jdbc从0到1
JDBC:
??? jdbc程序是Java语言官方定义的一系列接口,各大数据库厂商就实现了这些接口,我们Java代码需要与mysql数据库通信,mysql官方提供了java链接mysql数据库的工具,并封装成jar包,我们通过使用jar包中提供的方法与mysql数据库通信并执行操作
??? 固定的流程:
??????? 一:注册驱动(为了建立两个语言共同使用的环境)
???
??????? 选择要使用的数据库驱动比如:
???????
??????? 二:建立连接(通过账号密码等数据登录数据库)
??????? 三:创建对象(创建执行SQL语句的Java对象)
??????? 四:执行语句 (执行SQL语句)
??????? 五:处理结果(对SQL语句的结果进行处理)
??????? 六:关闭资源 (关闭使用过的对象,释放内存)
一.搭建环境
??? 如果需要使用jdbc程序就要准备环境:
??????? ?1.模块下创建一个目录,名称为lib
??????? ?2.复制驱动包,放入该目录
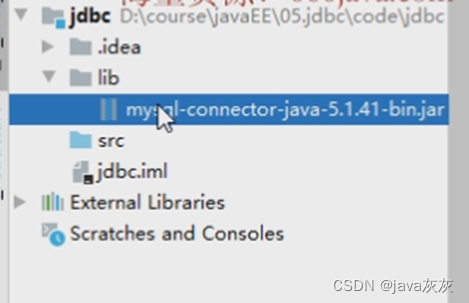
??????? ?3.鼠标右键选择该jar包,选择 add as lib....

选完之后点击OK

? ? 二.编写JDBC程序:
??????? 处理DML_DDL(增删改)语句:
package com.bjpowernode;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* 处理DML语句
* 处理DDL语句
*/
public class DML_DDL_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
// 一:注册驱动(为了建立两个语言共同使用的环境)
//通过反射技术,加载驱动包中的核心类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 二:建立连接(通过账号密码等数据登录数据库)
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bjpowernode",
"root",
"1234");
System.out.println(connection);
//三:创建对象(创建执行SQL语句的Java对象)
statement = connection.createStatement();
//四:执行语句 (执行SQL语句) DDL和DML语句
// String sql = "insert into dept(deptno,dname,loc) values (100,'销售部','深圳')";
// String sql = "update dept set dname='财务部' where deptno = 10";
String sql = "delete from dept where deptno = 20";
// String sql = "create table aaa(id int(11) primary key auto_increment,name varchar(40) not null)";
int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
// 五:处理结果(对SQL语句的结果进行处理)
if(i>0){
System.out.println("操作成功");
}else{
System.out.println("操作失败");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 六:关闭资源 (关闭使用过的对象,释放内存)
if(statement != null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
??????
处理DQL(查)语句:
package com.bjpowernode;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 处理DQL语句
*/
public class DQL_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
String sql = "select * from dept where deptno = 30";
try {
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.建立连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bjpowernode", "root", "1234");
//3.创建对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//4.执行语句
/**
* 结果集对象resultSet:可以存储查询语句的数据结果,是容器对象
* 需要从对象对象resultSet中将查询结果获取出来。
*/
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
//5.处理结果
while (resultSet.next()){ //一次循环可以获取到数据库表中的一条记录
//获取每条记录中的字段
//@param String 根据字段名称 @param int 根据字段的序号,序号从1开始
int deptno = resultSet.getInt("deptno");
String dname = resultSet.getString("dname");
String loc = resultSet.getString("loc");
System.out.println("编号:"+deptno+" 名称: "+dname+" 地址: "+loc);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//6.关闭资源
if(resultSet != null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(statement != null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
???
JDBC程序中的用到的:
??????? 对象:
??????????? Connection:连接对象,连接数据库
??????????? Statement:执行SQL语句的Java对象
??????????? ResultSet:查询时保存查询结果的对象
??????????? PreparedStatement:执行SQL语句的Java对象,不会出现问题
??????? 方法:
??????????? executeQuery():? DQL
??????????? executeUpdate(): DML
??? Statement:SQL语句中数据的拼接问题
??????? ? SQL语句注入问题:
无非就是前端传进来一个 空密码配合 or?1 = 1,即便传入的密码不正确,因为or?1 =1永远成立,所以即便用户没有输入正确的密码,依旧获取到了密码 或者说突破了登录,比如:
![]()
解决方案:
????????????????引入PreparedStatement,因为PreparedStatement对象中建立了占位符机制:使用?来替换真实的数据可以有效防止SQL注入,并且由于预编译的特性,其执行效率更高。
代码如下:
package com.bjpowernode;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* PreparedStatement对象解决程序中的拼接和注入问题
*/
public class PreparedStatementDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入账号:");
String uName = scanner.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String pwd = scanner.next();
/**
* sadsdw'or'1=1
* PreparedStatement对象中建立了占位符机制:使用?来替换真实的数据,占据一个位置
*
* ?占位符在SQL语言中的是不存在
*/
String sql = "select * from user where username = ? and password = ?";
System.out.println(sql);
try {
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.建立连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bjpowernode", "root", "1234");
//3.创建对象
/**
* 获取对象的方式解决了SQL注入:
* 获取对象时直接加载解析SQL语句,目的是为了确定SQL语句的语法结构,语法结构一旦确定,在整个
* 程序的运行不会更改,后续就是单纯的数据赋值(不在识别关键字,不在解析SQL语法)
*/
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
/**
* 在执行SQL语句之前,要判断sql语句中是否存在占位符,需要先将?占位符替换成要执行的数据
* @param1 占位符的位置 从1开始
* @param2 真实的数据
*/
preparedStatement.setString(1,uName);
preparedStatement.setString(2,pwd);
//4.执行语句
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//5.处理结果
if(resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//6.关闭资源
if(resultSet != null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(preparedStatement != null){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
? ? 三.封装一个工具类:
????????????????目的是简化JDBC程序fegn
package com.bjpowernode.util;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* jdbc工具类,目的是简化jdbc的使用
* 一:注册驱动(为了建立两个语言共同使用的环境),一次即可
* 二:建立连接(通过账号密码等数据登录数据库)
* 三:创建对象(创建执行SQL语句的Java对象)
* 六:关闭资源 (关闭使用过的对象,释放内存)
*/
public class JDBCUtils {
private static String driver;
private static String url;
private static String username;
private static String password;
static {
try {
//为属性赋值
//直接将常量数据赋值
//driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
//可以讲有可能会改变的数据值放在不需要编译可以直接应用的文件
//需要读取文件中的数据,为属性赋值
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties"));
driver = properties.getProperty("jdbc.driver");
url = properties.getProperty("jdbc.url");
username = properties.getProperty("jdbc.username");
password = properties.getProperty("jdbc.password");
//一:注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取连接对象的方法
* @return 连接对象
*/
public static Connection getConnection(){
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 关闭程序中所用的对象
*/
public static void closeAll(Connection connection, PreparedStatement preparedStatement, ResultSet resultSet){
if(resultSet != null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(preparedStatement != null){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 将六个步骤全部封装在工具类中,使用时直接调用该方法即可
* DML为例
* 该方法可以处理所有的DML语句
* @param sql 要执行的DML语句
* @param args DML语句中占位符数据
*/
public static int myExecuteUpdate(String sql,Object...args){
Connection connection = getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//判断sql语句中是否存在占位符
if(args != null){
for (int i=0;i<args.length;i++){
//为占位符赋值
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,args[i]);
}
}
//执行SQL语句
return preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtils.closeAll(connection,preparedStatement,null);
}
return -1;
}
}
四.测试工封装的工具类
package com.bjpowernode.test;
import com.bjpowernode.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TestJDBCUtils {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取连接对象
Connection connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
String sql = "delete from emp where sal < ?";
try {
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setDouble(1,2000);
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtils.closeAll(connection,preparedStatement,null);
}
}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!