我在代码随想录|写代码Day12之栈-.栈理论基础,232.用栈实现队列,225. 用队列实现栈,20. 有效的括号,1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
学习目标:
博主介绍: 27dCnc
专题 : 数据结构帮助小白快速入门
👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍
☆*: .。. o(≧▽≦)o .。.:*☆
主题: 栈
今日份打卡
- 代码随想录-栈
学习内容:
- 栈理论基础
- 用栈实现队列
- 用队列实现栈
- 有效的括号
- 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
1.栈理论基础
思考:
- C++中stack 是容器么?
- 我们使用的stack是属于哪个版本的STL?
- 我们使用的STL中stack是如何实现的?
- stack 提供迭代器来遍历stack空间么?
首先大家要知道 栈和队列是STL(C++标准库)里面的两个数据结构。
C++标准库是有多个版本的,要知道我们使用的STL是哪个版本,才能知道对应的栈和队列的实现原理。
那么来介绍一下,三个最为普遍的STL版本:
HP STL 其他版本的C++ STL,一般是以HP STL为蓝本实现出来的,HP STL是C++ STL的第一个实现版本,而且开放源代码。
P.J.Plauger STL 由P.J.Plauger参照HP STL实现出来的,被Visual C++编译器所采用,不是开源的。
SGI STL 由Silicon Graphics Computer Systems公司参照HP STL实现,被Linux的C++编译器GCC所采用,SGI STL是开源软件,源码可读性甚高。
接下来介绍的栈和队列也是SGI STL里面的数据结构, 知道了使用版本,才知道对应的底层实现。
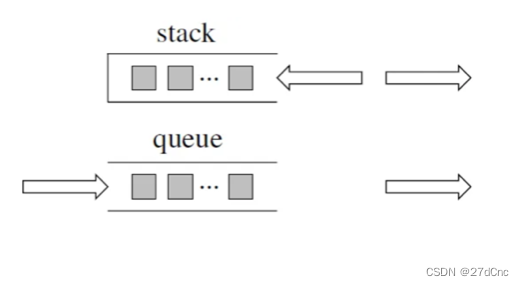
来说一说栈,栈先进后出,如图所示:
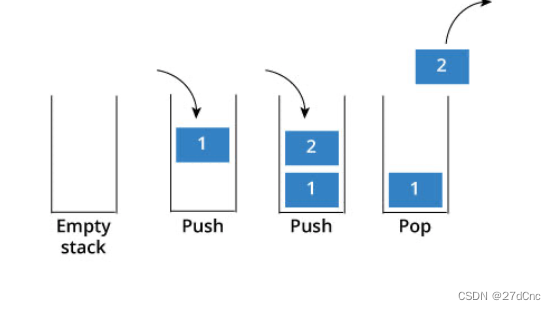
栈提供push 和 pop 等等接口,所有元素必须符合先进后出规则,所以栈不提供走访功能,也不提供迭代器(iterator)。 不像是set 或者map 提供迭代器iterator来遍历所有元素。
栈是以底层容器完成其所有的工作,对外提供统一的接口,底层容器是可插拔的(也就是说我们可以控制使用哪种容器来实现栈的功能)。
所以STL中栈往往不被归类为容器,而被归类为container adapter(容器适配器)。
那么问题来了,STL 中栈是用什么容器实现的?
从下图中可以看出,栈的内部结构,栈的底层实现可以是vector,deque,list 都是可以的, 主要就是数组和链表的底层实现。

我们常用的SGI STL,如果没有指定底层实现的话,默认是以deque为缺省情况下栈的底层结构。
deque是一个双向队列,只要封住一段,只开通另一端就可以实现栈的逻辑了。
SGI STL中 队列底层实现缺省情况下一样使用deque实现的。
232.用栈实现队列
题目

使用栈实现队列的下列操作:
- push(x) – 将一个元素放入队列的尾部。
- pop() – 从队列首部移除元素。
- peek() – 返回队列首部的元素。
- empty() – 返回队列是否为空。
代码
class MyQueue {
public:
MyQueue() {
}
void push(int x) {
s.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if(t.empty()&&s.empty()) return -1;
if(!t.empty()){//这里s改为t
int result = t.top();
t.pop();
return result;
}else{
while(!s.empty()){
t.push(s.top());//将t的栈顶元素出队列
s.pop();//输出s的元素
}
int result = t.top();
t.pop();
return result;
}
}
int peek() {
if(t.empty()&&s.empty()) return -1;
if(!t.empty()){
return t.top();
}else{
while(!s.empty()){
t.push(s.top());
s.pop();
}
return t.top();
}
}
bool empty() {
if(t.empty()&&s.empty()) return -1;
else return 0;
}
private:
stack<int> s;
stack<int> t;
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
思路 :
这是一道模拟题,不涉及到具体算法,考察的就是对栈和队列的掌握程度。
使用栈来模式队列的行为,如果仅仅用一个栈,是一定不行的,所以需要两个栈一个输入栈,一个输出栈,这里要注意输入栈和输出栈的关系。
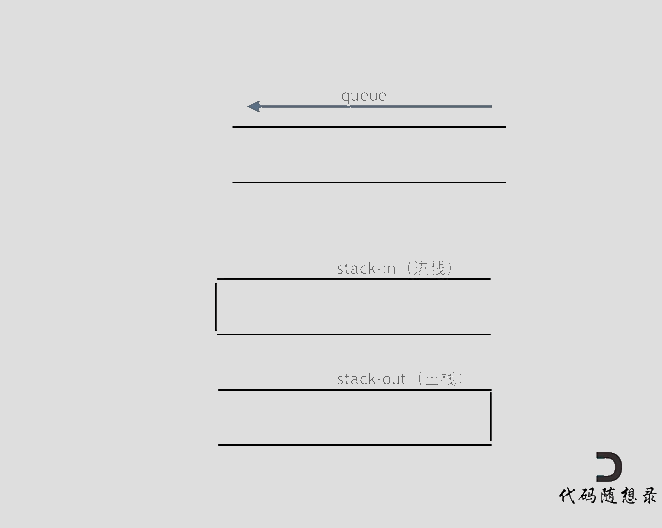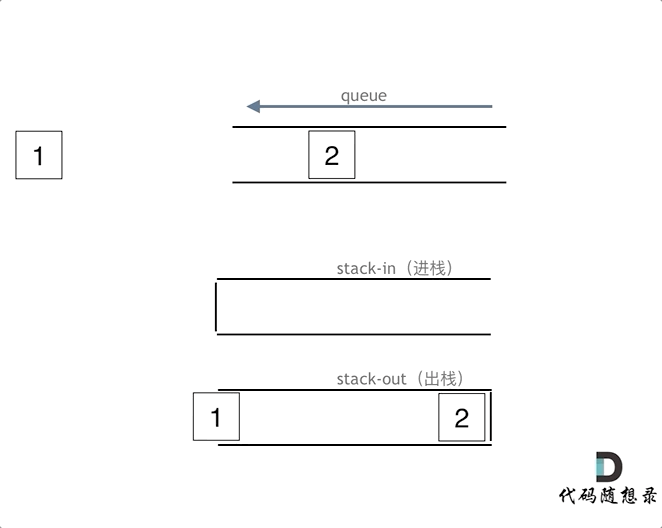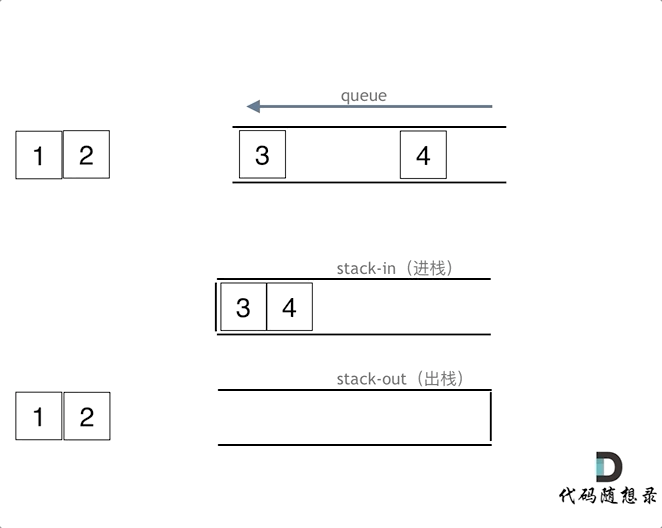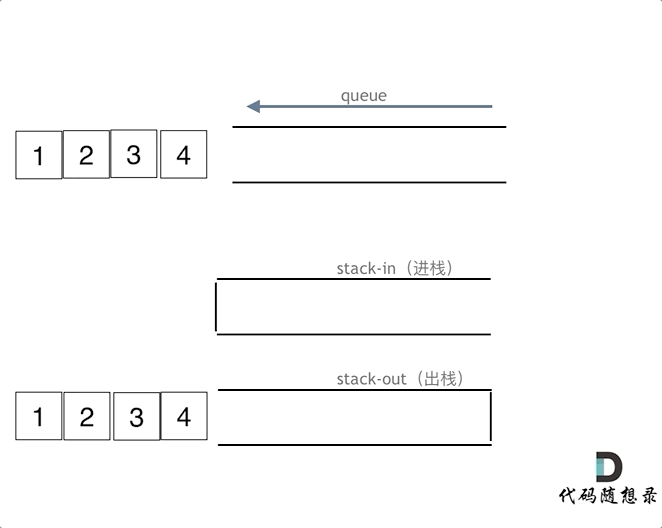
意思就是将元素放在s栈中等到要出队列的时候在移动到t栈中
其他语言
Python
class MyQueue:
def __init__(self):
"""
in主要负责push,out主要负责pop
"""
self.stack_in = []
self.stack_out = []
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
"""
有新元素进来,就往in里面push
"""
self.stack_in.append(x)
def pop(self) -> int:
"""
Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element.
"""
if self.empty():
return None
if self.stack_out:
return self.stack_out.pop()
else:
for i in range(len(self.stack_in)):
self.stack_out.append(self.stack_in.pop())
return self.stack_out.pop()
def peek(self) -> int:
"""
Get the front element.
"""
ans = self.pop()
self.stack_out.append(ans)
return ans
def empty(self) -> bool:
"""
只要in或者out有元素,说明队列不为空
"""
return not (self.stack_in or self.stack_out)
Java
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stackIn;
Stack<Integer> stackOut;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
stackIn = new Stack<>(); // 负责进栈
stackOut = new Stack<>(); // 负责出栈
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
stackIn.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
dumpstackIn();
return stackOut.pop();
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
dumpstackIn();
return stackOut.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return stackIn.isEmpty() && stackOut.isEmpty();
}
// 如果stackOut为空,那么将stackIn中的元素全部放到stackOut中
private void dumpstackIn(){
if (!stackOut.isEmpty()) return;
while (!stackIn.isEmpty()){
stackOut.push(stackIn.pop());
}
}
}
Go
type MyQueue struct {
stackIn []int //输入栈
stackOut []int //输出栈
}
func Constructor() MyQueue {
return MyQueue{
stackIn: make([]int, 0),
stackOut: make([]int, 0),
}
}
// 往输入栈做push
func (this *MyQueue) Push(x int) {
this.stackIn = append(this.stackIn, x)
}
// 在输出栈做pop,pop时如果输出栈数据为空,需要将输入栈全部数据导入,如果非空,则可直接使用
func (this *MyQueue) Pop() int {
inLen, outLen := len(this.stackIn), len(this.stackOut)
if outLen == 0 {
if inLen == 0 {
return -1
}
for i := inLen - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
this.stackOut = append(this.stackOut, this.stackIn[i])
}
this.stackIn = []int{} //导出后清空
outLen = len(this.stackOut) //更新长度值
}
val := this.stackOut[outLen-1]
this.stackOut = this.stackOut[:outLen-1]
return val
}
func (this *MyQueue) Peek() int {
val := this.Pop()
if val == -1 {
return -1
}
this.stackOut = append(this.stackOut, val)
return val
}
func (this *MyQueue) Empty() bool {
return len(this.stackIn) == 0 && len(this.stackOut) == 0
}
225. 用队列实现栈
题目

代码
class MyStack {
public:
MyStack(){
}
void push(int x){
s.push(x);
}
//问题是怎么样在第一个队列放一个元素
//让元素始终在一个队列中
int pop(){
int size = s.size();//通过队列长度确定->可以让队列剩下一个元素
size--;//留出一个元素空位
while(size--){
t.push(s.front());//这里将元素放在t队列中
s.pop();
}
int result = s.front();
s.pop();//这个时候s为空格
s = t;//为什么要讲t赋值给s=>让元素始终在一个栈中?
//这里让元素位置复原
while(!t.empty()) {
t.pop();
}
return result;
}
int top(){
return s.back();//返回队尾元素
}
bool empty(){
return s.empty();
}
private:
queue<int>s;
queue<int>t;
};
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = new MyStack();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
- push(x) – 元素 x 入栈
- pop() – 移除栈顶元素
- top() – 获取栈顶元素
- empty() – 返回栈是否为空
注意:
- 你只能使用队列的基本操作-- 也就是push to back, peek/pop from front, size, 和 is empty 这些操作是合法的。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用
list或者deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。 - 你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)
图解
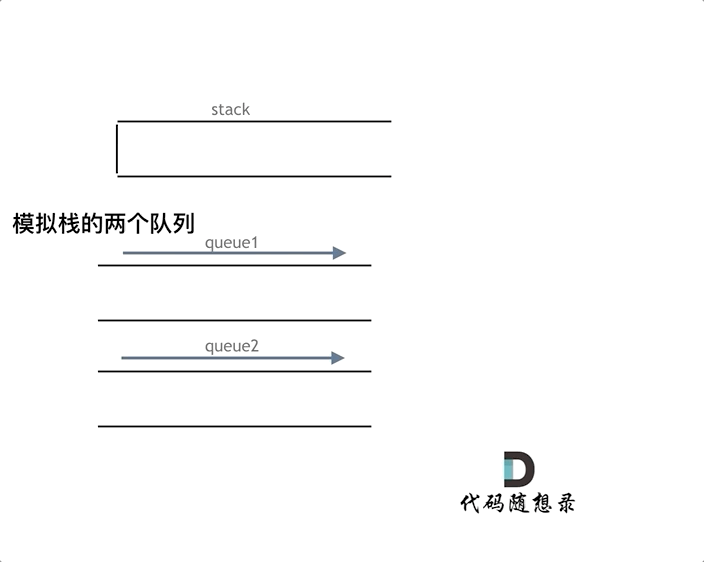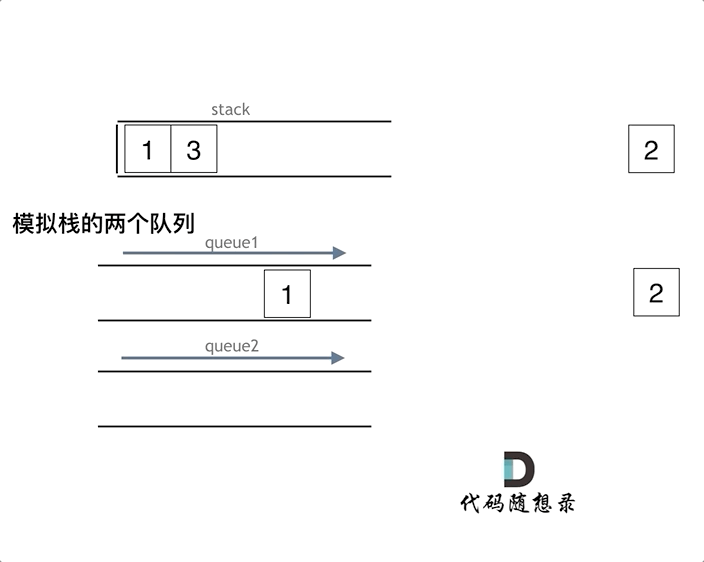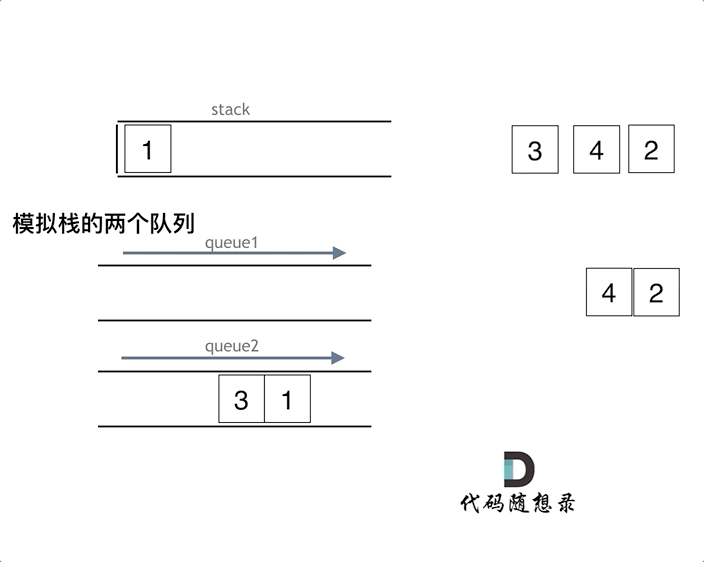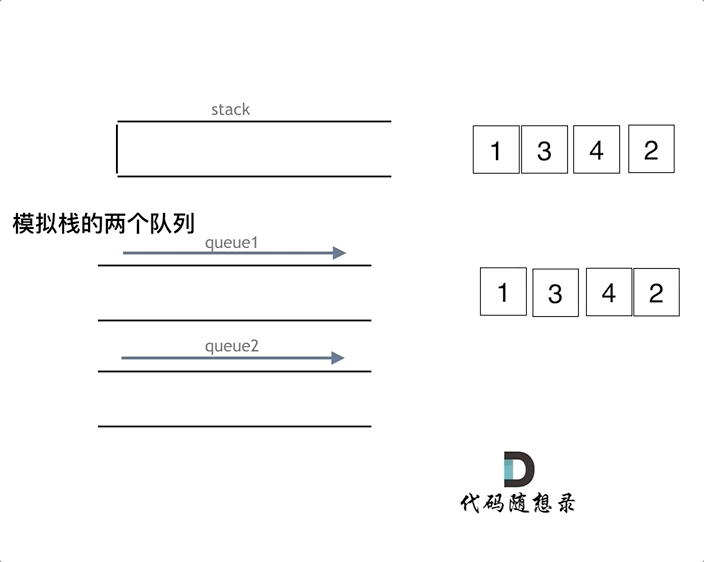
图片解释
- 一个数据入栈就是将元素放在一个队列中
- 然后出栈的时候将元素放在另一个队列中
3.一个用于进元素一个用于出元素
总结
- 面对
栈模拟队列和队列模拟栈都有一个通用思考方式- 一个
队列模拟进栈一个元素模拟出栈- 一个
栈模拟进队一个模拟出队
优化
其实这道题目就是用一个队列就够了。
一个队列在模拟栈弹出元素的时候只要将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部,此时再去弹出元素就是栈的顺序了。
优化代码
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que;
/*第1层*/
MyStack() {
}
/*第2层*/
void push(int x) {
que.push(x);
}
/**第3层**/
int pop() {
int size = que.size();
size--;
while (size--) { // 将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部
que.push(que.front());
que.pop();
}
int result = que.front(); // 此时弹出的元素顺序就是栈的顺序了
que.pop();
return result;
}
/**第4层*/
int top() {
return que.back();
}
/**第5层*/
bool empty() {
return que.empty();
}
};
其他版本
Python
from collections import deque
class MyStack:
def __init__(self):
"""
Python普通的Queue或SimpleQueue没有类似于peek的功能
也无法用索引访问,在实现top的时候较为困难。
用list可以,但是在使用pop(0)的时候时间复杂度为O(n)
因此这里使用双向队列,我们保证只执行popleft()和append(),因为deque可以用索引访问,可以实现和peek相似的功能
in - 存所有数据
out - 仅在pop的时候会用到
"""
self.queue_in = deque()
self.queue_out = deque()
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
"""
直接append即可
"""
self.queue_in.append(x)
def pop(self) -> int:
"""
1. 首先确认不空
2. 因为队列的特殊性,FIFO,所以我们只有在pop()的时候才会使用queue_out
3. 先把queue_in中的所有元素(除了最后一个),依次出列放进queue_out
4. 交换in和out,此时out里只有一个元素
5. 把out中的pop出来,即是原队列的最后一个
tip:这不能像栈实现队列一样,因为另一个queue也是FIFO,如果执行pop()它不能像
stack一样从另一个pop(),所以干脆in只用来存数据,pop()的时候两个进行交换
"""
if self.empty():
return None
for i in range(len(self.queue_in) - 1):
self.queue_out.append(self.queue_in.popleft())
self.queue_in, self.queue_out = self.queue_out, self.queue_in # 交换in和out,这也是为啥in只用来存
return self.queue_out.popleft()
def top(self) -> int:
"""
写法一:
1. 首先确认不空
2. 我们仅有in会存放数据,所以返回第一个即可(这里实际上用到了栈)
写法二:
1. 首先确认不空
2. 因为队列的特殊性,FIFO,所以我们只有在pop()的时候才会使用queue_out
3. 先把queue_in中的所有元素(除了最后一个),依次出列放进queue_out
4. 交换in和out,此时out里只有一个元素
5. 把out中的pop出来,即是原队列的最后一个,并使用temp变量暂存
6. 把temp追加到queue_in的末尾
"""
# 写法一:
# if self.empty():
# return None
# return self.queue_in[-1] # 这里实际上用到了栈,因为直接获取了queue_in的末尾元素
# 写法二:
if self.empty():
return None
for i in range(len(self.queue_in) - 1):
self.queue_out.append(self.queue_in.popleft())
self.queue_in, self.queue_out = self.queue_out, self.queue_in
temp = self.queue_out.popleft()
self.queue_in.append(temp)
return temp
def empty(self) -> bool:
"""
因为只有in存了数据,只要判断in是不是有数即可
"""
return len(self.queue_in) == 0
优化
class MyStack:
def __init__(self):
self.que = deque()
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
self.que.append(x)
def pop(self) -> int:
if self.empty():
return None
for i in range(len(self.que)-1):
self.que.append(self.que.popleft())
return self.que.popleft()
def top(self) -> int:
# 写法一:
# if self.empty():
# return None
# return self.que[-1]
# 写法二:
if self.empty():
return None
for i in range(len(self.que)-1):
self.que.append(self.que.popleft())
temp = self.que.popleft()
self.que.append(temp)
return temp
def empty(self) -> bool:
return not self.que
20. 有效的括号
题目

题目分析
** 三种不匹配的情况**
- 第一种情况,字符串里左方向的括号多余了 ,所以不匹配。
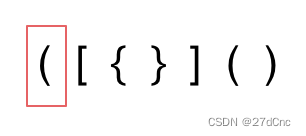
- 第二种情况,括号没有多余,但是 括号的类型没有匹配上。
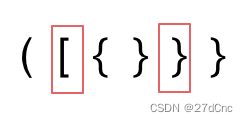
- 第三种情况,字符串里右方向的括号多余了,所以不匹配。
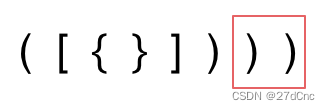
动画如下:
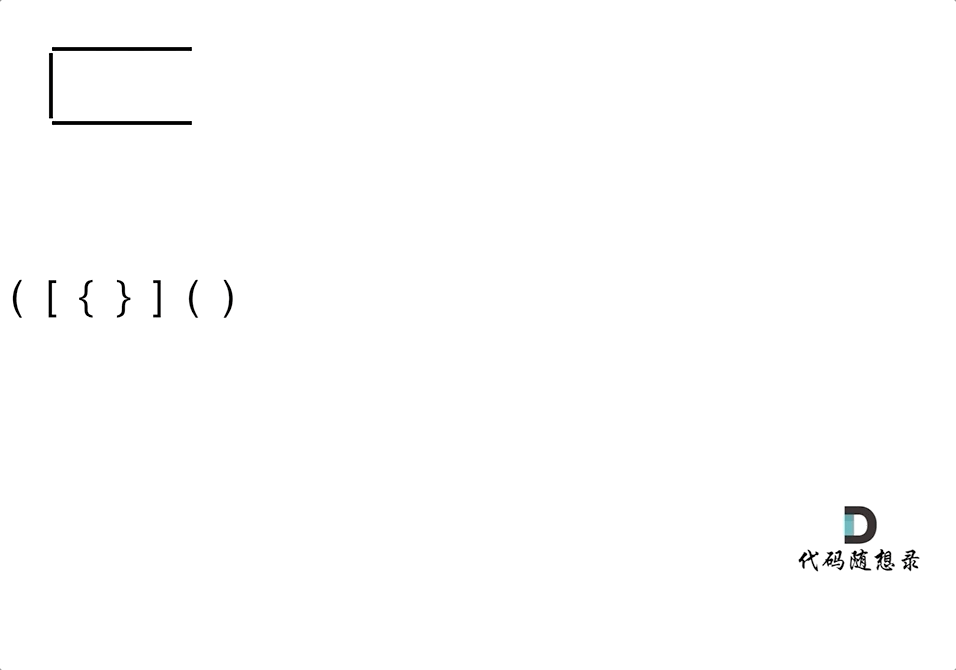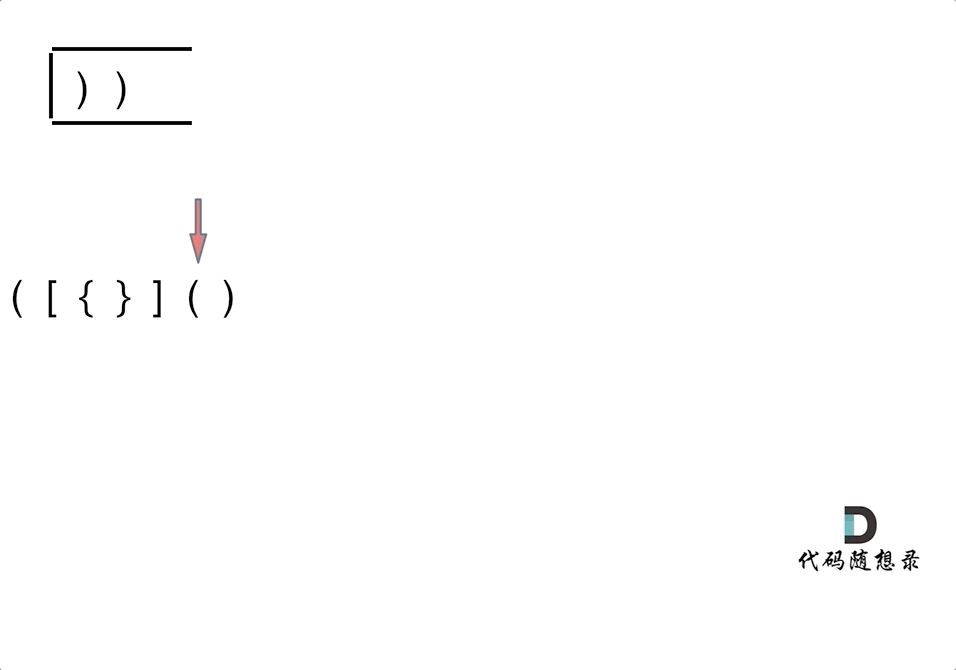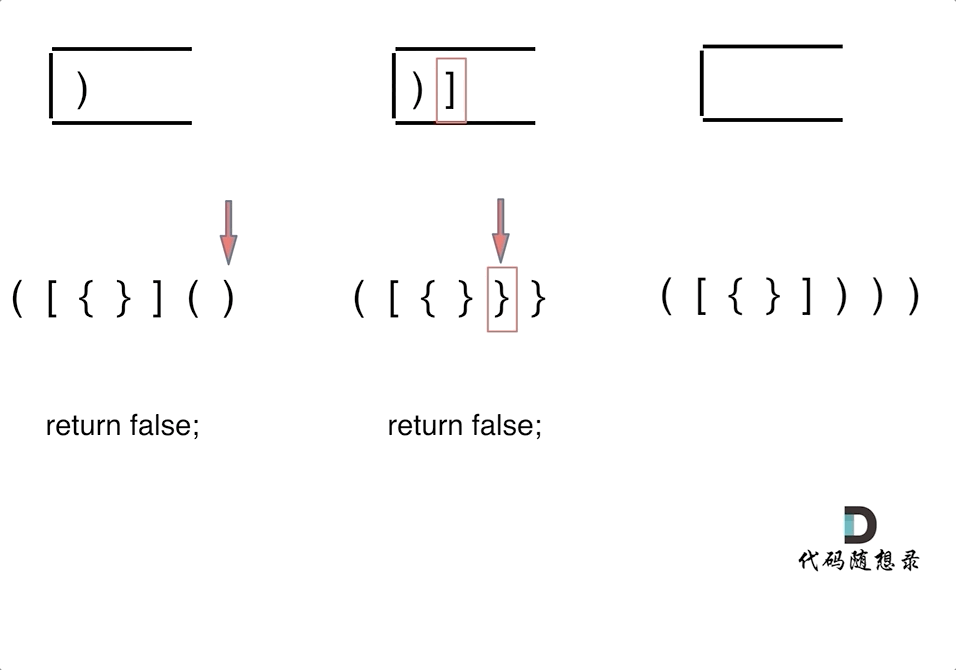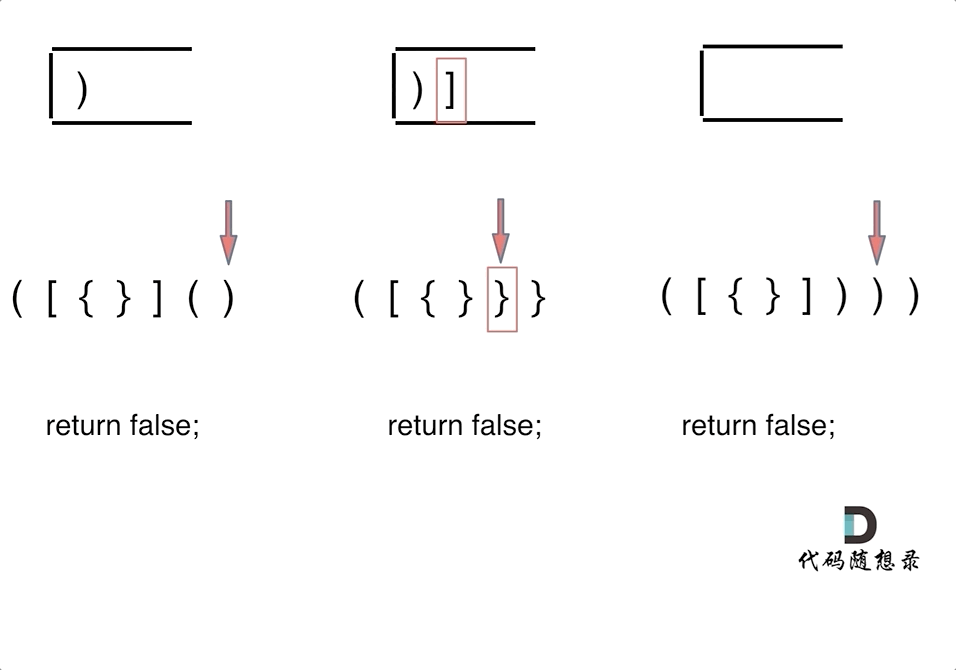
-
第一种情况:已经遍历完了字符串,但是栈不为空,说明有相应的左括号没有右括号来匹配,所以return false
-
第二种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,发现栈里没有要匹配的字符。所以return false
-
第三种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,栈已经为空了,没有匹配的字符了,说明右括号没有找到对应的左括号return false
代码
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
if(s.size() % 2 != 0) { return false; }
stack<char> t;
for(int i = 0;i < s.size();i++) {
if(s[i] == '(') { t.push(')'); }
else if(s[i] == '[') { t.push(']'); }
else if(s[i] == '{') { t.push('}'); }
else if(t.empty() || s[i] != t.top()) { return 0; }
else { t.pop(); }
}
return t.empty();
}
};
注释版
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
if (s.size() % 2 != 0) return false; // 如果s的长度为奇数,一定不符合要求
stack<char> st;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (s[i] == '(') st.push(')');
else if (s[i] == '{') st.push('}');
else if (s[i] == '[') st.push(']');
// 第三种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,栈已经为空了,没有匹配的字符了,说明右括号没有找到对应的左括号 return false
// 第二种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,发现栈里没有我们要匹配的字符。所以return false
else if (st.empty() || st.top() != s[i]) return false;
else st.pop(); // st.top() 与 s[i]相等,栈弹出元素
}
// 第一种情况:此时我们已经遍历完了字符串,但是栈不为空,说明有相应的左括号没有右括号来匹配,所以return false,否则就return true
return st.empty();
}
};
其他版本
Python
class Solution:
def isValid(self, s: str) -> bool:
stack = []
for item in s:
if item == '(':
stack.append(')')
elif item == '[':
stack.append(']')
elif item == '{':
stack.append('}')
elif not stack or stack[-1] != item:
return False
else:
stack.pop()
return True if not stack else False
Java
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Deque<Character> deque = new LinkedList<>();
char ch;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
ch = s.charAt(i);
//碰到左括号,就把相应的右括号入栈
if (ch == '(') {
deque.push(')');
}else if (ch == '{') {
deque.push('}');
}else if (ch == '[') {
deque.push(']');
} else if (deque.isEmpty() || deque.peek() != ch) {
return false;
}else {//如果是右括号判断是否和栈顶元素匹配
deque.pop();
}
}
//最后判断栈中元素是否匹配
return deque.isEmpty();
}
}
1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
题目

动图
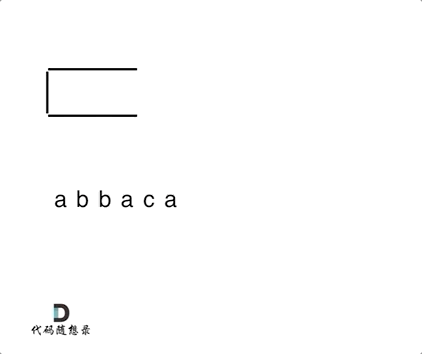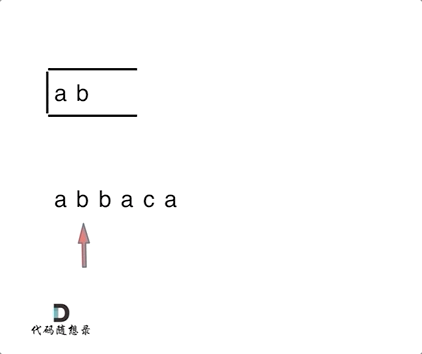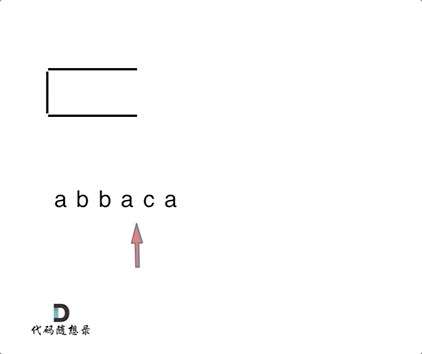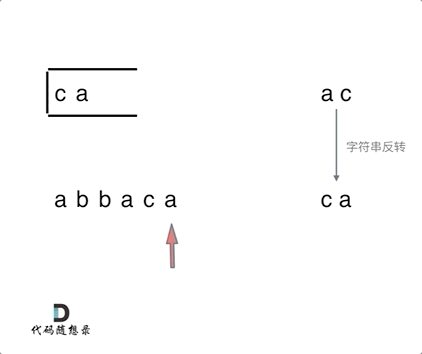
代码
class Solution {
public:
string removeDuplicates(string S) {
stack<char> st;
for (char s : S) {
if (st.empty() || s != st.top()) {
st.push(s);
} else {
st.pop(); // s 与 st.top()相等的情况
}
}
string result = "";
while (!st.empty()) { // 将栈中元素放到result字符串汇总
result += st.top();
st.pop();
}
reverse (result.begin(), result.end()); // 此时字符串需要反转一下
return result;
}
};
优化
class Solution {
public:
string removeDuplicates(string S) {
string result;
for(char s : S) {
if(result.empty() || result.back() != s) {
result.push_back(s);
}
else {
result.pop_back();
}
}
return result;
}
};

其他版本
Python
1
# 方法一,使用栈
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, s: str) -> str:
res = list()
for item in s:
if res and res[-1] == item:
res.pop()
else:
res.append(item)
return "".join(res) # 字符串拼接
2
# 方法二,使用双指针模拟栈,如果不让用栈可以作为备选方法。
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, s: str) -> str:
res = list(s)
slow = fast = 0
length = len(res)
while fast < length:
# 如果一样直接换,不一样会把后面的填在slow的位置
res[slow] = res[fast]
# 如果发现和前一个一样,就退一格指针
if slow > 0 and res[slow] == res[slow - 1]:
slow -= 1
else:
slow += 1
fast += 1
return ''.join(res[0: slow])
Java
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicates(String s) {
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
int fast = 0;
int slow = 0;
while(fast < s.length()){
// 直接用fast指针覆盖slow指针的值
ch[slow] = ch[fast];
// 遇到前后相同值的,就跳过,即slow指针后退一步,下次循环就可以直接被覆盖掉了
if(slow > 0 && ch[slow] == ch[slow - 1]){
slow--;
}else{
slow++;
}
fast++;
}
return new String(ch,0,slow);
}
}
学习时间
- 周一至周五晚上 7 点—晚上9点
- 周六上午 9 点-上午 11 点
- 周日下午 3 点-下午 6 点
学习产出
- 技术笔记 2 遍
- CSDN 技术博客 3 篇
- 习的 vlog 视频 1 个
🔥如果此文对你有帮助的话,欢迎💗关注、👍点赞、?收藏、??评论,支持一下博主~
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- HTML-基础知识-基本结构,注释,文档说明,字符编码(一)
- 基于鲸鱼算法优化的BP神经网络实现温度数据预测
- 通过WinSW将windows可执行程序注册为windows服务
- 使用官方标定工具Dynamic Calibrator对RealSense D435i进行标定(二)
- 分享一个免费易用的3d模型格式在线转换链接
- 新版EDGE卸载
- vcruntime140_1.dll文件详细解析,多种不一样的vcruntime140_1.dll缺失解决方法
- aopalliance-1.0.jar
- 2024年【天津市安全员C证】找解析及天津市安全员C证模拟考试题
- 使用集群提交作业步骤