据包对象封装发出去
byte[] bytes="我是客户端".getBytes();
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length, InetAddress.getLocalHost(),6666);
//3、开始发送数据包的数据
socket.send(packet);
System.out.println("客户端数据发送完毕~");
socket.close();
}
}
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.SocketException;
public class Sever {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("----服务端启动-----");
//1、创建一个服务端对象注册端口
DatagramSocket scoket=new DatagramSocket(6666);
//2、创建一个数据包对象,用于接收数据
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024*64];
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(buffer,buffer.length);
//3、开始正式使用数据包来接收客户端发来的数据
scoket.receive(packet);
//4、从字节数组中,把接收到的数据直接打印出来
int len = packet.getLength();
String rs=new String(buffer,0,len);
System.out.println(rs);
}
}![]()

多发多收
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1、创建客户端对象
DatagramSocket socket=new DatagramSocket();
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
//2、创建数据包对象封装发出去
while (true) {
System.out.println("请说:");
String msg=sc.nextLine();
if("exit".equals(msg)){
System.out.println("欢迎下次光临!退出成功");
socket.close();
break;
}
byte[] bytes=msg.getBytes();
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length, InetAddress.getLocalHost(),6666);
//3、开始发送数据包的数据
socket.send(packet);
}
}
}public class Sever {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("----服务端启动-----");
//1、创建一个服务端对象注册端口
DatagramSocket scoket=new DatagramSocket(6666);
//2、创建一个数据包对象,用于接收数据
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024*64];
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(buffer,buffer.length);
while (true) {
//3、开始正式使用数据包来接收客户端发来的数据
scoket.receive(packet);
//4、从字节数组中,把接收到的数据直接打印出来
int len = packet.getLength();
String rs=new String(buffer,0,len);
System.out.println(rs);
System.out.println(packet.getAddress().getHostAddress());
System.out.println(packet.getPort());
System.out.println("-----------------");
}
}
}TCP通信

public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1、创建socket对象,并同时请求与服务端程序的连接
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
//2、从Socket通信管道中得到一个字节输出流,用来发数据给服务端程序
OutputStream os=socket.getOutputStream();
//3、把低级的字节输出流包装成数据输出流
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(os);
//4、开始写数据出去
dos.writeUTF("在一起");
dos.close();
socket.close();
}
}
public class Sever {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("----服务端启动成功----");
//1、创建SeverSocket的对象,同时为服务端注册窗口
ServerSocket serverSocket=new ServerSocket(8888);
//2、使用severSocket对象,调用一个accept方法,等待客户端的连接请求
Socket socket=serverSocket.accept();
//3、从socket通信管道中得到一个字节输入流
InputStream is=socket.getInputStream();
//4、把原始的字节输入流包装成数据输入流
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(is);
//5、使用数据输入读取客户端发送过来的消息
String rs=dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(rs);
System.out.println(socket.getRemoteSocketAddress());
dis.close();
socket.close();
}
}多发多收
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1、创建socket对象,并同时请求与服务端程序的连接
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
//2、从Socket通信管道中得到一个字节输出流,用来发数据给服务端程序
OutputStream os=socket.getOutputStream();
//3、把低级的字节输出流包装成数据输出流
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(os);
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请说:");
String msg=sc.nextLine();
if("exit".equals(msg)){
System.out.println("欢迎你下次光临!退出成功!");
dos.close();
socket.close();
break;
}
//4、开始写数据出去
dos.writeUTF(msg);
dos.flush();
}
}
}
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.*;
public class Sever {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("----服务端启动成功----");
//1、创建SeverSocket的对象,同时为服务端注册窗口
ServerSocket serverSocket=new ServerSocket(8888);
//2、使用severSocket对象,调用一个accept方法,等待客户端的连接请求
Socket socket=serverSocket.accept();
//3、从socket通信管道中得到一个字节输入流
InputStream is=socket.getInputStream();
//4、把原始的字节输入流包装成数据输入流
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(is);
while (true) {
try {
//5、使用数据输入读取客户端发送过来的消息
String rs=dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(rs);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(socket.getRemoteSocketAddress()+"离线了");
dis.close();
socket.close();
break;
}
}
}
}与多个客户端同时通信
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1、创建socket对象,并同时请求与服务端程序的连接
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
//2、从Socket通信管道中得到一个字节输出流,用来发数据给服务端程序
OutputStream os=socket.getOutputStream();
//3、把低级的字节输出流包装成数据输出流
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(os);
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请说:");
String msg=sc.nextLine();
if("exit".equals(msg)){
System.out.println("欢迎你下次光临!退出成功!");
dos.close();
socket.close();
break;
}
//4、开始写数据出去
dos.writeUTF(msg);
dos.flush();
}
}
}import java.net.*;
public class Sever {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("----服务端启动成功----");
//1、创建SeverSocket的对象,同时为服务端注册窗口
ServerSocket serverSocket=new ServerSocket(8888);
while (true) {
//2、使用severSocket对象,调用一个accept方法,等待客户端的连接请求
Socket socket=serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("有人上线了:"+socket.getRemoteSocketAddress());
//3、把这个客户端对应的socket通信管道,交给一个独立的线程负责处理
new SeverReaderThread(socket).start();
}
}
}import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SeverReaderThread extends Thread{
public SeverReaderThread(Socket socket){
this.socket=socket;
}
private Socket socket;
@Override
public void run() {
try {
InputStream is=socket.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(is);
while (true){
try {
String msg= dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(msg);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("有人下线了:"+socket.getRemoteSocketAddress());
dis.close();
socket.close();
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
综合案例
群聊
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1、创建socket对象,并同时请求与服务端程序的连接
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
//创建独立的线程,负责随机从socket中接收服务端发送来的消息
new ClinetReaderThread(socket).start();
//2、从Socket通信管道中得到一个字节输出流,用来发数据给服务端程序
OutputStream os=socket.getOutputStream();
//3、把低级的字节输出流包装成数据输出流
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(os);
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请说:");
String msg=sc.nextLine();
if("exit".equals(msg)){
System.out.println("欢迎你下次光临!退出成功!");
dos.close();
socket.close();
break;
}
//4、开始写数据出去
dos.writeUTF(msg);
dos.flush();
}
}
}import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
public class ClinetReaderThread extends Thread{
public ClinetReaderThread(Socket socket){
this.socket=socket;
}
private Socket socket;
@Override
public void run() {
try {
InputStream is=socket.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(is);
while (true){
try {
String msg= dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(msg);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("自己下线了:"+socket.getRemoteSocketAddress());
dis.close();
socket.close();
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}import java.net.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Sever {
public static List<Socket> onLineSocket=new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("----服务端启动成功----");
//1、创建SeverSocket的对象,同时为服务端注册窗口
ServerSocket serverSocket=new ServerSocket(8888);
while (true) {
//2、使用severSocket对象,调用一个accept方法,等待客户端的连接请求
Socket socket=serverSocket.accept();
onLineSocket.add(socket);
System.out.println("有人上线了:"+socket.getRemoteSocketAddress());
//3、把这个客户端对应的socket通信管道,交给一个独立的线程负责处理
new SeverReaderThread(socket).start();
}
}
}import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SeverReaderThread extends Thread{
public SeverReaderThread(Socket socket){
this.socket=socket;
}
private Socket socket;
@Override
public void run() {
try {
InputStream is=socket.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(is);
while (true){
try {
String msg= dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(msg);
//分发给客户端接收
sendMsgToAll(msg);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("有人下线了:"+socket.getRemoteSocketAddress());
Sever.onLineSocket.remove(socket);
dis.close();
socket.close();
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private void sendMsgToAll(String msg) throws Exception{
//发送给全部在线的管道
for (Socket onLineSocket : Sever.onLineSocket) {
OutputStream os = onLineSocket.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeUTF(msg);
dos.flush();
}
}
}Java高级
单元测试


public class StringUntil {
public static void printNumber(String name){
if(name==null){
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
System.out.println("名字长度是:"+name.length());
}
public static int getMaxIndex(String data){
if(data==null){
return -1;
}
return data.length()-1;
}
}import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
public class StringUtilTest {
@Test
public void testPrintNumber(){
StringUntil.printNumber("admin");
StringUntil.printNumber(null);
}
@Test
public void testGetMaxIndex(){
int index1 = StringUntil.getMaxIndex(null);
System.out.println(index1);
int index2 = StringUntil.getMaxIndex("admin");
System.out.println(index2);
Assert.assertEquals("方法内部有不过!",4,index2);
}
}
常见注解

反射

public class Test1class {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class c1= Student.class;
System.out.println(c1.getName());
System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName());
Class c2 = Class.forName("com.au.Student");
System.out.println(c1==c2);
Student s=new Student();
Class c3 = s.getClass();
System.out.println(c3==c2);
}
}
获取类的构造器

package com.au;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
public class Test1class {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
@Test
public void TestGetConstructors(){
Class c= Cat.class;
Constructor[] constructor = c.getConstructor();
for (Constructor constructor : constructor) {
System.out.println(constructor.getName()+"-->"+constructor.getParameterTypes());
}
}
}
}本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【JavaWeb】Servlet
- 通过DTS实现PG14迁移到人大金仓V8R6
- 参数化
- PostgreSQL的缓存管理器原理——出自云贝教育
- 【办公技巧】excel中设置选项按钮的方法
- 训练营第四十六天 | ● 139.单词拆分 ● 关于多重背包,你该了解这些! ● 背包问题总结篇!
- ubuntu系统(9):ubuntu 20.02安装pydot
- 生成式AI在软件开发中的革新:自动化、效率、理解、创新与安全的综合考察
- Vue中的keep-alive缓存组件的理解
- mongoAltas使用