小白浅学Vue3
目录
前端环境
编码工具: VSCode
依赖管理:NPM
项目构建: Vuecli
NPM的全称是Node Package Manager,是一个NodeJS包管理和分发工具,已经成为了非官方的发布Node模块(包)的标准。2020年3月17日,Github宣布收购npm,GitHub现在已经保证npm将永远免费。
依赖管理NPM安装配置
NPM官网
https://nodejs.org/en/download/

下载安装完成后
验证 Node.js 是否已成功安装
node -v

在nodejs安装目录创建node_global和node_cache文件夹

cmd命令,依次输入:
npm config set prefix "D:\Nodejs\node_global"
npm config set cache "D:\Nodejs\node_cache"
npm config set prefix “D:\Nodejs\node_global”:将 Node.js 全局安装包的安装路径设置为 “D:\Nodejs\node_global”。在使用 npm install -g 命令全局安装 Node.js 模块时,将会将模块安装到指定的目录中。
npm config set cache “D:\Nodejs\node_cache”:将 Node.js 模块缓存路径设置为 “D:\Nodejs\node_cache”。在使用 npm install 命令安装 Node.js 模块时,将会将模块缓存到指定的目录中。
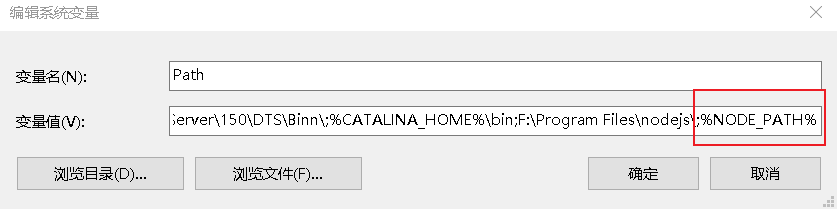
修改系统环境变量

F:\Program Files\nodejs\node_global

NODE_PATH
F:\Program Files\nodejs\node_modules

使用npm install express -g全局安装 Express 模块

说明文件权限不够,允许完全控制得以解决

更改 npm 的默认源为淘宝源
npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org
恢复默认的 npm 官方源
npm config set registry https://registry.npmjs.org
![]()
查看当前npm 源的 URL

使用淘宝源全局安装 cnpm。cnpm 是一个基于 npm 的淘宝定制版,可以在国内更快地安装 Node.js 包
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org


创建Vue项目
npm init vue@latest

安装依赖npm install

VITE v5.0.11? ready in 479 ms
? ?? Local:?? http://localhost:5173/
? ?? Network: use --host to expose
? ?? press h + enter to show help
模板语法
文本插值{{? }}
最基本的数据绑定形式是文本插值,“Mustache”语法
支持三元表达式
<template>
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
msg:"123"
}
}
}
</script>v-html
插入HTML,使用v-html,而{{? }}只是插入纯文本
<template>
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
<p>{{ ok ? 'yes':'no' }}</p>
<p><span v-html="insertHtml"></span></p>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
msg:"123",
ok:true,
insertHtml:"<a href='https://www.baidu.com'></a>"
}
}
}
</script>属性绑定
{{? }}不能在attributes中使用,绑定arrtibute需要使用v-bind, v-bind的缩写:className
v-bind将元素的attribute与组件的dynamicld属性保持一致。如果绑定的值是null遇undefined,则将attribute从渲染的元素上移除

<template>
<div v-bind:class="divColour">
123
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
divColour:"Colourclass"
}
}
}
</script>
v-bind简写
<template>
<div :class="divColour">
123
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
divColour:"Colourclass"
}
}
}
条件渲染
v-if 、v-else-if 、v-else
<template>
<!-- <div v-if="no">看不见</div>
<div v-if="ok">看得见</div>
<div v-else>123</div> -->
<div v-if="no">1</div>
<div v-else-if="ok">2</div>
<div v-else>3</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
ok:true,
no:false
}
}
}
</script>v-show
<div v-show="true">666</div>
相同点:v-if与v-show都可以动态控制dom元素显示隐藏
不同点:v-if显示隐藏是将dom元素整个添加或删除,而v-show隐藏则是为该元素添加css--display:none,dom元素还在。
v-if是惰性的,也是真实的按条件渲染,应为它确保了在切换时,条件区块内的事件监听器和子组件都会被销毁与重建。条件区块只有条件首次变为true时才被渲染。
v-show元素无论初始条件如何,始终会被渲染,只有CSS的display属性会被切换
v-if有更高的切换开销,而v-show有更高的初始化渲染开销。
v-if应用场景更适合初始化,只渲染一次
v-show应用场景更适合频繁的切换
列表渲染v-for
<div>
<p v-for="name in names">{{ name }}</p>
</div>
Index,数组下标
<div>
<p v-for="(name,index) in names">{{ index }} : {{ name }}</p>
</div>
可以使用of代替in,of更接近javaScript迭代器语法
<div>
<p v-for="(name,index) of names">{{ index }} : {{ name }}</p>
</div>
<div>
<p v-for="(value,key,index) of user"> {{ key }} :{{ value }} : {{ index }} </p>
</div>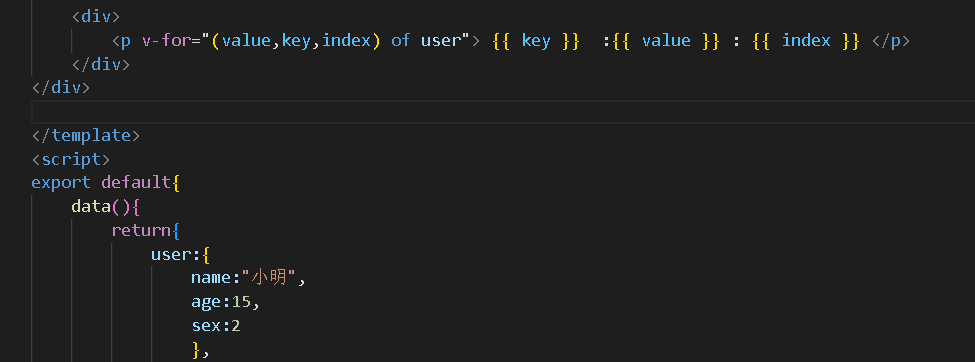
状态管理
Vue默认通过“就地更新”策略来更新通过v-for渲染的元素列表。当数据项的顺序改变时,Vue就地更新每一个元素,不会移动位置,确保元素在原本的指定位置上。
为给Vue一个提示,以便可以跟踪每个节点的标识,从而重用和重新排序现有元素,需为每个元素提供唯一的attribute(key)
v-for中添加key是通过v-bind绑定特殊attribute
推荐在任何时候为v-for提供唯一的attribute(key)
实际场景中不推荐使用index作为key,使用数据源中的唯一值,如数据库表中的唯一ID
<div>
<p v-for="(value,key,index) of user" :key="index"> {{ key }} :{{ value }} : {{ index }} </p>
</div>
事件
用法:v-on:click=”handler” 或 @click=”handler”
事件
- 内联事件:事件被触发执行的内联javaScript语句(类似onclick)
- 方法事件:指组件上指定的方法的属性名或路径
内联事件处理
内联事件通常用于简单场景
<button @click="count++">+1</button>
? ? <p>{{ count }}</p>

方法事件处理
推荐使用
<button @click="addCount">+1</button>
<p>{{ count }}</p>
methods:{
addCount(){
this.count +=1;
}
},
事件传参
<input type="text" v-model="message">
<button @click="addCount(message.$event)">+1</button>
<p>{{ message }}</p>
methods:{
//event对对象
addCount(msg,e){
console.log(msg);
//e.target.innerHTML ="+"+this.count
this.count +=1;
}
},
事件修饰符
处理事件时经常调用event.stopPropagation()或event.preventDefault()。
Vue为v-on提供了常用的修饰符
.stop ?.privent ?.once ?.enter等
.privent阻止触发
<a @click.prevent="clickhandle" href="https://www.baidu.com/">baidu</a>.stop 阻止冒泡事件
<div @click="clickhandle">
<p @click.stop="addCount('P')">冒泡</p>
</div>以下类推
.once只执行一次
.enter回车触发
…
数组变化监听
变更方法
Vue能够侦听响应式数组的变更方法,并在它们被调用时触发相关的更新。
以下方法引起UI自动更新
Push()、pop()、shift()、unshift()、sort()、reverse()
<button @click="addname">add name</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(name,index) of names" :key="index">{{ name }}</li>
</ul>methods:{
addname(){
//pushu()方法引起UI自动更新
//this.names.push("小明");
//concat()不会引起UI自动更新
this.names = this.names.concat(["小王"])
},计算属性
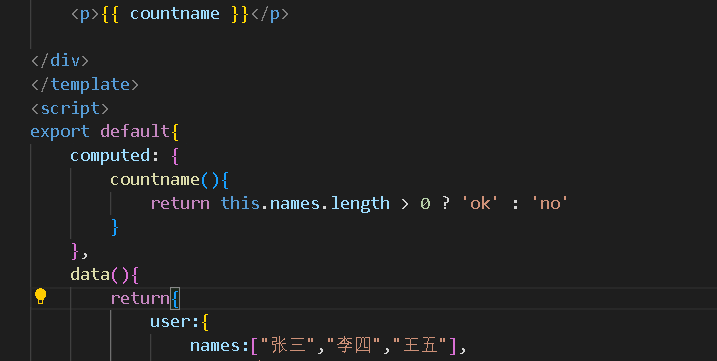
计算属性: 计算属性值基于响应式依赖缓存。一个计算属性仅会在响应式依赖更新时才重新计算
方法:方法调用总会重新渲染发生时执行函数
<p>{{ countname }}
{{ getcountnames() }}
</p>
computed: {
countname(){
return this.names.length > 0 ? 'ok' : 'no'
}
},
methods:{
countname(){
return this.names.length > 0 ? 'ok' : 'no'
},Class绑定
Vue为class的v-vind提供了功能增强
单个calss绑定
<template>
<p :class="{'active':isActive}">class</p>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
isActive:true
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.active{
color: burlywood;
font-size: 35px;
}
</style>多calss对象绑定
<template>
<p :class="classObject">class</p>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
classObject:{
active:true,
active2:true
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.active{
color: burlywood;
font-size: 35px;
}
.active2{
background-color: rgb(170, 222, 135);
}
</style>
Class数组绑定
<template>
<p :class="classObject">class</p>
<p :class="[arractive,arractive2]">class数组</p>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
classObject:{
active:true,
active2:true
},
arractive:"active",
arractive2:"active2"
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.active{
color: burlywood;
font-size: 35px;
}
.active2{
background-color: rgb(170, 222, 135);
}
</style>Style绑定
对象绑定
<p :style="{color:activeColoe,fontSize: fontSize}">style</p>
<p :style="styleObject">style2</p>
侦听器
侦听页面响应式数据的变化
<template>
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button @click="updata">点击</button>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
message:"hello"
}
},
methods:{
updata(){
this.message="word"
}
},
watch:{
message(newValue,oldValue){
console.log(newValue+":"+oldValue)
}
}
}
</script>
v-model表单的输入绑定
v-model修饰符常用 .lazy .number .trim
??? .lazy 懒惰的? 输入完在显示
??? .number 只接受输入的值为数字
??? .trim 去掉前后空格
<template>
<form>
<input type="text" v-model="msg">
<input type="text" v-model.lazy="msg">
<input type="text" v-model.number="msg">
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
<!-- v-model修饰符常用 .lazy .number .trim
.lazy 懒惰的 输入完在显示
.number 只接受输入的值为数字
.trim 去掉前后空格
-->
</form>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
msg:""
}
}
}
</script>模板引用
使用ref 属性,挂载结束后引用会暴露在$refs.
<template>
<div class="container" ref="container">{{ container }}</div>
<button @click="getinfo">获取数据</button>
</template>
<script>
export default{
methods:{
getinfo(){
console.log(this.$refs.container)
}
},
data(){
return{
container:"demo"
}
}
}
</script>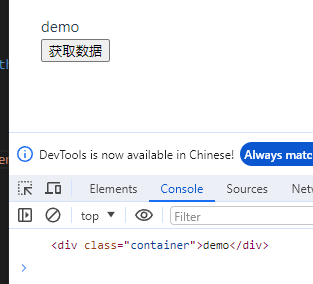
console.log(this.$refs.container.innerHTML="test")

<template>
<input type="text" ref="name">
<button @click="getinfo">获取数据</button>
<div class="container" ref="container">{{ container }}</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
methods:{
getinfo(){
this.$refs.container.innerHTML= this.$refs.name.value
}
},
data(){
return{
container:"demo",
name:""
}
}
}
</script>
Vue组件
组件的优点:可复用性
组件构成
<template>
</template>
<script>
export default{
}
</script>
<style>
</style>组件引入

组件的生命周期钩子
每个 Vue 组件实例在创建时都需要经历一系列的初始化步骤,比如设置好数据侦听,编译模板,挂载实例到 DOM,以及在数据改变时更新 DOM。在此过程中,它也会运行被称为生命周期钩子的函数,让开发者有机会在特定阶段运行自己的代码。
创建期:beforeCreate、created
挂载期:beforeMount 、mounted
更新期:beforeUpdate、updated
销毁期:beforeUnmount 、unmountd
<script>
export default{
beforeCreate(){
console.log("创建之前")
},
created(){
console.log("创建之后")
},
beforeMount(){
console.log("挂载之前")
},
mounted(){
console.log("挂载之后")
},
beforeUpdate(){
console.log("更新之前")
},
updated(){
console.log("更新之后")
},
beforeUnmount(){
console.log("销毁之前")
},
unmountd(){
console.log("销毁之后")
}
}
</script>
组件嵌套关系

组件允许将ui划分为独立的、可重用的部分,并且可以对每个部分进行单独的思考。在实际项目中,组件是层层嵌套的树形结构,每个组件内封装自定义内容与逻辑。
取消main.css依赖

Article.vue
<template>
<H3>Article</H3>
</template>
<style scoped>
h3{
width: 80%;
margin: 0 auto;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
box-sizing: border-box;
margin-top: 25px;
background: #bdbaba;
}
</style>
Item.vue
?
<template>
<H3>Item</H3>
</template>
<style scoped>
h3{
width: 80%;
margin: 0 auto;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
box-sizing: border-box;
margin-top: 25px;
background: #bdbaba;
}
</style>Hrader.vue
<template>
<H3>Header</H3>
</template>
<style scoped>
h3{
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
border: 5px solid #999;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>Main.vue
<template>
<div class="main">
<H3>Main</H3>
<Article/>
<Article/>
<Article/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Article from "./article.vue"
export default{
components:{
Article
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.main{
float: right;
width: 85%;
height: 500px;
border: 5px solid #999;
box-sizing: border-box;
text-align: center;
}
</style>Aside.vue
<template>
<div class="aside">
<H3>Aside</H3>
<Item/>
<Item/>
<Item/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Item from './Item.vue';
export default{
components:{
Item
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.aside{
float: left;
width: 14%;
height: 500px;
border: 5px solid #999;
box-sizing: border-box;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
效果

组件注册
局部注册(建议使用)
在一个组件中进行注册

全局注册
在main.js中全局注册
全局注册很方便,但是在全局注册中,没有被使用的组件无法在生成打包的时候被自动移除(“tree-shaking”),依然出现在打包后的js文件中。
在项目嵌套较多的时候,全局注册的依赖关系不明确,可能影响应用长期维护性。

组件数据传递props
组件之间是可以传递数据,而传递数据的解决方案是props,注:props传递数据只能父级传递子级。
组件传递的数据类型:数字、对象、数字等。任何类型的值都可以作为props的值传递
组件间传递数据应用场景: 父传子

Parent.vue
<template>
<h3>Parent</h3>
<input v-model="msg">
<Child :title="msg" test="数据"/>
</template>
<script>
import Child from './Child.vue';
export default{
data(){
return{
msg:""
}
},
components:{
Child
}
}
</script>Child.vue
<template>
<h3>Child</h3>
<p> {{ title }} </p>
<p>{{ test }}</p>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
}
},
//接收数据
props:["title","test"]
}
</script>传递效果

传递数组,对象
Parent.vue
<template>
<h3>Parent</h3>
<input v-model="msg">
<Child :title="msg" test="数据" :names="names" :user="user" :number1="number1"/>
</template>
<script>
import Child from './Child.vue';
export default{
data(){
return{
msg:"",
names:["张三","李四","王五"],
user:{
name:"张三",
age:20
},
number1:123
}
},
components:{
Child
}
}
</script>Child.vue
<template>
<h3>Child</h3>
<p> {{ title }} </p>
<p>{{ test }}</p>
<p v-for="(name,index) of names" :key="index">{{ index }} : {{ name }}</p>
<p>{{ user.name }} {{ user.age }}</p>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
}
},
//接收数据
props:["title","test","names","user"]
}
</script>传递对象

类型验证
<template>
<h3>Child</h3>
<p> {{ title }} </p>
<p>{{ test }}</p>
<p v-for="(name,index) of names" :key="index">{{ index }} : {{ name }}</p>
<p>{{ user.name }} {{ user.age }}</p>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
}
},
//接收数据
props:{
title:{
type:[String,Number,Array,Object]
},
names:{
type:Array
},
user:{
type:Object,
//必选项
required:true
},
test:{
type:String
},
number:{
type:Number,
default:0
}
}
}
</script>Props实现子传父

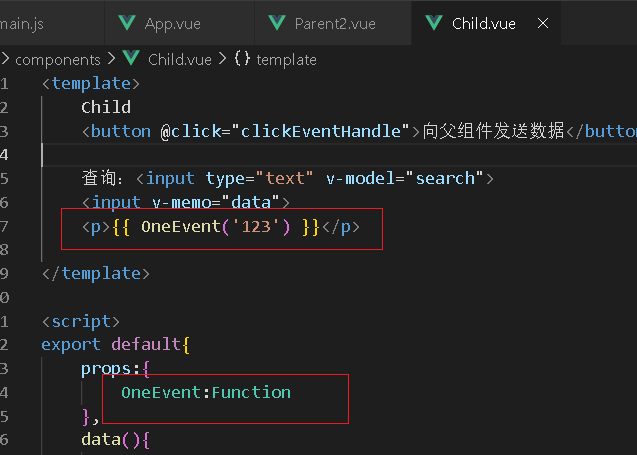
组件数据传递$emit
组件模板表达式中,可以使用$emit方法触发自定义事件
组件间传递数据应用场景:子传父
Child.vue
<template>
Child
<button @click="clickEventHandle">向父组件发送数据</button>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
msg:"传递数据"
}
},
methods:{
clickEventHandle(){
this.$emit("eventDemo",this.msg)
}
}
}
</script>Parent2.vue
<template>
<Child @eventDemo="getHandle"/>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "./Child.vue"
export default {
components:{
Child
},
methods:{
getHandle(data){
console.log(data)
}
}
}
</script>

组件+v-model

查询:<input type="text" v-model="search">
watch:{
search(newValue,oldValue){
this.$emit("searchEvent",newValue)
}
},
透传
透传attribute指的是传递给一个组件,没有被该组件声明为props或emits的arrtibute或者v-on事件监听器。最常见的例子就是class、id、style。
一个组件以单个元素为根做渲染时,透传的attribute会自动被添加到根元素上
App.vue

Attr.vue
<template>
<h2>透传属性测试</h2>
</template>
<style>
.colorDemo{
color: aqua;
}
</style>效果 
禁用透传attribute
export default{
inheritAttrs:false
}Slots插槽
插槽 slot 通常用于两个父子组件之间,最常见的应用就是使用一些 UI 组件库中的弹窗组件时,弹窗组件的内容是可以自定义,这就是使用了插槽的原理。

SlotsDemo.vue
<template>
<slots></slots>
</template>
<script>
export default{
}
</script><slot>元素是一个插槽出口(slot outlet),表示父类提供的插槽内容渲染的位置

插槽的作用域
插槽内容可以访问父组件的数据作用域,插槽的内容本身就是在父组件模板中定义

默认值
在父组件没有传递数值的情况下显示
<template>
<slots>默认值</slots>
</template>具名插槽
给插槽提供名字
App.vue
<SlotsDemo>
<template v-slot:h1>
<h2>标题</h2>
</template>
<template v-slot:h2>
<p>{{msg}}</p>
</template>
</SlotsDemo>SlotsDemo.vue
<template>
<slot name="h1">默认值</slot>
<slot name="h2">默认值</slot>
</template>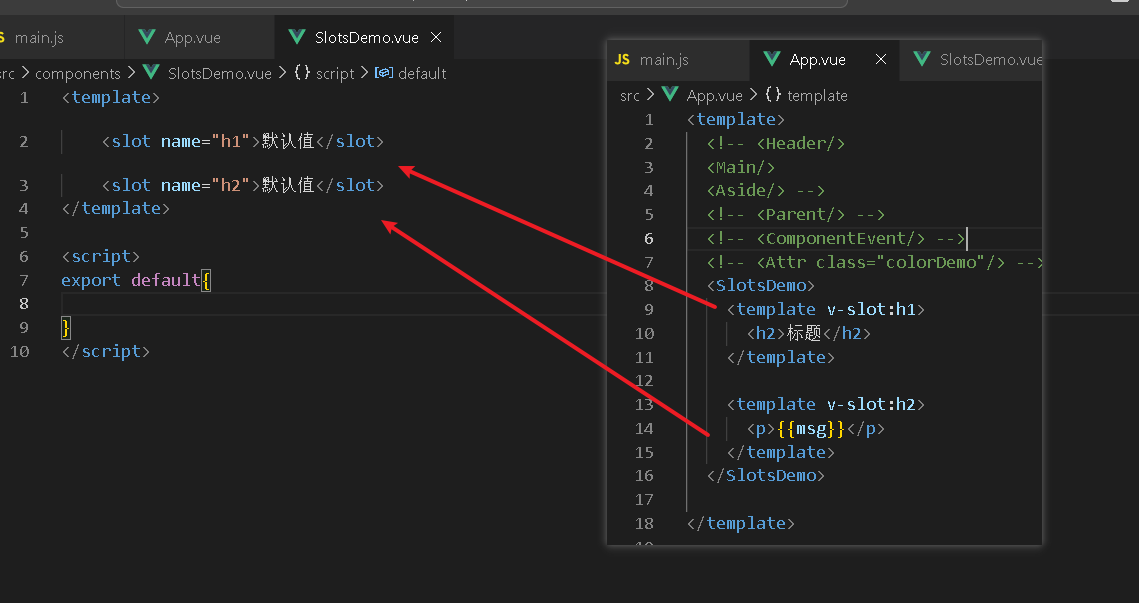
v-slot简写#
<template #h1>
<h2>标题</h2>
</template>
<template #h2>
<p>{{msg}}</p>
</template>插槽数据传递
插槽的内容可能同时获取给父组件作用域和子组件作用域的数据,可以类似props,在插槽的出库是传递arrtibutes
将子组件的数据传递给父组件
子组件
<template>
<slot :childmsg="childmsg"></slot>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
childmsg:"child"
}
}
}
</script>父组件

<SlotsDemo v-slot="slotProps">
{{ slotProps.childmsg }}+{{ msg }}
</SlotsDemo>具名+插槽数据传递
子组件
<template>
<slot name="h1">默认值</slot>
<slot name="h2" :childmsg="childmsg"></slot>
</template>父组件
<SlotsDemo >
<template #h1>
<h2>标题</h2>
</template>
<template #h2="slotProps">
<p> {{ slotProps.childmsg }}+ {{msg}}</p>
</template>
</SlotsDemo>本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- C++——小案例:学生通讯录
- uniapp踩坑之项目:canvas第一次保存是空白图片
- flowable任务分配方式篇动态部门经理:固定分配、表达式分配、监听器分配
- 流程控制语句(关键字break和continue的使用)、质数(素数)判断
- K8S部署的pod一直处于Pending状态问题解决
- 目标检测YOLO实战应用案例100讲-基于图像增强的鸟类目标检测
- apkpure下载Google Play中APP的APK安装包
- 【开源】基于JAVA语言的高校宿舍调配管理系统
- 使用 MinIO 构建兼容 S3 的股票市场数据湖
- 【开源工程及源码】数字孪生乡村—经典开源项目实景三维数字孪生